Micro Exam 1
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
135 Terms
What type of genome does Measles have?
(-)ssRNA
Is measles enveloped or non enveloped?
Enveloped
what are the 6 classical childhood exanthems? (rash causing viral illness)
1, Measles
Scarlet Fever
Rubella
Dukes’ Disease
Erythema Infectiosum
Roseola Infantum
What makes measles high contagious?
shedding before and after symptom onset through aerosol droplets
What are the 3c’s of measles
Cough, Coryza (nose inflammation), Conjunctivitis (red face)
What symptom is pathognomonic for measles
Koplik Spots in mouth
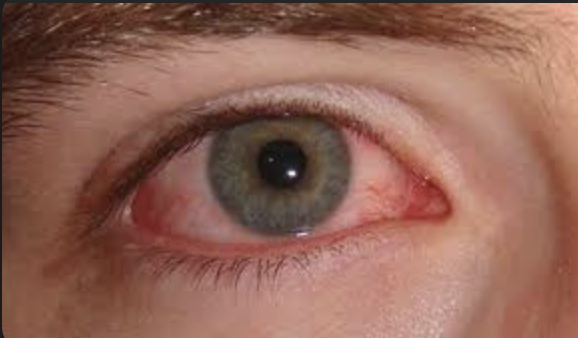
what is conjunctivitis a symptom of?
Measles
one of the 3c’s
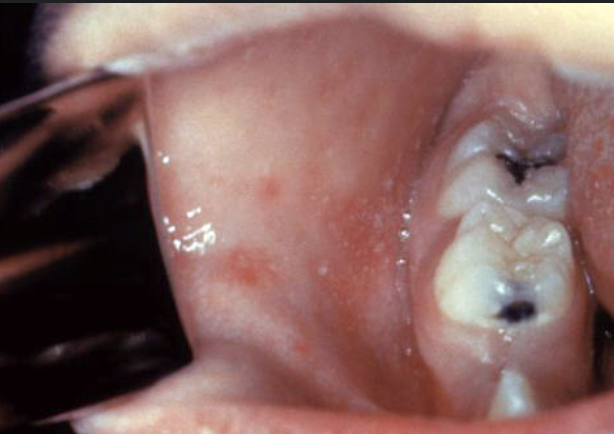
Where are koplik spots found?
On the Buccal Mucosa opposite the 1st and 2nd upper molars
What type of rash does measles cause?
Maculopapular Rash
What are the most common cause of death in Measles patients. Children and Adult
Children - pneumonia
Adult - Encephalitis (brain swelling)
How are measles diagnosed (3 things)
Clinically (usually)
IgM ELISA (IgM appears first)
RT-PCR (RNA virus)
What can be given to children with Measles to reduce severity?
Vitamin A
What type of genome does Mumps have?
(-)ssRNA
Name the genomes of Mumps, Measles, Rubella?
Mumps - (-)ssRNA
Measles - (-)ssRNA
Rubella - (+)ssRNA (outlire)
Is Mumps enveloped or non enveloped?
enveloped
What receptors does Mumps Bind?
Sialic Acid
Which 2 viruses we have covered uses Hemagglutinin (HA) and or Neuraminidase (NA) HN
Influenza A&B
Measles
Which Virus can shed in urine for up to 14 days after onset?
Mumps
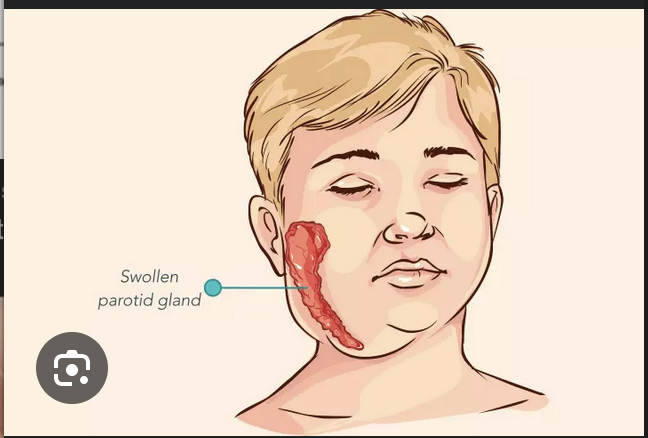
Parotitis is the most common feature of what diseases
Mumps
Menigitis, Oophoritis (ovary swelling), Orchitis (ball swelling), and Encephalitis are common symptoms of what virus?
