ketones and aldehydes
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
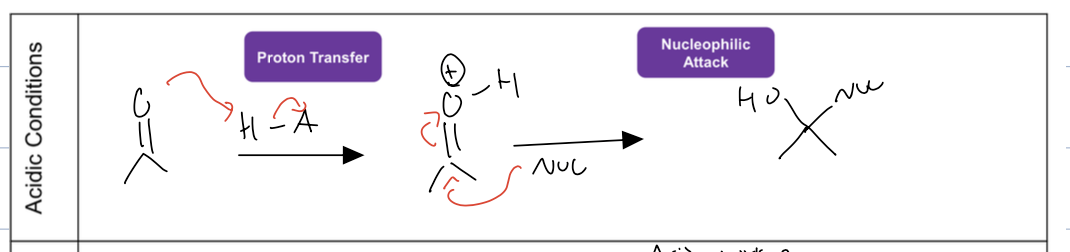
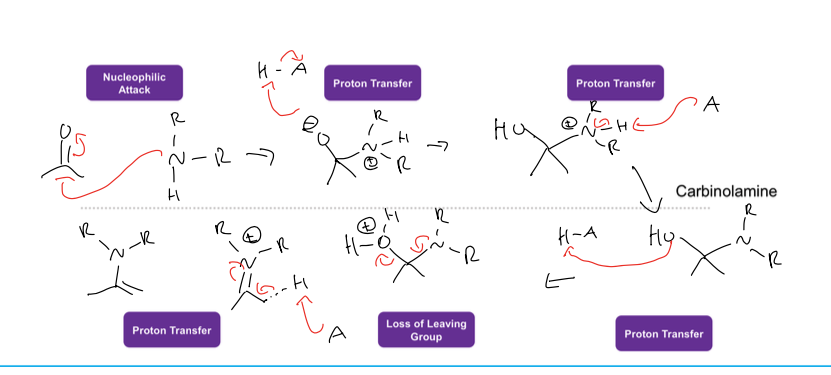
what is the rxn under acidic conditions for nucleophilic addition
the acid halide is attacked by carbonyl, and then the nuc attacks the elec. carbon .
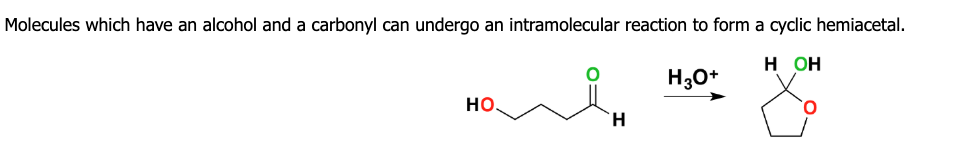
how does a cyclic hemiacetal form
what to do for hydrolysis of imine and enamine
find where bond formed with ketone and break it to fom ketone and secondary or primary amine
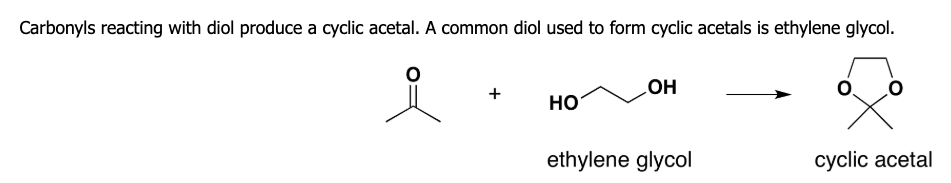
how does. cyclic acetal form
which is also how to protect cabonyls
if you have a molecule with two ketones and one of them stays intact in the product what must you use
