Unit 7: Development and Industry Cumulative Set
1/183
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
184 Terms
acid deposition
sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides, emitted by burning fossil fuels, that enter the atmosphere--where they combine with oxygen and water to form sulfuric acid and nitric acid--and return to Earth's surface
acid precipitation
conversion of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides to acids that return to Earth as rain, snow, or fog
air pollution
concentration of trace substances, such as carbon monoxide, sulfur dioxide nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, and solid particulates, at a greater level than occurs in average air
biochemical oxygen demand (BOD)
the amount of oxygen required by aquatic bacteria to decompose a given load of organic waste; a measure of water pollution
break-of-bulk point
a location where transfer is possible from one mode of transportation to another
chlorofluorocarbon (CFC)
a gas used as a solvent, a propellant in aerosols, a refrigerant, and in plastic foams and fire extinguishers
ferrous
metal, including iron, that are utilized in the production of iron and steel
Greenhouse effect
The anticipated increase in Earth's temperature caused by carbon dioxide (emitted by burning fossil fuels) trapping some of the radiation emitted by the surface
Labor-intensive industry
an industry for which labor costs comprise a high percentage of total expenses
Maquiladora
an EPZ--a factory built by a U.S. company in Mexico near the U.S. border, to take advantage of the much lower labor costs in Mexico
Nonferrous
metals utilized to make products other than iron and steel
Nonpoint-source pollution
pollution that originates from a large, diffuse area
Outsourcing
a decision by a corporation to turn over much of the responsibility for production to independent suppliers
Ozone
A gas that absorbs ultraviolet solar radiation, found in the stratosphere, a zone 15 to 50 kilometers (9 to 30 miles) above Earth's surface
Photochemical smog
an atmospheric condition formed through a combination of weather conditions and pollution, especially from motor vehicle emissions
Point-source pollution
pollution that enters a body of water from a specific source
Right-to-work law
a U.S. law that prevents a union and a company from negotiating a contract that requires workers to join the union as a condition of employment
Sanitary landfill
a place to deposit solid waste, where a layer of earth is bulldozed over garbage each day to reduce emissions of gases and odors from the decaying trash, to minimize fires, and to discourage vermin
Site factors
location factors related to the costs of factors of production inside a plant, such as land, labor, and capital
Situation factors
location factors related to the transportation of materials into and from a factory
textile
a fabric made by weaving, used in making clothing
vertical integration
an approach typical of traditional mass production in which a company controls all phases of a highly complex production process
active solar energy systems
solar energy systems that collects energy that collect energy through the use of mechanical devices such as photovoltaic cells or flat-plate collectors
biomass fuel
fuel that derives from plant material and animal waste
developed country (more developed country [MDC] or relatively developed country)
a country that has progressed relatively far along a continuum of development
developing country (less developed country [LDC])
a country that is at a relatively early stage in the process of economic development; those countries, including Africa, except for South Africa, and parts of South America and Asia, that usually have low levels of economic productivity, low per-capita incomes, and generally low standards of living
development
a process of improvement in the material conditions of people through diffusion of knowledge and technology
fair trade
an alternative to international trade that emphasizes small businesses and worker-owned and democratically run cooperatives and requires employers to pay workers fair wages, permit union organization, and comply with minimum environmental and safety standards
fission
the splitting of an atomic nucleus to release energy
foreign direct investment (FDI)
investment made by foreign company in the economy of another country
fossil fuel
an energy source formed from the residue of plants and animals buried millions of years ago
fracking (hydraulic fracturing)
the pumping of water at high pressure to break apart rocks in order to release natural gas
fusion
creation of energy by joining the nuclei of two hydrogen atoms to form helium
geothermal energy
energy from steam or hot water produced from hot or molten underground rocks
housing bubble
a rapid increase in the value of houses followed by a sharp decline in their value
literacy rate
the percentage of a country's people who can read and write
maternal mortality ratio
the number of women who die giving birth per 100,000 births
passive solar energy systems
solar energy systems that collect energy without the use of mechanical devices
photovoltaic cell
a solar energy cell, usually made from silicon, that collects solar rays to generate electricity
potential reserve
the amount of a resource in deposits not yet identified but thought to exist
productivity
the value of a particular product compared to the amount of labor needed to make it
proven reserve
the amount of a resource remaining in discovered deposits
purchasing power parity (PPP)
the amount of money needed in one country to purchase the same goods and services in another country; __________ adjusts income figures to account for differences among countries in the cost of goods
radioactive waste
materials from a nuclear reaction that emit radiation; contact with such particles may be harmful or lethal to people; therefore, the materials must be safely stored for thousands of years
structural adjustment program
economic policies imposed on less developed countries by international agencies to create conditions encouraging international trade, such as raising taxes, reducing government spending, controlling inflation, selling publicly owned utilities to private corporations, and charging citizens more for services
supply
the quantity of something that producers have available for sale
uneven development
development of core regions at the expense of those on the periphery
value added
the gross value of a product minus the cost of raw materials and energy
brick-and-mortar business
traditional businesses with actual stores in which trade or retail occurs; it does not exist solely in the Internet
conglomerate corporation
a firm that is comprised of many smaller firms that serve several different functions
core
national or global regions where economic power, in terms of wealth, innovation, and advanced technology, is concentrated.
