Computer Science - OCR GCSE - 1.3.1 - Computer Networks And Topologies
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
What are advantages of computer networks:
File Sharing/collaboration:
Files can be stored on a server and accessed by authorised users. Users can work on the same files, possibly at the same time.
Access to files:
Files can be accessed on any device that's connected to the network
Resource sharing:
Hardware sources can be shared over a network e.g. Printer
Software sources can be shared over a network e.g. Google Docs
Software programs can be distributed from a central server rather than have to be installed on every computer e.g. SolidWorks
Networks allow you to share an internet connection
Communication:
It is easier and quicker to communicate with any other user on the network than other means, and texts and emails etc. are sent via a network
Centralised Management:
User profiles and security can all be managed centrally and software can be distributed across the network rather than installing it on an individual computer
Disadvantages of computer networks:
Confidential data can be hacked
Malware such as viruses can spread from one computer to another
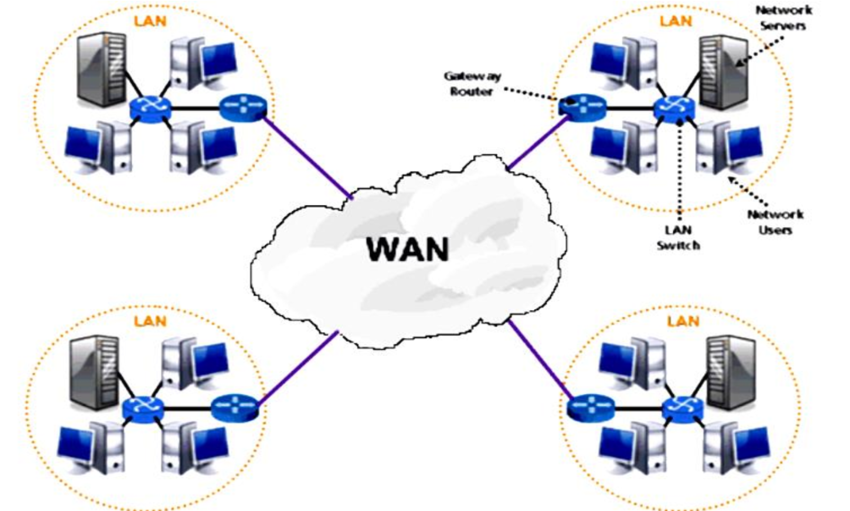
Summarise the differences between Wide Area Networks and Local Area Networks:
Key point to research | LAN | WAN |
Area it covers | Building -Small Geographical area e.g. School or Office | A large geographical area e.g Cities or Countries |
Connection | By ethernet cabling | WiFi connections for portable devices Fibre optic cables send data as light Telephone cables |
Speed | Faster than WAN due to shorter distances and more stable connections e.g. Internet | Slower |
Cost | Costly but not as much as WAN | More expensive, you need more hardware and you need to pay subscriptions to telephone companies e.g. BT |
Security | Less users, less difficult to control | More users, more difficult to control |
Example | School, Home | Internet, Country-wide network bank branches |
Describe the use of a Network Interface Card:
NIC:
The network card shown has an ethernet cable input, and is simply fitted into a spare slot at the back of the computer to connect to the motherboard.
On most current computers, the network interface card is integrally designed and fitted into the motherboard, as networking is now considered to be the norm and not an extra feature.
Describe the use of Switch in the production of a network:
A switch is a device for connecting many network devices, such as computers and printers.
It has several ports through which these devices are connected. It receives data from the sending computer and forwards data to the intended recipient only.
It identifies recipients using their MAC address.
