Week 10 Combined (Except Pregnancy Changes)
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
Chapter 1: Contraception
Overview
Strategies/devices used to prevent pregnancy or reduce risk of fertilization/implantation.
Human ovum can be fertilized for up to 24 hours after ovulation.
Motile sperm can fertilize the ovum for approximately 48 to 72 hours.
Nursing Actions
Assess client's contraceptive needs, desires, and preferences.
Discuss benefits, risks, and alternatives of contraceptive methods thoroughly (ensures informed decision-making).
Discuss postpartum contraception options prior to discharge.
Client Education
Contraceptive methods should be chosen jointly by sexual partners (e.g., vasectomy, tubal ligation).
Include discussions on future contraceptive plans in postpartum instructions.
Methods of Contraception
Natural family planning
Fertility awareness methods
Barrier methods
Hormonal methods
Intrauterine devices (IUD)
Surgical procedures
Assessment Prior to Contraceptive Initiation
Comprehensive physical exam may be recommended:
Pap smear
Blood tests (Hgb, Hct)
STI screening
Document medical and obstetric history thoroughly.
Abstinence
Client Education:
Discuss permissible sexual activities without intercourse.
Advantages:
Most effective contraceptive method.
No chemicals or foreign objects.
Can prevent STIs if no genital contact occurs.
Disadvantages:
Requires self-control.
High failure rate if adherence is inconsistent.
Risks:
None if maintained.
Coitus Interruptus (Withdrawal)
Client Education:
Pre-ejaculatory fluid may contain sperm, risking fertilization.
Advantages:
Option if other methods unavailable for monogamous couples.
Disadvantages:
Least effective contraceptive method.
No STI protection.
Risks:
Possible pregnancy.
Calendar Rhythm Method
Tracks menstrual cycles to estimate fertile period (ovulation typically occurs ~14 days before next menstrual cycle).
Client Education:
Track menstrual cycles (minimum 6 cycles).
Start of fertile period: shortest cycle length minus 18 days.
End of fertile period: longest cycle length minus 11 days.
Abstain from intercourse during fertile days.
Advantages:
Effective when combined with other methods (e.g., basal body temperature, cervical mucus).
Cost-effective.
Disadvantages:
Low reliability.
Requires accurate record-keeping.
No STI protection.
Risks:
Possible pregnancy due to calculation errors or irregular cycles.
Calendar Rhythm Method Example
Shortest cycle, 26 - 18 = 8th day
Longest cycle, 30 - 11 = 19th day
Fertile period is days 8 through 19.
Refrain from intercourse during these days to avoid conception.
Standard Days Method
Color-coded beads track fertile days (days 8-19 fertile in typical cycles)
Client Education:
Rubber ring moves one bead daily.
Red bead: cycle start
White beads: fertile days
Brown beads: infertile days
Advantages:
Easy adherence, visual aid.
Mobile apps available.
Disadvantages:
Not suitable if cycles shorter than 26 days or longer than 32 days.
Easy to lose track of days.
Risks:
Pregnancy risk if cycles irregular or method misused.
Less effective with hormonal contraceptives, breastfeeding, or IUDs.
Basal Body Temperature (BBT)
Measures slight temperature rise after ovulation due to progesterone.
Client Education:
Take temp immediately upon waking, before rising.
Use thermometer recording to tenths; chart temperature daily.
Fertile period: temp elevation lasting 3 consecutive days after ovulation.
Combine with calendar method for best results.
Advantages:
Inexpensive, convenient.
Disadvantages:
Easily affected by stress, illness, sleep disturbances.
No STI protection.
Risks:
Possible pregnancy if method inaccurately used.
Billings Method
Cervical Mucus Ovulation Detection Method
Identifies fertility based on cervical mucus characteristics (thin, slippery mucus indicates ovulation; stretchiness = "spinnbarkeit").
Client Education:
Combine with calendar method.
Maintain hygiene; assess mucus daily starting after menstruation ends.
Obtain mucus externally; no need for internal assessment.
