Metabolic Pathways and Regulation of Glucose, Lipids, and Amino Acids
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
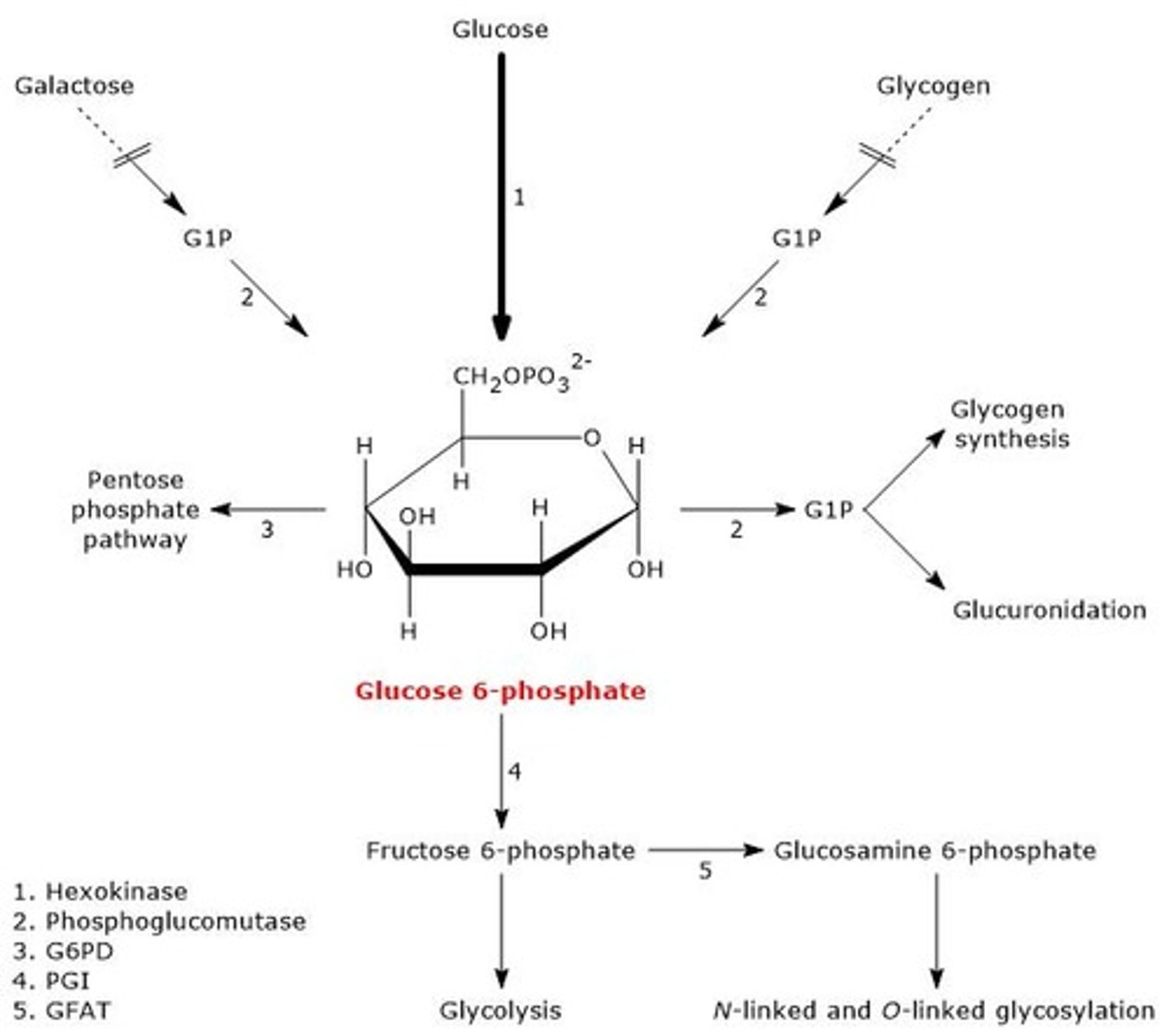
What are the primary metabolic fates of Glucose 6-phosphate?
Glycolysis for energy, Pentose Phosphate Pathway for NADPH, glycogen/starch synthesis, hexosamine pathway for protein glycosylation, and gluconeogenesis.
