Zoo-Lab (Sem-1) - Exercise 21: The Muscular System
1/235
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
236 Terms
muscular system
concerned with the various types of movements in the animals; groups vary in origin histology, distribution, and function
fibers/myofibers
muscle cells
skeletal; cardiac; smooth
types of vertebrate muscles
skeletal muscle
striated and voluntary; forms the bulk of the body wall
smooth muscle
involuntary; found in the walls of the digestive tracts and other visceral organs; controlled by the sympathetic nervous system
cardiac muscle
found in the heart; striated and involuntary
origin
the point of attachment of a muscle on the bone that will not move when the muscle contracts
insertion
the point of attachment of a muscle on the bone that will move when the muscle contracts
belly
middle part of the muscle; between the two points of attachment
heads
proximal and distal ends of a muscle
action
function of the muscle; accomplished by the contraction of the component muscle fibers
synergists
muscles which concur in action
antagonists
muscles which oppose in action
flexors
muscles that bend one part upon another
extensors
muscles that straighten a part
depressors
muscles that lower a part
levators
muscles that raise a part
rotator
muscles that rotate a part upon another
constrictor/sphincter
muscles that close an opening
dilator
muscles that antagonize the constrictor
adductor
muscle that draws a limb toward the ventral surface
abductor
muscle that draw a limb away from the ventral surface
fasciae
sheets or bands of connective tissue that cover groups of muscles of the body
fascia
sing. fasciae
tendon
a whole fibrous cord or band of dense regular connective tissues
aponeurosis
broad, flat, and ribbon-like loose connective tissue
body wall
made up of the skin or the integument forming the outer covering of the body; separated from the bulk of the body via the subcutaneous lymph spaces
subcutaneous lymph spaces
separated the body wall from the bulk of the body
depressor mandibuli; temporalis; masseter
3 muscles of the head (dorsal aspect)