Egg-white consistency indicates fertile mucus.
Avoid douching prior to assessment.
Advantages:
Encourages self-awareness and accurate self-assessment.
Helpful during breastfeeding.
Disadvantages:
Discomfort/self-analysis difficulty for some clients.
No STI protection.
Risks:
Pregnancy risk if mucus altered by intercourse, infections, medications, or inaccurate assessments.
Two-Day Method
Checks daily for presence of vaginal secretions; fertile if secretions present that day or previous day.
Client Education:
Abstain if secretions noted for two consecutive days.
Advantages:
Simple and easy.
Disadvantages:
Requires daily monitoring.
Risks:
Possible pregnancy.
Lactation Amenorrhea Method (LAM)
Breastfeeding suppresses ovulation/menstruation postpartum.
Client Education:
Criteria for effectiveness:
Infant younger than 6 months.
Exclusively breastfeed every 4 hours daytime, every 6 hours nighttime.
No supplemental feeding.
No menstrual periods resumed.
Advantages:
Natural, no chemicals.
Disadvantages:
Effective only up to 6 months postpartum.
Risks:
Possible pregnancy if breastfeeding exclusivity not maintained.
Penile Condom
Client Education:
Place on erect penis, leave space at tip for semen.
Withdraw immediately after ejaculation, holding condom base.
Use with spermicide to enhance effectiveness.
Check expiration date.
Latex/polyurethane condoms protect against STIs; lambskin condoms do NOT (due to pores).
Use only water-based lubricants with latex condoms (prevents breaking).
Advantages:
Protects against most STIs
Accessible, involves male partner, no adverse effects
Disadvantages:
Can interrupt spontaneity, decrease sensation.
Penis must be erect to apply.
One-time use, replacement costs.
Doesn't protect from lesions (HPV, HSV, syphilis).
Risks/Complications:
Potential breakage or leakage causing pregnancy.
Latex allergies possible.
Vaginal Condom (Female Condom)
Client Education:
Closed end inserted vaginally; open end covers labia externally.
Dispose after one-time use.
Do NOT combine with penile condom.
Advantages:
STI & pregnancy protection.
Some protection against HPV, HSV, syphilis.
Disadvantages:
Bulky, complicated insertion, noisy during use.
Higher cost compared to penile condoms.
Spermicide (Chemical that destroys sperm; increases vaginal acidity.)
Client Education:
Insert 15 min before intercourse; effective for 1 hour; leave in vagina at least 6 hrs post-intercourse.
Reapply for each intercourse act.
Available as gel, foam, suppository, cream, or film.
Advantages:
Non-prescription, easy access.
Enhances other contraceptive methods.
Disadvantages:
Messy, frequent reapplication, no STI protection.
Risks/Contraindications:
Avoid with cervical infections.
Frequent use (>2/day) of nonoxynol-9 increases HIV risk, lesions.
Diaphragm (Silicone dome fitting over cervix, used with spermicide gel or cream.)
Client Education:
Fit/refit diaphragm professionally (every 2 years, after childbirth, surgery, or major weight changes).
Insert with spermicide ≤6 hours before intercourse; leave in 6-24 hrs post-intercourse.
Reapply spermicide each intercourse.
Empty bladder prior to insertion.
Clean with mild soap, warm water after use.
Advantages:
Client-controlled contraception; simple insertion.
Disadvantages:
Requires fitting/prescription, reapplication interferes with spontaneity, no STI protection.
Risks/Contraindications:
Not recommended for history of TSS, recurrent UTIs, prolapse.
Increased risk of TSS (fever, faintness, rash, muscle aches).
Allergic reactions and UTIs possible.
Cervical Cap (Silicone cap fitting tightly around cervix, used with spermicide.)
Client Education:
Insert ≤6 hrs before intercourse; leave in 6-48 hrs afterward.
Replace/refit every 2 years, or after surgery, childbirth, major weight changes.
Advantages:
Extended use, no additional spermicide needed per act.
