reproductive system
1.0(2)
1.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
1
New cards
what are gonads?
the gonads are the organs that produce sex cells
2
New cards
what are the male gonads?
testes (=testicles)
\[one testis\]
\[two testes\]
\[one testis\]
\[two testes\]
3
New cards
what are the male sex cells?
sperm
4
New cards
sperm is the only cell in humans that has a _____
tail
5
New cards
what are gametes?
sex cells
6
New cards
the testis is divided into compartments, what does each compartment contain?
each compartment contains a tiny coiled tube called a semineferous tubule
7
New cards
what do the cells that make up the wall of the semineferous tubule do?
cells that make up the wall of the semineferous tubule divide to form sperm cell by a type of cell division
8
New cards
what is this cell division called?
meiosis
9
New cards
when and for how long does a male produce sperm?
a male starts producing sperm when he goes thru pubrety (at the age of 10-12) and continues to do so for the rest of his life
10
New cards
what is scrotum?
a sac of skin containing the testes
11
New cards
where are the testes?
the testes are in the scrotum (outside the core of the body)
12
New cards
why are the testes outside of the body?
because … they need to be cooler than the temperature inside the body
13
New cards
why do the testes need to be cooler than the temprature inside the body?
for meiosis to occur proprely
14
New cards
where do immature sperm cells travel to to finish maturing?
the epididymis
15
New cards
sperm cells stay in the epididymis until…?
ejaculation
16
New cards
what is ejaculation?
the release of semen during orgasm
17
New cards
what is semen?
sperm cells and liquid produced by 3 glands
18
New cards
which 3 glands produce semen?
1. prospate gland
2. seminal vesicles
3. cowper’s gland
19
New cards
what do these fluids do? (2)
these fluids
1) protect the sperm from the acidity of the vagina
2) contain nutrients (e.g. fructose) that provide a source of energy for the sperm cells
1) protect the sperm from the acidity of the vagina
2) contain nutrients (e.g. fructose) that provide a source of energy for the sperm cells
20
New cards
