IB Biology exam review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/253
Last updated 2:50 AM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
254 Terms
1
New cards
Who was the first person to use the word cell and looked at many plants and discovered a trend?
Robert Hooke
2
New cards
What is the cell theory?
States that cells are the fundamental building blocks of all living organisms.
3
New cards
Light microscope
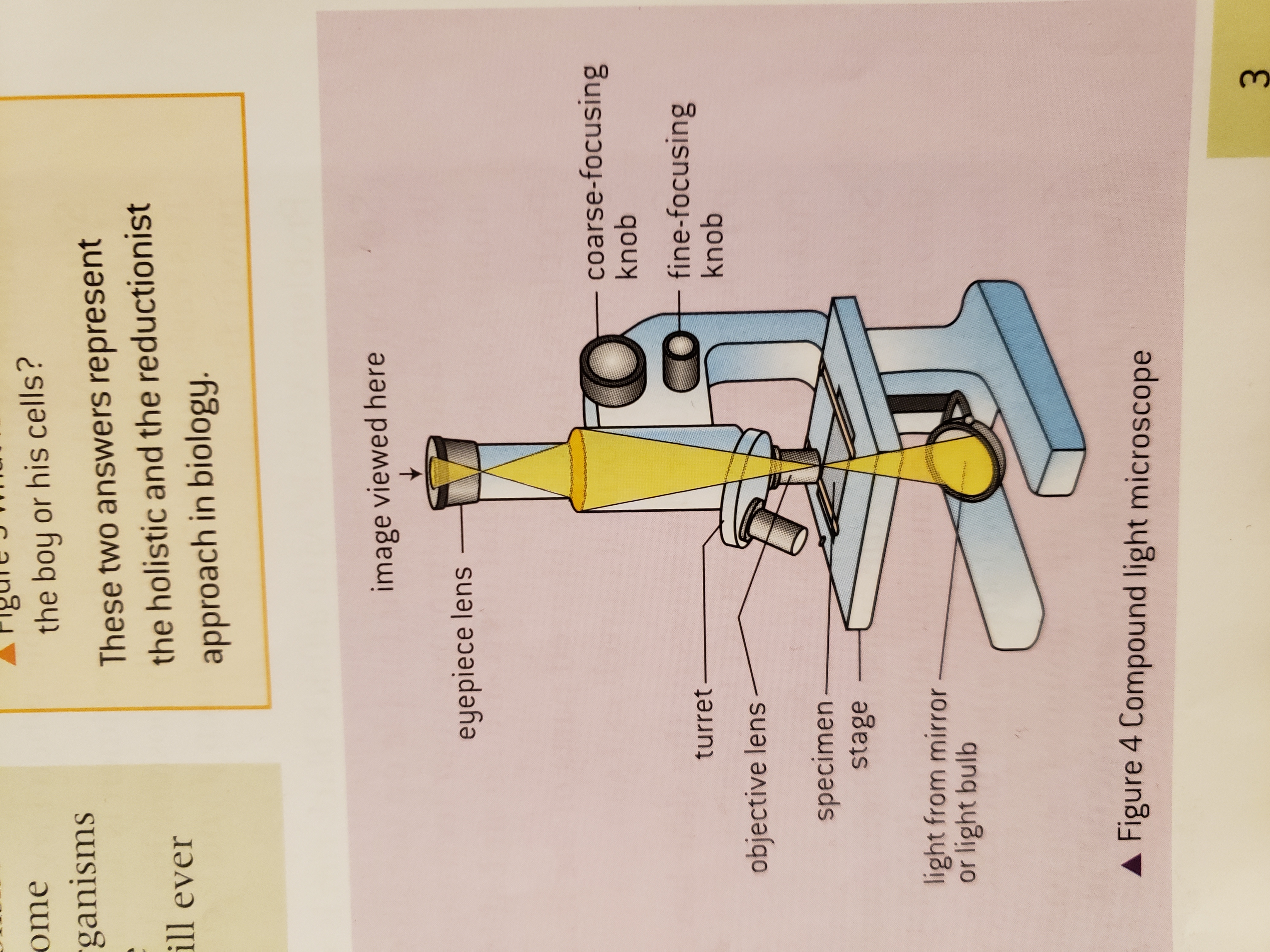
4
New cards
What is striated muscle and what is it used for?
A type of tissue used for changing the position of our body
5
New cards
What is the average length of a muscle fiber?
30 mm
6
New cards
What is the average length of a human cell?
0\.03 mm
7
New cards
What are hyphae?
White Fungi with thread-like structures. In some types of fungi, hyphae are divided up into small cell-like sections by cross walls called septa.
8
New cards
What are algae?
