MT 37 (LEC): Gram-positive cocci 1
1/144
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
145 Terms
Micrococcaceae, Staphylococcaceae
Cocci Classifications (Family)
MICROCOCCI
gram + cocci in the family: micrococcaceae
Normal flora: skin, mucosa, and oropharynx
contaminants of clinical specimens
rarely implicate as cause of infections in humans
MICROCOCCI
May cause brain abscess, meningitis, pneumonia, and endocarditis in immunocompromised patients
MICROCOCCI
Gram-positive cocci in packets of four (tetrads) or eight cocci
M. Flavus, M. Luteus, M. Lylae, M. Roseus, M. Dentrificans, M. Varians, M. Freudenreichii
Species from the genus Microccocus
M. roseus
Micrococcus Found in the dust of the air
M. dentrificans
Micrococcus found in soil
M. colpogenes
Micrococcus found in marine waters
M. flavus
Microccocus in Skin, skin glands, or skin-gland secretions of vertebrates
Usually found in humans
M. luteus, M. varians, and M. freudenreichii
“Milk micrococci”
Cause spoilage of milk
M. lylae
microccocus found on the skin, dust, and water
STAPHYLOCOCCI
Growth requires supplementation with various amino acids and other growth factors (Enriched Media)
NF: skin, mucous membrane, and intestine
STAPHYLOCOCCI
Facultative anaerobe & catalase (+)
Facultative anaerobe
It can thrive with or without the presence of oxygen
with oxygen = aerobic respiration
without oxygen = fermentation to produce ATP
Catalase
enzyme that detoxifies hydrogen peroxide to prevent bacterial cell wall disruption
Results to the “bubble” reaction if positive
produced by Staphylococci
Positive catalase reaction
bubble forms due to the conversion of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) into H2O + O2
Staphylococci
Nonmotile, non-spore-former, and glucose fermenter
Staphylococci
Grows in 7.5% NaCl (halotolerant)
Staphylococci
Resistant to heat and drying, and thus can persist for long periods on fomites (inanimate objects)
Staphylococci
Species are initially differentiated by coagulase test
Coagulase test
enzyme causes coagulation by converting fibrin to fibrinogen
Coagulation in tube test
Agglutination in plasma (slide test)
Blood Agar Plate (BAP)
Culture media for STAPHYLOCOCCI
Staphylococci in BAP
4-8mm colonies,
creamy, white to light gold,
“buttery-looking” (unique charact.)
some species are grayish & ßhemolytic
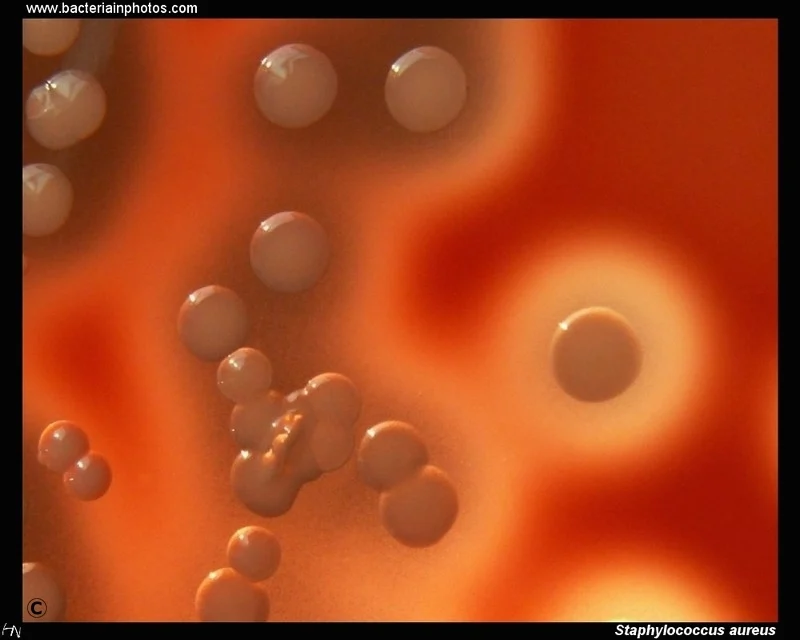
Buttery-looking
Unique characteristic of staphylococcus growing in BAP
Alpha hemolysis, beta hemolysis, gamma (non-hemolytic)
Hemolytic Reactions in SBA
Alpha hemolysis
green zone around colony
Narrow or wide
Partial lysis of RBCs
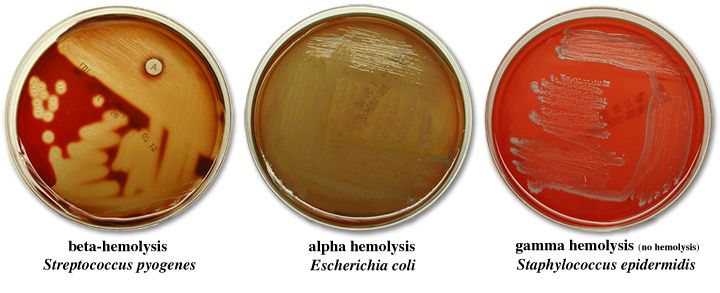
Beta hemolysis
clear zone around colony
Narrow or wide
Complete lysis of RBCs
Gamma (non-hemolytic)
no zone of hemolysis
No lysis
Staphylococcus aureus
Normal flora: Anterior nares, nasopharynx, perineal area, skin, and colonizer of mucosa
Staphylococcus aureus
Endogenous strain: sterile site by traumatic introduction
Direct contact: person-to-person, fomites
Indirect contact: aerosolized
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Normal flora: Skin, mucous membranes
Endogenous strain, Direct Contct
MOT of Staphylococcus epidermidis, S. haemolyticus, S. lugdunensis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Normal flora: skin, genitourinary tract, mucosa
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Endogenous strain: sterile urinary tract, notably in young, sexually active females