what % of the volume of semen consists of sperm cells?
5%
21
New cards
how many \~# sperm cells are in a single ejaculation
\~250 million
22
New cards
what is the path taken by a sperm cell thru a man’s body?
testes → epididymis → vas deferens → urethra
23
New cards
what is a vasectomy? (2)
\- a surgery in which the 2 vas deferens are cut and tied off
\- a permanent form of birth control
\- a permanent form of birth control
24
New cards
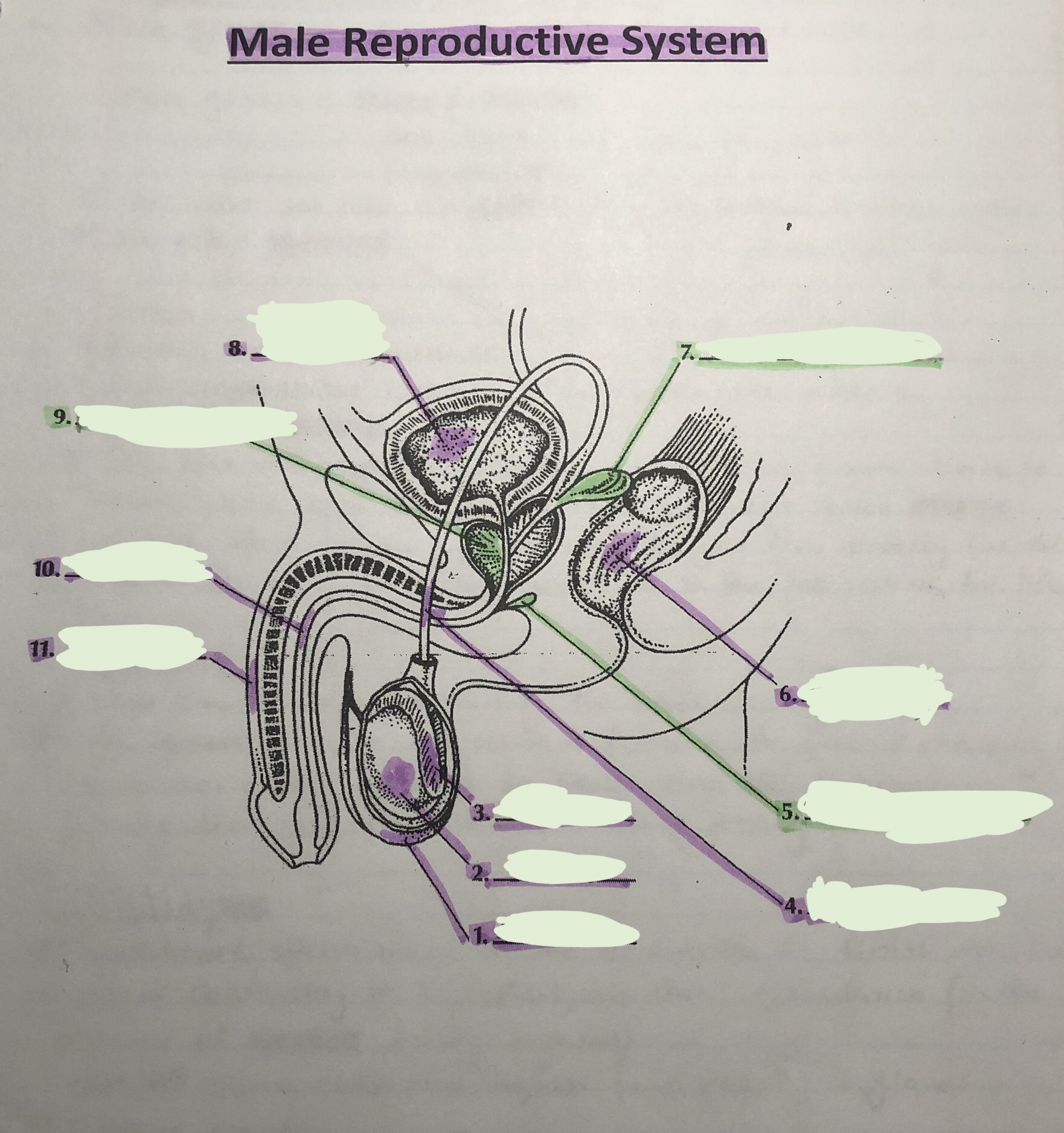
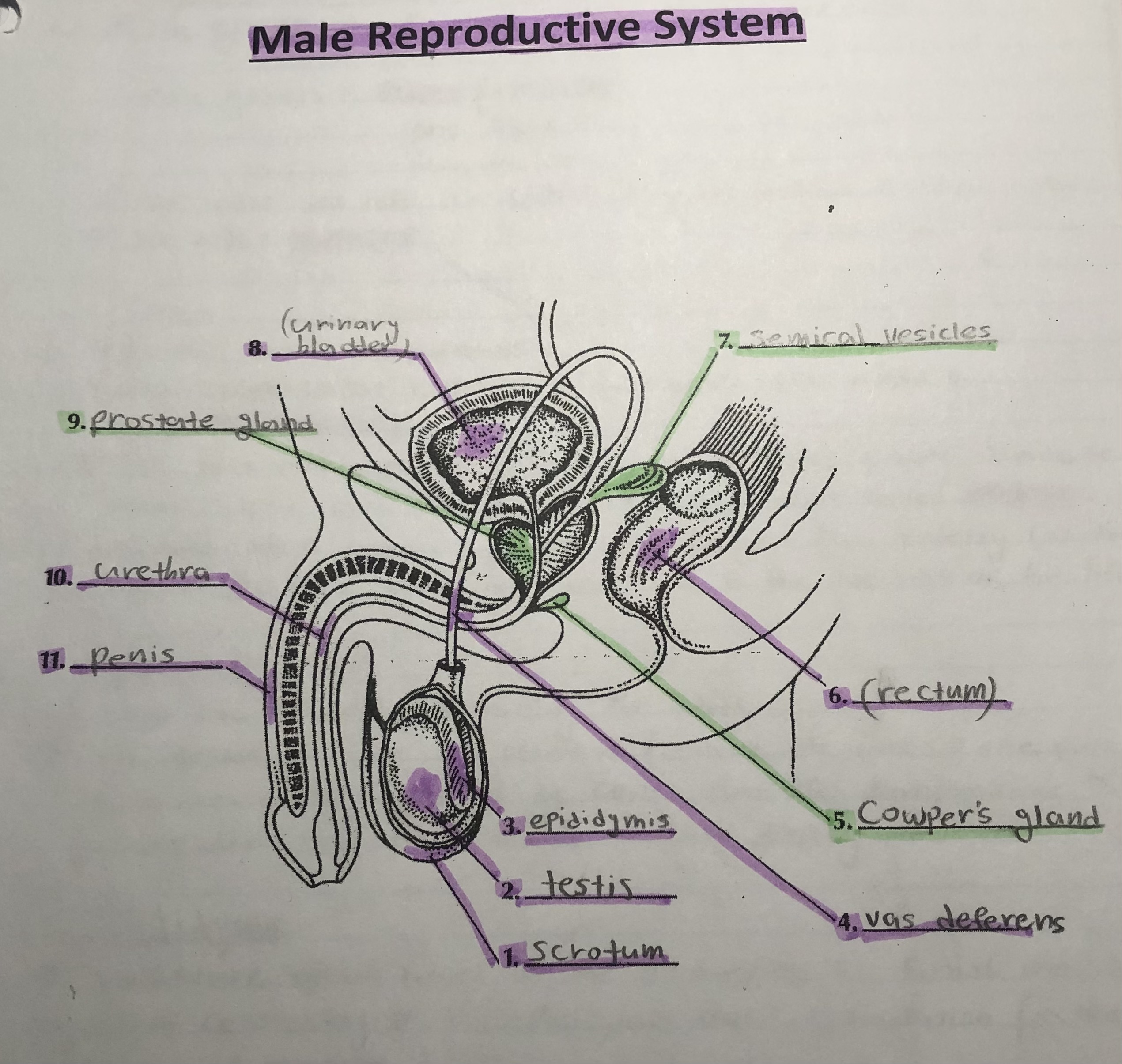
label the male reproductive system
answer key
25
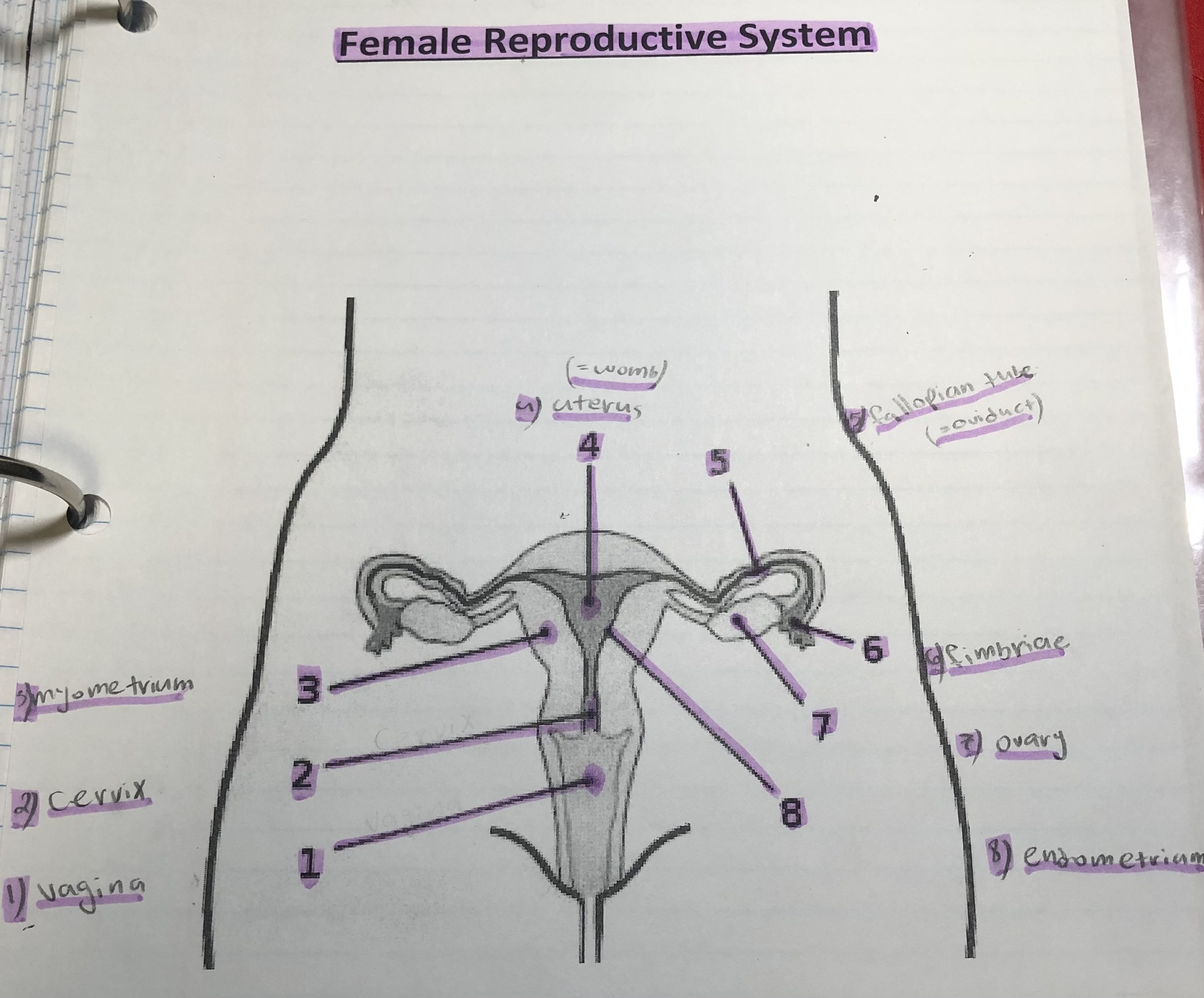
New cards
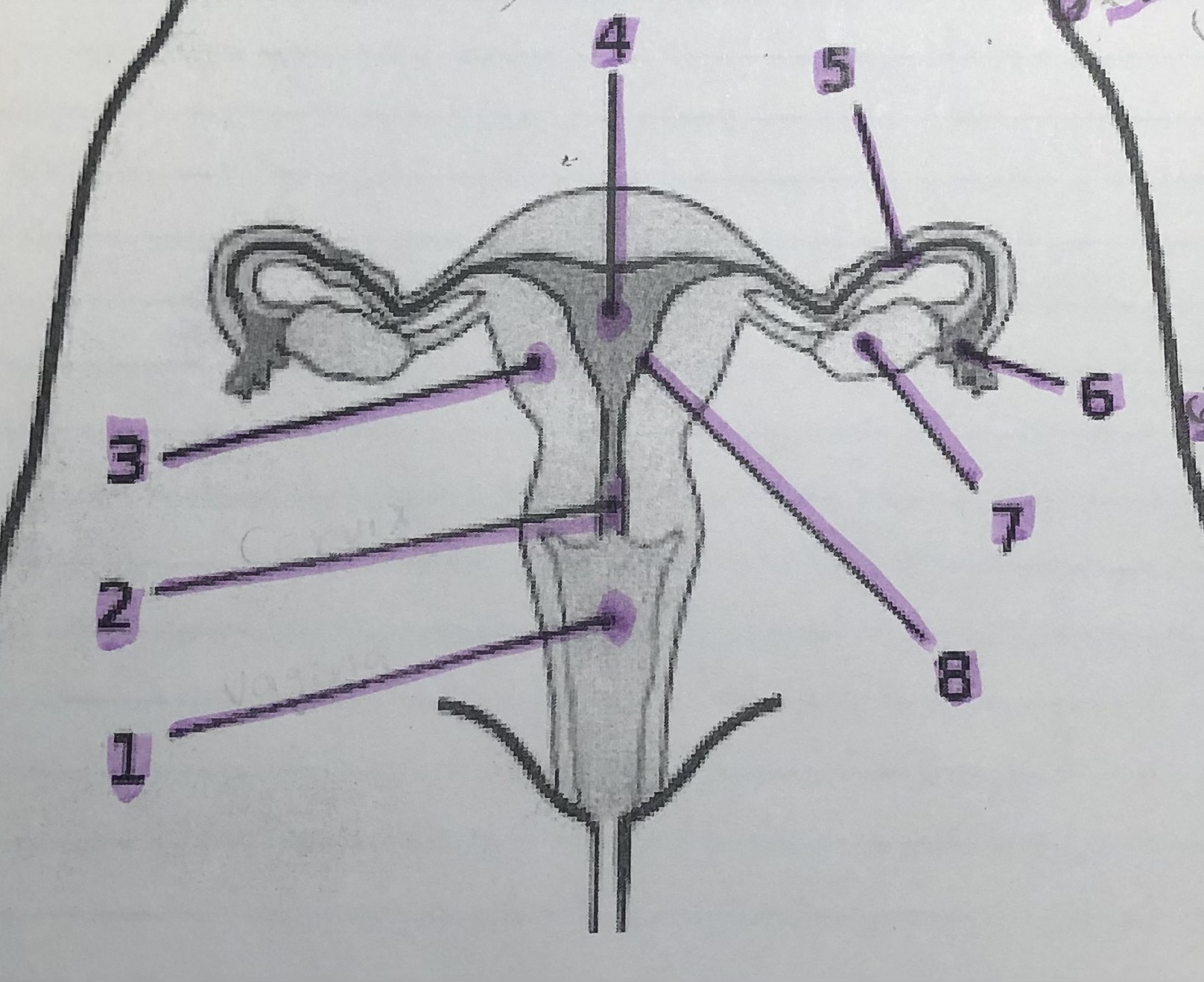
label the female reproductive system
answer key
26
New cards
what are the female gonads?
