Trade protection and exchange rates
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
Barriers to trade
Obstacles to international trade, imposed by a government to safeguard national interests by reducing the competitiveness of foreign firms.
Tariffs
A specific tax on imported goods and services
Aim of tariffs
Increase production costs for a foreign firm to increase the price of a good or service and make domestically produced goods more competitve.
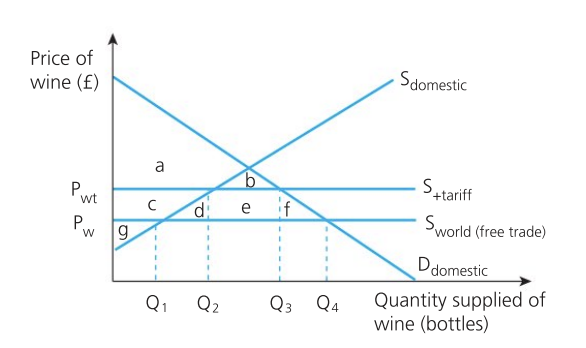
Effect of tariff on consumers
higher prices
reduced variety of good and service
consumer surplus decreases from a + b + c + d + e + f to a + b
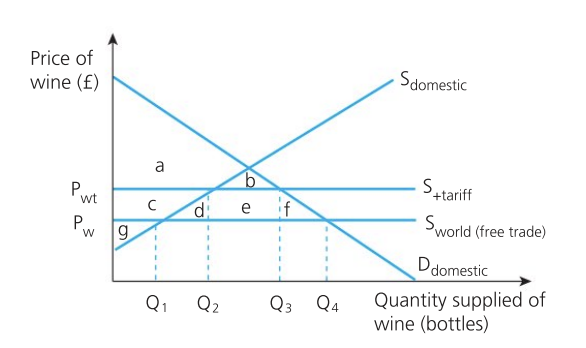
Effect of tariff on producers
domestic producers:
benefit in the short run as they are able to compete more effectively despite their lack of comparative advantage
increase in producer surplus from g to c + g
increase in producer revenue as domestic demand increases from Q1 to Q2
in the long run they may experience a reduction in export revenues due to retaliation from foreign governments
foreign producers:
lose revenue
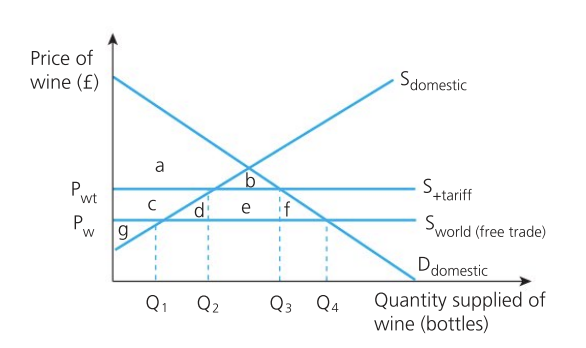
Effect of tariff on government
tax revenue e
protecting jobs in the domestic industry so they will have to pay less unemployment benefits so taxpayers are also benefited
burden of costs of enforcing the tariff
may also face action from the World Trade organization such as fines or sanctions
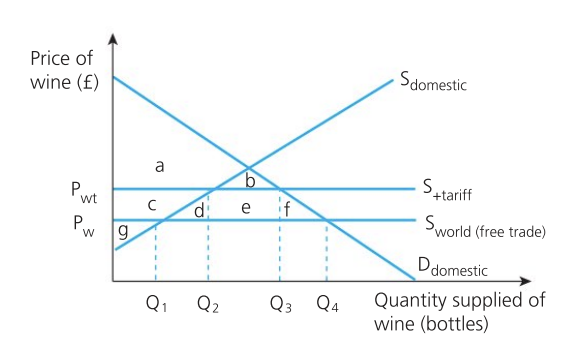
Effect of tariff on market efficiency and welfare
consumer surplus decreases from a + b + c + d + e + f to a + b
producer surplus increases to from g to c + g
thus, social surplus decreases from a + b + c + d + e + f + g to a + b + c + g
efficiency is lower and there is a welfare loss represented by d + f
f is loss of consumers and d represents inefficient production by firms
Non-tariff barriers
Restrictions to international trade that do not involve a tax or duty (tariff), such as quotas, export subsidies and administrative barriers.