What is pyruvate converted to for aerobic respiration?
Acetyl-CoA.
What happens to pyruvate during anaerobic fermentation?
It is converted to lactate.
What is the role of oxaloacetate in metabolism?
It is involved in gluconeogenesis, amino acid metabolism, and the citric acid cycle.
What does oxaloacetate convert to for glucose production?
Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP).
What is the main function of Acetyl CoA?
Energy production via the Krebs Cycle and fatty acid synthesis.
What is metabolic syndrome?
A cluster of conditions including insulin resistance, high blood pressure, abnormal lipids, and abdominal obesity.
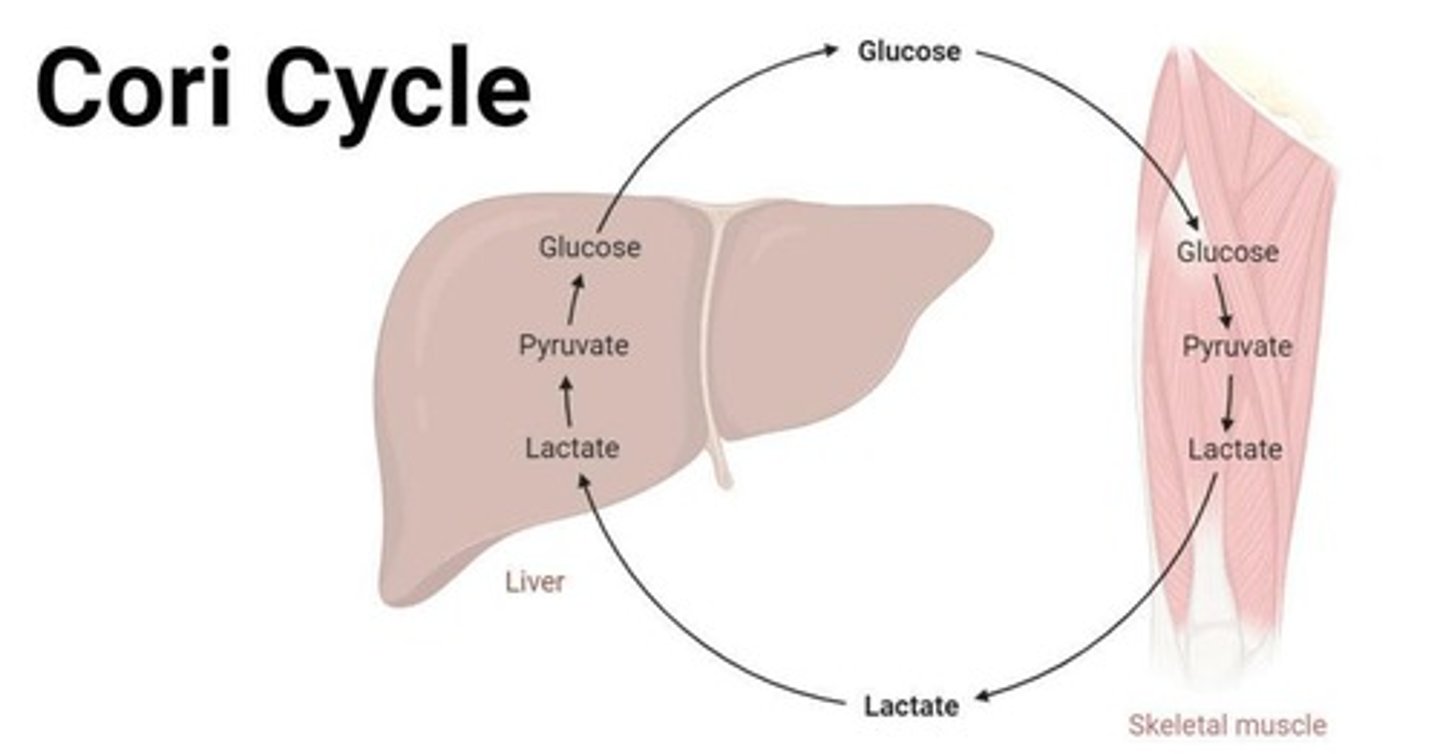
What is the Cori Cycle?