ovaries
27
New cards
what do the ovaries produce?
the female gamates
28
New cards
what are the female gametes?
ova (=eggs)
29
New cards
how many eggs does each ovary contain?
Each ovary contain \~200,000 eggs
30
New cards
what is an ovarian follicle?
= consists of an ovum surrounded by many **follicle cells**
31
New cards
how does a girl get her follicles?
A girl is born with all of the follicles that she will ever have
32
New cards
what is ovulation?
= the process by which a follicle bursts releasing an ovum
33
New cards
On average, a woman ovulates once every ___ days
28
34
New cards
how many eggs does a woman ovulate during her life?
\~500
35
New cards
what is the fimbriae?
what do the fimbriae do?
what do the fimbriae do?
\- The fimbriae are finger-like structures found at the end of a fallopian tube
\- Fimbriae bring the ovulated egg into the fallopian tube
\- Fimbriae bring the ovulated egg into the fallopian tube
36
New cards
An egg is moved down a fallopian tube toward the uterus by?
**1) Cilia that line the fallopian tubes that beat and make a current**
**2) Muscles** in the **wall** of the **fallopian tubes** create peristaltic contractions
**2) Muscles** in the **wall** of the **fallopian tubes** create peristaltic contractions
37
New cards
what is fertilization?
= the process by which an egg cell and a sperm cell fuse to form a fertilizied egg
38
New cards
what is another name for a fertilized egg?
zygote
39
New cards
where does fertilization usually occur?
Fertilization usually occurs in the top **⅓** of a fallopian tube
40
New cards
The zygote begins to divide by cell division to form an **_____**
embryo
41
New cards
what is implantation?
= the process by which an embryo attaches to the **endometrium**
42
New cards
what is the endometrium?
(=inner lining of the uterus)
43
New cards
what is an ectopic pregnancy?
occurs when implantation occurs somewhere other than the uterus
44
New cards
what % of all pregnancies are ectopic?
2%
45
New cards
where do 90% of ectopic pregnancies occur?
in the fallopian tube
46
New cards
what is the menstrual cycle?
= a 28-day cycle that a woman experiences from puberty until menopause
47
New cards
what’s a word that means a time when a woman is most likely to get pregnant? + when is a woman that?
fertile
A woman is fertile (=most likely to get pregnant) **during a certain part of her menstrual cycle**
A woman is fertile (=most likely to get pregnant) **during a certain part of her menstrual cycle**
48
New cards
what happens in day 1 of the menstrual cycle?
**Day 1** of the menstrual cycle is when a woman “gets her period” (**=menstruates**)
49
New cards
what is menstruation? + what does it consists of? + what does it indicate? + when does it happen during the menstrual cycle?
\- = the process by which the endometrium detaches from the uterus and exists the body thru the vagina
\- Menstrual flow consists mostly of blood and extra tissue from the lining of the uterus
\- Indicates that a woman is **not** pregnant
\- Day 1-5
\- Menstrual flow consists mostly of blood and extra tissue from the lining of the uterus
\- Indicates that a woman is **not** pregnant
\- Day 1-5
50
New cards
The menstrual cycle is regulated by __ _________
4 hormones
51
New cards
what is a hormone?
