Cells and control UP TO 2.13 (adaptations of neurones heading in notes)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
stages of the cell cycle
interphase, mitosis cytokinesis
stages of mitosis
prophase
metaphase
anaphase
telophase
stages of mitosis acronym
PMAT
interphase
the cells spends most of it's life in this phase
the DNA in chromosomes copies itself ready for mitosis
prophase
- nuclear membrane disappears
- the DNA unwinds and condenses into chromosomes
- spindle fibres become visible
metaphase
- chromosomes line up along the centre of the cell
- spindle fibres attach to the chromosomes
anaphase
- chromatids are pulled to the edges of the cell
- by the spindle fibres
telophase
- nuclear membrane forms around each of the sets of chromosomes at each end of the cell
- separating them from one another
cytokinesis
splits the cytoplasm to create 2 identical diploid daughter cells
what is mitosis required for?
growth
repair
asexual reproduction
role of mitosis in growth
mitosis produces new cells
role of mitosis in repair
to replace damaged or dead cells
role of mitosis in asexual reproduction
mitosis produces offspring that are genetically identical to the parent
describe mitosis
division of a cell by mitosis results in:
- the production of 2 daughter cells
- each with identical sets of chromosomes in the nucleus to the parent cell
- resulting in the formation of two genetically identical diploid daughter cells
cancer
- cancer is the result of mutations in the DNA
- where cell division is rapid and uncontrolled
- resulting in the formation of a tumour
through what processes do animals grow?
cell division (mitosis + meiosis)
cell differentiation
through what processes do plants grow?
cell division (mitosis + meiosis)
cell differentiation
cell elongation
cell differentiation
where a cell becomes specialized for a specific structure or function.
cell elongation in plants
where hormones, such as auxin, cause cells to grow longer in response to certain stimuli e.g. sunlight
importance of cell differentiation
Differentiated cells are important in a multicellular organism because they are able to perform vital specialised functions in the body. (eg. sperm)
cell differentiation in animals
in an animal, most cells differentiate at an early stage of it's development, with mature animals mainly restricted to repair and replacement of cells, not growth
the only cells able to differentiate throughout the life of an animal are adult stem cells
cell differentiation in plants