depressor mandibuli
a broad muscle behind the tympanic ring
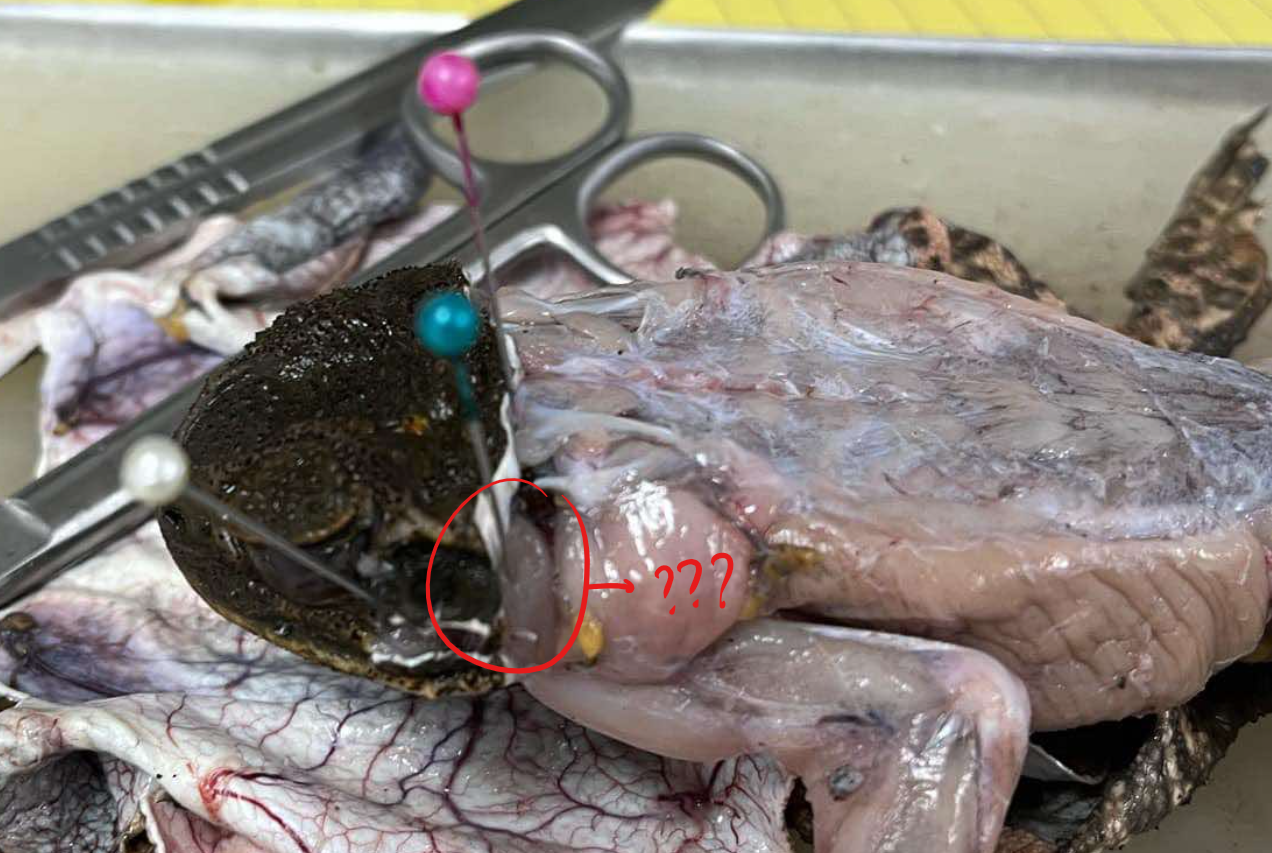
origin - depressor mandibuli
behind the tympanic ring
insertion - depressor mandibuli
caudal portion of the lower jaw
action - depressor mandibuli
closes the mouth
temporalis
a small muscle that extends from the tip of the suprascapula to the region between the tympanic ring and the eye
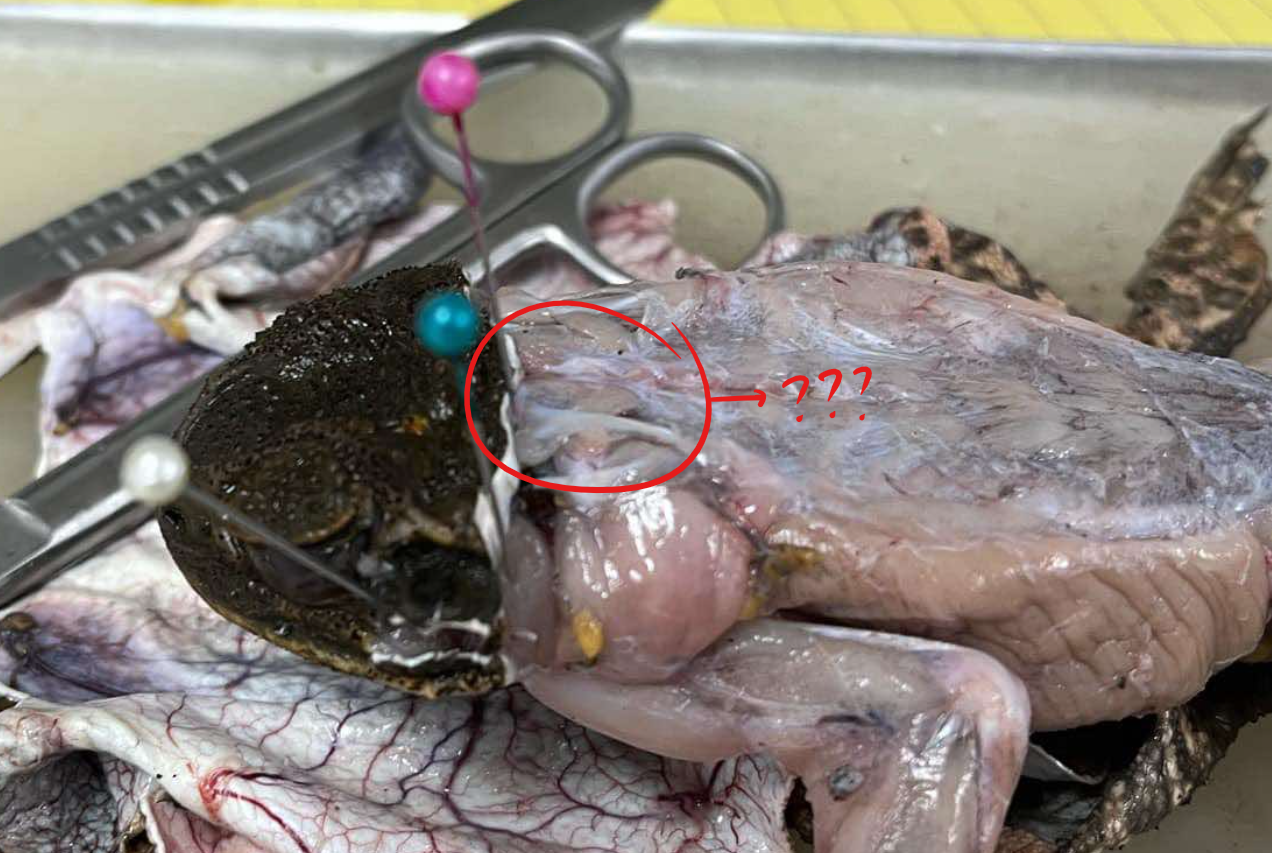
origin - temporalis
dorsal border of the suprascapula
insertion - temporalis
dorsal lower jaw
action - temporalis
opens the mouth
masseter
a small muscle located in front of the tympanic ring
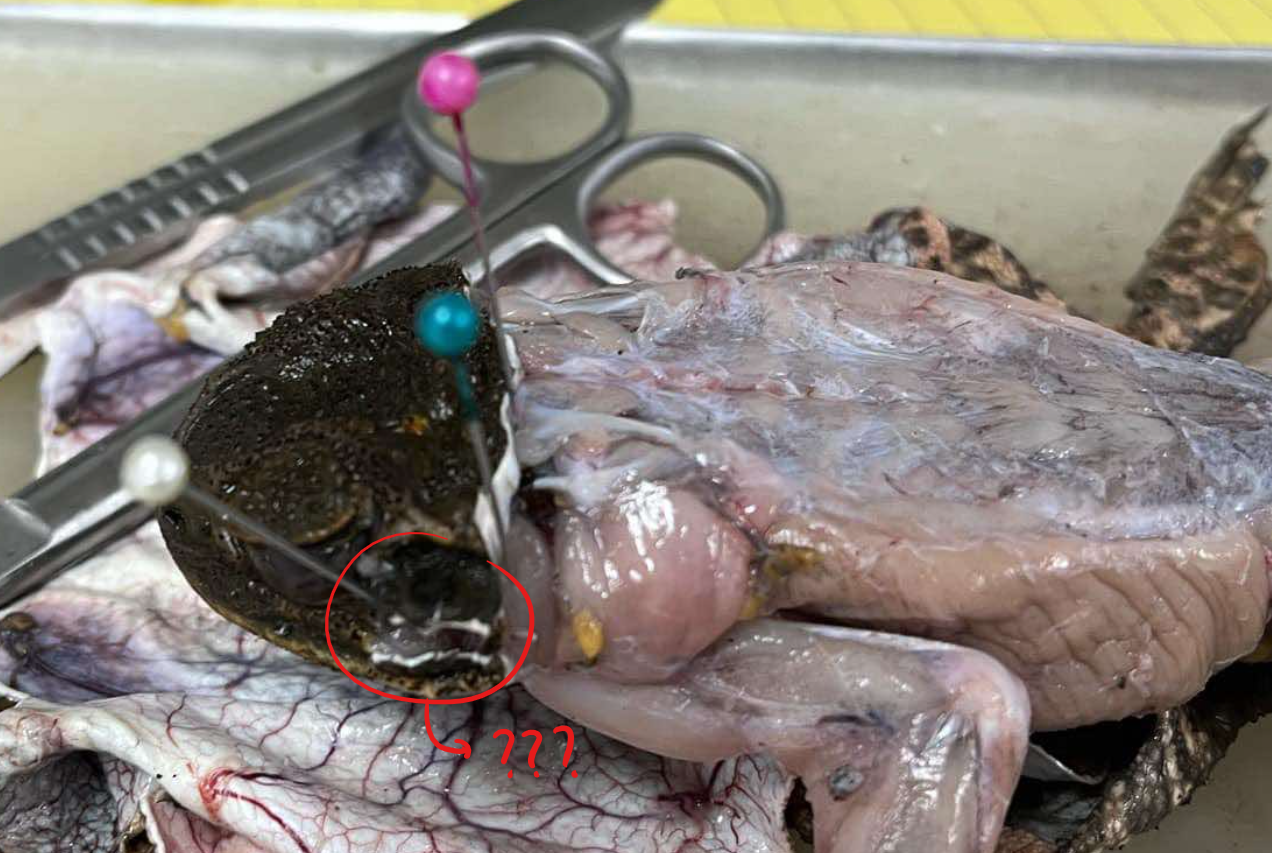
origin - masseter
tympanic ring and adjacent bones
insertion - masseter
outer surface of the lower jaw
action - masseter
raises the lower jaw and closes the mouth
submental; mylohyoid/submaxillaris; median raphe; sternohyoid
4 muscles of the head (ventral aspect)
submental
a transversely oriented muscle connecting the distal mandibular tips, contributing to the formation of the floor of the buccal cavity