= a chemical that is formed in one part of the body, travels thru the blood, and affects the function of cells elsewhere in the body
52
New cards
what are endocrine glands?
An organ that releases hormones
53
New cards
what does FSH stand for? + what does it cause? + where is it released from?
**- FSH –>** **F**ollicle **S**timulating **H**ormone
\- The hormone that causes the growth of several follicles in the ovaries during the first half of the menstrual cycle
**- FSH** is released from the **pituitary gland**
\- The hormone that causes the growth of several follicles in the ovaries during the first half of the menstrual cycle
**- FSH** is released from the **pituitary gland**
54
New cards
when does ovulation occur + what does it indicate?
\- Occurs on (or around) day 14
\- This is when a woman is most fertile
\- This is when a woman is most fertile
55
New cards
what does LH stand for? + what does it cause? + where is it released from?
**- LH –>** **L**uteinizing **H**ormone
\- The hormone that specifically causes ovulation
\- **LH** is released from the pituitary gland
\- The hormone that specifically causes ovulation
\- **LH** is released from the pituitary gland
56
New cards
what happens after menstruation is complete (day 5)?
\- Thickening Of The Endometrium
\- After menstruation is complete (day 5), the endometrium begins to get thicker in preparation for a possible pregnancy
\- After menstruation is complete (day 5), the endometrium begins to get thicker in preparation for a possible pregnancy
57
New cards
what are the 2 other hormones? + what do they cause? + where are they made?
Estrogen & Progesterone
\- The hormone that causes the endometrium to get thicker
**- Estrogen** is made by the ovaries
\- Progesterone is made by the **corpus luteum**
\- The hormone that causes the endometrium to get thicker
**- Estrogen** is made by the ovaries
\- Progesterone is made by the **corpus luteum**
58
New cards
what does corpus luteum consist of?
it consists of the left over cells after a follicle has ovulated its egg
59
New cards
what does testesterone cause? + what does it include?
\- The development of the **secondary sex characteristics** in the male
\- Body hair, muscle development and deep voice.
\- Body hair, muscle development and deep voice.
60
New cards
Why are the testes in the scrotum, outside the body? + What is this necessary for?
\- The scrotum keeps the testes at a temperature slightly lower than the rest of the body
\- This is necessary for the production and storage of sperm
\- This is necessary for the production and storage of sperm
61
New cards
What would happen if the testes become too warm? + what would happen if they become too cool?
\- If the testes become too warm, muscles in the scrotum relax, allowing the testes to fall away from the body
\- If the testes become too cool, the scrotal muscles pull them closer to the body
\- If the testes become too cool, the scrotal muscles pull them closer to the body
62
New cards
Where do the testes form? When? And what happens after? when?
\- The testes form inside the body
\- during development
\- they move down into the scrotum
\- In the last month before birth
\- during development
\- they move down into the scrotum
\- In the last month before birth
63
New cards
Can testes that stay within the body make sperm? Why or why not?
\- No
\- Testes that stay within the sperm cannot make sperm because the temperature is too high
\- Testes that stay within the sperm cannot make sperm because the temperature is too high
64
New cards
sometimes one, or both testes do not pass into the scrotum. What can be done about it?
\- They can be moved **surgically** or with **hormone treatment**
65
New cards
What is each testis made up of? (define) + What is it called? + What is made in there?
\- Each testis is made up of small, coiled tubes.
\- Called the seminiferous tubules
\- Premature sperm are made in the seminiferous tubules
\- Called the seminiferous tubules
\- Premature sperm are made in the seminiferous tubules
66
New cards
How many seminiferous tubules are in each testis?
300-600
67
New cards
What is the epididymis?
A storage area on the upper rear part of each testis
68
New cards
What is the vas deferens?
A tube that carries the sperm out of the testes
69
New cards
What is the urethra?
The passageway for the excretion of urine
70
New cards
Where do the two vas deferens empty into? + What about mammals?
\- Into the urethra
\- In mammals, it is also the passageway thru which sperm leave the body
\- In mammals, it is also the passageway thru which sperm leave the body
71
New cards
In the human male, where does the urethra pass?
The urethra passes thru the penis to the outside of the body
72
New cards
What happens as sperm enters the urethra?
As sperm enters the urethra, the seminal vesicles, cowper’s glands and the prostate gland all secrete fluids into the urethra.