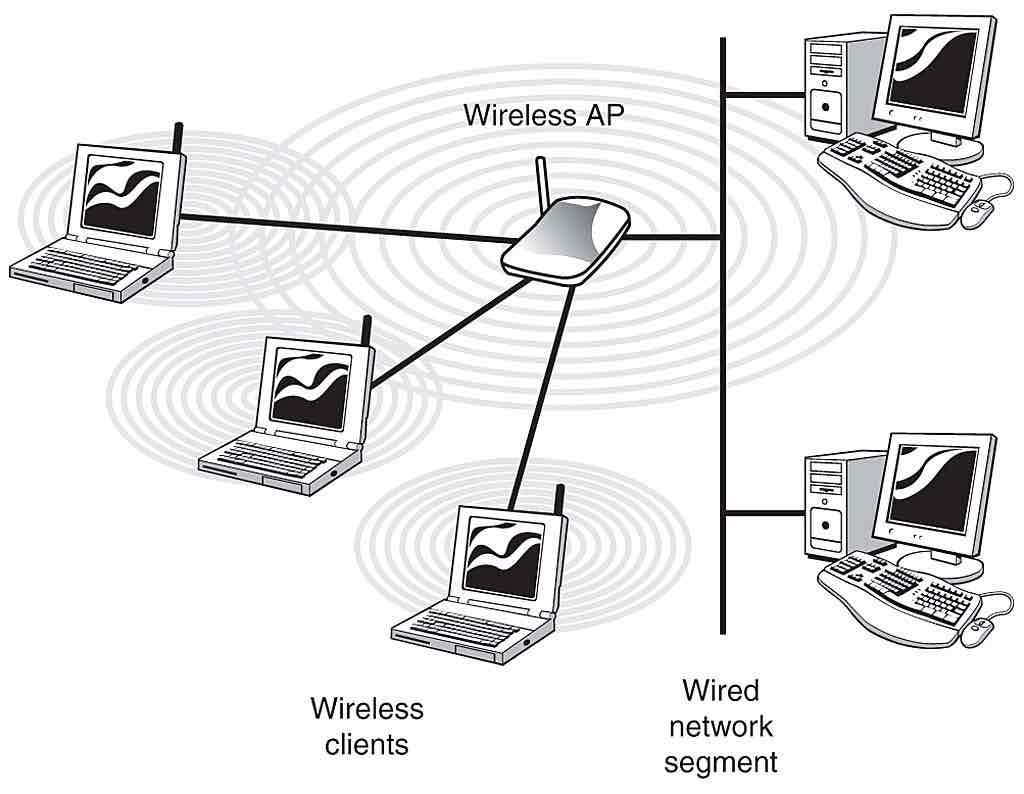
Describe the use of a Wireless Access Point in the production a network:
WAP:
This technique is used to support modern Wi-Fi computing and connectivity and is based on transmitters sending and receiving data at radio frequencies from a wireless access point.
Computers and other network devices have transmitter/receiver Hardware to communicate with the wireless access point.
The wireless access point will be usually connected to a router which is then connected to the Internet .
Alternatively the WAP can be connected into a wired LAN, by being connected to a switch which is connected to the LAN.
Look at the picture of the WAP and its role in a Network:
Wireless clients:
Describe the use of a Router in the production a network:
A router is designed to route data packets across a wide area network such as the Internet.
Each router in a WAN receives packets of data and forwards them along the most efficient route to the next router for their final destination node.
Packets contain information on the destination node which they are intended for, in the form of an IP address.
The router uses this to decide the route to forward the packet on.
Describe the use of a Transmission media in the production a network:
Network components can be connected together using cables such as coaxial or twisted pair cable (uses copper), or fibre optic cable (uses light pulses) for higher speed transfer.
In addition, many modern computer systems connect devices wirelessly as it gives the network a high degree of flexibility.
Compare Copper (Twisted Pair) and Fibre Optic cabling:
Cost:
Copper (Twisted pair) is less expensive than Fibre Optic
Speed (Bandwidth):
Fibre Optic has a much wider bandwidth
Signal Security:
Fibre Optic has a higher security
Signal Strength:
Copper has a lower strength and needs repeaters
Fibre Optic has a high strength and doesn’t lose as much
Interference:
Copper is much more susceptible to suffer from electrical interference
Fibre Optic is not affected by electromagnetic interference
What is bandwidth?
Speed - Bits per second
Look at the definitions of these devices:
Twisted Pair:
The least expensive transmission media that consists of two wires that wrap around each other. Used as a standard (Ethernet)
Coaxial Cable:
A transmission media that consist of a central wire, surrounded by insulation and a shield of braided wire to minimise interference.