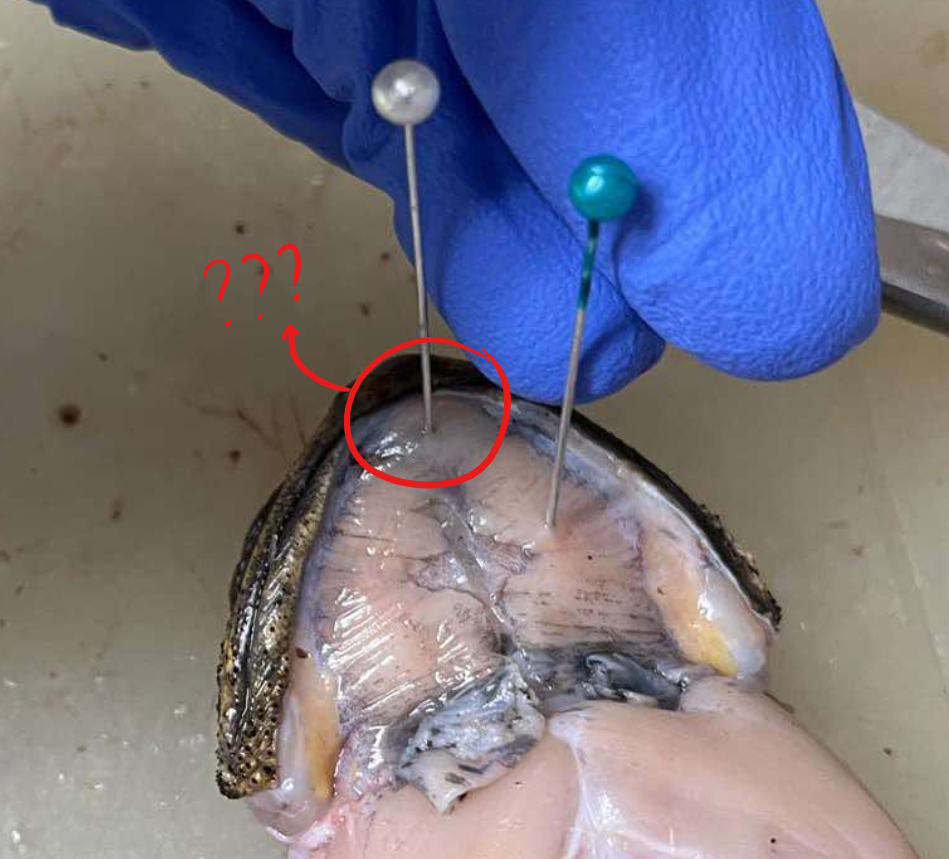
mylohyoid/submaxillaris
a very thin sheet of muscle at the ventral surface of the head region, the floor of the mouth
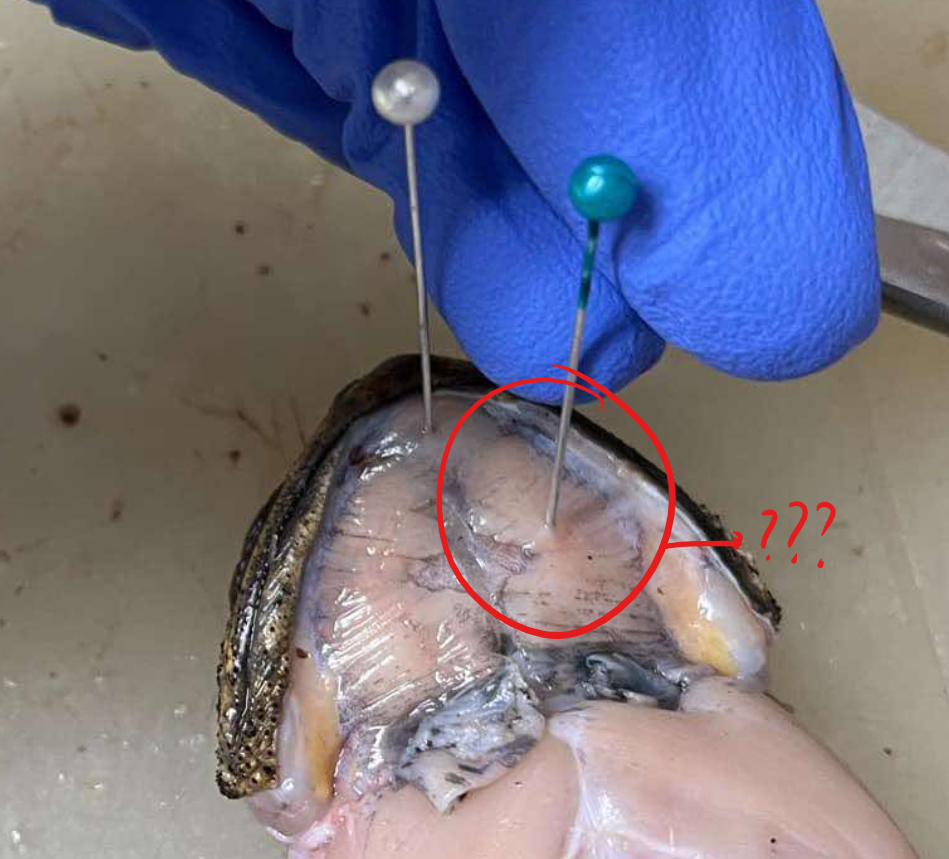
origin - mylohyoid/submaxillaris
ventral lower jaw
insertion - mylohyoid/submaxillaris
median raphe
action - mylohyoid/submaxillaris
pulls the floor of the mouth downward in breathing
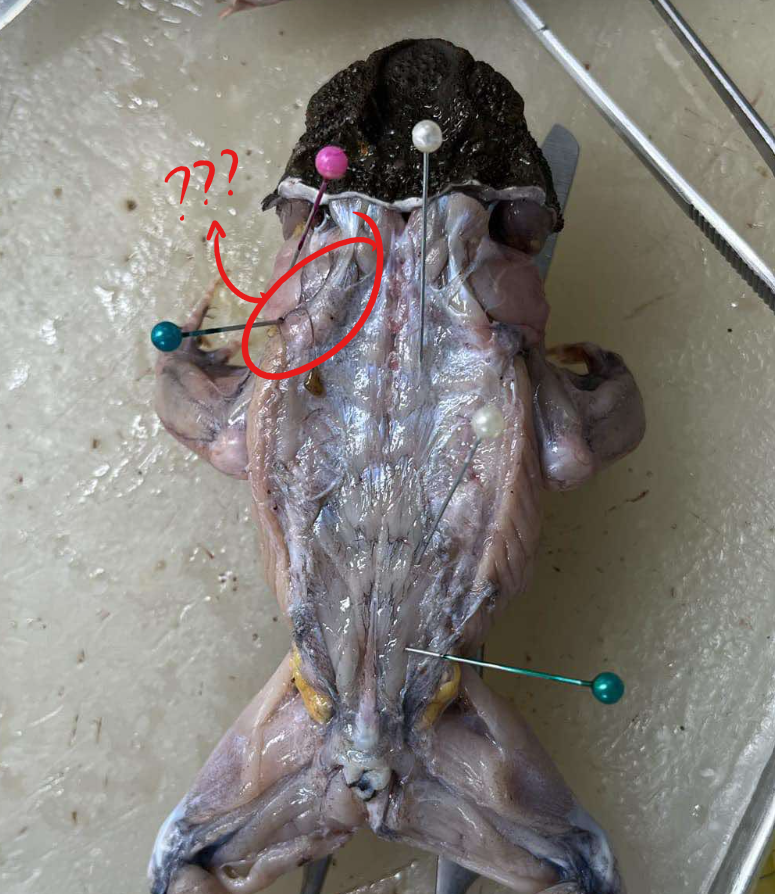
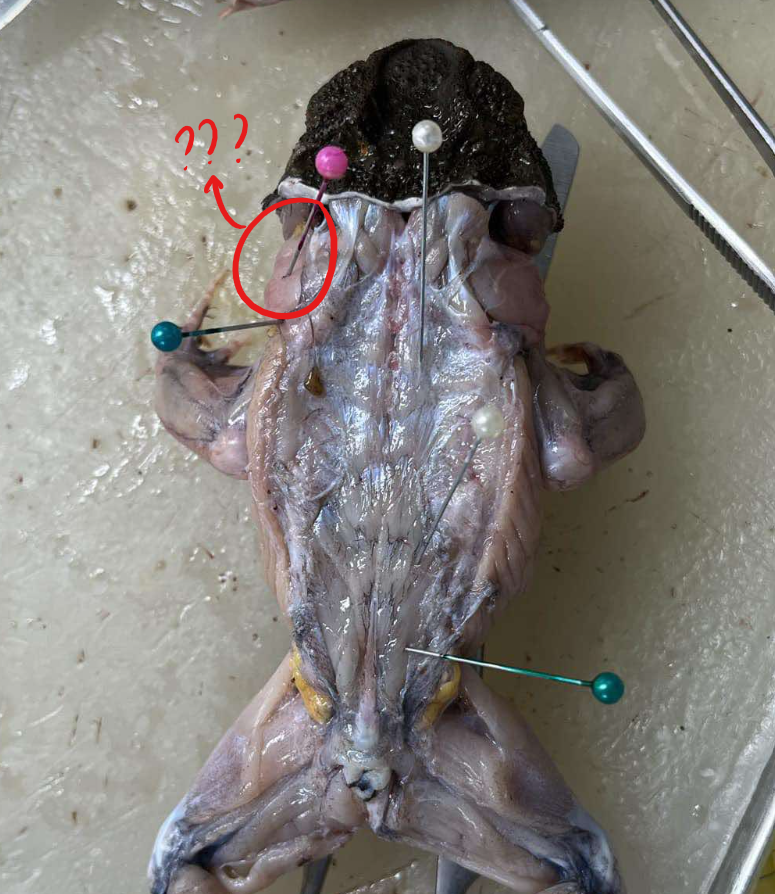
sternohyoid
the continuation of the rectus abdominis forward to the head under episternum
origin - sternohyoid
coracoid and clavicle
insertion - sternohyoid
hyoid bone
action - sternohyoid
pulls the hyoid backward, thus lowering the floor of the mouth in respiration
latissimus dorsi; dorsalis scapulae (infraspinatus); longissimus dorsi; coccygeo-sacralis; coccygeo-iliacus
5 muscles of the back and girdles
latissimus dorsi
small muscle overlapping the caudal portion of the suprascapula
origin - latissimus dorsi
fascia of the back just behind the shoulder blade
