IMMUNOLOGY LAB
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
define the antibody-antigen complex
when the antigen binds to its specific antibody and the molecules link
are antibodies and antigens soluble
yes, they are separate soluble substances
is the antibody-antigen complex soluble
no, it is an insoluble precipitate
which substances is known as the precipitin
the antibody, because they mediated the precipitation reaction
what is serum
the liquid portion of blood containing substances like albumin and antibodies
it does not contain clotting factors
what is antiserum
serum used as a source of antibodies
what is a positive result in a precipitation reaction
if a precipitate forms
what media can a one ring test be conducted in
liquid or solidifed
which media is better for a one ring test
both will result in a precipitate, but the liquid media provides a result in minutes, whereas the solidified media can take days
in order, list what is included in the name of an antiserum
name of the species the antiserum was raised in
anti-
antigen with which the serum reacts
antiserum
in order, list what is included in the name of an antibody
name of species the antibody was raised in
anti-
antigen with which the antibody reacts
antibody
what reaction is the one ring test an example of
a precipitation reaction
what reaction is ABO blood grouping an example of
agglutination reaction
what is agglutination
the visible aggregation of an insoluble antigen as a result of a reaction between the antigen and its specific antibody
which antibody mostly results in agglutination
IgM (complete antibodies)
what are incomplete antibodies
antibodies which are often unable to agglutinate particles
what are the 4 ABO blood group
A
B
AB
O
what is ABO blood grouping based on
the presence of absence of the A and B antigens
which blood group is the universal recipient
AB
which blood group is the universal donor
O
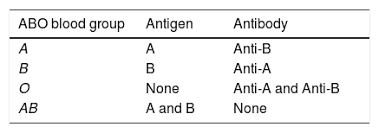
name the antigens and antibodies present for each ABO blood group
name some other blood grouping systems
rhesus, MNS, Duffy, Kidd, Lewis
what is being tested in forward grouping
we test for the presence of antigens on the cell surface
what is beng tested for in reverse grouping
we are testing for the presence of antibodies in serum
often confirming the results of forward grouping
how do we forward group
and known antiserum to unkow blood sample and observe for agglutination
how do we reverse group
add an unkown serum to a known blood sample and observe for agglutination
what does an antibody titration determine
how much of an antibody is present in a particular sample
how do we do an antibody titration
we dilute serum, and the dilution at which the serum still produces a visible agglutination with an antigen is related to the amount of antibody present
how do we interpret antbody titrations
the more dilute the serum that is still able to produce a visible reaction, the more antigen must have been present in the original neat sample
what are the 4 reactions be record in an antibody titration
positive +++ → granular button fo cells, irregular agglutinated mass
positive ++ → sheet of agglutinated cells, cover whole base of well
positive + → button of cells, hazy edges, granular collections of cells may be present
negative 0 → small discrete button of cells, small diameter with well defined boundaries
how do we determine the titre of the serum
the titre is the reciprocal of the highest dilution which have a positive reaction
when might we use antibody titration
to see if immunisation process is successful
as procedure goes on, the titre should increase
what is normal serum
it is used in the antibody assay to see if anything exists in the serum normally that might cause agglutination beside the antibody being tested
has low or undetectable level of the antibody
why do we use a phosphate buffered saline in an antibody titration
the buffered saline should not agglutinate, so we use it to increase confidence in our results
what are the 2 control groups in an antibody titration
the phopshate buffered saline and the normal serum