Invert. Zoology
1/168
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Midterm 1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
169 Terms
“Bauplan”
Blueprint; limit of organism
Radical symmetry
oral-aboral axis; no “behind”, slow
“perfect; symmetry
1 axis, infinite planes,
Biradial symmetry
1 axis, 2 planes; sensory structures in front, blind spots
Endoderm
outside; protective tissues, neurons
Mesoderm
Middle; circulatory, muscles
Endoderm
Inside; gut tube, liver
Diploblastic
only ectoderm & endoderm
Triploblastic
all 3 germ layers
What is a body cavity?
fluid filled space between gut and body wall
Acoelomate
filled in with solid tissues (flatworms)
Pollastocoelmate
Surrounded by muscle
Coelomate
“true” body cavity
kinds of skeletal structures
exoskeleton, endoskeleton, rigid
Hydrostatic
muscle acts against body fluid (noncompressable)
Rigid
Endo/exto skeleton; muscles act against hard skeleton (no change in shape)
“Antagonistic”
muscles; in pairs- one pull, one relax
complete gut
specialized; through
incomplete
less specialized; blind
Intracellular digestion
chemical digestion inside gut
Extracellular digestion
chemical digestion outside gut
Gut shapes
through, pouch, U-shaped
Feeding stategies
Suspension, deposit, herbivory, carnivore/ scavenging,
Open circulation
blood leaves arteries
Closed circulation
closed loop (blood never leaves vessels)
Kinds of nervous system
nerve net, nerve cord, brain/ganglia
Mechanoreceptors
feeling, grabbing
Chemoreceptors
tongue, nose, antenna, detection
Photoreceptor
light, image
Asexual reproduction
fragmentation, budding, fission, parthenogenesis
External fertilization
Spawning
Internal fertilization
Hermaohoritism
Holoblastic
complete cell division; dependent on yolk
Meroblastic
incomplete separation; embriotic
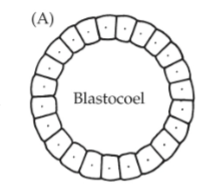
Coeloblastula
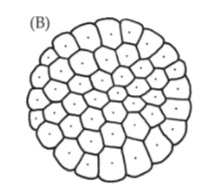
Discoblastula
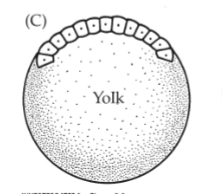
Stereoblastula
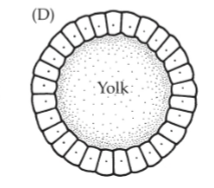
Periblastula
Ingression
folding the gut
Coelum formation: Schizocoley
forms from splitting in the mesoderm
Coelum formation: Entercoely
forms from outpocketing in developing gut
Radical cleavage
echnoderms; cells divide perpendicular to embryos’ vertical axis
Spiral cleavage
mollusks; oblique cell division; creating spirals
Planktotrophic
Can eat on its own, off the bat
Lecithotropic
eat moms yolk
Indirect development
larvae may be feeding/ non-feeding, larve go through metamorphosis, R-selected
Direct development
no true free-living larval stage, juvenile→ adult, k-selected
Mixed development
internal fertilization, limited parental care
Placozoan cells
gland (mucus, digestive enzymes)
cover cells
fiber cells
cylinder cells
How is Placozoan an animal?
animal cells, moves with purpose
Placozoan: Feeding/ Digestions
No mouth/ gut
extra/intra-cellular digestion (phagocytosis)
Phagocytosis
takes in extracellular fluids + other dissolved fluids → engulfe in membrane
Placozoan; body systems
no muscles
no circulatory structures
no neurons
no excretory system- diffuses waste
no basement layer
Porifera
(phylum) “pore bearer”
Porifera; Calcarea
skeletal spicules of calcium carbonate
~ 685 species
Porifera; Hexactinellida
Glass sponges; 6-rayed silica spicules
deep sea- uses current
~ 690 species
Porifera: Demospongiae
silica spicules and/or organic skeleton (spongin)
~7,400
Porifera: Homoscleromorpha
lack spongin, lack spicules
basement membrane
~85 species
Porifera: bauplan
lacking/ radical symmetry
lack organs= colony of cells
no tissues, no basement layer
no germ layers (no body cavity)
no gut
Porifera; Pinacoderm
outer body wall
Porifera: choanoderm
middle body wall
Porifera: mesonyl
inner body wall
Porifera: Cell types
Pinacocytes; outer skin, pores, protection
Choanoctyes; “caller cell’, do everything
Sclerocytes; “tube cell”, water passes through
Archaneocytes; “Stem”, becomes anything
Porifera: skeleton
in mesonyl
mycicytes- muscle cells
“sneezing’- contractinf
Inorganic spicules
calclium carbonate, silica
Sclerocytes
Organic spicules
collagen fibers, spongin
Ostia
water in
Ostulum
water out
Porifera: Feeding
no mouth/gut
canals~ choanoctes: pumps
Porifera: Coeanocytes
coordinate with other cells
captures particles with collar
Phagocytosis
carnivorous sponges- sharp spicules
Porifera: circulation,gas exchange, excretion
no specialized structure
diffusion only!
