NURS 124
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:34 AM on 4/21/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
1
New cards
intrapersonal communication
one's thinking, is also known as self talk or inner thoughts. This develops self awareness, positive self concept, self expression and improves health and self esteem.
2
New cards
interpersonal communication
direct, face-to-face communication between two or more people, patient to nurse
3
New cards
contextual knowledge
Research about the history, location, culture, economics, relationships, politics and beliefs, attitudes and values related to a character or text will provide contextual knowledge. \n \n building block to providing context-based and relevant care
4
New cards
Initiative (in relational practice)
initiative assesses or initiates things independently, nurses can reach out and listen to patient needs and concerns.
5
New cards
authenticity (in relational practice)
being genuine or real, being spontaneous and genuine, aware of in the moment experience of the patient
6
New cards
Reflexivity
being aware of your own pattern of communication and response to communication, as well as the response you are evoking in others.
7
New cards
message
the content of communication
8
New cards
Perception
it is information gathered by the five senses (sight, hearing, taste, touch, and smell), the mentally organizing it to come to a conclusion based on this sensory information
9
New cards
perceptual biases
human tendencies that interfere with accurately perceiving and interpreting messages from other people, nurses can use critical thinking and self reflection to overcome this.
10
New cards
mutuality and mutual understanding
having respect and understanding beliefs, morals and values between the patient and nurse
11
New cards
Relational Practice
\
\
The art and skill of being able to connect with people across differences by joining with them as they are and where they are.
12
New cards
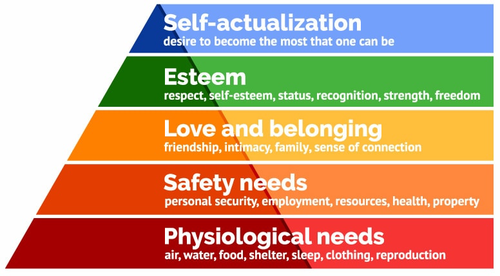
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
communication theory
13
New cards
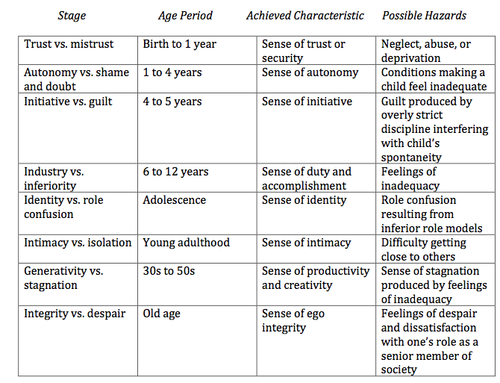
Erikson
theorist who studied psychosocial development across the lifespan.
14
New cards
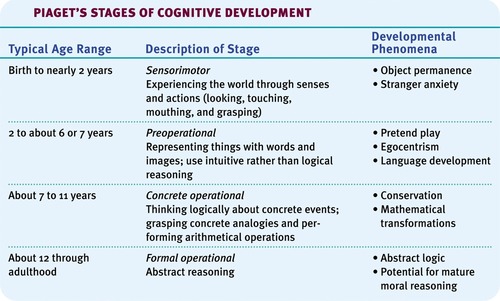
Piaget's stages of cognitive development
1\. sensorimotor \n 2. preoperational \n 3. concrete operational \n 4. formal operational
15
New cards
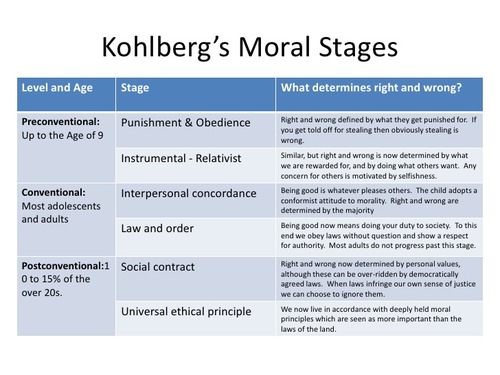
Kholberg's stages of moral development
preconventional, conventional, postconventional
16
New cards
Factors that impact development
* genetic forces
* environmental forces
* interactions between the two
* environmental forces
* interactions between the two
17
New cards
Traps of interviewing
\- Providing False Reassurance \n - Giving Unwanted Advice \n - Using Authority \n - Using Avoidance Language \n - Engaging in Distancing \n - Using Profession Jargon \n - Using Leading or Biased Questions \n - Talking too much \n - Interrupting \n - Using "why" Questions
18
New cards
defense mechanisms
the ego's protective methods of reducing anxiety by unconsciously distorting reality
19
New cards
barriers to relationships
Anxiety \n Stereotyping and bias \n Overinvolvement \n Violation of personal space \n Time limitations \n Gender differences \n Cultural
20
New cards
clarifying
The process of making sure you have understood the meaning of what was said
21
New cards
Summarizing
Briefly stating the main points and key details of a work in your own words.