deglomeration
the dispersal of an industry that formerly existed in an established agglomeration
deindustrialization
loss of industrial activity in a region
economic backwaters
regions that fail to gain from national economic development
export-processing zone
areas where governments create favorable investment and trading conditions to attract export-oriented industries
fast world
areas of the world, usually the economic core, that experience greater levels of connection due to high-speed telecommunications and transportation technologies
manufacturing region
a region in which manufacturing activities have clustered together. The major US industrial region has historically been in the Great Lakes, which includes the states of Michigan, Illinois, Indiana, Ohio, New York, and Pennsylvania. Industrial regions also exist in southeastern Brazil, central England, around Tokyo, Japan, and elsewhere
net national product
a measure of all goods and services produced by a country in a year, including production from its investments abroad, MINUS the loss or degradation of natural resource capital as a result of productivity.
offshore financial center
country or territory whose financial sector features very few regulations and few, if any, taxes
EX: tropical island nations like the Bahamas, Cayman Islands, etc.
periphery
countries that usually have low levels of economic productivity, low per-capita incomes, and generally low standards of living. The world economic __________ includes Africa (except for South Africa), parts of South America, and Asia
regionalization
the process by which specific regions acquire characteristics that differentiate them from others within the same country. In economic geography, __________________________ involves the development of dominant economic activities in particular regions.
semiperiphery
those newly industrialized countries with median standards of living, such as Chile, Brazil, India, China, and Indonesia. ___________ countries offer their citizens relatively diverse economic opportunities but also have extreme gaps between rich and poor.
service-based economies
highly developed economies that focus on research and development, marketing, tourism, sales, and telecommunications
spatially fixed costs
an input cost in manufacturing that remains constant wherever production is located
spatially variable costs
an input cost in manufacturing that changes significantly from place to place in its total amount and in its relative share of total costs
specialty goods
goods that are not mass-produced but rather assembled individually or in small quantities
transnational corporations