acetol to protect
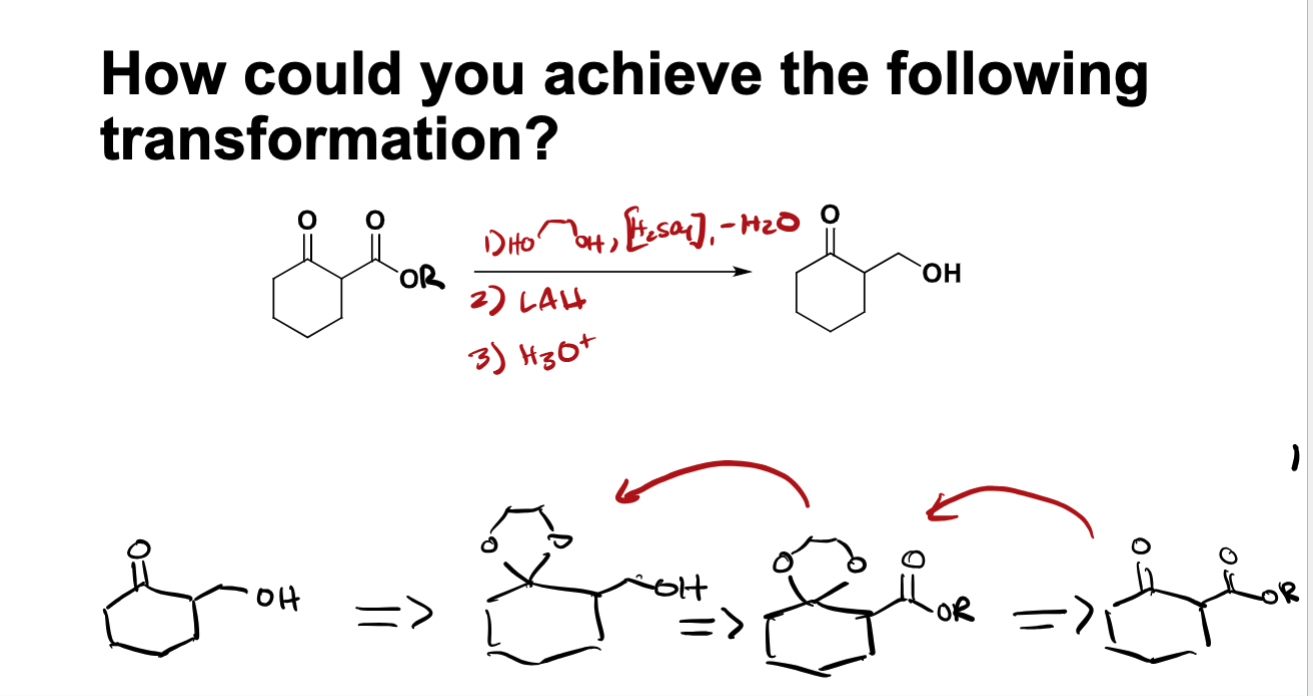
whats the difference between nuc attack in hydration rxn cond
the mechanisms are the same in both conditoins but for hydration h20 acts as nucleophile in acidic and OH does in basic conditions
what to remeber for acetla formation mechanism
after first alcohol attacks the original O will be protonated and become water and leave, where the first alcohol that attacksed will create double bond for second alcohol to attack new elec. carbon
what is the rxn under basic conditions for nuc addition
the nucleophile attacck elec. carbon and thenpushes double bond up to oxygen and then the O is protonanted in an acid workip by an acid halide
