Chapter 4 - The structure of atoms
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What kind of wave is light?
An electromagnetic wave
Visible light and color
For visible light, wavelength determines color. The visible spectrum runs from wavelengths of about 400nm to roughly 750 nm (from violet to red)
Where does light come from
Photons
Wave particle duality
The idea that light sometimes behaves as a waves and at other times like a particle. Which behavior is observed depends on the particular experiment.
When is a photon released?
When an electron jumps from one allowed orbit to another. When it goes up it absorbs energy and when it jumps down it releases energy and releases a photon that emits a light.
What is the energy that is found in a system where the electron orbits around the nucleus?
The energy of such a system is the sum of kinetic and potential energy.
The kinetic energy follows from the speed of the orbiting electron
The potential energy originates from electrical coulomb interactions between nucleus and electron.
Formula for energy in orbital
RH is called the Rydberg constant
n is the quantum number (the orbit number)
RHhc in total has a number of 2.18 × 10-18 J
This formula states that the energy of an hydrogen atom only can take specific values.
ONLY WORKS FOR HYDROGEN
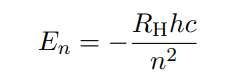
Limitation Bohr model
Only works for atoms with one electron
Formula Bohr for charged one electron atoms
Z is the atomic number which is equal to the number of protons in the nucleus.
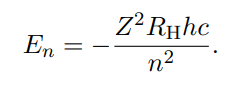
Motion of electrons
waves
Correct equation after Bohr’s equation
H stand for the Hamiltonian operator, a set of mathematical operations that represent the total energy (kinetic and potential) of the electron
E stands for the actual energy of the electron.
The symbol v is the wave function that represents the standing wave form of the electrons.
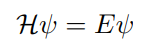
What does quantum mechanics say about where electrons are
Quantum mechanics tells us that it is impossible to know precisely where an electron is and where it travels.
We can only know the probability for an electron to be somewhere.
Wavefunction ψ
The wave function (v) tells us something about the probability for an electron to be somewhere
The square of the wave function tells us the probability density, that is the probability per unit volume for an electron to be at a certain location.
Quantum numbers
These numbers determine the shape of the standing wave in a vibrating string. Since the orbitals are standing waves in three dimensions we need three quantum numbers to fully describe them.
The three types of quantum numbers
The principle quantum number
The angular momentum quantum number
The magnetic quantum number
The principle quantum number
Positive integer
Related to the size and energy of the orbital
As n increases, the orbital becomes larger and the electrons spends more time farther away from the nucleus.
Therefore the energy of the electron also increases with increasing n, because the attraction to the nucleus is weaker.
The angular momentum quantum number
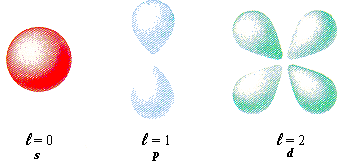
An integer that can take values from 0 to n-1
This quantum number is related to the shape of the atomic orbitals
Each value of l is also assigned a letter: l = 0 = s orbital
l = 1 = p orbital
l = 2 = d orbital
l = 3 = f orbital
The magnetic quantum number
-I, …, +I
Orientation in space
The photoelectric effect
When you shoot a specific wavelength on a sheet of metal than it will release energy
When you decrease wavelength (higher frequency) the electron emitted has more energy
Line spectra formula
n1 < n2
final < initial
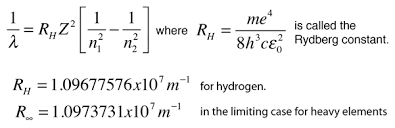
wavelength fromula
wavelength = c/v
v= frequency
Formula Broglie
wavelength = h/mv
V IS NOT FREQUENCY HERE BUT VELOCITY IN (M S-1)
what is ionization
movement of electron up an orbital