unlike animals, plant cells can fully differentiate throughout the plant's life, not just in the early stages of development
why are growth charts used?
to monitor the growth of an organism by comparing it's growth to the usual trends for that particular organism
how to read a growth curve
- find your child's weight and height and find where they intersect
- if a baby is on the 25th percentile, it means that they are lighter than 75% of babies their age, and heavier than 25% of babies their age
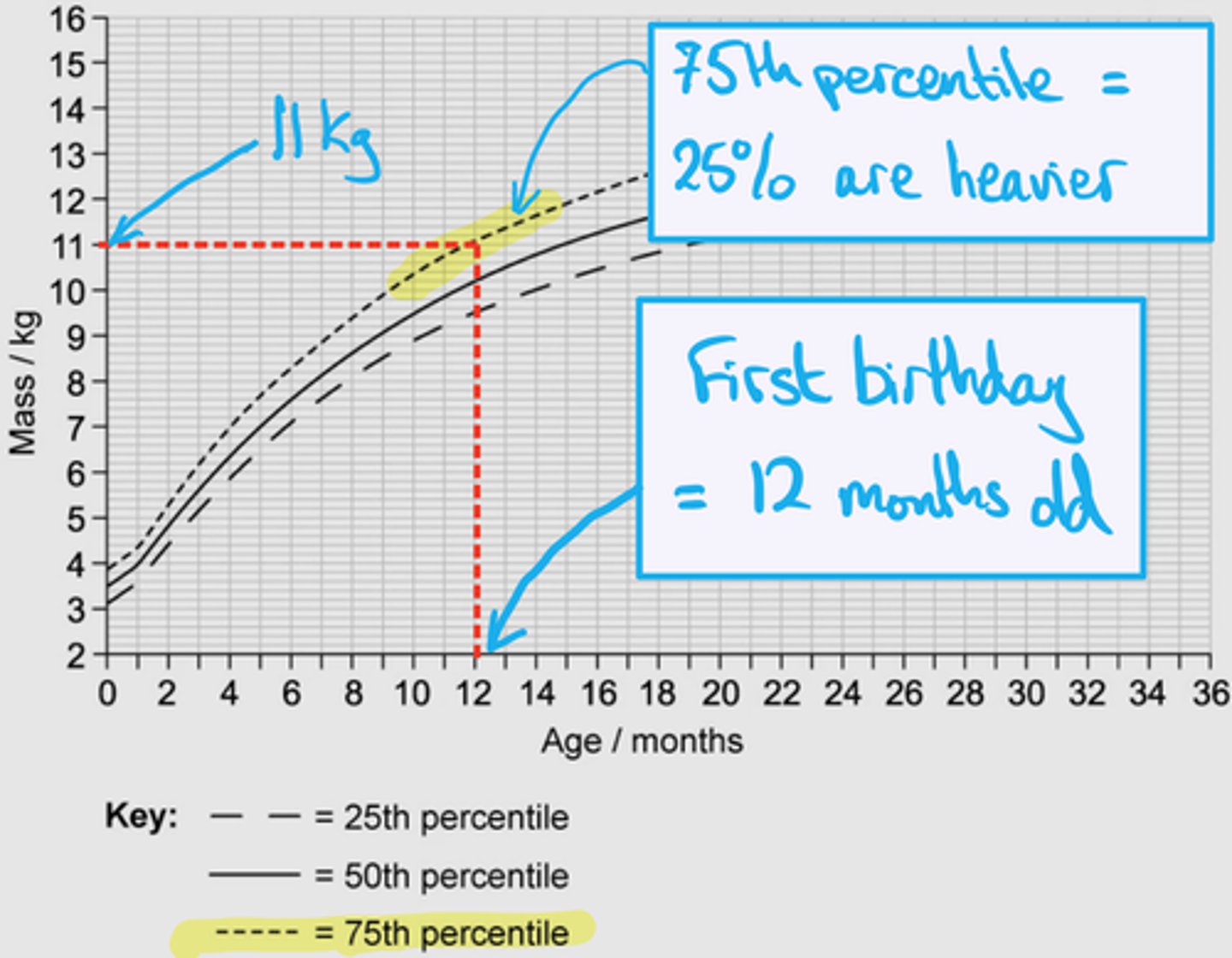
when is growth abnormal?
if someone moves from e.g. The 5th to 70th percentile in a short space of time
embryonic stem cells
- an undifferentiated stem cell
- form when an egg and sperm cell fuse to form a zygote
- can differentiate into any type of cell in the body
how can embryonic stem cells be used in medicine?
because they are undifferentiated, they can be stimulated to produce any type of cell
they can:
- repair damaged tissue
- replace damaged cells
in order to treat a variety of diseases e.g. Parkinson's, and replace damaged tissue e.g. nerve cells.
how can adult stem cells be used?
if found in bone marrow, adult stem cells can be used to form some types of cell including blood cells
stem cells in plants
found in meristems