insertion - latissimus dorsi
deltoid ridge of the humerus
action - latissimus dorsi
abducts the arm and pulls the arm upward and backward
dorsalis scapulae (infraspinatus)
muscles covering the outer surface of the suprascapula
origin - dorsalis scapulae (infraspinatus)
scapula
insertion - dorsalis scapulae (infraspinatus)
tendon joining the latissimus dorsi
action - dorsalis scapulae (infraspinatus)
raises the arms towards the body
longissimus dorsi
long muscle running close and along the vertebral column
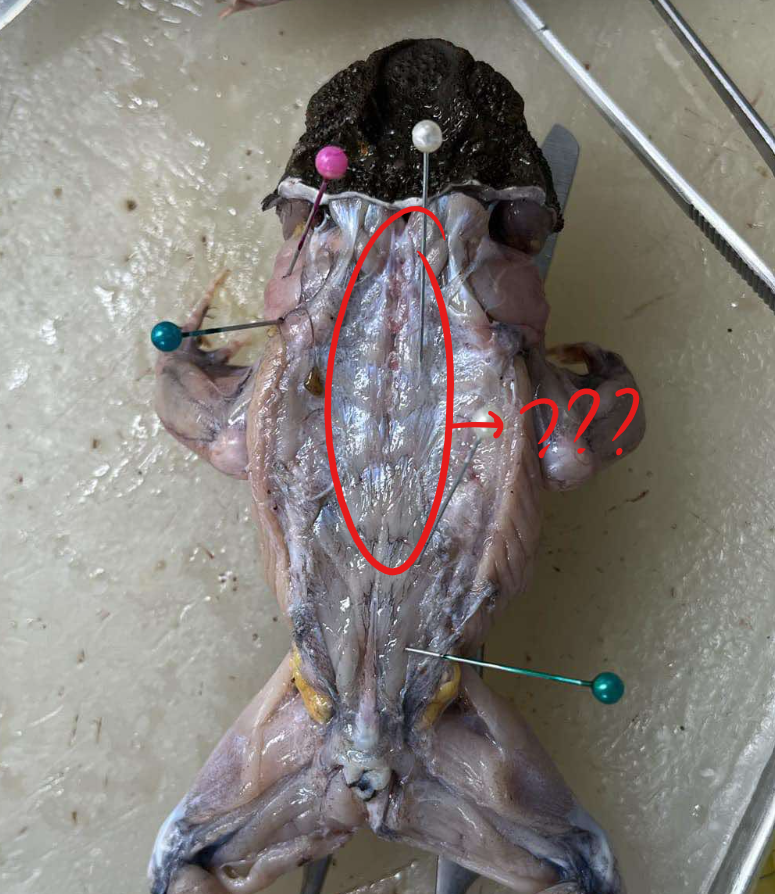
origin - longissimus dorsi
anterior third of the urostyle
insertion - longissimus dorsi
vertebrae and skull
action - longissimus dorsi
raises the head and straightens the back
coccygeo-sacralis
a narrow muscle located posteriorly to the longissimus dorsi and extends posterior in oblique postion
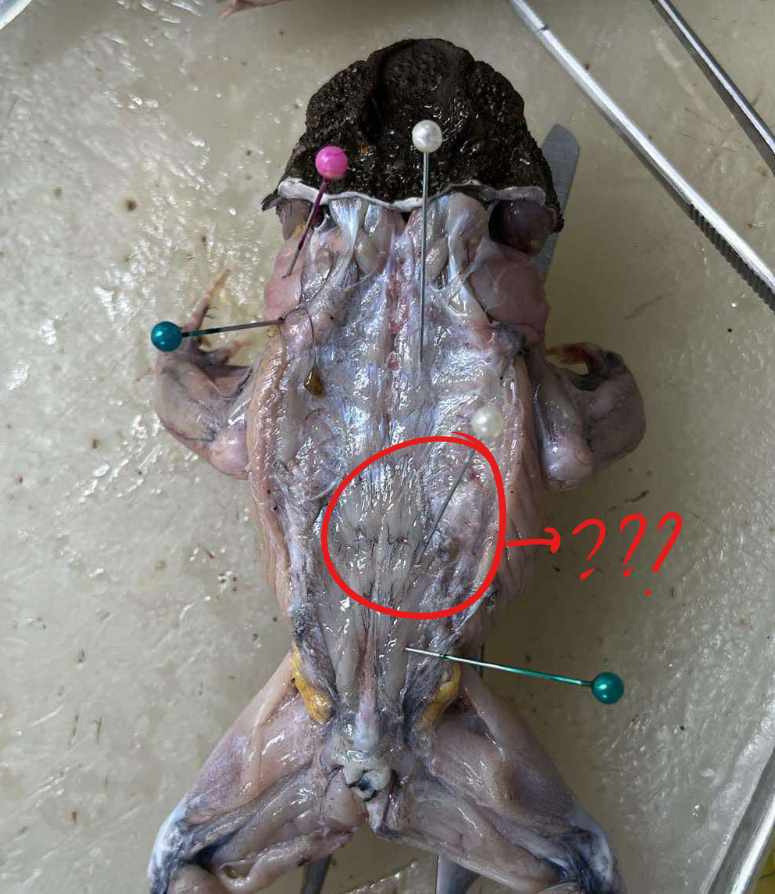
origin - coccygeo-sacralis
sacralis urostyle
insertion - coccygeo-sacralis
transverse process of the sacral vertebra
action - coccygeo-sacralis