Common cause UTI
Staphylococcus haemolyticus, Staphylococcus lugdunensis
Normal flora: skin, mucous membranes (low numbers)
Staphylococcus aureus
Most clinically significant species of staphylococci
the most virulent species of staphylococcus
False, true-coagulase positive
S. aureus is true coagulase-negative (TRUE/FALSE)
Facultatively anaerobic
What type of anaerobe is S. aureus?
False, it is non-motile and non-spore-forming
S. aureus is motile, spore-forming (TRUE/FALSE)
Positive; negative
S. aureus is catalase ___ and oxidase ___
7.5%
S. aureus: Tolerance to ____ sodium chloride
Mannitol
What does S. aureus ferments what sugar alcohol?
Hyaluronidase
What enzyme does S. Aureus produce?
Capsule, slime layer, peptidoglycan, techoic acid, Protein A
Enumerate the VIRULENCE FACTORS
Virulence factors
Helps the bacteria evade the immune system
Capsule
Inhibits chemotaxis and phagocytosis;
inhibits proliferation of mononuclear cells
Neutrophils, Macrophages, Phagocytes
Wbcs that perform phagocytosis
Biofilm
a thin, slimy film of bacteria that adheres to a surface.
Slime layer
Facilitates adherence to foreign bodies;
inhibits phagocytosis
Prevents penetration of antibiotics
Slime layer
Prevents penetration of antibiotics
Peptidoglycan
Provides osmotic stability;
inhibits phagocytosis
Peptidoglycan
leukocyte chemoattractant (abscess formation);
Peptidoglycan
stimulates production of endogenous pyrogen (endotoxin-like activity);
Abscess formation
difficult to treat with antibiotics due to failure to penetrate
Made by S. aureus
can be removed through drainage (if deep within tissue)
Boils, furuncles, carbuncles
Examples of abscess formations due to S. aureus
Peptidoglycan
thick layer in the cell wall in S. aureus
What contains the crystal violet within the cell wall
Teichoic acid
for adherence
Binds to fibronectin
Protein A
Inhibits antibody-mediated clearance by binding IgG, IgG2, and IgG4 Fc receptors;
anti-complementary by creating a pore in the cell wall or cell-membrane
Protein A
leukocyte chemoattractant;
Staphylocoagulase/Coagulase, Hyaluronidase, Lipase, DNAse and phosphatase, β-lactamase
Virulence factors: Enzymes and toxins produced by S. aureus
Staphylocoagulase/Coagulase
Coagulates fibrinogen in plasma (causes abnormal clotting)
Promotes the formation of a fibrin layer around the staphylococcal abscess thereby protecting the bacteria from phagocytosis
Cell-bound coagulase or clumping factor, Unbound or free coagulase
2 types of coagulase
Cell-bound coagulase or clumping factor
Bound to the cell wall and clots human, rabbit, or pig plasma by directly converting fibrinogen into fibrin
Detected by slide method
Slide method
Detects Cell-bound coagulase or clumping factor
Faster method compared to tube method
Unbound or free coagulase
An extracellular enzyme that is not bound to the cell wall;
Performed by tube method because it requires incubation
Tube method
Detects Unbound or free coagulase
Requires incubation (18-24 hours)
Unbound or free coagulase
causes clot formation when bacterial cells are incubated with plasma
Hyaluronidase
Spreading factor enzyme
Helps the bacteria reach more places to infect
Enhances invasion and survival of S. aureus in the tissue and skin
Hyaluronidase
Breaks down hyaluronic acid that is present in the intracellular ground substance of connective tissues, resulting in the spread of bacteria
fibrinolysin
Staphylokinase Is Also known as?