Quotas
Quantitative limits on the importation of a good into a country
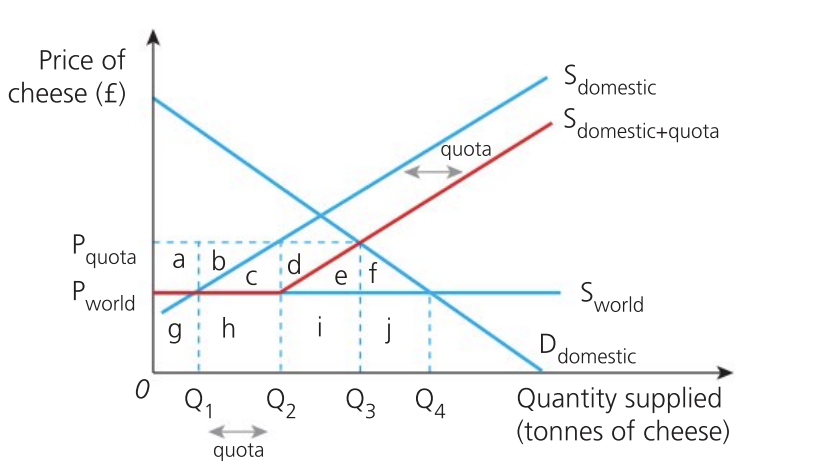
Effect of quota on consumers
introduction of quota from Q1 to Q2 creates greater scarcity causing an increase in price to Pquota
reduction in variety and choice
consumer expenditure increases from g + h + i + j to a + b + c + d + e + g + h + i
loss in consumer surplus is a + b + c + d + e + f
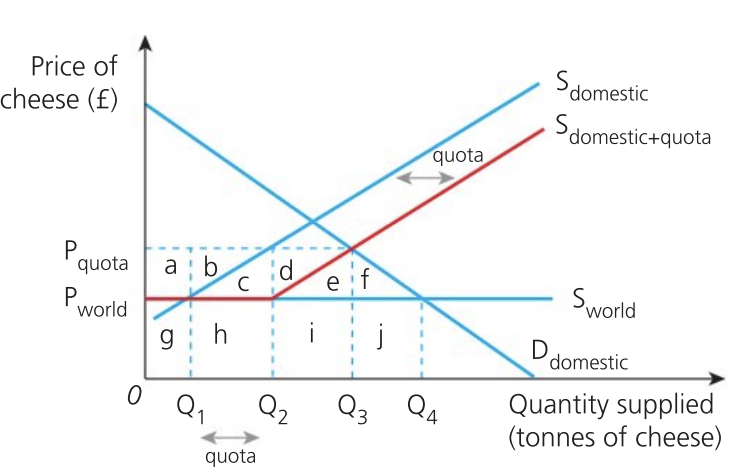
Effect of quota on producers
domestic producers:
revenue increases from g + h + i + j to a + g + d + e + i
could lead to economies of scale increase profits
foreign producers:
reduction in revenue from h + i + j to b + c + h
still receive a higher price per good but it is likely to lead to lower revenues due to limit on their supply
depends on the price elasticity of demand and supply
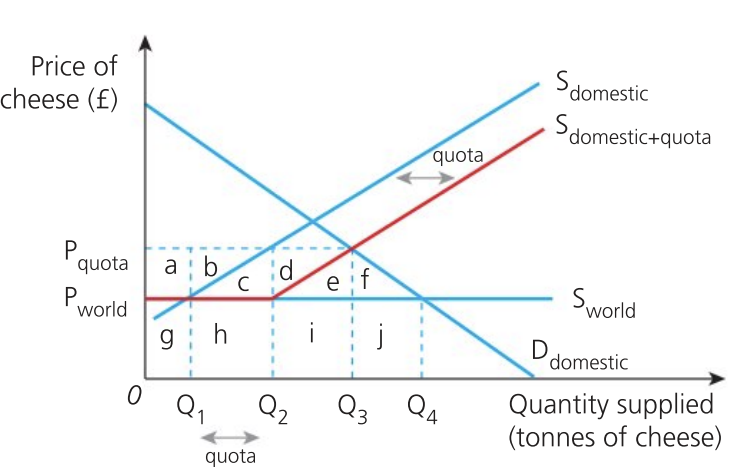
Effect of quota on the government
will receive some revenue from sale of import licences