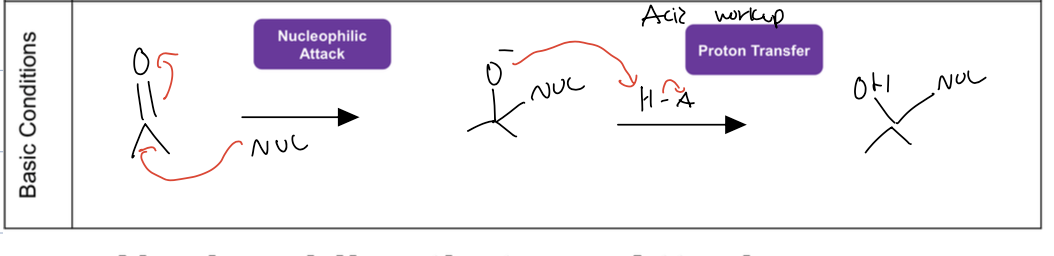
what is the reaction of hydration under acid conditions
the carbonyl attacks H3o+ and then water acts like nuc and attacks more elec carbon, and then the water deprotonates to give diol
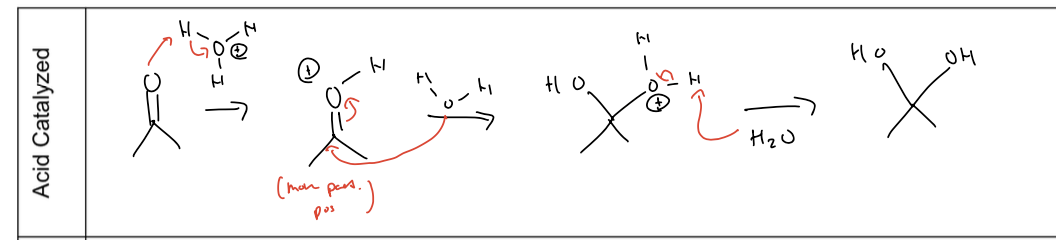
what is hydration rxn under basic conditions
hydroxide attacks elec carbon kicking doubke bond up and then the alcoxide deprotonate to form an alcohol
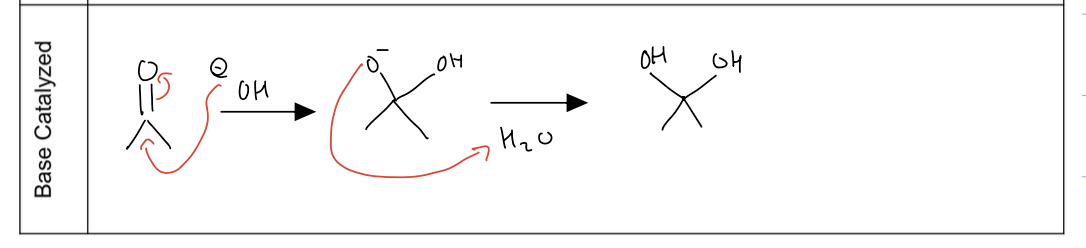
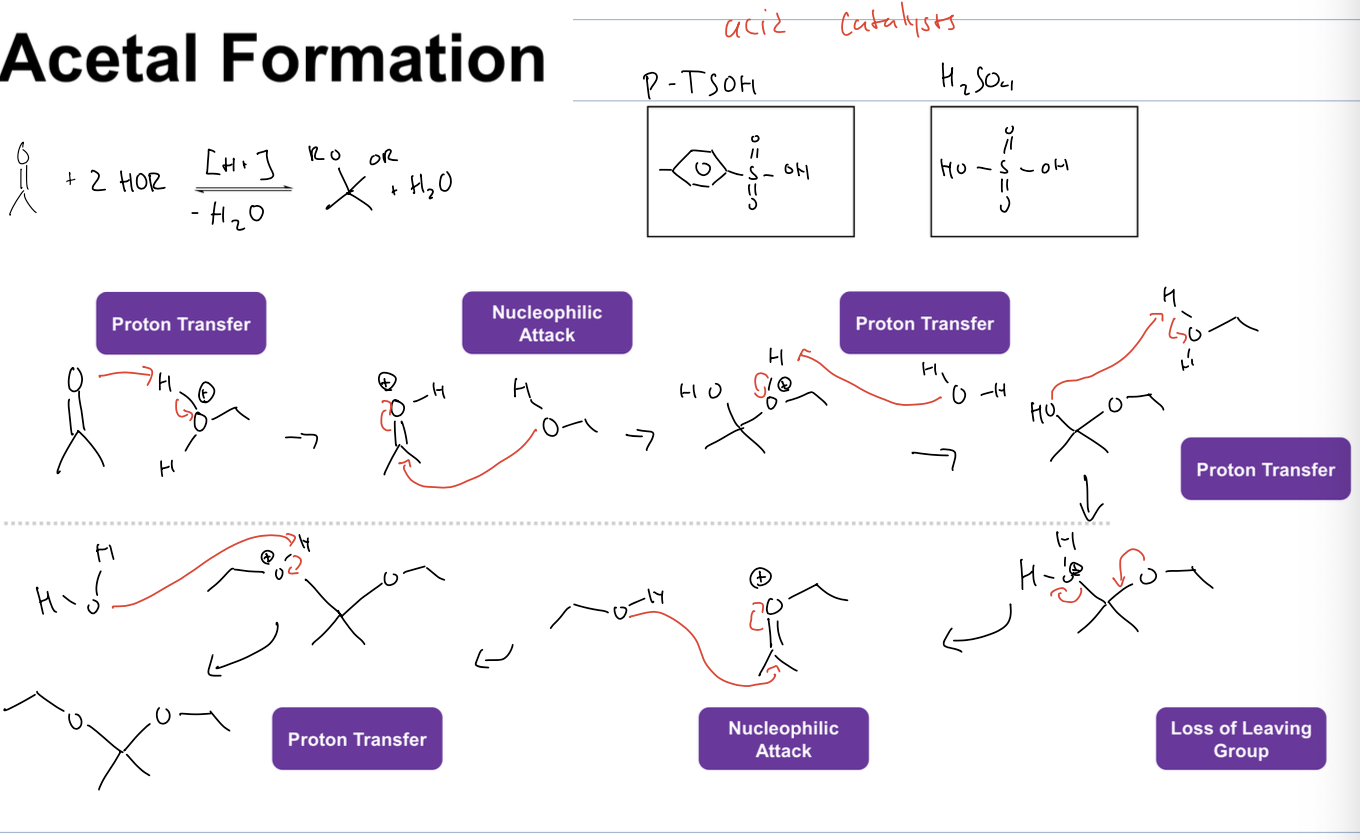
what is acetal formation
using alcohol as a nucleophile
what is rxn for acetal formation
reagents
acid catalyst (h2So4, and then removing H2O)