a firm that conducts business in at least two separate countries; also known as multinational corporations
Millenium Development Goals (MDGs)
The UN's creation of eight goals for economic development and social progress in 2000. Members agreed to reach the goals by 2015.
1. Eliminate extreme poverty
2. Guarantee universal education
3. Promote equality for women
4. Reduce child mortality rates
5. Better maternal health services and reduction of maternal mortality rate
6. Reduce spread snd improve treatment for HIV/AIDS and other diseases
7. Environmentally sustainable development
8. Global development partnerships among member nations
World Systems Theory (Wallerstein)
Core regions make decisions for the world, semi-periphery make decisions for themselves and the areas around them, periphery areas are dominated by core and semi-periphery, have little influence
Human Development Index (HDI)
Indicator of level of development for each country, constructed by United Nations, combining income, literacy, education, and life expectancy
Inequality-adjusted HDI (IHDI)
Modification of the HDI to account for inequality within a country
Brandt Line
divides the more developed north from the less developed south
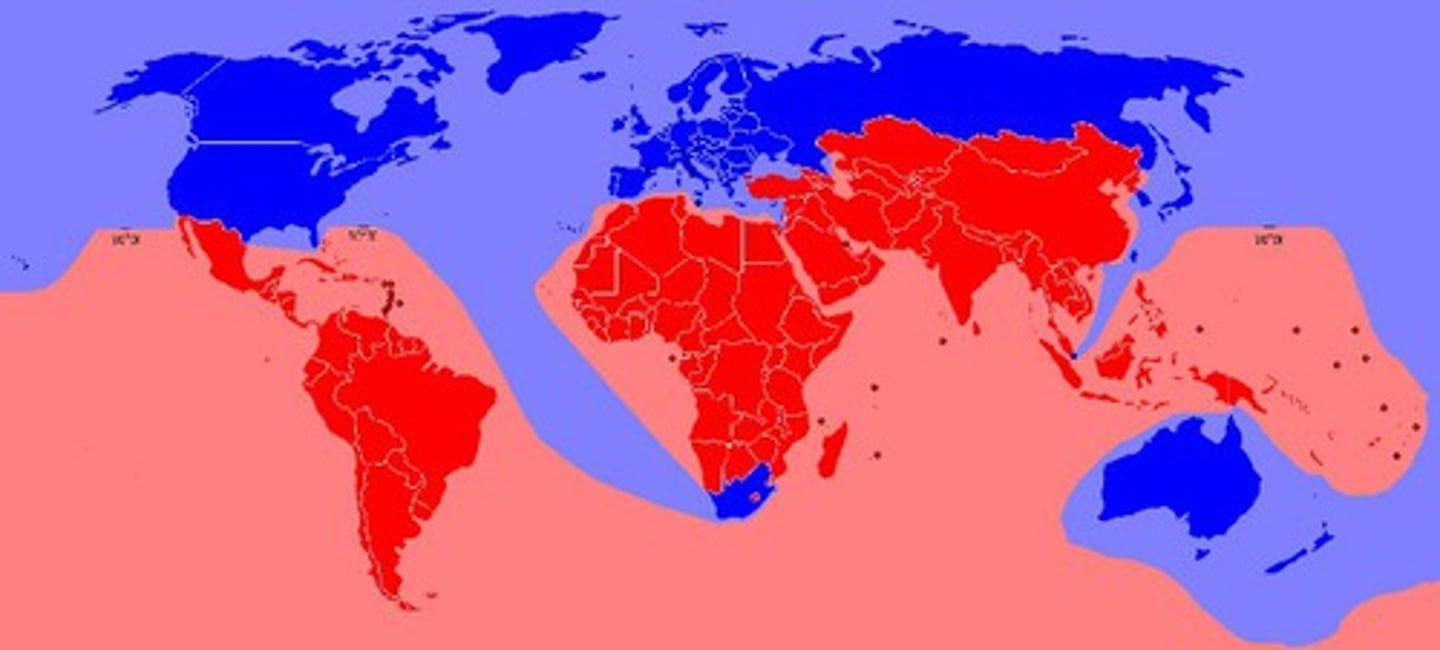
standard of living
Quality of life based on ownership of necessities and luxuries that make life easier.
Four Asian Dragons (Tigers)
Hong Kong, South Korea, Taiwan & Singapore. Their economies began to boom in the 1960's as they followed the export-oriented industrialization economic model.
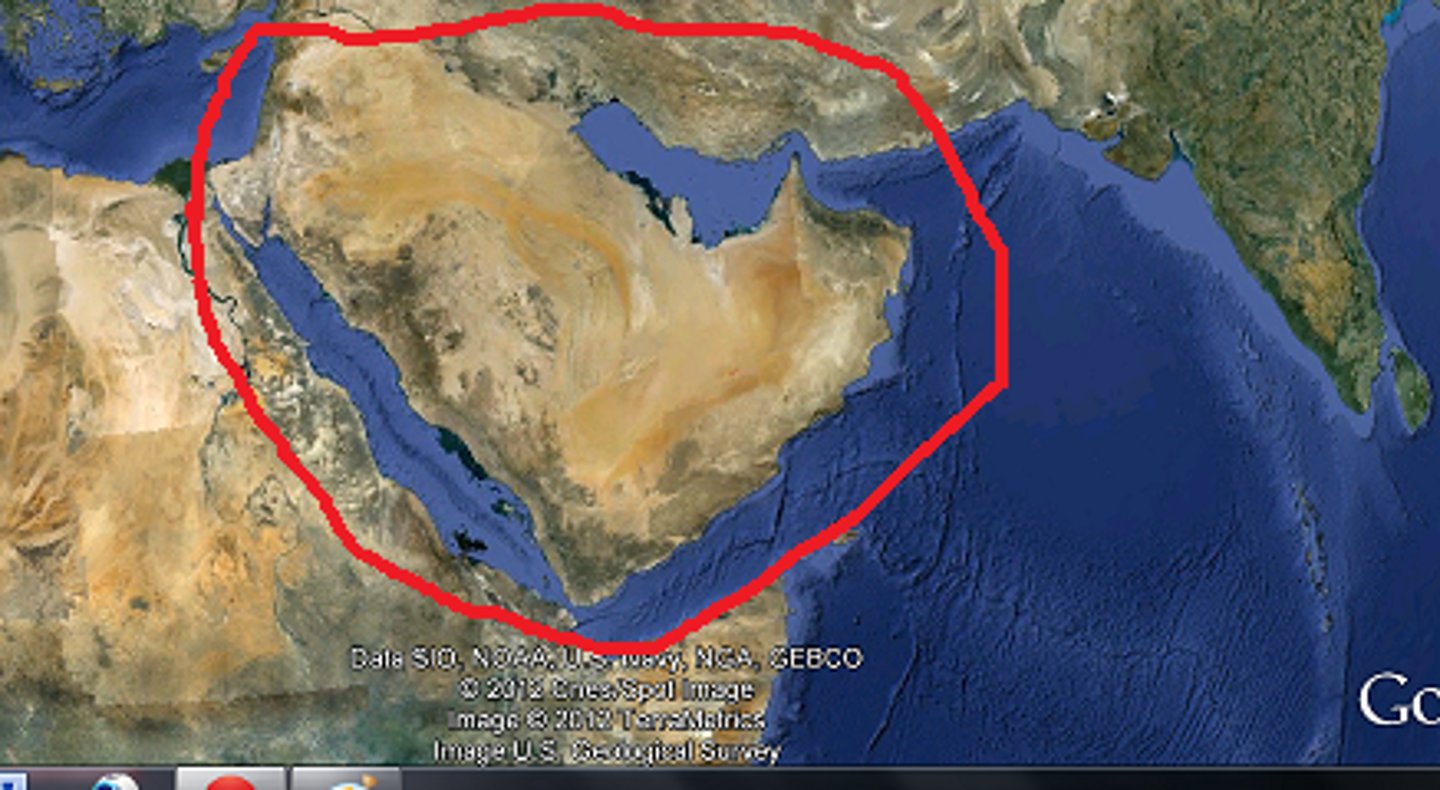
Arabian Peninsula states
Petroleum-rich
Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Bahrain, Oman, and United Arab Emirates (UAE)
Rostow's Stages of Development
A model of economic development that describes a country's progression which occurs in five stages transforming them from least-developed to most-developed countries.
1. Traditional Society
2. Preconditions for Takeoff
3. Takeoff
4. Drive to maturity
5. Age of Mass Consumption
Traditional Society
the first stage of Rostow's economic development; this stage can last for thousands of years unless there is an impetus for growth in the mercantile and manufacturing areas and a change in the institutions necessary to make the transition to a more modern capitalist society.
Preconditions for takeoff
the second stage of Rostow when an elite group starts economic activity; educated leaders start to take charge of the economy
Takeoff stage
The third stage of Rostow: rapid growth
- societies moving away from traditional norms, practices, and institutions and are embracing economic development with a sense of purpose and growing practices of savings and investment