enforcement costs from administering it, selling the license and deterring smuggling operations
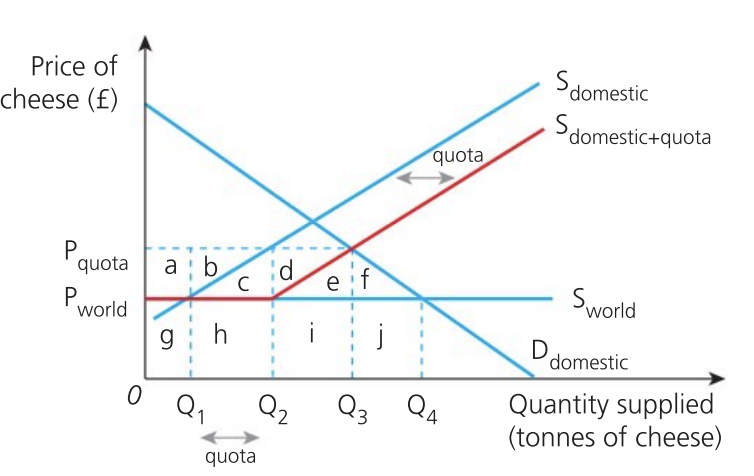
Effect of quota on welfare (society)
loss of efficiency due to lower levels of competition and less choice for domestic consumers
welfare loss represented by e + f
base of triangle is loss in imports of cheese and the height is the higher price
thus, society is worse off
Subsidies
A form of financial assistance to domestic firms by lowering their costs of production in order to help them compete against foreign imports
Production subsidies
Most common, used to help reduce the production costs of domestic firms
Export subsidies
Less wide-ranging as they are targeted at protecting specific export orientated firms
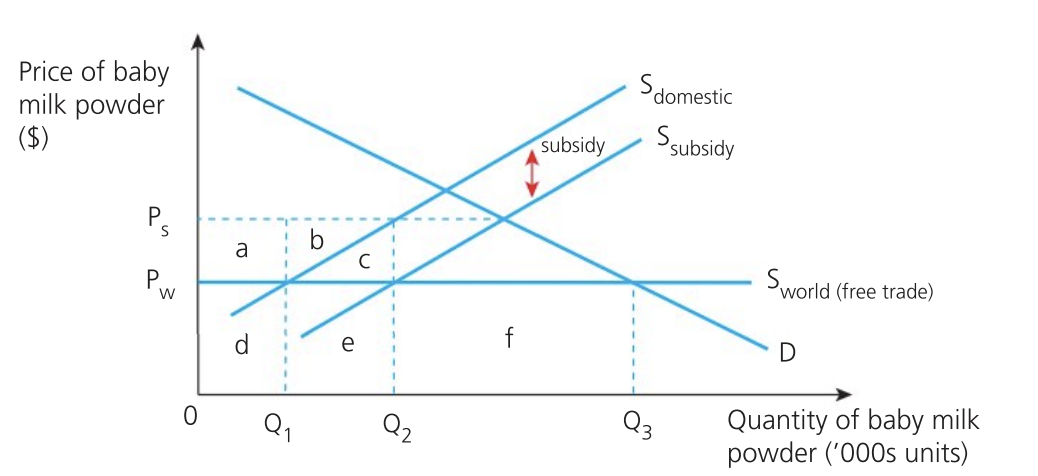
Effect of subsidy on consumers
consumption and price are unaffected
buy more domestic goods so gain or lose depends on the quality difference