the carbonyl de protonates H3O+, then the alcohol acts as nucleophile and attacks elec. carbon, and then water deprontonates the alcohol to give an ether, then the alcohol deprotnates H3O+ again, and then the water leaves and the ether drops a lone pair down to reform double bond. then the other alcohol attacks new elec carbon and gets deprontonated by water to add both ethers
the alcohols that attack can also be different
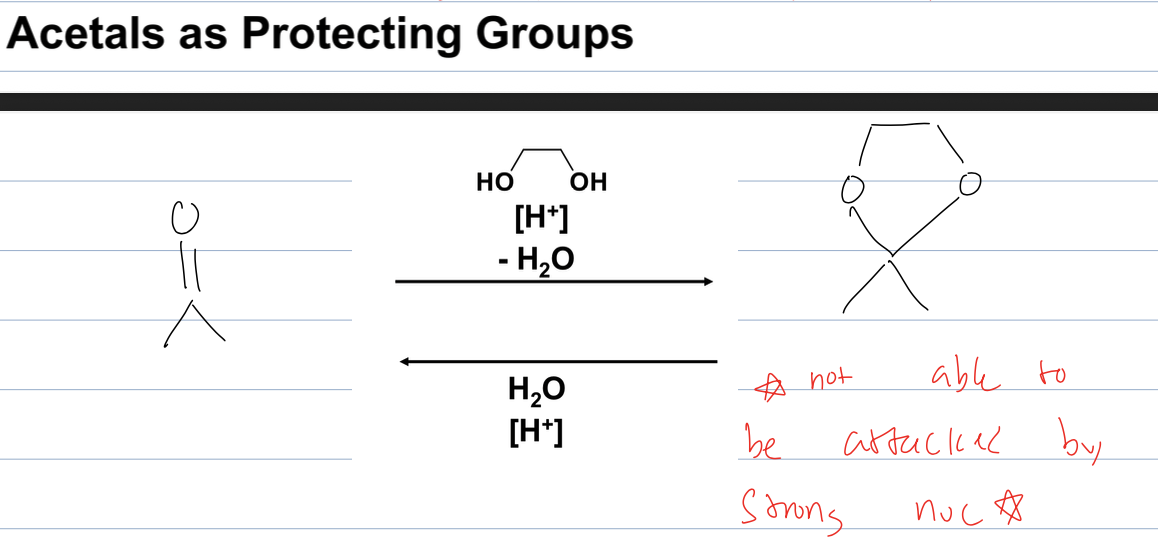
how can you use acetals as protecting groups
you can add them to a ketone so they cannot be attacked by a strong nuc
and then can unprotect by adding water with acid catalyst
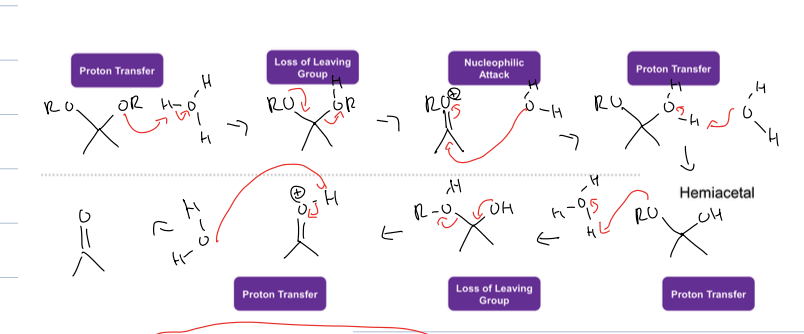
what is the rxn for hydrolysis of acetals
it can be undone by acid to make ketone
what is imine formation
