L7 telescopes
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
refraction
bending of light when it passes between substances, based on refractive indices of the two different media
refracting telescope
lens can bend parallel light rays to converge to a focus, but lenses must be large and heavy
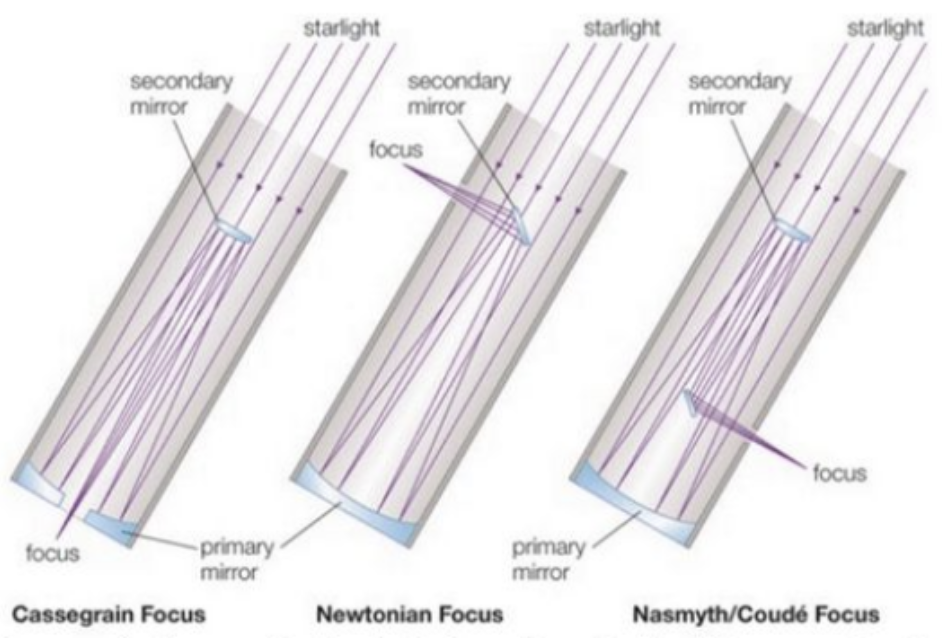
reflecting telescope
can have a much greater diameter, focuses light with mirrors
light collected with a curved primary mirror that reflects light up to a secondary mirror
eye has 3 color receptors, _, peaking in the _
blue, green and red; green
broadband or narrowband filters
placed on telescope to only let certain range of color or specific colors through, then combined after to form a full color image
time monitoring
progression of events on human timescales can be observed, like supernovae
type 1 supernovae
binary system, white dwarf accretes material from other star, eventually reaching critical density and exploding, possibly emitting gamma ray beams
type 2 supernovae
end of star’s life, core collapses in on itself, rebounds and releases gas to form a nebula; neutron star or black hole left behind
telescope properties
wavelengths that can be collected, light-collecting area (surface area = good), angular resolution (larger distances can take greater detail images)
light collecting area equation
A = π(d/2)²
ways to increase collecting area
build array of many telescopes and connect digitally e.g. CHIME
CHIME’s large field of view helps it monitor
fast transients e.g. radio bursts
limit to resolution comes from
interference of light waves within a telescope; less in a larger telescope
angular resolution equation
θ=1.22λ/D
interferometry
linking multiple telescopes so they have the angular resolution of a single large one
adaptive optics
deforming mirror to compensate for aberration’s in light’s path, i.e. atmospheric turbulence