consumer expenditure (Pw x Q3): d + e + f
consumer surplus stays the same
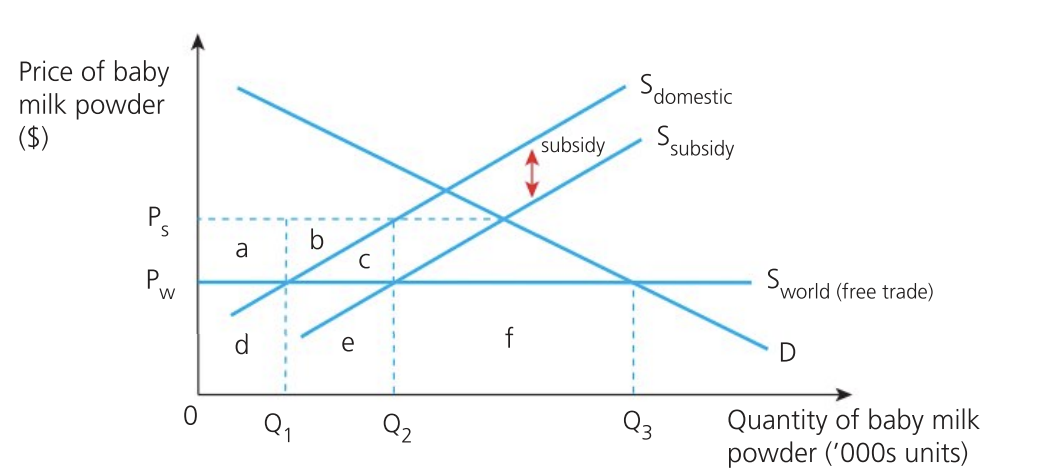
Effect of subsidy on producers
domestic firms:
sell at world price but receive Ps
gain more as they supply at Q2 rather than Q 1
revenue increases from d to a + b + c + d + e
foreign producers:
decrease in exports from Q3-Q1 to Q3-Q2
revenue decreases from e + f to e
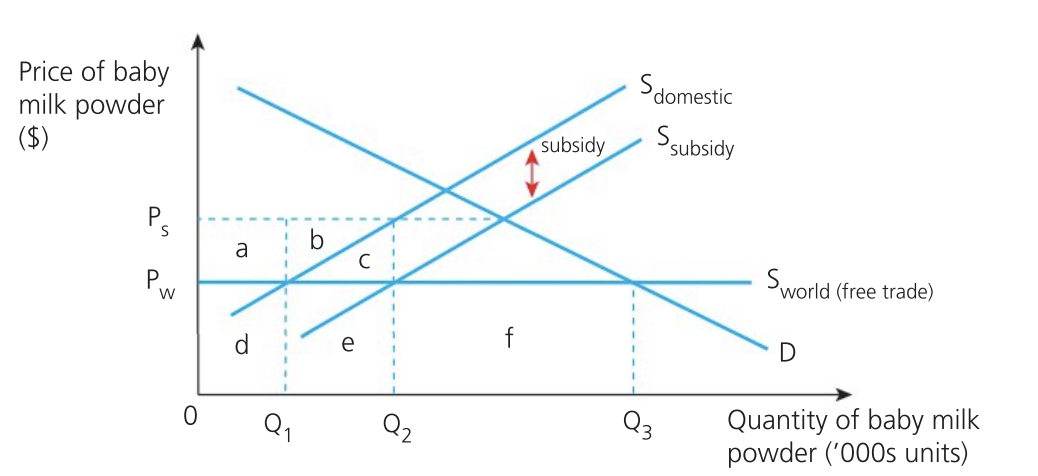
Effect of subsidy on the government
increased expenditure to a + b + c
tax payers are worse off due to opportunity cost
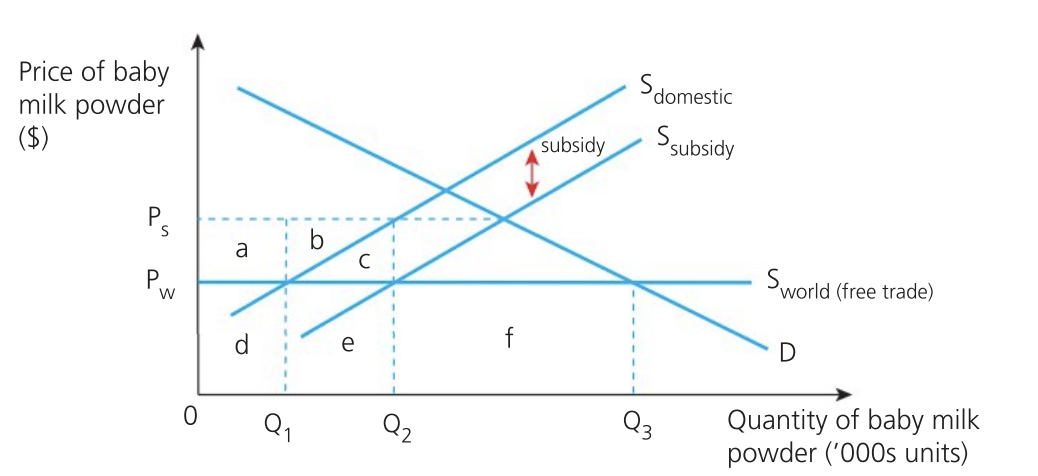
Effect of subsidy on welfare (society)
encourages inefficient output from domestic firms
welfare loss represented by C
Administrative barriers
The application of bureaucratic standards and regulations imposed on foreign firms in order to protect domestic firms and consumers.
For example, strict rules regarding food safety, environmental standards and product quality.