22
New cards
ADPIE
\- Assessment \n - Diagnosis: \n - Planning \n - Implementation: \n - Evaluating:
23
New cards
assessment
The ability to communicate includes gathering data about the many contextual factors. sorts and analyzes a patient's health information using evidence-informed tools to learn more about a patient's overall health, symptoms, and concerns. Finding information regarding physical and emotional factors, developmental factors, sociocultural factors, and gender.: 1st step, subjective and objective data
24
New cards
diagnosis
A nursing diagnosis is a clinical judgment concerning a human response to health conditions/life processes, or a vulnerability for that response, by an individual, family, group, or community
25
New cards
planning
prioritizing problems, determining goals, plan of care. once taking information found in the assessment and diagnoses you use this information to set goal. Using nursing interventions to make improvements in their health, then pick a measurable goal based on the problem at hand.
26
New cards
implementation
nursing action (rather than medical action)Carrying out the care plan made. Throughout this process, it is important to use therapeutic communication techniques.
27
New cards
evaluation
comparing outcomes, communicate and document findings
28
New cards
SMART goals
Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Realistic, Timely
29
New cards
DARP charting
Data - subjective or objective information that supports the stated focus or describes the patients status at the time of a significant event or intervention \n \n Action - Completed or planned nursing intervention based on the nurses assessment of the patient's status \n \n Response - Description of the impact of the interventions on patient outcome \n \n Plan
30
New cards
SOAPIER charting
S = subjective data (e.g., how does the client feel?) \n O = objective data (e.g., results of the physical exam, relevant vital signs) \n A = assessment (e.g., what is the client's status?) \n P = plan (e.g., does the plan stay the same? is a change needed?) \n I = intervention (e.g., what occurred? what did the nurse do?) \n E = evaluation (e.g., what is the client outcome following the intervention?) \n R = revision (e.g., what changes are needed to the care plan?)
31
New cards
narrative documentation
records information as a sequence of events in a story-like manner
32
New cards
Continuity of care
* Relational Continuity
* Informational Continuity
* Management Continuity
* Informational Continuity
* Management Continuity
33
New cards
relational continuity
interpersonal components of the COC model across time and care settings
34
New cards
informational continuity
data exchanges among providers and provider systems, and between providers and patients for the purpose of providing continuously coordinated, quality care.
35
New cards
management continuity
consistent, coherent case management approach, which can be flexibly adjusted, as the patient's needs change
36
New cards
SBAR
* situation
* background
* assessment
* recommendation/request
* background
* assessment
* recommendation/request

37
New cards
IDRAW
•IDENTIFICATION
•DIAGNOSIS
•RECENT CHANGE/S
•ANTICIPATED CHANGE/S
•WHAT TO WHAT FOR
38
New cards
inter-professional communication
The ability to communicate with patients, families, communities and other health care professionals in a responsive and responsible manner that supports a team approach to the maintenance of health and the treatment of disease
39
New cards
Pre-interaction phase
task- gathering information, anticipating , set up an interaction \n \n purpose- to become prepared for an effective interaction \n \n skills- non verbal, reading, processing, synthesizing data attending to enviroment
40
New cards
orientation phase
task - Clarifying purpose of relationship & roles \n Establishing trust \n Making inferences; \n identifying needs & strengths \n Defining the problem & goals \n \n purpose -To determine how the client views the problem, and client strengths that might be used to resolve problem \n To find out how the client would like to be; how things would be if the problems were solved.
41
New cards
working phase
when the nurse and the patient work together to solve problems and accomplish goals, talk about values and feelings, empowerment \n \n \n purpose- to wokr towards resolution, enable changes in thoughts feelings and behaviours \n \n skills- influencing, feedback, slience, controntation, sharing observations
42
New cards
Termination phase
tasks - Prepare for termination \n Evaluation: were the patient goals met & were the interventions appropriate \n Transition to other caregivers or self-care \n \n purpose- To evaluate the effectiveness of the changes, interaction & separate \n \n skills- Influencing; positive feedback; validation; summarizing