can be used to make clones of teh plant, may be useful if the parent plant has certain desirable characteristics e.g. disease resistance
benefits of embryonic stem cells in medicine
- can be differentiated into any type of cell
- can be used to replace damaged cells or repair damaged tissue to treat/reduce symptoms of diseases e.g. arthritis
risks of using embryonic stem cells in medicine
- stem cells continue to divide and could cause cancer
- cells could be rejected
- removal of stem cells kills the embryo= ethical objections
cerebellum location
back of brain
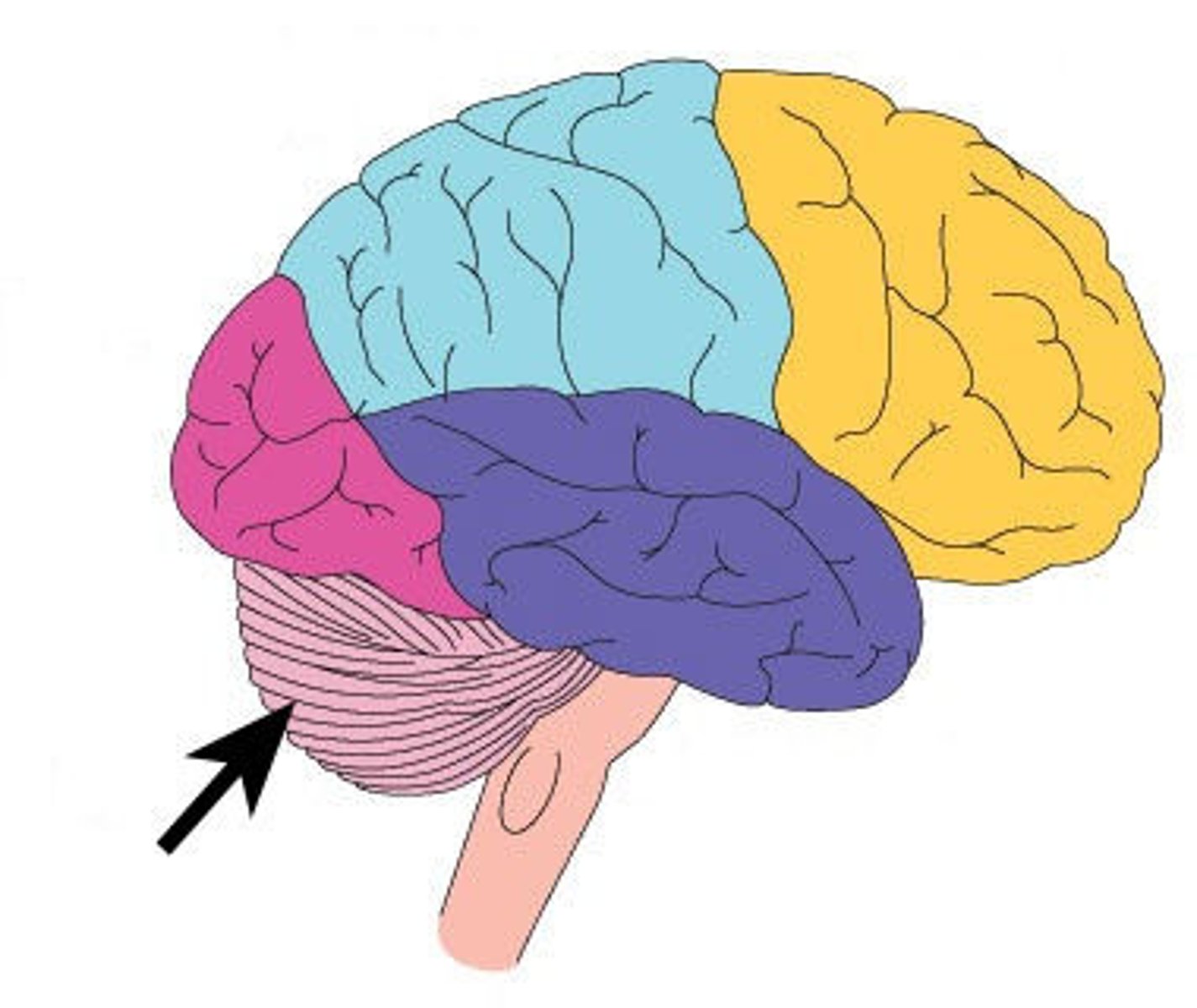
cerebellum function
controls balance, movement and fine motor skills
medulla oblongata location
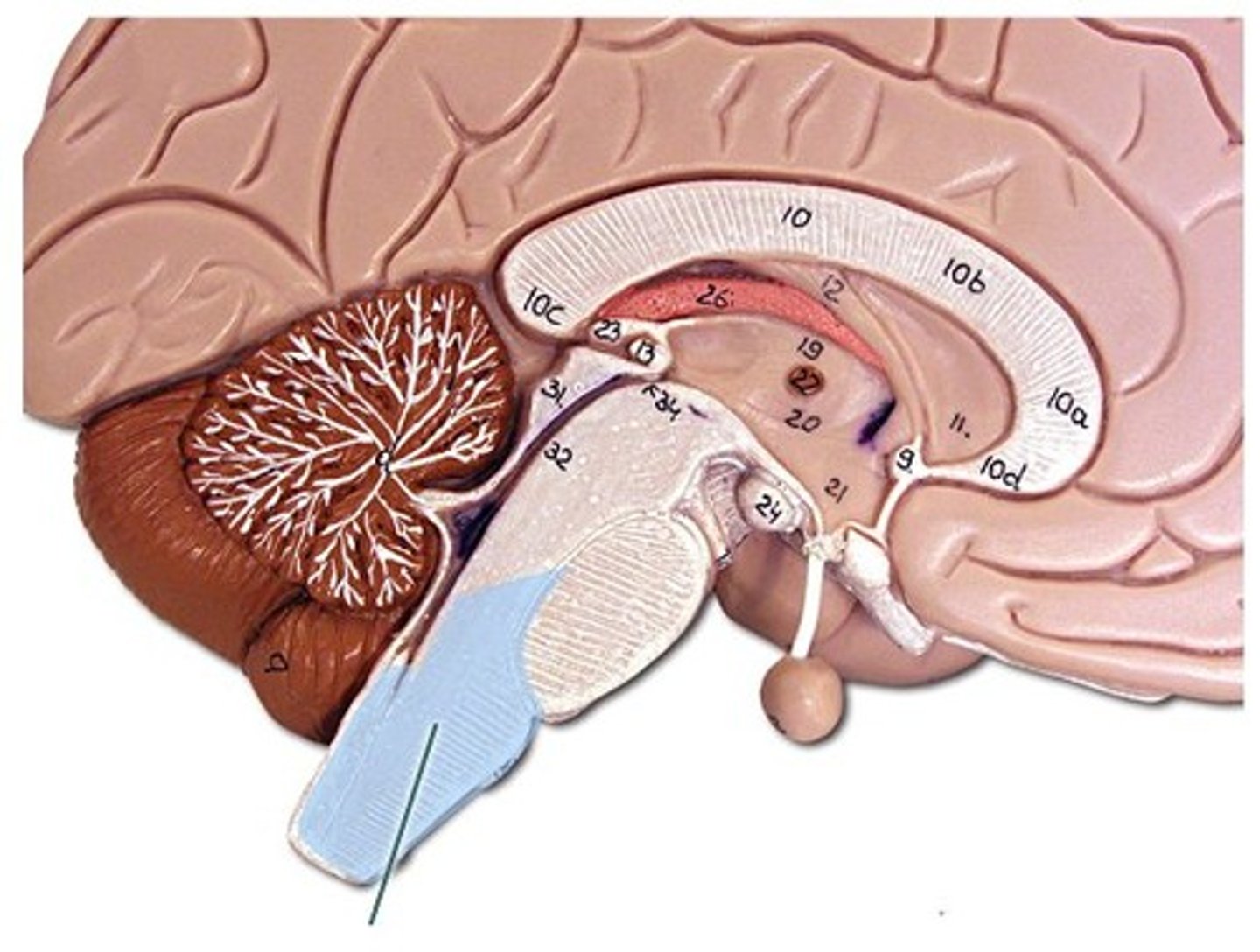
medulla oblongata function
connects brain to rest of nervous system
controls unconcious activities e.g. heart rate, breathing etc
cerebral cortex location
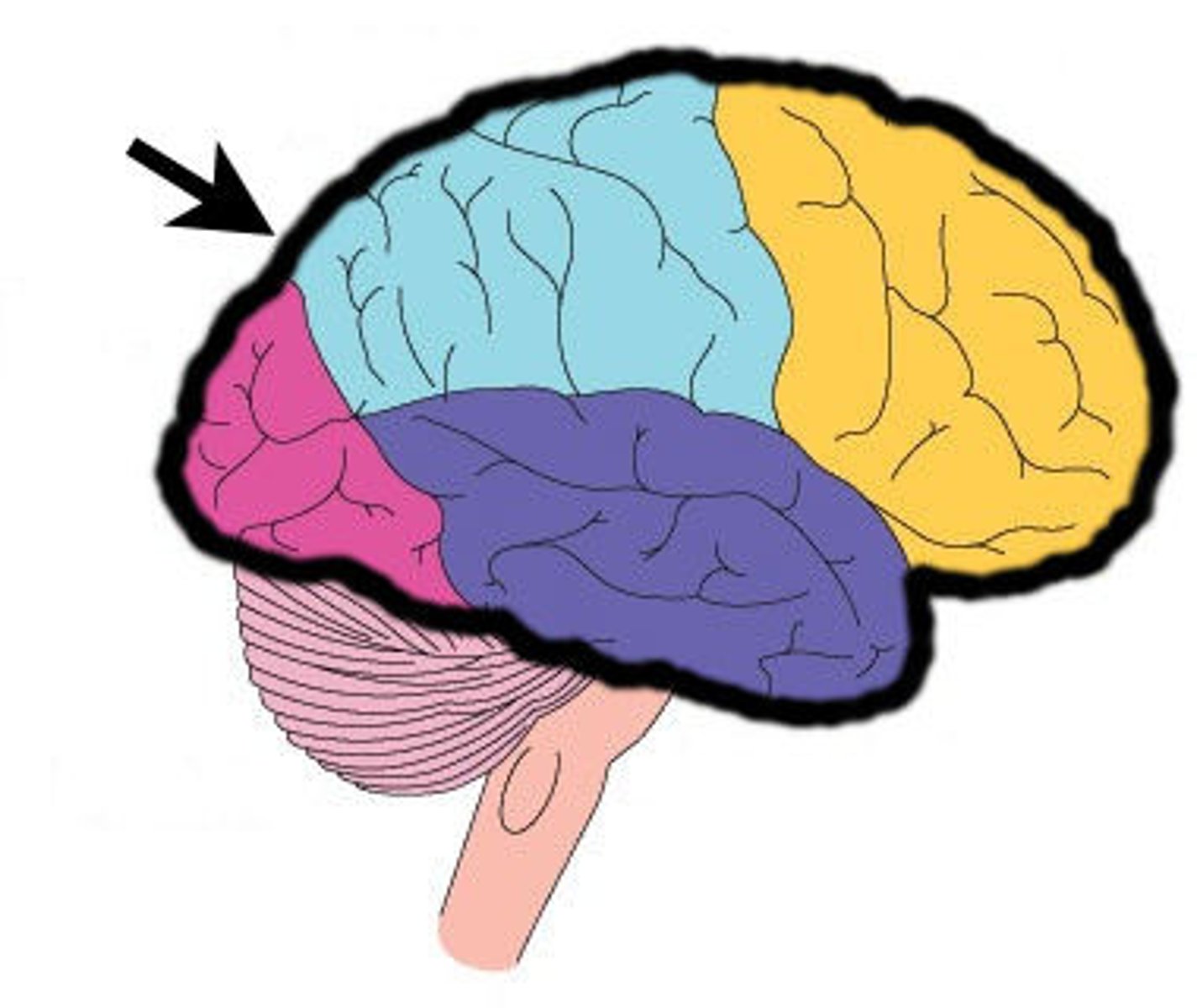
cerebral cortex function
split into 2 hemispheres- left hemisphere communicates with right side of body and vice versa
controls language, memory, emotion and behaviour
2 types of scan we can use on the brain
CT
PET
why do we use CT and PET scans
the brain is very delicate so surgery is very risky
scanners mean that we can investigate brain function without resorting to surgury
CT scans
Multiple X-Rays of successive slices of the brain.
Show brain structure.
PET scans
Show areas of brain activity
Patient is injected with radioactive glucose. the areas that use up more glucose are the ones with the most activity because the cells are respiring. These areas become radioactive so can be spotted
This is why PET scans are often used to detect cancer
limitations in treating brain tumours
surgery to cut out the tumour is difficult because:
- the brain is protected by the skull so difficult to access
- there is a significant risk of damage to the brain
limitations in treating spinal cord injuries
damaged neurones cannot be repaired or replaced by the body
but stem cell injections are getting developed
what is the central nervous system (CNS)?
brain and spinal cord
neurone definition
specialised cells adapted to rapidly carry electrical charges (nerve impulses) from one part of hte body to another
a bundle of neurones= a nerve
what are the 3 types of neurone?
sensory
relay
motor
role of sensory neurones
carry impulses from sense organs to CNS (brain/spinal cord)
role of relay neurones
in the CNS
connect the sensory + motor neurones
role of motor neurones
carry impulses from CNS to effectors (muscles or glands)