What is needed for diffusion to work
high surface area touching water at all times
very thin (1-2 ml)
Porifera: Nervous system
no nuerons
cell-to-cell communication
→ choanocytes beat together- water circulation
Porifera Asexual Reproduction
budding- piece comes off, grows
fragmentation- sponge falls apart, pieces become singular
*regenerative*
Gemmule→ only freshwater! (seed-like)
Porifera: Sexual Reproduction
seperate sexes + herm.
gametes from other cells (interstitial)
broadcast spawning (sperm)
→ Choanoctyles, differentiate between sperm/ egg, move to deliver, carrier cell
Oviparity
yolk in egg, no additional input, not live birth
Ovovivparity
yolk-fed, live-birth, internal ferilization
Viviparity
live birth, placenta- not yolk, direct nutrients
Porifera: Development
different cleavage patterns
cilia covered, short-lived larva
free-living larva: mixed/indirect development
Cnidarians
“Nettles”
~13,400 species
Anthozoa; Anthozoa
“flower animal”
polyps
lack medusae stage
Medusaozoa; Hydrozoa
“snake hair”
alteration of generation
medusae w/ venom
often colonial
Medusozoa: Scyphozoa
→ lions mane, moon jelly
medusa stage dominant
lack venom
Medusozoa: Cubozoa
metamorphosis: polyps→ medusa
square, cube shaped
tentacle from padalia
Myxozoa
intracellular parasites
lack most cnidarian traits
Cnidarians: Bauplan
radical symmetry
oral-aboral body axis
true tissues present
Diploblastic + mesoglea
alteration of generations (diff body, same genes)
Cnidarians: Ectoderm
Epiderms
Cnidarians: Endoderm
Gastrodermis
Cnidarians: polyp
sessile
solitary/ colonial (asexual reproduction)
mouth + tentacle up, disc down
trunk + gastrovascular cavity
Cnidarians: Medusa
motile, pelagic
solitary
mouth+ tentacle down
umbrella up
gastrovascular cavity in canals
Cnidarians
Epidermis: protection
Mesoglea: structure
Gastrodermis: digestion, circulation
Cnidarians Cell Types
Myoepithelial - muscles, skin cells
Muscus gland cell- produce mucus
Digestive gland cells- break down food
Nuerons
Interstitial- stem cells (become things)
Chinocytes- stinging cell
Cnidarians Skeleton
Hydrostatic- flexible
Rigid - perisac of hydrozoan polyps; “Shell”
Cnidarians: Locomotion
circular, longitudinal extension from myoepithelial
elastic fibers
polyps; contraction, swimming, digging
medusae; jet propulsion
Cnidarians: Feeding/ Digestion
All carnivore/ parasitic
Cnidoctyes- stinging cells
→ Nematocyst: organelle inside cnidoctyes- prey moves to mouth
secretory glands of gastrovascular
Phagocytosis
waste sent back through mouth
Cnidarians: alt. feeding
mucus net-suspesion
autotrophic symbionts
→ Zooxanthellae (brown/gold- marine), Zoochlorellae (green-freshwater)
Cnidarians: circulation, gas exchange, excretion
no specialized structures
diffusion
Cnidarians: nervous system/ sensory
neurons form nerve net
no cephalization
naked + nonpolar
Rhopalia
Statolith
pigment spots/cup- “eyes”
Rhopalia
seen easily on young
concentration of different kinds of sensory structures
chemoreceptors- tongue (taste and texture)
Statolith
equilibirum!!