Fibre Optic Cable:
A transmission media that consists of a bunch of glass or plastic threads.
Wireless Access Point:
A device that allows other devices to connect to a network using standards such as Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
Network Interface Card:
A hardware device internal to a computer that allows a computer to connect to a network.
Hub:
A connection point for devices in a network. Unintelligent – packets are broadcast to every device
Router:
Connects together different networks and forwards data packets along a network.
Switch:
Filters and forwards data packets within a single network. This creates a direct connection between devices (intelligent)
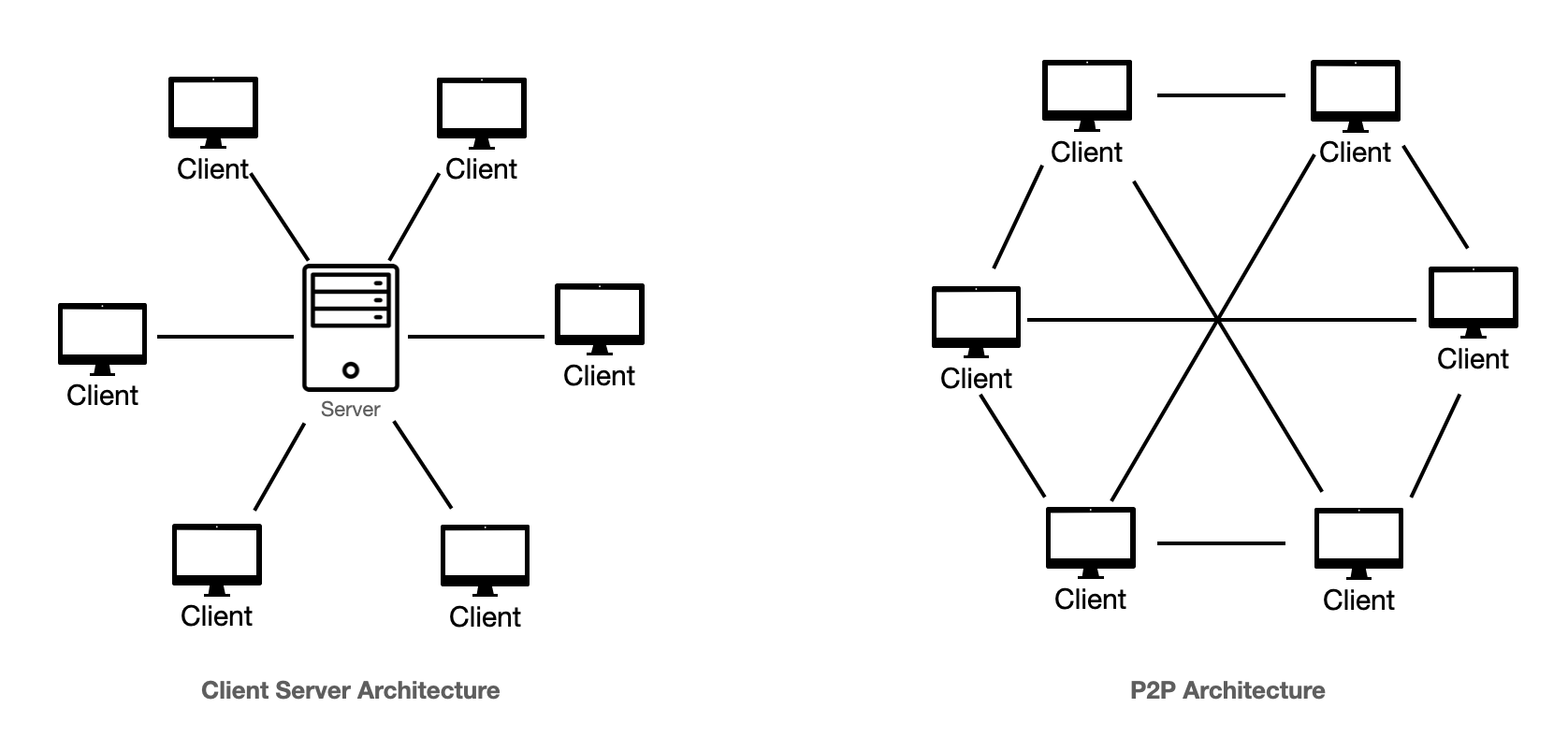
Characteristics of Client-Server networks:
Computers are networked together
It has a central computer that provides all the services to the network
Most commonly found in larger offices and organisations