humps the back when the two muscles of the sides of the body act together, when they act singly, turns the back to one side
coccygeo-iliacus
running diagonally in the space between the ilia and the urostyle just caudal of the preceding muscle
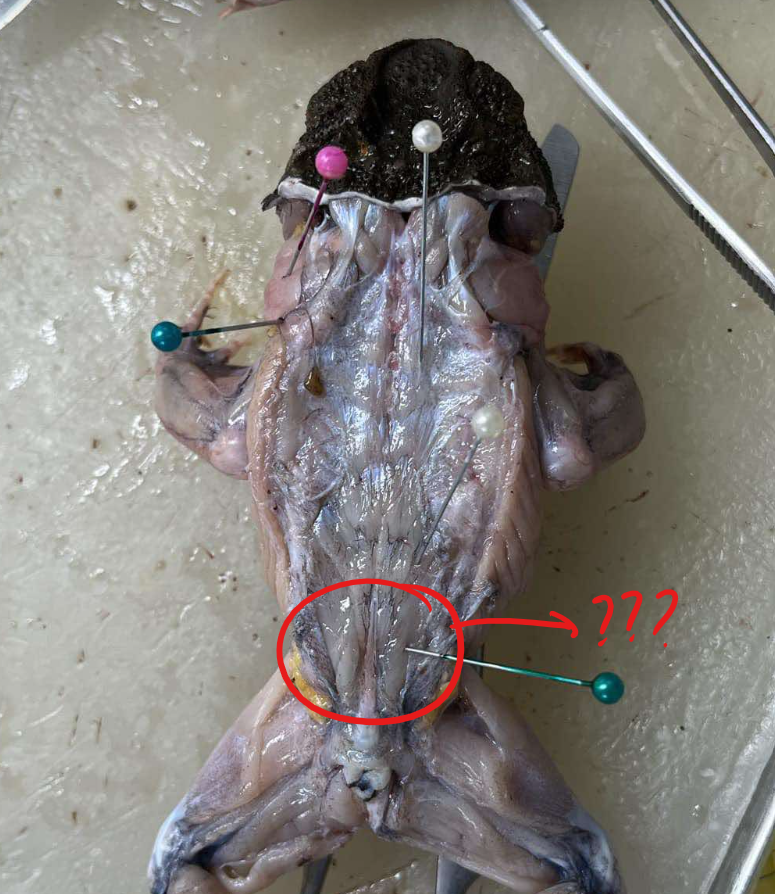
origin - coccygeo-iliacus
iliacus urostyle
insertion - coccygeo-iliacus
anterior part of the ilium
action - coccygeo-iliacus
holds urostyle in place
rectus abdominis; external oblique; internal oblique/transverse abdominis
3 muscles of the abdomen
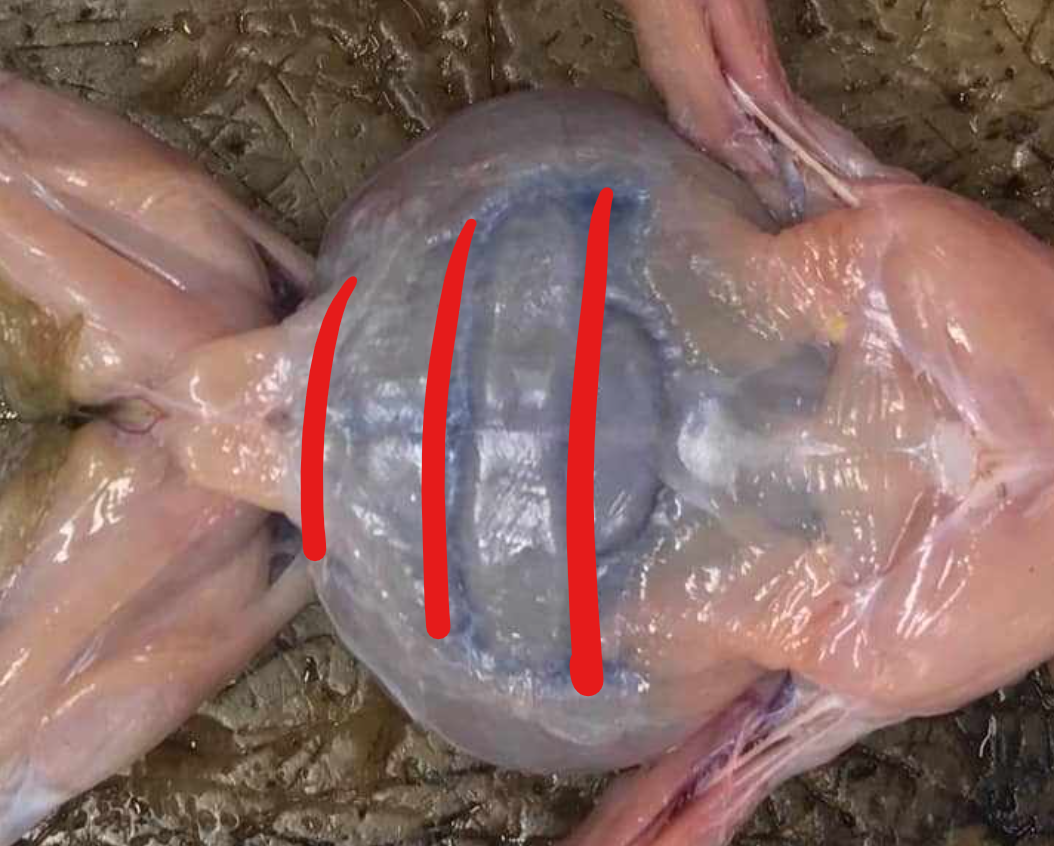
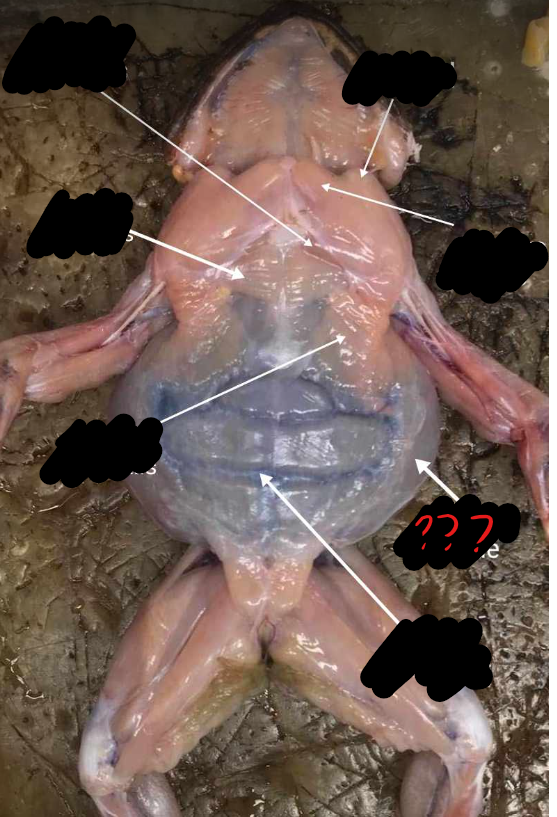
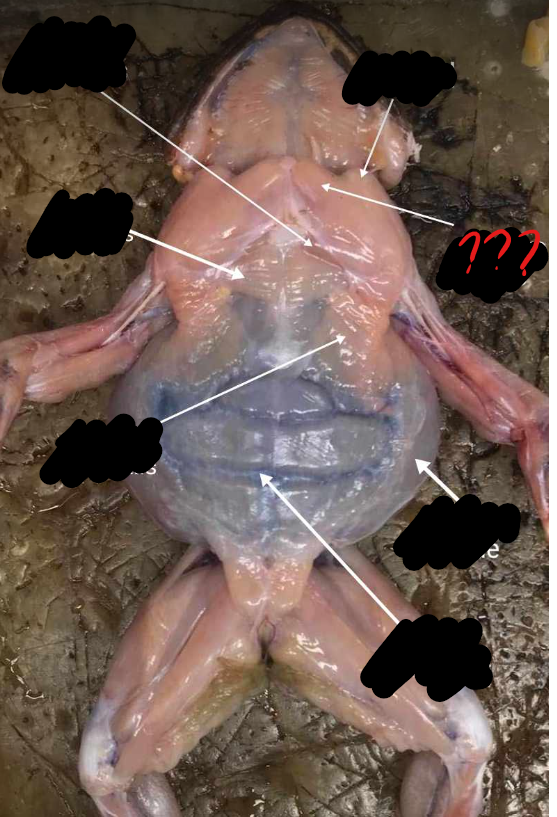
rectus abdominis
broad, thin muscle covering the ventral side of the abdomen; two parts separated by the linea alba, marked by crosswise faint lines called the ventral inscriptiones tendinae
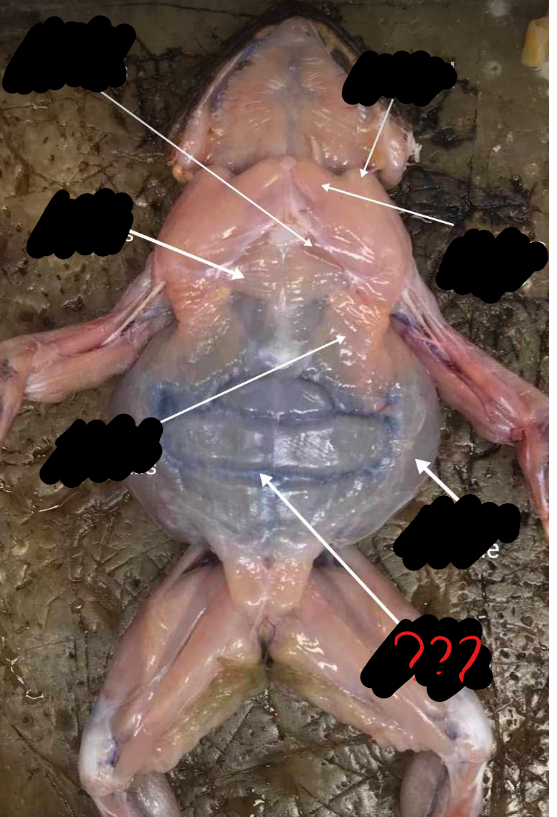
linea alba
mid-ventral line; separates the two recti abdominis; appears red because of the presence of the blood vessel, the ventral abdominal vein
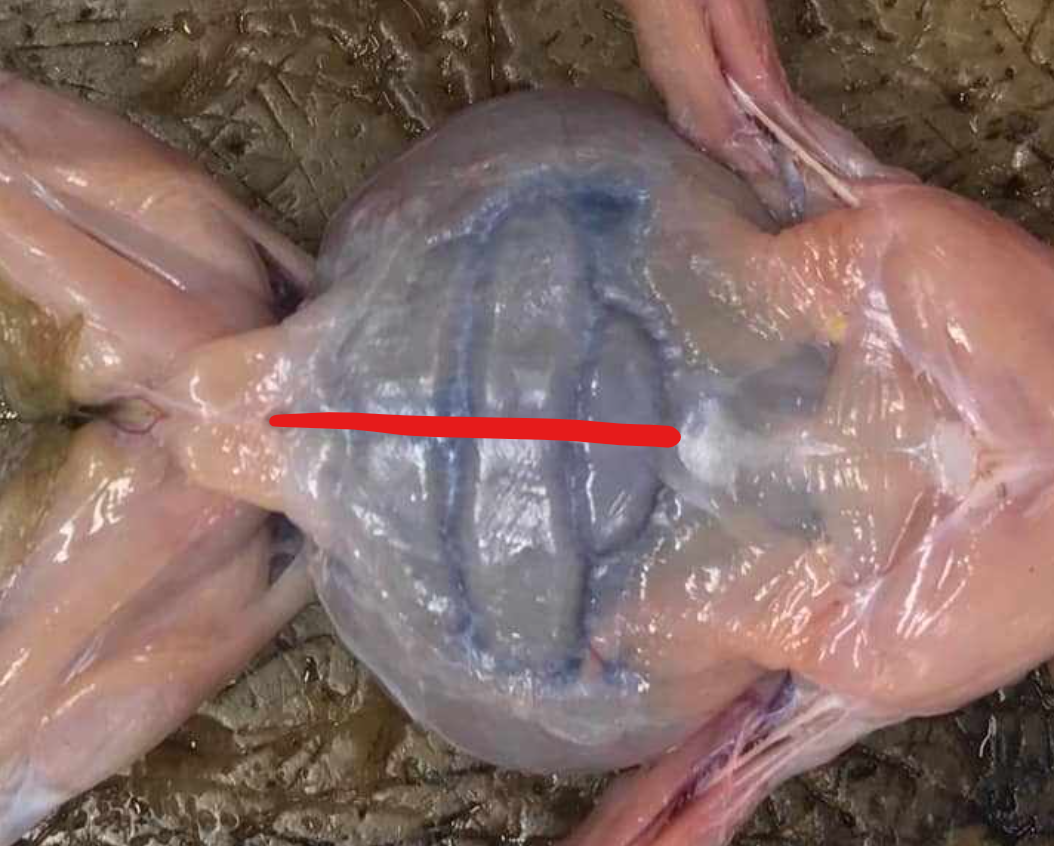