Disadvantages:
TSS risk, allergic reactions, no STI protection.
Risks/Contraindications:
Avoid with abnormal Pap tests or TSS history.
Contraceptive Sponge (Polyurethane sponge containing spermicide; placed over cervix)
Client Education:
Moisten with water before insertion.
Insert before intercourse, leave ≥6 hrs post-intercourse (protection lasts up to 24 hrs).
Advantages:
Allows multiple intercourse acts, easy insertion.
Disadvantages:
No STI protection.
Risks/Complications:
TSS risk if remains >24 hrs in vagina.
Combined Oral Contraceptives (COCs) (Estrogen + progestin pills suppress ovulation, thicken cervical mucus, and alter uterine lining)
Client Education:
Take pill daily at same time.
If missed dose, follow instructions for backup contraception.
Report chest pain, shortness of breath, severe headaches, visual changes, or leg pain immediately (signs of clotting).
Advantages:
High effectiveness, regulates menstrual cycles, reduces menstrual cramps.
Decreased risk of ovarian, endometrial, colorectal cancer, benign breast disease, ovarian cysts.
Disadvantages:
No STI protection.
Increased risk of thrombosis, breast tenderness, nausea, headaches.
Effectiveness reduced by certain meds
Contraindications:
Thromboembolic disorders, cardiovascular disease, breast cancer, pregnancy, lactation <6 weeks postpartum, heavy smokers over 35 years, liver issues, uncontrolled hypertension.
Progestin-Only Pills (Minipill) (Oral progestin prevents fertilization, implantation.)
Client Education:
Take consistently at same time daily.
Use backup contraception in first month.
Immediately take missed pills; backup contraception needed.
Advantages:
Fewer side effects compared to other pills.
Safe for breastfeeding.
Disadvantages:
Less effective at suppressing ovulation.
No STI protection.
Irregular bleeding, nausea, headaches, breast tenderness.
Contraindications:
Bariatric surgery, severe liver conditions, current or past breast cancer.
Emergency Oral Contraceptive (Morning-After Pill - w/in 72 hours)
Client Education:
Antiemetic recommended before use (due to nausea risk).
Pregnancy evaluation if no period within 21 days.
Copper IUD within 5 days is an alternative (requires prescription).
Advantages:
Non-regular use, accessible over-the-counter for all ages.
Disadvantages:
Nausea, heavy bleeding, abdominal pain, fatigue.
Not for regular contraception, doesn't terminate existing pregnancies.
No STI protection.
Contraindications:
Existing pregnancy, abnormal vaginal bleeding.
Transdermal Contraceptive Patch
Client Education:
Replace weekly on abdomen, buttocks, upper outer arm, torso (not breasts)
Use for 3 weeks; remove for the 4th week.
Advantages:
Stable hormone levels, no daily pills, unaffected by gastrointestinal metabolism.
Disadvantages:
Increased thromboembolism risk compared to oral contraceptives.
Skin irritation, less effective if over 198 lb.
No STI protection.
Injectable Progestins (Medroxyprogesterone) (M/subcutaneous injections every 11-13 weeks to inhibit ovulation.)
Client Education:
Initial injection within first 5 days of menstrual cycle or postpartum period.
Follow-up required.
Ensure calcium, vitamin D intake, weight-bearing exercise.
Do not massage injection site.
Advantages:
Highly effective, fewer periods, reduces uterine cancer risk, safe in breastfeeding.
Disadvantages:
Decreased bone density, weight gain, irregular bleeding, delayed fertility return.
Not for long-term use (>2 years).
Contraindications:
Breast cancer, cardiovascular disease, abnormal liver function, diabetes concerns.
Contraceptive Vaginal Ring (Flexible silicone ring releasing hormones vaginally.)
Client Education:
Replace every 3 weeks; insert new within 7 days.
If removed >4 hrs, use backup contraception for 7 days.
Advantages:
Simple use, no daily pills, lower hormone dose due to vaginal delivery.
Disadvantages:
Discomfort during intercourse, no STI protection, requires prescription.