Files can be automatically backed-up to a central location from each computer on the network
Peripherals (Devices connected to computers) on the network can be shared
An expensive network to set up as more hardware needs to be purchased
Files can be shared using the network
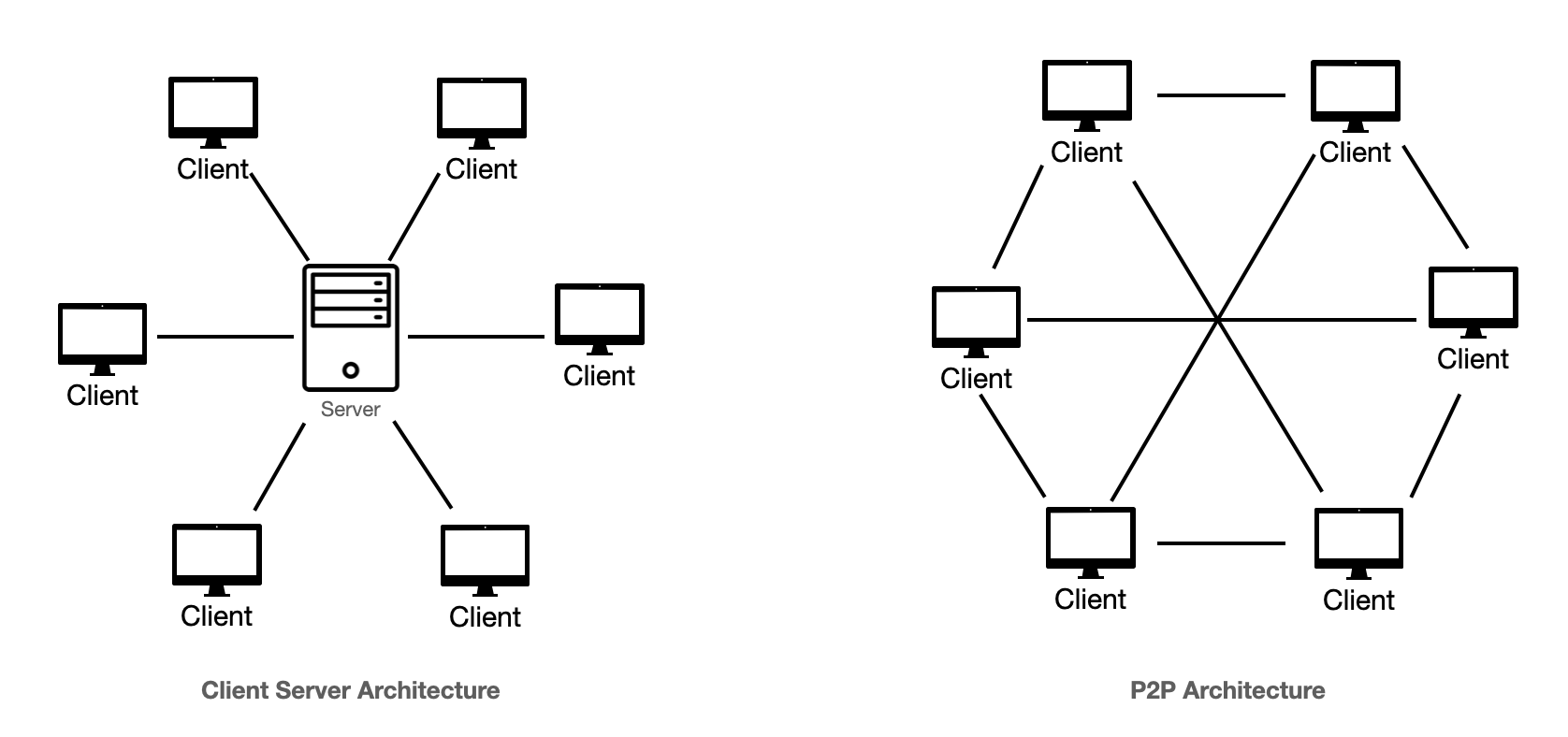
Characteristics of Peer-To-Peer networks:
Computers are networked together
Each computer in the network is equal, there is no central computer controlling services
Most commonly found in a home or small office
Each computer can share resources, such as files, with other computers on the network
Peripherals (Devices connected to computers) on the network can be shared
A cheaper network to set up as less hardware needs to be purchased
Files can be shared using the network
Each computer on the network needs to be maintained separately
Why is Peer-2-Peer network more suitable for a small office and home network?
