Chemical pulping Föreläsning 7 module 4: Pulping and processing
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
What is the main goal in chemical pulping?
To remove lignin and release strong and bleachable cellulose fibers.
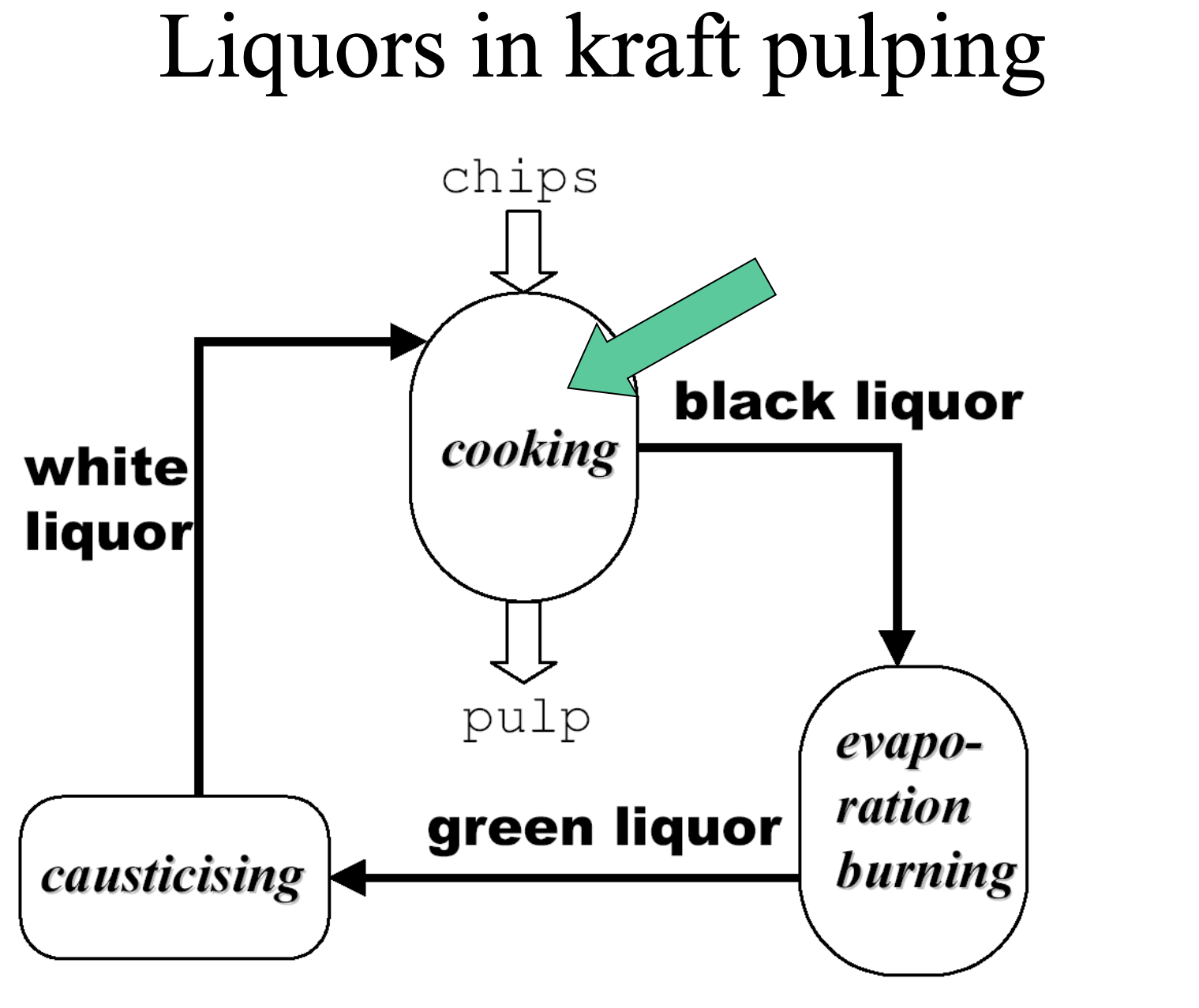
Describe this picture.
Wood chips are cooked with white liquor (NaOH and Na2S) , which release pulp and forms Black Liquor (lignin and extractives). The black liquor is evaporated and burned, and forms Green liquor. Green liquor is formed back into White liquor during the causticising process.
Describe two methods for chemical pulping
Soda cook: OH- as active component. mainly used for non-wood fibres.
Kraft cook: OH- and SH- as active components. The most important method. Exclusive journal paper, book paper etc.
Why is phenolic units in lignin more reactive?
They have sour OH-groups that easily forms into phenolate ions in alkaline media.
Why does a low sulphide concentration lead to a decreased delignification?
Because it benefits the formation of the side product enol ether.
What is the peeling reaction and why is it unwished?
Peeling reaction is stepwise removal of monosacharides located in the end of the chain ——> decrease the Pulp yield.
How is Xylan stabilized during Kraft-cooking?
Through a Stopping reaction - the side chain Arabinose is eliminated instead of the Xylan whole Xylan chain - Makes Xylan more stable during Kraft Cooking.
Why do we want to remove HexA in bleaching?
It yellows the bleached pulp and increase the consumption of bleaching chemicals.
In what phase of the kraft cooking has the most selective delignification?
During the bulk-phase. In the residual phase, when there is a small amount of lignin left, the selective decreases.
Why is hardwood delignified faster than softwood?
Hardwood contain a higher amount of S-units with easily cleaved β–O–4’- bonds. Softwood contain higher amounts of G-units. G units has C-C bonds, harder to cleave
What hemicellulose is degraded the fastest during Kraft cooking and why?
Glucomannan, because it has fewer side chains and is more reactive in base.