Review for Chem final
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/123
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:49 PM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
1
New cards
Bond forming
releases energy (exothermic)
2
New cards
Bond breaking
endothermic (requires energy)
3
New cards
Spontaneous
\-ΔG, Decreasing the amount of available energy to perform work, happens naturally or without effort
4
New cards
Nonspontaneous
ΔG, Increasing the amount of available energy to preform work, does not happen naturally or with effort
5
New cards
Enthalpy
A measure of heat in a system
6
New cards
Entropy
How much energy is spread out
7
New cards
ΔH
Enthalpy
8
New cards
ΔS
Entropy
9
New cards
ΔG
Gibb's Free Energy
10
New cards
How does adding a catalyst affect the rate of reaction?
It lowers the activation energy
11
New cards
+ΔS
Increasing entropy/energy spreads out
12
New cards
The change in entropy
ΔS
13
New cards
heat of formation equation
sum of products - sum f products
14
New cards
How does lowering the temperature affect a reactions rate?
The reaction gets slower
15
New cards
How does decreasing the concentration of the reactants affect a reactions rate?
The reaction will increase
16
New cards
Q\=mc∆T
specific heat formula
17
New cards
∆G=∆H-T∆S
Gibb’s free energy equation
18
New cards
Activation energy
the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction
19
New cards
Activated complex
The state of the particles that is in between the reactants and products
20
New cards
Does the potential energy graph slope up or down in an endothermic reaction?
Up
21
New cards
Does the potential energy graph slope up or down in an exothermic reaction?
Up a little bit an then down a lot
22
New cards
Heat formation is defined as
The amount of heat absorbed
23
New cards
Convection
A cyclic heat transfer in a liquid or solid
24
New cards
Conduction
Heat is transferred between 2 objects that are in contact
25
New cards
Radiation
Heat transfer without something touching
26
New cards
1st law of thermodynamics
Energy cannot be created or destroyed
27
New cards
What happens to the entropy of a solid to a liquid
Get bigger(more randomness)
28
New cards
What happens to the entropy of a gas to a solid
Gets smaller(less randomness)
29
New cards
What is equilibrium?
When the forward reactions equal the rate of the reverse reactions. The concentrations of its products and reactants will remain unchanged.
30
New cards
What does K mean?
The equilibrium constant
31
New cards
K>>1
The reaction if product-favored
32
New cards
K<
The reaction is reactant-favored
33
New cards
K=1
The reaction favors neither.
34
New cards
LE CHATELIER’S PRINCIPLE
If an equilibrium is stressed, the equilibrium shifts in the direction that relieves the stress.
35
New cards
What does not stress a system?
Catalysts and nobel gases
36
New cards
What is a Reaction Quotient(Q)?
Describes the concentrations of a system to compare to the equilibrium constant (Kc) to determine if the system is at equilibrium.
37
New cards
Q>K
then the reaction has more products than reactants, so we shift to the left! (Create more reactants)
38
New cards
Q=K
then the reaction is at equilibrium!
39
New cards
Q
then the reaction has more reactants than products, so we shift to the right! (Create more products)
40
New cards
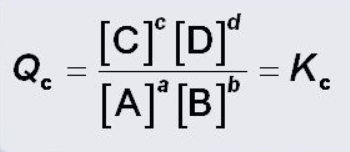
what is this?
Reaction Quotient equation
41
New cards
What happens when you increase the concentration of the reactants?
shift the equilibrium to the right (more product is created).
42
New cards
What happens when you increase the concentration of the products?
shift the equilibrium to the left (more products dissociate into reactants)
43
New cards
What happens when you decrease the concentration of the reactants?
shift the equilibrium to the left (less reactants to create products, so more products dissociate into reactants).
44
New cards
What happens when you decrease the concentration of the products?
shift the equilibrium to the right (less products dissociate into reactants, so more reactants create products)
45
New cards
What happens when you increase the pressure of a system?
the concentration of the molecules to increase on the side with more moles on it. Equilibrium shifts in the opposite direction.