Drive to maturity
Fourth stage of Rostow's development: technology diffuses, industrial specialization occurs, international trade expands, population growth slows
Age of Mass Consumption
Fifth stage of Rostow's Development: Economy shifts from production of heavy industry to consumer goods
World Bank
an international bank that offers low-interest loans, advice, and information to developing nations
Stimulus Strategy
Governments spend more to put people to work, then later pay off their debt (Large bureaucracy)
Austerity Strategy
Governments spend less to keep debt from increasing (Small bureaucracy)
Dependency Theory
a model of economic and social development that explains global inequality in terms of the historical exploitation of poor nations by rich ones
Gender Development Index (GDI)
Measure that aims to take into account gender-sensitive dimensions into the level of development of a country.
usually a decimal; closer to 1 = higher development for women
labor force
the total number of workers, including both the employed and the unemployed
adolescent fertility rate
The number of births per 1,000 women ages 15 to 19
coal reserves
The quantities of discovered, but not yet mined, coal in sedimentary rock of the continents.
LARGE amounts:
- US
- Russia
- China
coal
A fossil fuel that forms underground from partially decomposed plant material
SOLID form
petroleum
liquid fossil fuel; oil
reserves: Russia, Saudi Arabia, Nigeria, Venezuela
natural gas
A fossil fuel in the gaseous state
reserves: Russia, USA, SW Asia
renewable energy sources
sources of energy able to be replaced through ongoing natural processes
nonrenewable energy sources
An energy source with a finite (limited) supply, primarily the fossil fuels and nuclear fuels
neo-colonialism
control by a powerful country of its former colonies (or other less developed countries) by economic pressures
nuclear energy
The potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom; a little material, a LOT of energy. SUPER dangerous and expensive
hydroelectric power
Power generated from moving water. Can alter (sometimes poorly) ecosystems.
wind power
energy from moving air
solar energy
energy from the sun
- "cells" or batteries for this are expensive
- panels are expensive
- batteries are inefficient and don't store a lot of this type of energy
Industrial Revolution
A series of improvements in industrial technology that transformed the process of manufacturing goods.
- late 1700s/early 1800s UK
- spread through Europe first
- changed the cottage industry system