Organisms that feed themselves by photosynthesis and store their genes inside nuclei
9
New cards
Which 7 functions of life do unicellular organisms carry out?
Nutrition
Metabolism
Growth
Response
Excretion
Homeostasis
Reproduction
Metabolism
Growth
Response
Excretion
Homeostasis
Reproduction
10
New cards
Why is the surface area to volume ratio of a cell important?
For metabolism to continue, substances used in chemical reactions have to enter the cell and waste products have to leave the cell. Therefore, if the ratio is too small, the substances can't enter the cell quickly causing an excess amount of waste products. If the ratio is too small, the cells can overheat due to the metabolism of heat.
11
New cards
What are multicellular organisms?
Organisms consisting of a single mass of cells, fused together.
12
New cards
What are emergent properties?
The characteristics of the whole organism, including the fact that is alive.
13
New cards
What are tissues?
A group of cells specialized in the same way to perform the same function.
14
New cards
What is differentiation?
The development of cells in different ways to carry out specific functions.
15
New cards
What does it mean if a gene is being expressed?
It means the gene is being used in the cell. It is switched on and the information in it is used to synthesize proteins or other gene products.
16
New cards
What is an embryo?
When a zygote divides to give two cells.
17
New cards
What are stem cells?
The zygote and the early stage embryos. They can divide again and again to produce copious quantities of new cells. Therefore, can be useful for the growth of tissues or the replacement of cells that have been lost or damaged. They are not differentiated.
18
New cards
How is leukemia caused?
Excess white blood cells that are created.
19
New cards
The invention of what led to greater understanding of cell structure?
Electron microscopes
20
New cards
What do light microscopes see in a cell?
Unicellular organisms, chromosomes, the process of mitosis, meiosis, gamete formation, and organelles.
21
New cards
Light microscopes cannot produce clear images of structures smaller than (blank) micrometers (μm)
0\.2 μm
22
New cards
How thick are membranes in cells?
About 0.01 μm
23
New cards
What is electron tomography?
A method of producing 3D images by electron microscopy
24
New cards
Which has a higher resolution? Light or electron microscopes?
Electron microscopes
25
New cards
What is the smallest size for objects which the human eye can see?
0\.1 mm
26
New cards
What is making the separate parts of a object distinguishable by eye called?
Resolution
27
New cards
What is the wavelength of light?
400-700 nm
28
New cards
How could viruses be seen?
With an electron microscope
29
New cards
In prokaryotes, the cell wall contains what?
Peptidoglycan
30
New cards
What is the only organelles that unicellular organisms have? What is their size?
Ribosomes. 70 Svedberg units (S)
31
New cards
What are the parts of the cytoplasm that appear lighter under electron microscopes called? What does it contain?
A nucleoid that contains naked DNA which isn’t associated with proteins.
32
New cards
What is cell division in prokaryotes called?
Binary fission
33
New cards
What are the benefits of a cells being compartmentalized?
1) enzymes and substrates for particular processes are more concentrated
2) damaging substances can be kept inside organelles
3) pH levels can be maintained for particular processes
4) organelles and their contents can move around within the cell
2) damaging substances can be kept inside organelles
3) pH levels can be maintained for particular processes
4) organelles and their contents can move around within the cell
34
New cards
What are uncoiled chromosomes called?
Chromatin
35
New cards
what are flattened membrane sacs called? Where can they be found?
Cisternae can be found in the rough endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus of the cell
36
New cards
What are the two different types of gland cells?
Exocrine and endocrine cells
37
New cards
What do endocrine gland cells do?
Secrete hormones into the bloodstream
38
New cards
What do exocrine gland cells do?
Secrete digestive enzymes into a duct that carries them to the small intestine to digest foods.
39
New cards
What kind of cells carries out photosynthesis?
Palisade mesophyll cells
40
New cards
Are water molecules polar or non polar?
Water molecules are polar
41
New cards
What kind of bond forms between water molecules?
A hydrogen bond forms between water molecules.
42
New cards
What kind of bond makes up a water molecule?
A polar covalent bond makes up a water molecule meaning there are unequal shares of electrons.
43
New cards
What are the charges of the 2 hydrogen atoms and 1 oxygen atom in a water molecule?
The 2 hydrogen atoms have a partial positive charge and the 1 oxygen atom has a partial negative charge
44
New cards
What makes up the 2 different poles in a water molecule?
Water is bent instead of linear, therefore, the 2 hydrogen atoms are on the same side and form one pole and the water atom forms the other pole.
45
New cards
What kind of bond is formed by a positive ion and negative ion attracting each other?
An ionic bond is formed by a positive ion and negative ion attracting each other.