rxn with a primary amine and aldehyde or ketone
reagents: acid catalyst, amine, and -H2O
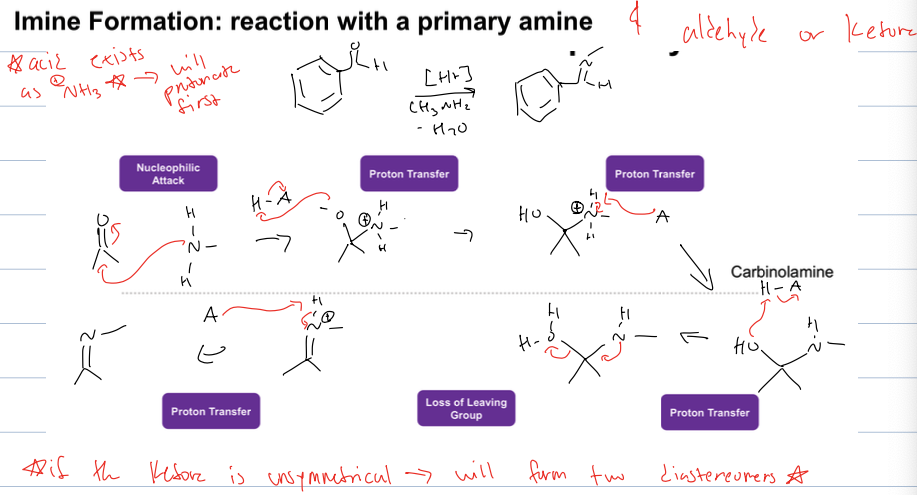
if the acid exists as NH3 it will protonate first and not attack
what is enamine formation rxn
reaction with a secondary amine and aldehyde or ketone
reagents: acid catalyst, amine, and -H2O
if ketone is unsymmetrical, the major product will be less sub. alkene and the minor will be more sub. alkene
what is major difference in enamine and imine mechanism
after the lone pair on N drops down to form double bond the N cannot be deprotonated in an enamine rnx, so an elimination occurs and creates new double bond to stabilize pos charge on N
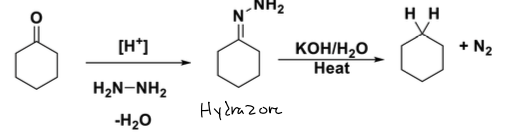