Risks:
Clots, hypertension, stroke
Implantable Progestin (Subdermal rod releasing progestin continuously; effective 3 years.)
Client Education:
Avoid trauma to insertion site.
Condom use recommended for STI protection.
Advantages:
Reversible, immediately effective postpartum, abortion, miscarriage.
Disadvantages:
Irregular bleeding, acne, mood changes, decreased bone density.
Insertion site scarring possible, no STI protection.
Risks:
Increased ectopic pregnancy risk if pregnancy occurs, infection at site.
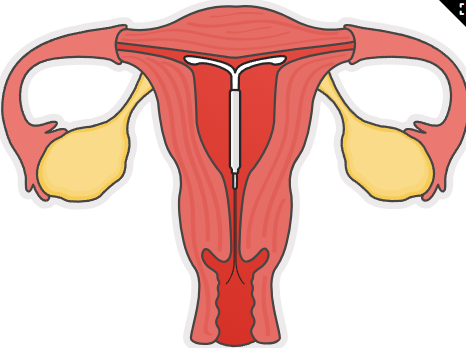
Intrauterine Device (IUD) (T-shaped device inserted into uterus, prevents fertilization; hormonal or copper types available.)
Client Education:
Monthly checks post-menstrual for string placement.
Consent required; pregnancy/STI testing prior insertion.
Sonogram if pregnancy suspected post-insertion.
Advantages:
Highly effective (3-10 years), reversible, immediate return to fertility post-removal.
Disadvantages:
Risk: PID, expulsion, ectopic pregnancy.
No STI protection, may increase menstrual pain
Contraindications:
Active pelvic infections, abnormal bleeding, severe uterine shape distortion.
Transcervical Sterilization (Flexible inserts placed through cervix into fallopian tubes causing scar tissue to block tubes (method currently discontinued))
Client Education:
Resume normal activities typically within 1 day.
Use alternative birth control for 3 months; tube blockage must be confirmed by examination.
Advantages:
Non-hormonal, highly effective (99.9%).
Quick, no general anesthesia.
Rapid recovery to daily activities.
Disadvantages:
Permanent, not reversible.
Not suitable postpartum.
Delayed effectiveness (3 months).
No STI protection.
Risks/Complications:
Potential expulsion or uterine perforation.
Pregnancy risk within initial 3 months.
Increased ectopic pregnancy risk if pregnancy occurs.
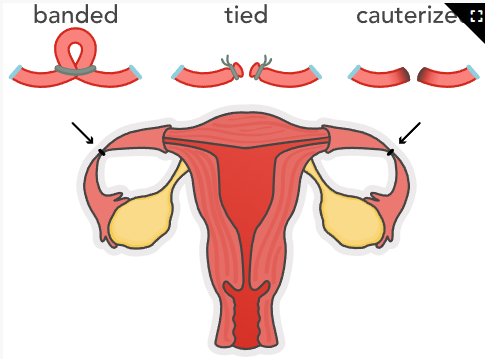
Female Sterilization (Bilateral Tubal Ligation)
Client Education:
Permanent contraception; reversible attempts are complex and often unsuccessful.
Resume sexual activities after comfort returns, typically within days post-surgery.
Advantages:
Permanent and effective immediately.
No hormonal influence.
Disadvantages:
Surgical risks, anesthesia required.
No STI protection.
Risks/Complications:
Bleeding, infection, anesthesia complications.
Rare ectopic pregnancy if failure occurs.
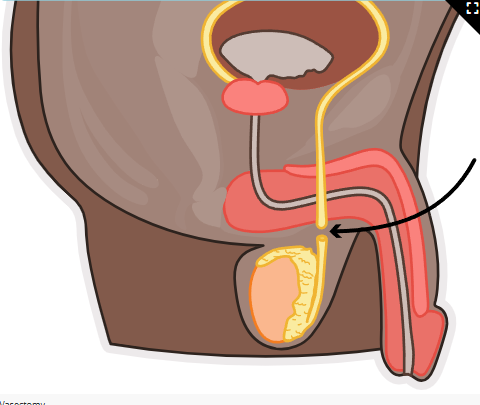
Male Sterilization (Vasectomy) (Surgical cutting or blocking vas deferens preventing sperm release.)