46
New cards
What was believed to be a genetic material for the creation of cells? Why?
RNA because it can store genetic material like DNA and it can self-replicate and act as a catalyst (act as an enzyme)
47
New cards
Why are enzymes important?
They are needed for DNA to replicate and for genes to be passed to offspring.
48
New cards
What are the 4 hypothesis of how cells were formed?
1) production of carbon compounds such as sugars and amino acids
2) assembly of carbon compounds into polymers
3) formation of membranes
4) development of a mechanism for inheritance
2) assembly of carbon compounds into polymers
3) formation of membranes
4) development of a mechanism for inheritance
49
New cards
What is the theory of endosymbiotic?
It is a theory used to explain the evolution of eukaryotic cells. It refers to mitochondria being once free-living prokaryotic organisms that have developed through aerobic cell respiration. The large prokaryotic cells which could only respire anaerobically took these mitochondria in by endocytosis and allowed them to live as long as the smaller prokaryotic cells grew and divided as fast as the larger ones. This was a symbiotic and mutualistic relationship.
50
New cards
What relationship does natural selection favor?
Endosymbiotic relationships
51
New cards
What are features of mitochondria and chloroplast that indicate they might have evolved from independent prokaryotes?
\--They have their own genes, on a circular DNA molecule like prokaryotes
\--They have their own 70S ribosome of a size and shape typical of some prokaryotes
\--They transcribe DNA and use mRNA to synthesize some of their own proteins
\--They can only be produced by division of pre-exsisting mitochondria and chloroplasts.
\--They have their own 70S ribosome of a size and shape typical of some prokaryotes
\--They transcribe DNA and use mRNA to synthesize some of their own proteins
\--They can only be produced by division of pre-exsisting mitochondria and chloroplasts.
52
New cards
What are the properties of water?
Cohesive, adhesive, thermal and solvent
53
New cards
What does the cohesive property of water refer to? What is an example?
It refers to the binding of two molecules of the same type (they stick to each other). An example of this is the transport of water in plants where water is sucked through xylem vessels at low pressures.
54
New cards
What does the adhesive property of water refer to? What is an example of this?
It refers to the connection of water molecules and other polar molecules. An example of this is when water adheres to the cellulose molecules in the cell walls of leaves. Adhesiveness causes water to be pulled out from the nearest xylem vessel.
55
New cards
What does the high specific heat capacity thermal property of water refer to?
It refers to the hydrogen bonds restricting the movement of water molecules and increasing the water temperature by the hydrogen bonds being broken. This requires enormous amounts of energy.
56
New cards
What does the high latent heat of vaporization thermal property of water refer to?
It refers to the evaporation of molecule from other molecules in a liquid which becomes a vapor molecule through latent heat.
57
New cards
What does the high boiling point thermal property of water refer to?
It refers to the highest temperature which a substance in the liquid state can reach.
58
New cards
What does hydrophilic mean?
Water-loving
59
New cards
What does hydrophobic mean?
“Water-fearing” meaning the substances are insoluble in water. Substances that are neither positive ions or negative ions are non polar and therefore hydrophobic. EX: lipids and oils
60
New cards
What is methane?
It is a waste product of anaerobic respiration in certain prokaryotes that live in habitats where oxygen is lacking.
61
New cards
Is water a coolant?
Yes, water is! It helps cool our bodies.
62
New cards
How does water cool our bodies?
Sweat is secreted by glands in the skin and carried along narrow ducts to the surface of the skin where it spreads out. The heat needed for this is taken from the tissues of the skin which reduces temperature. Solutes in sweat are sometimes left on the skin and can be detected by their salty tastes.
63
New cards
What is transported in blood plasma?
Sodium chloride, amino acids, glucose, oxygen, fat molecules, and cholesterol.
64
New cards
What is sodium chloride?
An ionic compound that is freely soluble in water, dissolving to form sodium ions and chloride ions which are carried in blood plasma.
65
New cards
What are amino acids in relation to transport in blood plasma?
They have positive and negative charges, therefore, they are soluble in water based on their R group.
66
New cards
What is glucose in relation to transport in blood plasma?
A polar molecule which is freely soluble in water and is carried dissolved in blood plasma.
67
New cards
What is oxygen in relation to blood plasma transport?
A non polar molecule and is sparingly dissolved in water making water saturated in oxygen at relatively low concentrations.
68
New cards
What is the purpose of hemoglobin in the transport of blood plasma?
It has binding sites for oxygen and increases the capacity of blood in oxygen transport.
69
New cards
What happens to the oxygen when the water temperature rises?
The solubility of oxygen decreases.
70
New cards
What are fat molecules in relation to the transport in blood plasma?