Cheaper and easier to set up. Technical expertise are not required
A computer on a peer-to-peer is often described as a client and a server - What does this mean?
Computers on a peer to peer can supply resources therefore acting as a server or use resources therefore acting as a client
In a client-sever what is the role of:
the client
the server
Client:
The client requests services and resources from a server e.g. Printer, Files, Software, Internet connection
Server:
Provides services and resources that the client requests
Provides centralised security e.g. User accounts, passwords, access levels, a firewall, anti-virus software
What are the differences between Client-Server and Peer-to-Peer?
Cost of setup/maintenance:
Peer-to-Peer is cheaper than Client Server as there is less hardware and software to install
Easier to setup and don't require specialist staff
Technical expertise required:
Peer-to-Peer doesn’t require technical expertise whereas Client-Server does as it is complex
Single point of failure:
Peer-to-Peer can lead to exposure of confidential information as it is not as secure
Client-Server has a high set-up and maintenance costs and users are reliant on the server
Security:
Peer-to-Peer the computers are not centrally controlled so it is independent on each separate computer
Client-Server is done centrally by the server
Backups:
Peer-to-Peer the users must back up manually
Client-Server the server backups automatically and centrally
Number of users:
Peer-to-Peer has small number e.g. 8-10 users
Client-Server can support more users
Operating system:
Peer-to-Peer does not require a special operating system
Client-Server requires a special expensive server based operating system
Describe the factors that affect network perfromance:
Factor: | Description: |
Bandwidth: |
|
Number of users/devices: |
|
Errors is transmission/interference: |
|
Latency: |
|
Transmission media: |
|
Describe the internet as a network:
The Internet can be thought of as a massive network of networks where it connects millions of computers together globally, forming a network in which any computer can communicate with any other computer providing they are both connected to the Internet.
The success of the Internet is in no small way because it uses a standard set of protocols, allowing computers to communicate with each other.
Information that travels over the Internet does so using the TCP/IP protocol (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol) to transport data packets over the Internet.
The internet is an infrastructure- a facility for sending data between computers.
It is often confused with the world wide web , which is the collection of web pages hosted on the Internet.
The internet can be used for email, file sharing , telephone conversations and many other purposes in addition to looking at web pages.
Describe the different parts of the URL of http://www.bbc.co.uk/news:
URL part | Explanation |
http(s) | Hypertext transfer protocol - Get command - Get me that address (s)=secure |
www | World Wide Web |
Domain | |
news | Folder on the web server |
A domain name is used to provide a name against a server on the Internet.
Identify, in the correct order, the stages a computer goes through when using DNS to locate a web page:
Computer attempts to look up the web server’s IP address in its own DNS address book
The ISP attempts to resolve the web server IP address on its own DNS server
Alternative DNS servers are used if the ISP cannot find the web server’s IP address
The IP address of the server is sent back to the computer
HTTP request sent from user’s web browser to the web server IP address
The web server sends the web page back to the user’s web browser
Explain the purpose of an IP address:
Uniquely identifies devices on the internet including its location
Explain the advantages of using DNS servers:
Humans do not have to remember or type in numerical addresses
If the IP address change at some point the DNS servers can update their databases and the users can continue using the same domain names
Many distributed DNS servers means that everyone that access to all addresses from their local DNS server
What is a web host?