Client Education:
Not immediately effective; requires ~20 ejaculations or semen analysis confirmation (typically after 3 months).
Alternate contraception required until sperm-free confirmation.
Permanent; reversal is difficult and not guaranteed.
Advantages:
Permanent, safe, short recovery time, outpatient procedure.
Disadvantages:
Permanent; not reversible easily.
Requires backup contraception initially.
No STI protection.
Risks/Complications:
Bleeding, infection, hematomas, kidney stones, mild discomfort, rare sperm granulomas.
Male and Female Sterilization: Nursing Considerations
Pre-Procedure Care:
Ensure informed consent, verify client's understanding of procedure permanence.
Evaluate psychological readiness, ensure client not coerced.
Post-Procedure Care:
Monitor vital signs, surgical sites, manage discomfort.
Educate on signs of complications (infection, severe pain, fever).
Discuss emotional reactions post-procedure.
Chapter 2: Infertility
inability to conceive/sustain pregnancy after ≥12 months of unprotected intercourse.
Subfertility: reduced fertility; potential conception with assistance.
Common Factors:
Decreased sperm production
Endometriosis
Ovulation disorders
Tubal blockage
Impact on Clients:
Stress due to physical inability, cost, relationship strain, lack of support.
Initial Fertility Assessment: Risk Factors to Identify (Table)
Nursing Action:
Obtain thorough fertility history from both partners.
Educate clients about infertility risks and lifestyle modifications.
Infertility Diagnostics Procedures
Pelvic Examination: Checks for uterine or vaginal anomalies.
Hormone Analysis: Evaluates prolactin, FSH, LH, estradiol, progesterone, thyroid levels.
Postcoital Test: Assesses intercourse technique, mucus quality, sperm-cervical mucus interaction.
Ultrasonography: Visualizes reproductive organs (transvaginal/abdominal).
Hysterosalpingography: Radiographic dye test for fallopian tube patency; iodine allergy precautions.
Hysteroscopy: Evaluates uterine cavity for defects or scarring.
Laparoscopy: Uses gas insufflation and general anesthesia to examine internal organs.
Semen Analysis: Initial infertility test; less invasive, evaluates male fertility (repeated for accuracy).
Ultrasonography (Males): Visualizes testes, scrotum abnormalities; assesses ejaculatory ducts.
Infertility Therapeutic Procedures
Nonmedical & Lifestyle Interventions:
Nutrition/dietary modifications
Stress reduction (yoga, exercise)
Prescribed herbal medications
Acupuncture
Avoiding high scrotal temperatures
Medical Therapy:
Ovarian Stimulation (induces ovulation):
Clomiphene citrate
Letrozole
Supportive medications:
Metformin (ovulation induction support)
Progesterone (endometrial support)
Antibiotics for infections
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
Intrauterine Insemination (IUI):
Placing prepared sperm into uterus at ovulation.
In vitro fertilization-embryo transfer (IVF-ET):
Egg retrieval, fertilization in lab, embryo placement into uterus.
Gamete Intrafallopian Transfer (GIFT):
Eggs and sperm placed into fallopian tube via laparoscopy; fertilization occurs naturally.
Donor Oocyte:
IVF procedure using donated eggs implanted into recipient's uterus; hormonal preparation required.
Donor Embryo (Embryo Adoption):
Donated embryo transferred into hormonally-prepared recipient's uterus.
Gestational Carrier (Embryo Host):
IVF-created embryo placed into carrier with no genetic relation.
Surrogate:
Carrier inseminated with sperm, has genetic connection to offspring.
Therapeutic Donor Insemination:
Insemination using donor sperm
Nursing Interventions for Infertility
Encourage emotional support (support groups, counseling).
Educate about available diagnostic tests, treatments, medications.