73
New cards
why does the sperm need these fluids?
These fluids nourish the sperm and protect them from the acidity of the female reproductive tract (vagina)?
74
New cards
What is semen?
The mixture of sperm and fluids
75
New cards
What is ejaculation?
\- A process
\- Involuntary muscular contraction forces the semen thru the urethra and out of the body.
\- Involuntary muscular contraction forces the semen thru the urethra and out of the body.
76
New cards
What happens for a short time before, during and after ejaculation? + what does this prevent?
\- for a short time before, during and after ejaculation, reflex actions keep the outlet of the urinary bladder closed
\- This prevents urine from entering the urethra and mixing with the semen
\- This prevents urine from entering the urethra and mixing with the semen
77
New cards
Where are premature sperm made? Where does it go from there?
\- In the seminiferous tubules
\- From there the immature sperm, pass to the epididymis
\- From there the immature sperm, pass to the epididymis
78
New cards
How long does it take sperm to mature in the epididymis?
about 18 hours
79
New cards
Where does the sperm leave the epididymis thru?
thru the vas deferens
80
New cards
What do the ovaries make?
eggs
81
New cards
What are the eggs?
the female gametes
82
New cards
What do the ovaries secrete?
The female sex hormone - **estrogen**
83
New cards
What does estrogen cause? (2) + What are the female secondary sex characteristics?
\- Estrogen causes the development of female secondary sex characteristics
\- Also plays a big role in the menstruation cycle
* Breasts
* A broadened pelvis
* The distribution of body fat
\- Also plays a big role in the menstruation cycle
* Breasts
* A broadened pelvis
* The distribution of body fat
84
New cards
How many ovaries are there? + Where are they found? + size?
\
\- There are **two** ovaries
\- They are found in the lower part of the abdomen
\-They are about 4cm long and 2cm wide
\- There are **two** ovaries
\- They are found in the lower part of the abdomen
\-They are about 4cm long and 2cm wide
85
New cards
What does each ovary contain? + What is it called? + What can you find in each follicle?
\- Each ovary contains about 200,000 tiny egg sacs
\- Called follicles
\- An immature egg
\- Called follicles
\- An immature egg
86
New cards
Are immature eggs present at the time of birth? + About how many eggs mature during the life of a female?
\- yes
\- no more than 500
\- no more than 500
87
New cards
What happens to an egg’s follicle when the egg matures? + What is this process called?
\- When an egg matures, its follicle moves to the surface of the ovary
\- The follicle then breaks, releasing the egg
This process called **ovulation**
\- The follicle then breaks, releasing the egg
This process called **ovulation**
88
New cards
What is the time frame of when an egg can be fertilized after ovulation?
An egg can be fertilized for **about 24 hours** after ovulation
89
New cards
What’s near every ovary but NOT connected to it? + what is it also known as?
An oviduct
AKA fallopian tube
AKA fallopian tube
90
New cards
What is the oviduct (fallopian tube)?
The oviduct is a tube with a funnel-like opening
91
New cards
What lines the oviduct (fallopian tube)? + why?
\- cilia
\- Cilia lining the oviduct create a current that draws the released egg into the tube
\- Cilia lining the oviduct create a current that draws the released egg into the tube
92
New cards
The _____ is where the _____ may be fertilized if any _____ are present
\- oviduct
\- egg
\- sperm
\- egg
\- sperm
93
New cards
Where does the egg go from the oviduct (fallopian tube)?
From the oviduct, the egg passes into the **uterus**
94
New cards
What is the uterus?
A thick-walled, muscular, pear-shaped organ
95
New cards
If the egg has been fertilized, where does it finish its development? + attached to what?
\- It finished its development in the uterus
\- attached to the uterine wall
\- attached to the uterine wall
96
New cards
What is the cervix?
the narrow neck of the vagina
97
New cards
What does the cervix open to? + what else is it known as?
\- the cervix opens into the vagina
\- AKA birth canal
\- AKA birth canal
98
New cards
What does the vagina (birth canal) lead to?
the outside of the body
99
New cards
In the early stages of the human female embryo, the ____ joins the ____, as does the _____ _____ in the male
\- vagina
\- urethra
\- vas deferens
\- urethra
\- vas deferens
100
New cards
During later development a ______ ______ is formed for the vagina
second opening