Mumps (2)
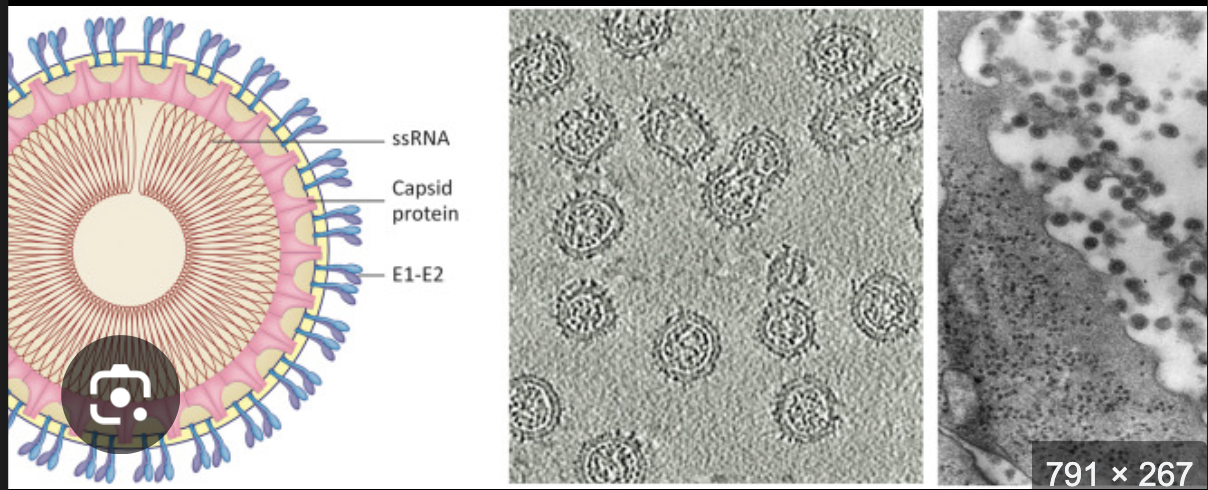
What type of genome does Rubella have?
(+)ssRNA, linear
(odd one out in MMR)
Which of the MMR is a very dangerous Teratogen (vertical Transmission)
Rubella
How could Rubella be distinguished from Measles?
Rash resolves within 3 days with usual lifelong immunity
At what time is Rubella usually cause CRS?
First Trimester
What virus is Petechiae common for?
Rubella
not specific but common
How are the MMR diagnosed?
Usually Clinically with IGM ELISA and RT-PCR
What type of genomes does HPV (human Papillomavirus) have?
dsRNA, circular
What determines viral tropism?
Spike proteins that bind host receptors
The spike proteins on SARS-Co2 bind what host receptor
ACE2
Which form of RNA can be translated immediately by ribosomes?
(+)ssRNA
What is needed to turn (-)ssRNA into (+)ssRNA?
RNA-dependent RNA Polymerase
Influenza A has a segmented genome and goes through reassortment which cause _______ which leads to Pandemics
Antigenic Shift
(major changes, abrupt genetic change)
Which mutate faster, RNA viruses or DNA viruses? Why?