Monitor medication effectiveness and side effects.
Provide pre/post-procedure care instructions.
Support informed decision-making regarding assisted reproductive options.
Complications of Infertility Treatments
Ectopic Pregnancy
Implantation outside uterus (fallopian tube or abdominal cavity).
Risk: Rupture, severe bleeding, infertility recurrence.
Management: Surgical removal or methotrexate therapy.
Multiple Gestations
Increased likelihood with assisted reproductive technologies.
Higher risk for pregnancy complications, maternal/fetal outcomes.
Genetic Counseling
Recommended if family history of genetic disorders (e.g., birth defects, sickle cell anemia), or maternal age >35.
Assess risks via prenatal genetic testing (e.g., amniocentesis).
Clarify genetic risks; provide emotional support throughout the process.
Nursing Actions:
Compile detailed family medical histories.
Provide emotional support for grief, guilt, denial, anger, or blame.
Refer to specialized counseling/support services as needed.
Chapter 8: Infections in Pregnancy
Prompt identification and management essential to prevent maternal/fetal complications. Routine screening during prenatal visits is crucial.
Common Screening Tests:
Syphilis
Hepatitis B/C
HIV
Gonorrhea, Chlamydia
HPV (via Pap smear)
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) in 3rd trimester
Additional screenings as needed: COVID-19, TORCH infections (Toxoplasmosis, Other infections [Hepatitis, Syphilis, etc.], Rubella, Cytomegalovirus, Herpes simplex), Trichomoniasis, BV, Candidiasis.
HIV/AIDS in Pregnancy
Retrovirus causing immunosuppression, can progress to AIDS.
Transmission risks: pregnancy, labor, birth, breastfeeding.
Complications (Untreated):
Preterm birth
Low birth weight
Perinatal transmission
Risk Factors:
IV drug use
Multiple sexual partners
History of multiple STIs
HIV/AIDS S/S
Flu-like symptoms: fatigue, diarrhea, weight loss, anemia
HIV/AIDS Labs/Dx
HIV/AIDS Interventions
Medications:
Antiretroviral Therapy (ART):
Continuous throughout pregnancy.
PO Zidovudine commonly used.
Combination therapy standard practice.
Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy (HAART):
IV Zidovudine intrapartum, PO postpartum.
Strict adherence essential.
Antepartum:
Goal: Maintain CD4 counts >500 cells/mm³, reduce transmission risk.
Educate on antiretroviral adherence, nutrition, rest, stress reduction.
Standard precautions for infection control.
Immunizations: Hep B, pneumococcal, Hib, influenza.
Condom use recommended.
Screen regularly for STIs.
Scheduled cesarean recommended if viral load >1,000 copies/mL.
Avoid invasive procedures (amniocentesis, episiotomies).
Intrapartum:
IV Zidovudine (AZT) recommended (if not on ART or viral load elevated).
Avoid procedures increasing maternal/fetal blood exposure (internal fetal monitors, episiotomy).
Delay newborn injections/blood testing until after first bath.
Avoid breastfeeding (due to transmission risk).
Postpartum:
Refer to specialist.
Emphasize NO breastfeeding.
Chlamydia in Pregnancy
Most common bacterial STI; often asymptomatic.