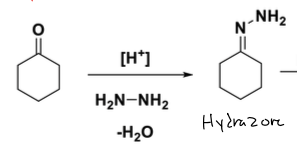
what is Wolff- Kishner Reduction rxn
goes from ketone to alkane and N2
reagents: form hydrazone [H+], H2n-NH2, -H2O
Reagents: to get alkane KOH, H2O, Heat
how to form hydazone in wolf kishner
you replace carbonyl with N-NH2
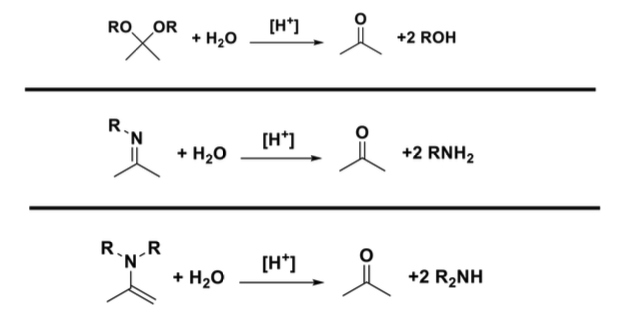
what are the products of hydrolysis for acetals, imine, and enamine
for acetals is ketone and 2 alcohols
for imine its ketone and two primary amines
for enamine its ketone and 2 secondary amines
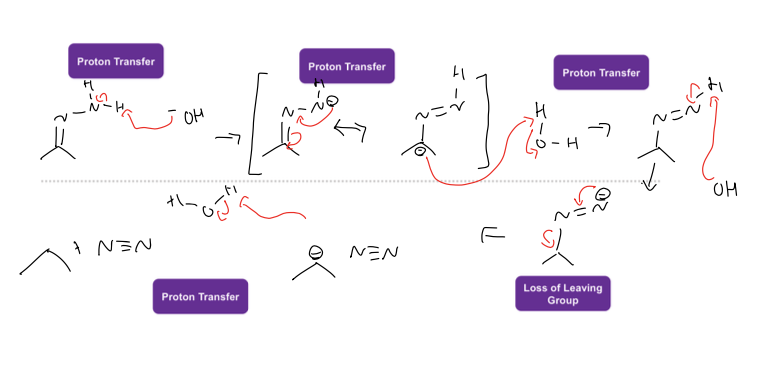
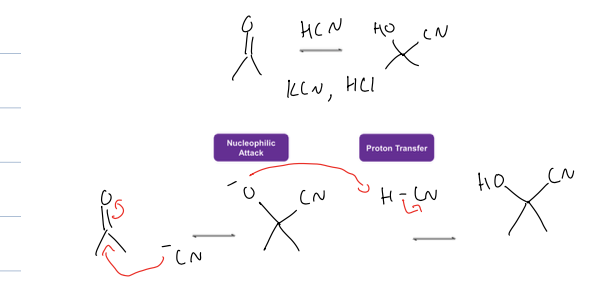
what is cyanohydrin formation rxn
ketone to alcohol and CN
reagents: HCN
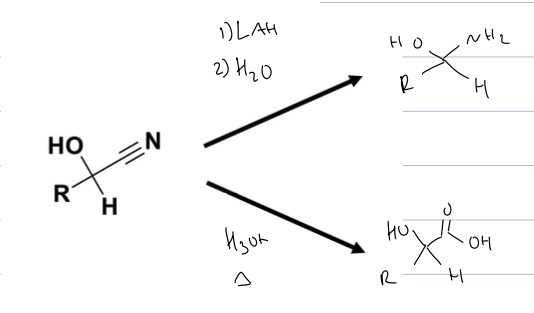
what other products can you form once you have a CN group and can reduce it