RNA viruses
due to lack of proofreading
Leads to Antigenic Drift
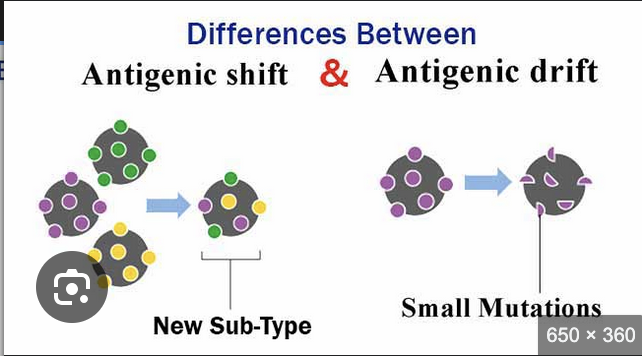
Antigenic Drift vs Shift
Drift - gradual changes in virus’s surface that may escape immunity
Shift - major, abrupt changes often from re-assortment from different viral species creating completely new strain, leads to pandencs
What is the difference between the entry of Enveloped vs Naked viruses?
Enveloped viruses can enter via fusion and endocytosis
Naked viruses exclusively enter through endocytosis, not direct fusion
naked viruses can directly penetrate and inject but do not enter
which are more environmentally stable naked or enveloped?
Naked
not susceptible to acids, detergents, drying, heat because they do not have a lipid bi layer that is easily disrupted
What are CPE’s and give examples?
visible changes or damage (with microscope), does not differentiate between viruses
examples - Inclusion bodies, syncytia, lysis, apoptosis
Which two viruses cause oncogenesis and how?
HPV and EBV
Able to perform transformation and integrates straight into host genome
What needs to occur before uncoating enveloped viruses? How is this different from Naked
Fusion
Naked - do not have to enter the cell in order to release viral genome
What is the function of Type 1 interferons?
first line defense. released by cells when cell detects viral infections. triggers transcription/production of antiviral genes
What is Acyclovir used for and how does it work? What class of drug is it?
ProDrug - needs viral enzymes to activate it
used to treat HSV and VZV
Nucleoside analog, NRTI
Drugs that end in -NAVIR are protease inhibitor, what are protease inhibitors commonly used to treat?
Protease Inhibitors
Used to treat HIV by preventing maturation
example - Atazanavir, Darunavir
NRTI vs NNRTI
NRTI - mimic natural nucleosides (example Acyclovir)
NNRTI - bind directly to reverse transcriptase
What is the primary infection of VZV and what is the reactivation?
Primary. - Chicken Pox
Secondary - Shingles
What virus causes Mononucleosis (mono)?
EBV
(also known as HHV-4)
What cells does EBV infect?
B Lymphocytes
Which virus causes Owl’s eye inclusions?
CMV
(also know as HHV-5)
What form of herpes causes Malignacy (tumor/cancer) in HIV patients?
HHV-8
HPV 1,2,4 cause what?
Skin warts (not genital)
Koilocytes are CPEs characteristic of what virus?
HPV
What does HPV 6,11,42,43,44 cause?
genital warts
mostly 6 and 11
If wart are found on the bottom of the feet what type of HPV is it likely to be?
HPV 1
What are the 4 major components of the Oral Microbiome?
Oral bacteriome
Oral Mycobiome (fungi)
Oral virome
Oral Parasitology
What species of fungi predominates the oral cavity?
Candida
“Candida Albicans”
What fungi is present in healthy oral cavities?
Malassezia
What can Candida Albicans grow as?
Hyphae (mold) or Yeast
Are Candida prokaryotic or Eukaryotic
Eukaryotic
reproduce sexually or asexually
what is the 2 substantial human defenses against fungi?
37 degrees Celsius - too high for fungi growth
Innate and Adaptive Immune cells
What do Polyenes (Amphotericin B) target
Bind Ergosterol
(toxic side effects possible)
What to Azoles (ketoconazole) target
inhibit ergosterol synthesis via cytochrome P450
What do Allylamines (Terbinafine)
inhibit squalene epoxidase
(fungi specific)
What do Echinocandins (Micafungin) target
inhibit B-Glucans in cell walls
(less side effects)
What major drug target is in the cell wall of fungi?