Staphylokinase
Causes fibrinolytic activities by dissolving fibrin clots
Proteolytic enzyme
Helps S. aureus establish skin infections
Staphylokinase, Hyaluronidase
Enzymes that Help S. aureus establish skin infections
Lipase
Produced by both coagulase-negative and coagulase-positive staphylococci
Fat-splitting enzyme
Lipase Is aka?
Lipase
Essential for bacterial survival in the sebaceous areas of the body
Found in armpits, hair follicles, and other areas that are rich in oil and fats
Lipase
Important in the formation of furuncles, carbuncles, and boils
DNAse and phosphatase
Lower the viscosity of exudates giving the pathogen more mobility
Exudates
mass of cells in fluid (nana)
Viscous
DNAse and phosphatase
Destroys DNA
β-lactamase
produced in response to antibiotics
Breaks down penicillin and other β-lactam drugs
β- lactam drugs
Inhibits cell wall synthesis like hindering peptidoglycan synthesis
Enterotoxins, Leukocidin, Exfoliatin serotypes A and B or Epidermolytic toxins A and B, Hemolysin, Toxic Shock Syndrome Toxin-1 (TSST-1)
VIRULENCE FACTORS: Toxins produced by S. aureus
Enterotoxins
heat-stable at 100°C for 30 minutes
30 minutes
Enteroxins are heat-stable at 100°C for?
30% to 50%
Enterotoxins are Produced by ___% to ___% of S. aureus isolates
Enterotoxins
Resistant to hydrolysis by gastric and jejunal enzymes
Enterotoxins A, B, and D
Enterotoxins responsible for food poisoning with A being the most common cause
Enterotoxins B, C, G, and I
Enterotoxins associated with TSS (Toxic shock syndrome)
Enterotoxin B
enterotoxin associated with pseudomembranous enterocolitis and is often found in contaminated milk products
Pseudomembranous enterocolitis
mainly cause by Clostridium difficile and sometimes by S. aureus
Enterotoxin
Neurotoxin
stimulates the vagus nerve (a nerve responsible for nusea center of brain)
if ingested by host, host keeps vomiting
Leukocidin
Attacks and kills white blood cells (PMN, macrophage, and monocytes)
Panton-Valentine Leukocidin (Cytolytic toxin)
Leukocidin is aka?
Leukocidin
Pore-forming exotoxin that suppresses phagocytosis
Leukocidin
Responsible for severe cutaneous infections and necrotizing pneumonia
Exfoliatin serotypes A and B (superantigens)
aka Epidermolytic toxins A and B
Exfoliatin serotypes A and B (superantigens)
Divides the intracellular bridges of the epidermis resulting to extensive sloughing to produce burn-like effect
Superantigens
overstimulates the immune system
Causes the host to Excessively produce cytokines
Eventually results to organ failure
Stratum granulosum
Exfoliatin serotypes A and B (superantigens) destroys what layer of the skin/
Bullous impetigo
Exfoliatin serotypes A and B (superantigens) Has been implicated in What disese?