can form amine with LAH
and can form Carbox acid with H3O
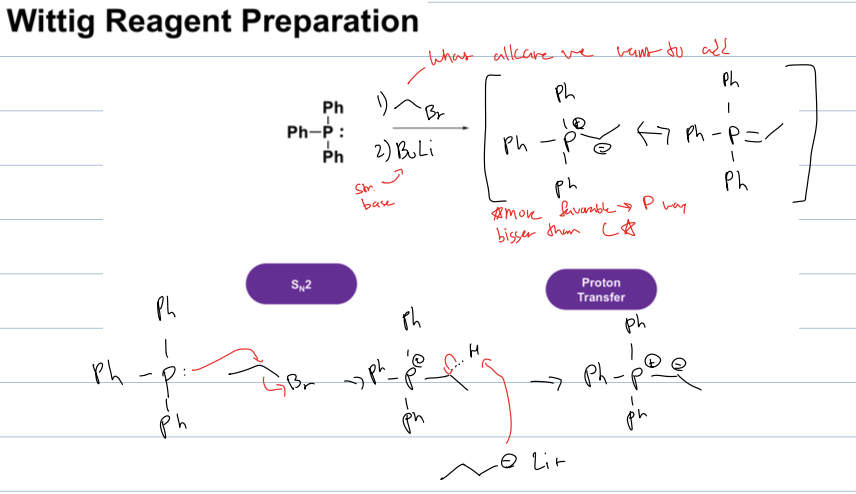
how do you make the wittig reagent
P Ph3, and react it with alkyl halide in an SN2 (or what alkane we want to add in wittig rxn) and then BuLi (strong base) to get neg charge on carbon
what is wittig rxn
a rxn that takes aldehyde or ketone and adds carbon chain to the alkene
reagent: wittig reagent (ylid)
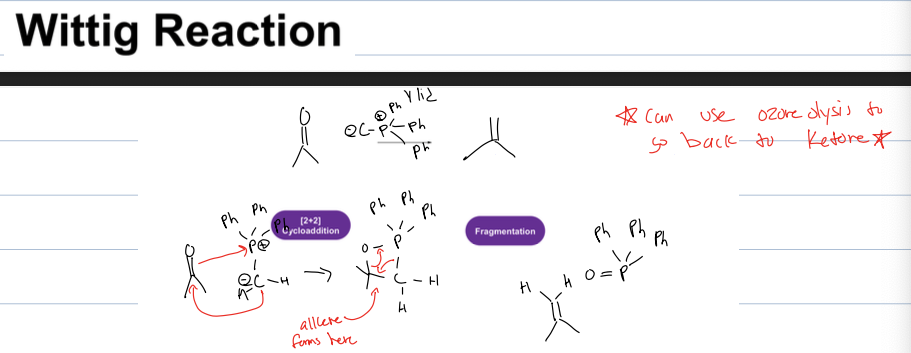
how do you go back to ketone after the wittig rxn
By ozonolysis
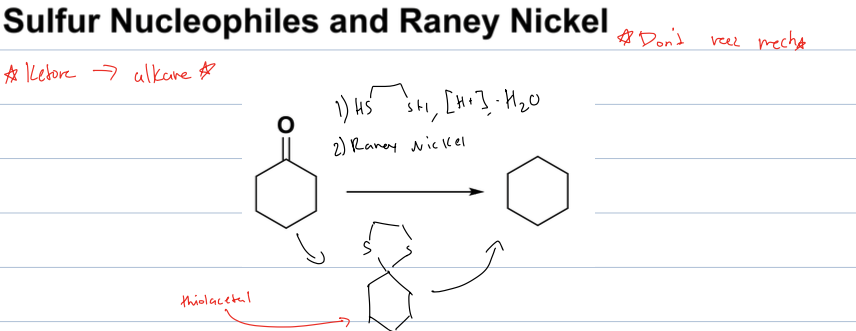
what is the rxn with sulfur nucleophiles and raney nickel
goes from a ketone to an alkane
reagents: 1)thiol, [H+], -H2O 2)raney nickel