Complications if Untreated:
Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
Preterm labor, postpartum endometritis
Neonatal conjunctivitis, pneumonia
Risk Factors:
Multiple partners, unprotected sex
Chlamydia S/S
Dysuria, urinary frequency, spotting/bleeding, itching, gray-white discharge
Physical exam: mucopurulent discharge, cervical bleeding
Chlamydia Dx
Endocervical swab or urine sample
Chlamydia Interventions
Treatment:
Recommended: Azithromycin (PO, single dose)
Alternative: Amoxicillin (PO, 7 days)
Doxycycline and levofloxacin contraindicated in pregnancy
Newborn prophylaxis: Erythromycin ointment at birth
Nursing Education & Actions:
Complete antibiotic therapy
Treat partners, retest after 3–4 weeks (test of cure)
Use condoms consistently
Reportable to health department
Gonorrhea in Pregnancy
Gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae)
Bacterial infection; genital-genital, oral-genital, anal-genital transmission
Gonorrhea
Complications if Untreated:
PID, salpingitis
Premature rupture of membranes (PROM)
Preterm birth, postpartum sepsis, endometritis
Neonatal infection (sepsis, ophthalmia neonatorum—can cause blindness, growth restriction)
Risk Factors:
Multiple partners, unprotected sex, age <25 sexually active
Gonorrhea S/S
Dysuria, pelvic/abdominal pain, purulent discharge
Physical exam: Yellow-green discharge, cervical bleeding
Gonorrhea Dx
Endocervical, urine, or anal/oral culture
Gonorrhea
Treatment:
Recommended: Ceftriaxone (IM) + Azithromycin (PO) if chlamydia not excluded
Newborn prophylaxis: Erythromycin ointment at birth
Nursing Education & Actions:
Complete antibiotic therapy, treat partners
Safe sex education, retest after treatment (3–4 weeks)
Reportable to health department
Erythromycin ointment to all newborns at birth
Syphilis in Pregnancy (spirochete Treponema pallidum)
Transmitted sexually or to fetus.
Complications if Untreated:
Brain/eye conditions, HIV risk, severe systemic conditions, fetal physical disabilities or death
Risk Factors:
Multiple partners, unprotected sex
Syphilis Dx
Non-treponemal (VDRL, RPR) for screening
Treponemal (EIA) tests for confirmation
Darkfield microscopy for lesion analysis
Syphilis S/S
Primary: Painless chancre (genital ulcer), enlarged lymph nodes
Secondary: Rash on palms/soles, lymphadenopathy
Latent: No symptoms
Tertiary: Organ damage, neurologic complications
Syphilis Interventions
Treatment:
Primary treatment: Benzathine penicillin G (IM, single dose)
If duration unknown: 3 doses recommended
Penicillin safe during pregnancy
Allergy management: Desensitization required (CDC recommendation)
Nursing Education & Actions:
Abstain from sex until sores healed
Test and treat partners
Encourage co-testing for chlamydia, gonorrhea, HIV
Consistent condom use
Reportable to health department
Hepatitis B in Pregnancy (Viral infection (HBV))
Spread via blood or sexual contact
Transmitted to fetus during pregnancy.
Complications (Untreated):
Neonatal infection, disability, death
Risk Factors:
Multiple sexual partners, unprotected sex
Healthcare employment (needlesticks)
Injectable drug use, blood transfusions
Hepatitis B S/S
Flu-like symptoms: fatigue, malaise, anorexia, abdominal discomfort
Hepatitis B Dx
Blood test for HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
Hepatitis B Interventions
Treatment:
No specific cure; supportive care
Newborn prophylaxis: Hepatitis B immune globulin + HBV vaccine within 12–24 hrs of birth
Nursing Education & Actions:
Avoid liver-damaging substances (medications/alcohol)
Well-balanced diet (high protein, low fat), adequate fluids
Household/partners need immunoprophylaxis
Safe sex education, personal hygiene (no shared items)
Group B Streptococcus (GBS)
Bacterial infection normally found in vaginal flora
Can transmit to fetus during delivery.
