2027 L4 Dermatopathology Part 1
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Epidermis
The outermost layer of skin, acting as a protective barrier against the external environment.
Epidermis Structure
Basal Layer: Home to stem cells that give rise to the other layers of the epidermis.
Stratum Spinosum: Cells here have a spiny appearance due to connections called desmosomes.
Stratum Granulosum: Characterized by granules that contribute to water-proofing the skin.
Stratum Lucidum: Present only in thick skin like palms and soles.
Stratum Corneum: Dead cells packed with keratin, providing a tough, outer layer.
Dermis
The layer of skin below the epidermis, containing blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue.
Hypodermis
The deepest layer of skin primarily composed of fat, providing insulation and connecting the skin to underlying tissues.
Keratinocyte
The primary cell type found in the epidermis, responsible for producing keratin.
Melanocyte
A cell in the basal layer of the epidermis that produces the pigment melanin. Branching, dendritic. Interacts with 40 keratinocytes, then transferred by melanosomes to shield DNA from UV damage
Langerhans cell
A type of dendritic cell in the skin that plays a role in the immune response by presenting antigens. In stratum spinosum of epidermis. From bloodstream. Become activated during inflammation and migrate to draining lymph nodes.
Merkel cell
A specialized sensory cell in the skin that functions as a mechanoreceptor for light touch. In basal epidermal layer. High in skin of digits, lips, hair follicles.
Sensory receptors
Free nerve endings
Non-myelinated fibres in skin and mucous membranes
Detect pain, temperature, sensations
Encapsulated nerve endings
Surrounded by specialised structures
Meissner’s corpuscles
Pacinian Corpuscles
Ruffini Endings
Krause End Bulbs
Meisnner’s Corpuscle
Type of encapsulated nerve ending found in the dermis, responsible for detecting light touch and vibration. Oval, light staining, wavy structures in dermal papillae.
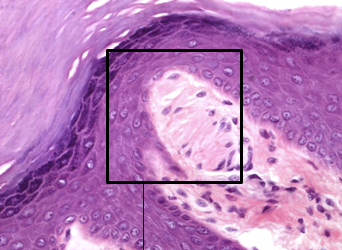
Pacinian Corpuscle
A type of encapsulated nerve ending located deeper in the dermis and subcutaneous tissue, responsible for detecting deep pressure and vibration. They are large, onion-like structures that respond to rapid changes in pressure.
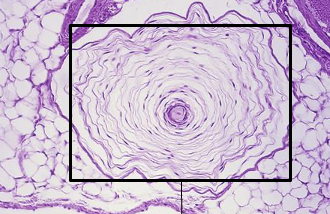
Ruffini Endings and Krause End Bulbs
are types of encapsulated nerve endings involved in detecting skin stretch and deep pressure, as well as cold sensations, respectively. Ruffini endings are spindle-shaped, while Krause end bulbs are bulbous structures. Not easily visible with H&E, require special stains.
Parakeratosis
A condition where nuclei are retained in the stratum corneum, which is not typical in healthy skin. Often used to diagnose psoriasis
Hyperkeratosis
Thickened skin with elongated rete ridges. Used to diagnose psoriasis. Elevated mitosis in basal layer, thin or absent granual layer. Special stain needed for amyloid deposition.
Incisional biopsy
DIAGNOSTIC. A biopsy technique that involves removing a portion of a lesion for diagnosis. Margins not important.
Excisional biopsy
THERAPEAUTIC. A biopsy technique that removes the entire lesion along with a margin of healthy tissue. When lesion is small.
Eccrine sweat glands
Sweat glands found throughout the body that primarily aid in thermoregulation, primarily in palms and soles
Apocrine sweat glands
Sweat glands associated with hair follicles, primarily located in specific regions like armpits, and involved in producing body odor. Thicker fluid, active during puberty.
Sebaceous glands
Glands that secrete sebum to lubricate skin and hair, preventing dryness. Waterproof.
Benign pathologies
Skin tags, seborrheic keratoses, lipomas and nevi are examples of benign pathologies that are generally non-cancerous and may require minimal treatment.
Inflammatory pathologies
Psoriasis, eczema, contact dermatitis and urticaria are inflammatory pathologies involving skin irritation and inflammation.
Autoimmune pathologies
Lupus erythematosus and pemphigus vulgaris are examples of autoimmune pathologies that occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body's own skin cells.
Pre-malignant pathologies
Actinic keratosis and dysplastic nevi are examples of pre-malignant pathologies that have the potential to progress to skin cancer if left untreated.
Malignant Pathologies
Basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma
Shave biopsy
Scalpel or dermablade
Horizontal slicing through dermis
Minimally invasive, avoids subcutaneous damage
For superficial lesions
Even surface post-biopsy
Immunofluorescence
A technique used to identify autoimmune conditions by visualizing immune complexes in skin samples.
Curettage & Cautery
A procedure that involves scraping away tissue from the surface of a lesion. Heat applied to seal blood vessels and promote healing. Good for superficial lesions. Not great because its difficult to orient tissue samples for diagnosis.
Mohs surgery
Advanced method for skin cancer removal e.g. basal cell carcinoma
Comprehensive margin assessment
Preserves healthy tissue, high cure rate
Punch biopsy
Removes cylindrical core
Penetrates epidermis to subcutaneous fat
Large biopsies preferred for better diagnostic visibility
For diagnosis of inflammatory or autoimmune skin conditions
Skin tags
Benign, soft skin-coloured growths. Loose collagen fibers and blood vessels. Removed for comsetic reasons or irritation. Very small; ischemic necrosis may occur if twisted as blood supply is cut. Can be frozen, burned, scalpel, tied
Psoriasis
Chronic, red, scaly skin, Rapid turnover of skin cells. Cycle of flare-ups and remissions, keratinocytes increase and dying is sped up, an accumulation of dead cells. Diagnosed visually then biopsied, typically bring on secondary infections since skin is compromised
Silver stain
A staining technique used to improve the contrast of certain structures, particularly microorganisms in tissue samples.