ventral abdominal vein
blood vessel which causes the linea alba to appear red
ventral inscriptiones tendineae
crosswise faint lines which mark the recti abdominis muscles
origin - rectus abdominis
pubic border
insertion - rectus abdominis
sternum and coracoid
action - rectus abdominis
support the abdominal viscera
external oblique
a thin sheet of muscle, which forms the outer layer of the body wall at the side of the abdomen; muscle fibers are directed obliquely caudal and ventral
origin - external oblique
dorsal fascia
insertion - external oblique
linea alba, dorsal to rectus and abdominis
action - external oblique
supports and compresses the abdomen
internal oblique/transverse abdominis
another sheet of oblique muscles internal to the preceding; muscle fibers here are directed obliquely in the opposite direction to the fibers for the external oblique; an incision in the external oblique is need to view this muscle
origin - internal oblique/transverse abdominis
transverse processes of 4th to 9th vertebrae, and ilium
insertion - internal oblique/transverse abdominis
coracoids, xiphisternum, and linea alba
action - internal oblique/transverse abdominis
supports and compresses the abdomen
deltoid; sternoradialis; anterior pectoralis; middle pectoralis; posterior pectoralis
5 muscles of the shoulder and chest
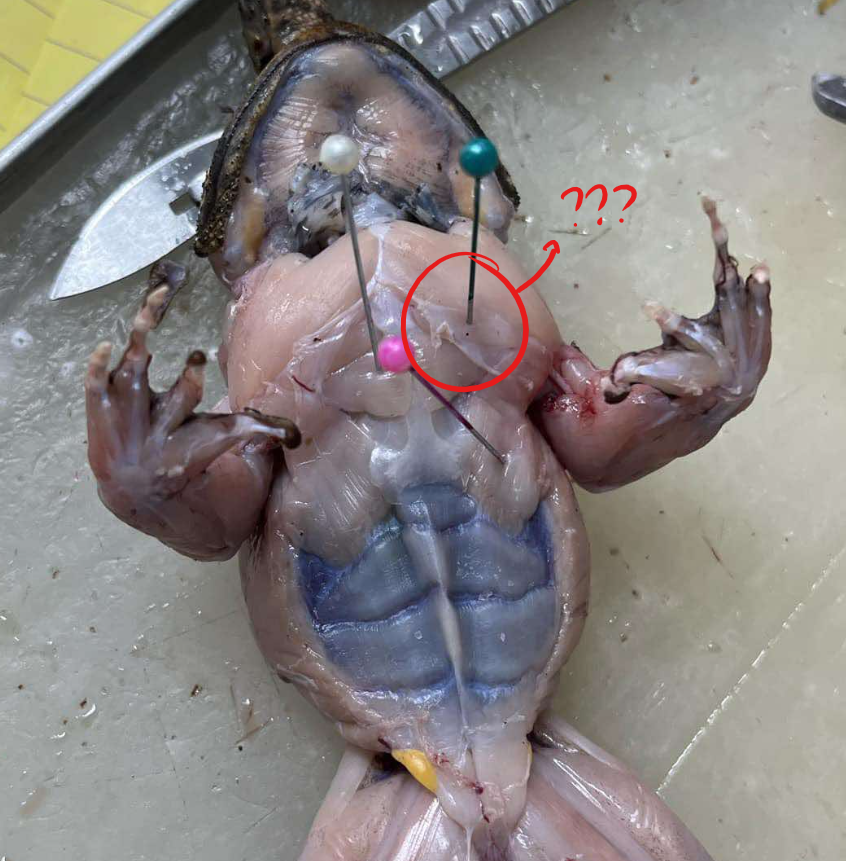
deltoid
a triangularly-shaped muscle that lies at the anterior border of the shoulder
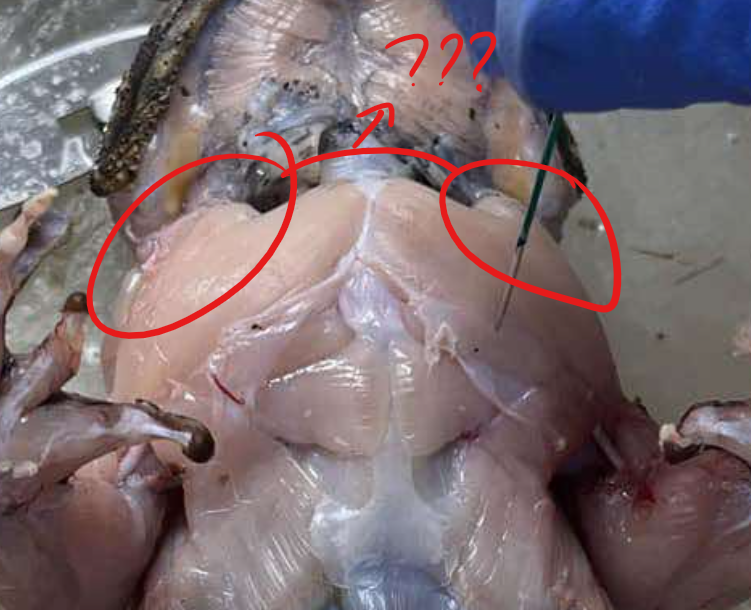
origin - deltoid
clavicle and scapula
insertion - deltoid
deltoid crest of the humerus
action - deltoid
raises and rotates the humerus
sternoradialis
next to the preceding (deltoid) and arises in the midventral line passing outwards, piercing the distal portion of the deltoid
origin - sternoradialis
episternum
insertion - sternoradialis
radius
action - sternoradialis
raises the humerus
anterior pectoralis
anterior muscle of the chest just next to the sternoradialis

origin - anterior pectoralis
anterior sternum and coracoid
insertion - anterior pectoralis
anterior deltoid ridge