Effect of administrative trade barriers
increases costs for foreign firms thereby giving an advantage to domestic firms
slow the supply chain of foreign goods and services creating a shortage and the gap can be filled by domestic firms
Embargoes
A form of administrative barrier that involves the use of bans on trade with a certain country, often due to political and/or economic disputes
Exchange controls
A form of administrative barrier involving restrictions on the quantity of foreign exchange that can be bought or sold by domestic residents.
Exchange rates
The value of one currency expressed in terms of another currency
Floating exchange rate
The value of a currency is determined by the demand for and supply of the currency in the foreign exchange market
Appreciation
A sustained increase in the value of one currency in terms of another under a floating exchange rate system
Depreciation
A sustained decrease in the value of one currency in terms of another under a floating exchange rate system
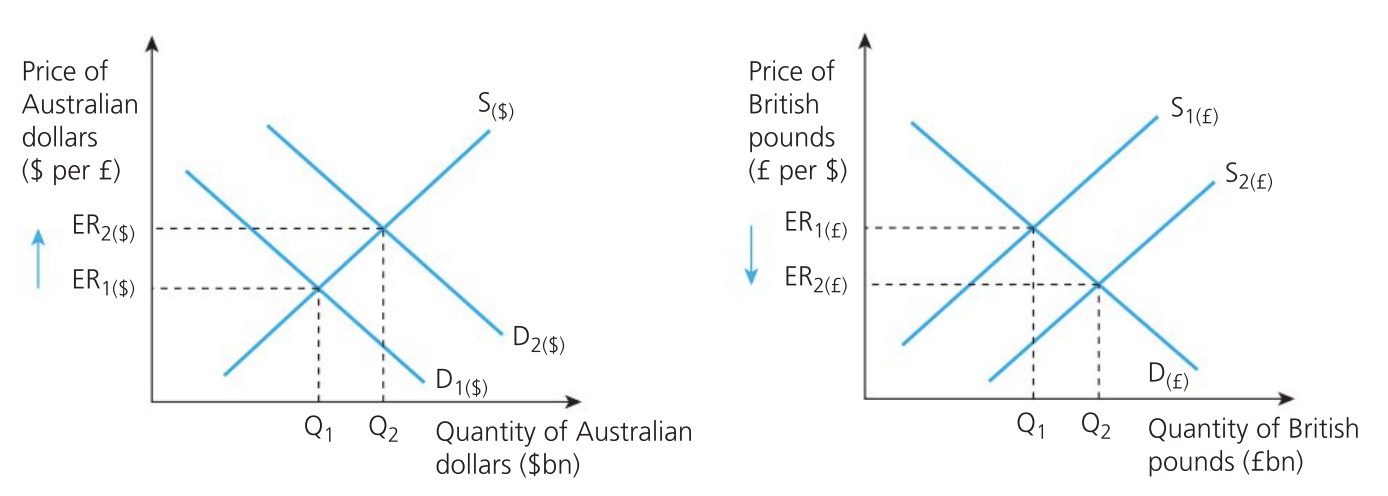
Appreciation of the Australian dollar
increased demand for AUD is caused by a higher demand in the UK for australian goods
this increases the supply of British pounds by British buyers who exchange their pounds for dollars
increase in the value of the Australian dollar against British pound from ER1 to ER2 is matched by a fall in the value of the British pound against the Australian dollar from ER1 to Er2
Creates incentive for holders of AUD to increase the quantity supplied of AUD in anticipation of a better price
leads to a new equilibrium exchange rate of ER2 and Q2 billions of AUD traded
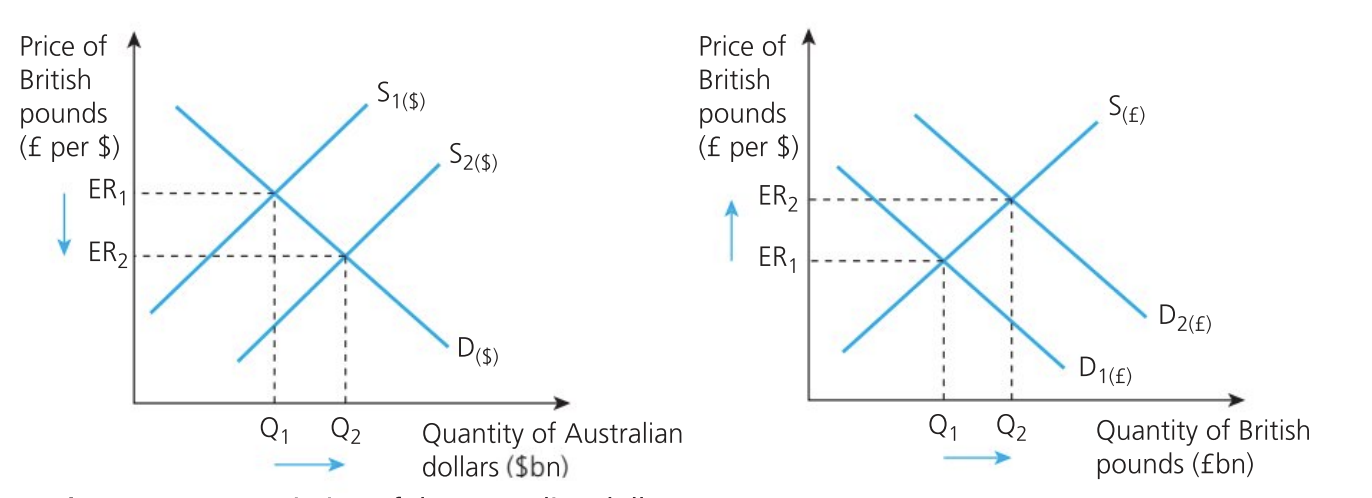
Depreciation of the Australian dollar
Australian dollars wish to purchase British pounds
They must first sell their dollars causing an increase in supply of dollars from S1 to S2
Causes a fall in the value of the dollar as the exchange rate drops from ER1 to ER2
AUD holders will accept lower bids for their dollars as they are less scarce (more supply)
signals to the amrket that price of AUD is likely to fall
increase in quantity demanded and a new equilibrium ER1 and Q2
Inward foreign direct investment
Refers to foreign multinational companies expanding their operations in the domestic economy
Outward foreign direct investment
Refers to multinational companies from the domestic economy expanding their operations in overseas markets.
Portfolio investment
The purchase of financial investments abroad, such as the purchase of stocks, shares and bonds of overseas firms and government.
Inward: spending in the domestic economy by foreign investors. Supply (sell) their own currencies and demand (buy the currency of the economy that they are investing in.
Outward: spending by an economy’s investors in overseas markets. Increases supply of domestic economy’s currency and demand for the currency of the other economy.
Reminttances