46
New cards
What happens when you decrease the pressure of a system?
Decreasing the pressure decreases the concentration of the side with more moles on it. equilibrium shifts in the opposite direction
47
New cards
What happens when you increase the temperature in an exothermic reaction?
By increasing the heat, more AB products will be destroyed, shifting equilibrium to the left.
48
New cards
What happens when you decrease the temperature in an exothermic reaction?
By decreasing the heat, more AB products will be created, shifting equilibrium to the right.
49
New cards
What happens when you increase the temperature in an endothermic reaction?
By increasing the heat, more AB products will be destroyed, shifting equilibrium to the right.
50
New cards
What happens when you decrease the temperature in an endothermic reaction?
By decreasing the heat, more AB products will be created, shifting equilibrium to the left.
51
New cards
What is a solid?
Definitive shape and volume.
52
New cards
What is a liquid?
Indefinite shape, but definite volume.
53
New cards
What is a gas?
Indefinite shape and indefinite volume.
54
New cards
What is plasma?
Gas with free flowing electrons
55
New cards
Temperature is…
Temperature is the measure of the average kinetic energy of the molecules in a substance.
56
New cards
What is melting?
Changing from solid to liquid
57
New cards
What is vaporization?
Changing from liquid to gas
58
New cards
What is condensation?
Changing from gas to liquid
59
New cards
What is freezing?
Changing from liquid to solid
60
New cards
What is sublimation?
Changing from solid to gas
61
New cards
What is deposition?
Changing from gas to solid
62
New cards
What are IMF’s?
are forces of attraction or repulsion between two molecules.
63
New cards
Ion-diploe
strongest IMF, metal and non-metal, polar and non-polar
64
New cards
Hydrogen Bonding
Hydrogen bonding is an attractive force that takes place between hydrogen atoms attached to ONLY Nitrogen, Oxygen, & Fluorine (NOF).
65
New cards
Diploe-Diploe
Dipole-dipole IMFs take place between two polar molecules. Any molecules that are polar have dipole-dipole between them.
66
New cards
LDF
All bonds are this, are weak partial attractions between two polar or nonpolar molecules
67
New cards
What is evaporation?
is the process of liquid molecules becoming gaseous at any temperature.
68
New cards
Does temperature change in a phase change?
NO!!!!
69
New cards
What is Triple Point?
Pressure and temperature at which the substance exists as all the states of matter
70
New cards
What is Critical Point?
Pressure and temperature when the compound becomes a supercritical fluid (fluid-gas hybrid)
71
New cards
Molarity equation
Molarity=moles/liters of solution(l)
72
New cards
What is diluting?
To dilute a liquid, means to make it less concentrated of a certain substance. This process is used to create a desired concentration from a substance.
73
New cards
Dilutions equation
M1V1=M2V2
74
New cards
What are COLLIGATIVE PROPERTIEs
Substances dissolve differently depending on the solute and solvent.
75
New cards
Like Dissolves Like
Polar molecules dissolve polar molecules, nonpolar molecules dissolve nonpolar molecules.
76
New cards
Soluble
Solid will dissolve
77
New cards
Insoluble
Solid will not dissolve
78
New cards
Miscible
Liquid will mix
79
New cards
Immiscible
Liquid will not mix
80
New cards
Unsaturated
More solute can be added to the mixture or the temperature can be decreased. No particles.(under the line)
81
New cards
Saturated
The exact amount of temperature and particles, so that no more particles can be dissolved.
82
New cards
Supersaturated
More solute exists in the solution than can be dissolved. Particles are present.