A company that stores a website’s files and data on a server so that others can access it through the internet
What additional services does a web host offer?
Domain name registration which ensures that the name chosen for the website has not already been taken
Website builders
What is cloud storage?
Saving data in an off-site network of servers maintained by a third party; it is accessible through the internet
Give an example of a cloud storage solution available today:
Google Drive, OneDrive, iCloud
State three benefits of cloud storage (Order of priority):
You can access data from anywhere when there is an internet connection
Backup is done externally by the provider
You can collaborate on files with other users online in different locations
Saves on local storage costs e.g. Servers and network equipment
Less need for in-house technical expertise
Cloud software do not have to be installed on a local hard disk of the computer
Users are always using the most updated and secure version of the software as updates are provided centrally
State two drawbacks of cloud storage:
You need an internet connection for it to be accessible
Hackers gaining access to data on cloud based servers
What is a web server?
A computer that hosts and stores a website that clients can access through the internet. A web server serves requests from clients for access to a website
What is a client?
A client is a computer that makes a request to a server for a service or resource e.g. a website
What is a network topology:
A network topology describes how all the parts of a network are arranged and connected together.
The topology includes the nodes (e.g. computers, printers, switches) and the connecting lines (cables).
What is a star topology?
In a star network topology there is a central computer or switch that all other computers are directly connected to.
Each computer is also indirectly connected to every other computer via the central computer or switch.
If a computer fails in the star topology it has no effect on the other computers, unless it is the switch in which case it is catastrophic.
Also, the security of a star topology is generally quite high as the traffic from each computer goes through the central computer or switch before interacting with another computer.
Data collisions can be an issue on a computer depending on the structure of a network.
This is not too much of a problem on a star network, though, as each computer has its own dedicated cable that connects it to the switch.
However, this network structure can be expensive to set up as it needs a central controlling computer and a large amount of cabling to connect each computer.
Give two advantages and two disadvantages of using a star network:
Advantages:
Robust and reliable since every device has its own connection to the central node
Minimises traffic since data is only directed to the intended node
Robust because the failure of one connection does not affect the others
Adding or removing devices is easy, and can be done without affecting the entire network
Disadvantages:
If the central switch fails, the whole network fails; a single center point of failure
Wired star networks require a lot of cabling, which can be intrusive and expensive
Network operation depends on the functioning of the central component (file server or switch) and if this fails, then so will the entire network.
What is a mesh topology?
A mesh topology can either be a full mesh or a partial mesh.
In a full mesh topology each computer in the network is directly connected to every other computer in the network.
In a partial mesh topology, computers that need to interact the most with each other, for example exchange data, are the ones that are connected together.
It is easy to add further computers into a mesh network, but this can often take quite a lot of cabling; this can be an expensive setup cost.
If one connection to a computer fails in this type of network, it has no effect on the network as the computer can find another working route to use instead.
There can sometimes be redundant connection in a mesh network; this is often why a partial mesh will be set up instead of a full mesh.
Advantages and Disadvantages of a Mesh network:
Advantages:
Very robust with no single point of failure, so used when reliable
In the event of a failure of a communication route, other routes are available
The more nodes and switches installed, the bigger and faster the network becomes due to the larger amount of routes the data can take
If one node on the network is faulty then there is an alternative route for the data
Disadvantages:
Wired full mesh networks require vast numbers of connections and are very expensive and impractical
The complexity of full mesh networks requires a significant amount of maintenance and technical expertise to manage and maintain it.
It requires a lot of cable and switches, as each computer is connected individually to all other computers
Summarise Star and Mesh topology:
Star:
Each node is connected to a single central switch using its own dedicated cable
Mesh:
Can come in full or partial
Full mesh, each computer is directly connected to every other computer
Partial mesh, each computer is connected to other computers that they interact with the most, but all computers are connected, at least indirectly
Define what is meant by a ‘virtual network’ and explain why an organisation might use one?
A virtual network is a group of devices that are connected using software (virtual switch) rather than solely hardware
A virtual network is used so that, even though computers are on different physical networks, data is only passed to trusted/relevant devices to prevent data interception