Ergosterol
True or False Candida have cell wall
True or False Cryptococcus havecell wall
True or False Aspergillus have cell wall
True
True (also has a capsule
True
What is Dimorphic Transition?
a type of virulence where fungi change from Yeast to Hyphae for tissue penetration
What type of viral infection is seem in AIDS patients?
HHV-8 or Kaposi’s Sarcoma
If you had a patient suffering from a naked virus spread primarily through the oral fecal route, what two viruses would you test for first?
Rotavirus and Norovirus
Out of Rotavirus and Norovirus, which has a vaccine available?
Rotavirus
what are the components of a virus/make up a virus?
genome (DNA or RNA), capsid (protein shell), lipid envelope (some), spike proteins
What determines viral TROPISM
spike proteins
Which are more environmentally stable Naked or Enveloped viruses?
naked
more stable against, heat, acid, and detergents
What are the 3 primary shapes of viral capsids
icosahedral (primary)
Helical
Complex
What type of viruses mutate faster due to lack of proofreading?
RNA viruses
What type of test would you used to detect CTEs like syncytia and Cowdry Bodies
Tzanck’s smear
not viral specific methods
What is the main goal of a Neuraminidase inhibitor?
prevent viral release
used largely in flu treatment
Of Hep A, B, and C which are acute risk and chronic risk
Hep A only acute infection
Hep B/C chronic risk
What are the most common viral oral infections
HSV and HPV
what are the smalled human viruses?
Picornaviridae
Picornaviridae are naked or enveloped, why?
naked
infect and shed in the intestinal tract VERY resistant to hard conditions (stomach pH, sewage systems)
What characteristic do enteroviruses share?
the ability to infect the intestinal tract and shed viruses without causing GI diseases
What is an enterovirus that doesn’t spread through the fecal oral route?
Rhinovirus A,B,C
What are the important members of the Picornaviridae (enterovirus) family?
poliovirus
enterovirus
coxsackievirus
echovirus
rhinovirus A,B,C
What age does Coxsackie virus affect?
mostly occurs children <5
increased summer incidence
What is true of most Coxackie infections
asymptomatic or mild
What is the leading cause of chronic hepatitis?
Hep B
What virus causes Hands-Foot-Mouth disease?
highly contagious
What 3 Clinical symptoms are caused by coxsackies?
Hands foot and Mouth
Herpangia (sores on back of throat and palate)
Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis (eye swelling, mucoid discharge)
Whats foot and mouth can be caused by coxsackies and what other virus?
enterovirus 71 (southeast Asia)
What differentiates HFMD from Herpangina?
HFMD causes lesions on the anterior part of the mouth
Herpangia is the posterior part of the mouth
What differentiates HSV lesions from Herpangina?
HSV legions are anterior part of mouth
Herpangina are in the back of the throat
How many types of adenovirus cause disease in humans?
57
What virus cause THE MOST common cause of viral conjunctivitis?
Adenovirus
(Cold/conjunctivitis/Epidemic Keratoconjunctivitis)
How does Adenovirus spread
through Aerosols
Fecal Oral
Direct Contact
(never fucking dies, 5 weeks on inanimate objects)
What virus can spread through pools?
Adenovirus
In what part of the body does the Adenovirus infection occur in and what type of infection is it?
persist and lymphoid
latent infection
what is Pharyngoconjunctival fever, what is it caused by, what symptoms does it cause?
combination of adenovirus, URT infection and conjunctivitis
causes fever, malaise, cough, sore throat, nasal congestion, follicular
common in children
What is Keratoconjunctivitis (EKC) caused by
Adenovirus
(pathognomonic for adenoviral infection)
What types of Adenovirus are treated with vaccine?
types for 4 and 7
What HIV type causes the most causes in US
HIV-1
How is most HIV spread?
Majority through sexual contacts (gay men)