Complications:
Preterm labor/birth
Infections (maternal sepsis, UTI, endometritis postpartum)
Neonatal infections (pneumonia, meningitis, sepsis)
Risk Factors:
Previous pregnancy with positive culture
Current pregnancy: positive culture, prolonged membrane rupture (≥18 hrs), preterm labor, fever during labor (>100.4°F), low birth weight
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) S/S
Asymptomatic
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Dx
Vaginal/rectal cultures at 36–37 weeks gestation
Group B Streptococcus (GBS) Interventions
Treatment:
IV Antibiotics: Penicillin G (preferred) or ampicillin during labor
Initial loading dose, then repeated doses every 4 hours until birth
Nursing Education & Actions:
IV antibiotic prophylaxis during labor (if positive or risk factors present)
Notify labor/delivery staff about GBS status
Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Most common STI; various strains (genital warts: 6,11; dysplasia/cancer: other strains)
Complications:
Cervical cancer
Genital warts causing birth canal obstruction (potential cesarean needed)
Risk Factors:
Multiple partners, unprotected sexual contact
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) S/S
Genital warts (small, cauliflower-like), vaginal discharge, discomfort/pain with intercourse, bleeding after intercourse
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Dx
Pap smear (abnormal cervical cells)
Visual examination for genital warts
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Interventions
Treatment:
Topical medications (safe in pregnancy): Trichloroacetic acid (TCA), bichloroacetic acid (BCA)
Contraindicated during pregnancy: Podophyllin, imiquimod
Procedures: Cryotherapy (freezing warts) safe during pregnancy
Nursing Education & Actions:
Regular follow-up, multiple treatments may be needed
Safe sex education or abstinence
Lesion care: oatmeal baths, clean/dry lesions, loose clothing
Cesarean may be planned based on wart severity/location
Trichomoniasis (Protozoan parasite Trichomonas vaginalis))
STI via sexual contact.
Complications (Untreated):
Preterm birth, PROM, PID
Higher HIV risk, neonatal small-for-gestational age
Trichomoniasis S/S
Frothy, yellow-green discharge, foul odor
Itching, dysuria, painful intercourse
Strawberry cervix, vaginal bleeding on exam
Trichomoniasis Dx
Wet mount microscopy (flagellated protozoa)
Urine or vaginal swab (NAAT, rapid tests)
Trichomoniasis Interventions
Treatment:
Metronidazole (safe in pregnancy; defer breastfeeding for 12-24 hrs post-dose)
Nursing Education:
No alcohol with metronidazole (severe vomiting)
Abstain until treated; treat partners; condom use
Retest in 3 months post-treatment
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV)
Bacterial infection due to imbalance of vaginal flora.
Complications (Untreated):
Preterm birth, PROM
Postpartum endometritis, infection risks
Increased susceptibility to other STIs
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) S/S
Fishy-smelling, thin, milky-gray/white discharge
Vaginal itching or irritation
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) Dx
Positive whiff test (fishy odor, KOH prep)
Clue cells on microscopic exam (wet mount)
Bacterial Vaginosis (BV) Interventions
Treatment:
Metronidazole PO or Clindamycin PO (safe in pregnancy)
Avoid intravaginal treatments in pregnancy
Nursing Education:
No alcohol with metronidazole (severe vomiting)
Condoms recommended; partner treatment not usually required
Candidiasis (Yeast Infection, Candida albicans)
Fungal infection
Risk Factors:
Pregnancy, diabetes, antibiotic use, obesity, sugary diet
Candidiasis S/S
Thick, creamy, cottage-cheese-like discharge
Severe vaginal/vulvar itching, redness
Painful urination due to excoriation
Candidiasis Dx
pH <4.5 (acidic),
KOH wet mount showing yeast/pseudohyphae
Candidiasis Interventions
Treatment:
Topical antifungals (safe during pregnancy)
Avoid oral antifungals during pregnancy
Nursing Education:
Loose cotton underwear, avoid damp clothing
Avoid douching; avoid yogurt with live cultures
Diabetes screening if recurrent
COVID-19 in Pregnancy (Viral infection (SARS-CoV-2))
Complications:
Maternal: respiratory distress, ICU admission, coagulopathies
Fetal: preterm birth, stillbirth
Risk Factors:
Pre-existing conditions (obesity, diabetes)
COVID-19 S/S
Respiratory symptoms, fatigue, loss of taste/smell, congestion
COVID-19 Dx
Rapid nasal swab antigen test
PCR tests
COVID-19 Interventions
Treatment:
Follow CDC recommendations for most current treatment guidelines
Nursing Education & Actions:
Encourage vaccination (CDC recommendation)
Follow infection control guidelines (masking, hygiene)