Refer to the movement of money when nationals working abroad send money back to their home country. Results in the depreciation of the currency of the economy that they are working in and appreciation of the currency of their home economy, ceteris paribus.
Speculation
Occurs when a financial asset, such as the domestic currency or a foreign currency, is purchased in the hope or anticipation that the resale value will be higher.
Relative inflation rates
Increase in the price of goods and services caused by inflation decreases the demand for exports. Leads to reduction in the demand for a currency and therefore depreciation of the currency. Speculators may choose to sell this currency and further depreciating it.
Relative interest rates
investors may wish to save in an economy that has higher interest rates than in their own country
to do this investors will need to purchase the currency of the foreign country where they will be saving their money. Increase in supply of the domestic currency and increase in demand for foreign currency.
Relative growth rates
higher levels of economic growth in a foreign economy leads to increase in AD
this causes demand-pull inflation and increases the likelihood of contractionary monetary policy
The higher interest rates will generate an increase in the demand for the currency of that economy, leading to the appreciation of it
Central bank intervention
A central bank may also restrict the supply or sale of its currency to control the money supply
These currencies are likely to face lower levels of demand as they become less desirable to speculators.
Fixed exchange rate system
Exists when the central bank buys and sells foreign currencies to ensure the value of its currency stays at a single, predetermined rate. Do this by buying (demanding) or selling (supplying) foreign currency reserves.
Foreign currency reserves
Stocks of foreign currencies held by a central bank, usually to influence the value of its currency.
Devaluation
Occurs when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially and deliberately lowered.
Can improve international competitiveness as exports become relatively cheaper and imports become more expensive.
Revaluation
Occurs when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially deliberately increased.
Governments may do this when they wish import more essential goods and services.
Managed exchange rate
A system where the government or central monetary authority intervenes periodically in the foreign exchange market to influence the exchange rate, when deemed necessary to maintain certainty and confidence in the economy
Crawling peg
A form of fixed exchange rate system in which a currency is permitted to fluctuate within predetermined bands of exchange rates.
Overvalued currency
Occurs when the value of a currency is above its equilibrium value in the long run.
Undervalued currency
Occurs when the value of a currency is below its equilibrium value in the long run.