83
New cards
Daltons Law
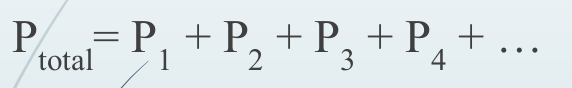
84
New cards
Boyle’s Law
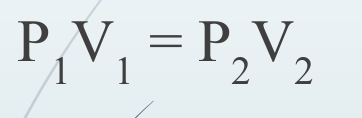
85
New cards
Charle’s Law
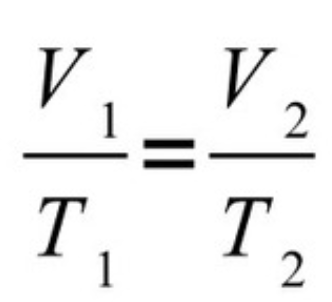
86
New cards
Gay-lussac’s law
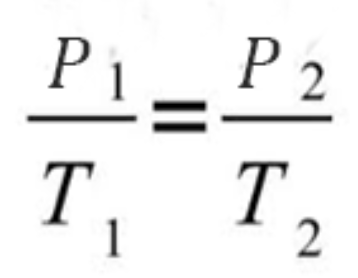
87
New cards
Avogadro’s law
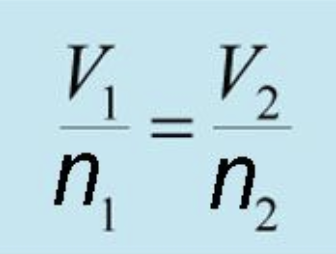
88
New cards
Combined Gas Law
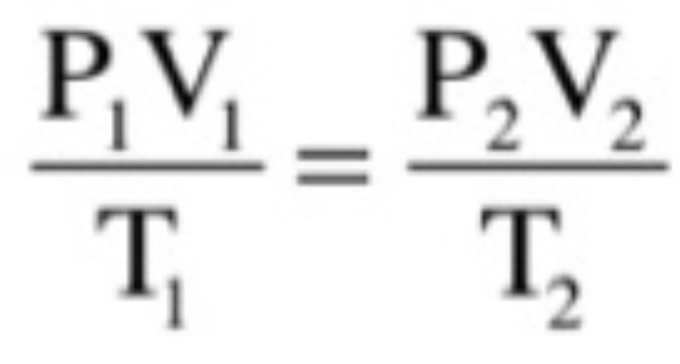
89
New cards
Ideal gas law equation
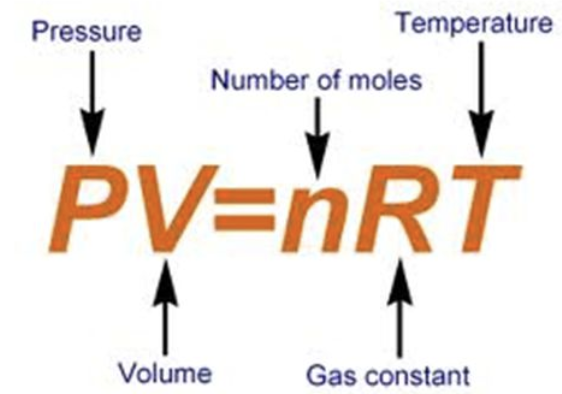
90
New cards
Moles at STP equal?
22\.4L
91
New cards
What is stoichiometry?
is the process of analyzing and calculating mass relationships in chemical reactions.
92
New cards
What is a limiting reactant?
the reactant that gets used up first in a chemical reactant
93
New cards
What is theoretical yield?
is the maximum amount of product that can be generated from a chemical reaction. Theoretically, all of the reactant will be used to create as much product as possible.
94
New cards
What is actual yield?
is the amount of product that is ACTUALLY generated during a chemical reaction.
95
New cards
What is percent yield?
The percent yield is the percentage of product that was actually created compared to what could theoretically be created.
96
New cards
How do you find percent yield?
Actual/Theoretical ᐧ 100 = % Yield
97
New cards
What is excess reactant?
the reactants that are not used up when the reaction is finished
98
New cards
Amphoteric
1. (of a compound, especially a metal oxide or hydroxide) able to react both as a base and as an acid.
99
New cards
What is fission?
Fission occurs when a neutron hits a large, unstable nucleus and causes it to break into two smaller nuclei.
100
New cards
What is critical mass?
is the amount of a substance that must be present in order for a chain reaction to occur.