They are entirely non polar, larger than oxygen and are insoluble in water. They are carried in blood in lipoprotein complexes.
71
New cards
What is cholesterol in relation to the transport in blood plasma?
Molecules that are hydrophobic and apart from a small hydrophilic region at one end of a phospholipid. They are transported in lipoprotein complexes with fats.
72
New cards
What are examples of monosaccharides?
Glucose, fructose, and ribose
73
New cards
What are monosaccharides?
They are single sugar units
74
New cards
What are disaccharides?
They are two monosaccharides linked together. EX: maltose (two glucose), and sucrose (one glucose and one fructose).
75
New cards
What are polysaccharides?
They are many monosaccharides linked together. EX: starch, glycogen, and cellulose (all made from glucose)
76
New cards
What is the process of monosaccharides combining called?
Condensation which is an anabolic process with energy needed. -OH from one molecule and -H from another molecule are lost which together forms H2O. Therefore, condensation involves the loss of water.
77
New cards
What is the most common link in two glucose molecules?
Between the -OH on the carbon atom 1 and 4. The -OH on carbon atom 6 is used to make branches in some polysaccharides.
78
New cards
What are the two types of glucose?
α-glucose (-OH carbon atom 1 points down) and β-glucose (-OH carbon atom 1 points up)
79
New cards
What type of glucose is linked together in cellulose?
β-glucose is used
80
New cards
How can condensation occur in cellulose?
When each β-glucose is added to the chain is has to be added at a 180⁰ position to the previous one.
81
New cards
Is cellulose a straight chain or curved chained?
Cellulose is a striaght chain because the glucose subunits in the chain are oriented alternately upwards and downwards.
82
New cards
How can cellulose create bundles of hydrogen bonds?
They are unbranched chains of β-glucose therefore, they can form bundles of hydrogen bonds linking the cellulose molecules called cellulose molefibrils. Which are used as the basis of plant cell walls because of their tensile strength which can prevent the plant cell from bursting even when there are very high pressures developing inside the cell because of osmosis.
83
New cards
What type of glucose makes up starch?
α-glucose is used
84
New cards
Is the starch molecule straight or curved?
Curved because the -OH groups both point downwards so all glucose molecules can be oriented the same way.
85
New cards
What are the different forms of starch?
Amylose (a chain of α-glucose molecules forming an unbranched chain and forms a helix).
Amylopectin (a branched chain that has a more globular shape).
Amylopectin (a branched chain that has a more globular shape).
86
New cards
How is starch made?
By plant cells
87
New cards
Are the molecules of starch hydrophobic or hydrophilic? How does this contribute to their purpose?
They are hydrophilic but they are too big to be soluble in water. Therefore, they can be used in cells where large amounts of glucose can be stored (like a storage) when glucose is being made faster than photosynthesis than it being transferred to other parts of the plant.
88
New cards
Is glycogen branched or unbranched?
It is branched, but there are more branching than starch, therefore, the molecule is more compact.
89
New cards
How is glycogen created? Where is is located?
Animals and some fungi create this and is stored in the liver and some muscles of humans
90
New cards
How are triglycerides formed?
They are formed by condensation from 3 fatty acids and 1 glycerol
91
New cards
Are fats liquid or solid at room and body temperature?
Liquid at body temperature and solids at room temperature.
92
New cards
Are oils liquid or solid at body and room temperature?
Liquid at both body and room temperature.
93
New cards
What kind of bond is created between each fatty acid and glycerol?
An ester bond
94
New cards
What are triglycerides used for?
They are used as energy stores. The energy can be released by anaerobic respiration. They are heat insulators because they don’t produce heat well.
95
New cards
Are lipids or carbohydrates more suitable for long term energy storage in humans?
Lipids are more suitable for this. Fats are used and stored in adipose tissues which is located immediately under the skin and around some organs like the kidneys. Lipids release double the energy than carbohydrates and has fats with aren’t associated with water therefore it can decrease our body mass. Lipids can also be heat insulators and a shock absorber.
96
New cards
What is used for short-term energy storage in humans?
Glycogen because it can be broken down into glucose and transported by the blood to where it is needed easily. They can also be used in aerobic or anaerobic respirations.
97
New cards
What makes up the carboxyl group?
\-COOH
98
New cards
How many carbon atoms do most fatty acids have?
14-20 carbon atoms
99
New cards
What kind of bond links the carbon atoms in a fatty acid?
Covalent bonds. Some fatty acids have single covalent bonds, while others may have areas with double covalent bonds. (There is always one double covalent bond in the carboxyl group)
100
New cards
How many hydrogens can a carbon atom bond with if it has a double covalent bond? (In relation to fatty acids)
One hydrogen atom