A metabolic pathway where lactate is converted back to glucose in the liver via gluconeogenesis.
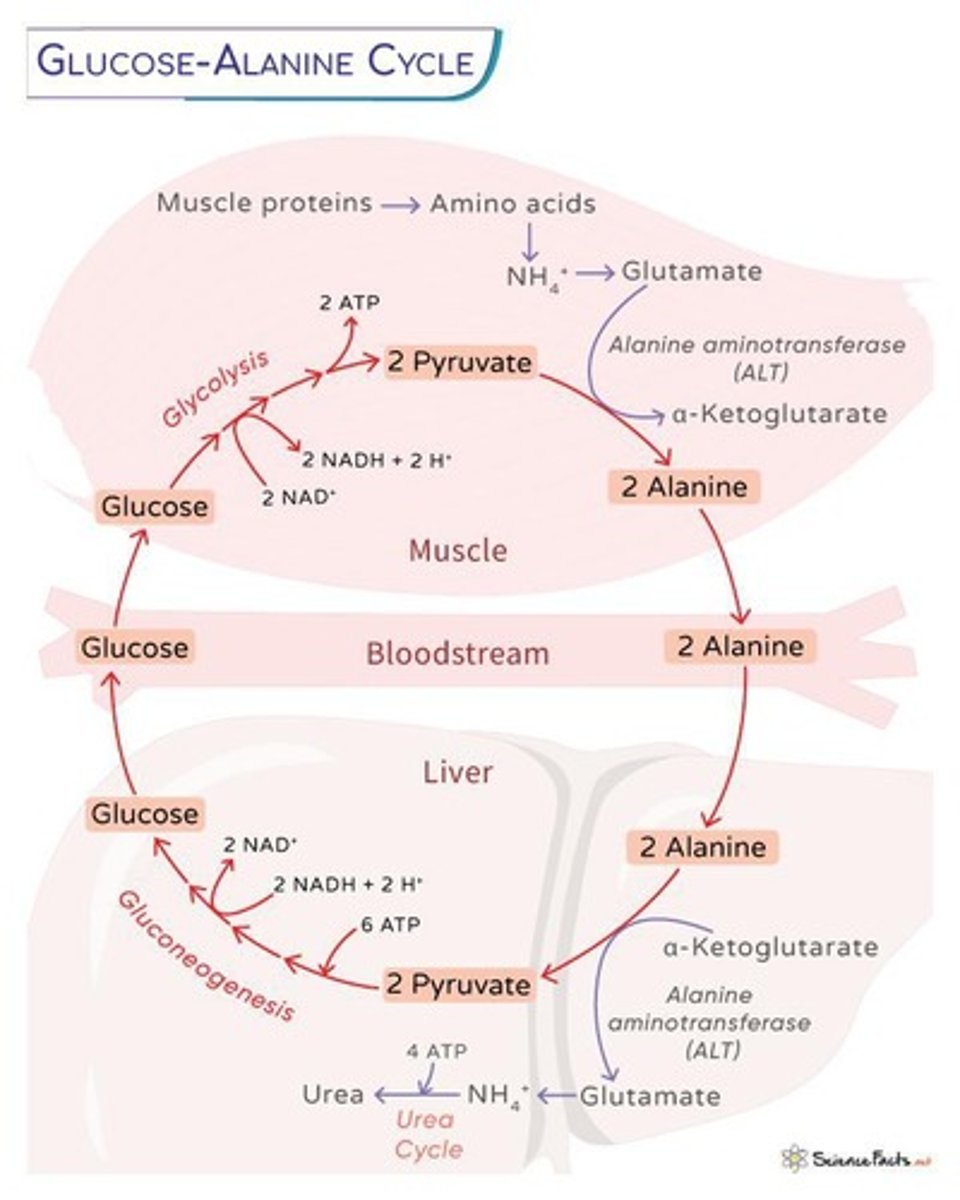
What is the Glucose-Alanine Cycle?
A pathway that moves nitrogen as ammonia and carbon from muscles to the liver for energy and safe disposal.
How does pH affect amino acid structure?
Acidic pH protonates groups to be positive, neutral pH favors zwitterion form, and alkaline pH deprotonates groups to be negative.
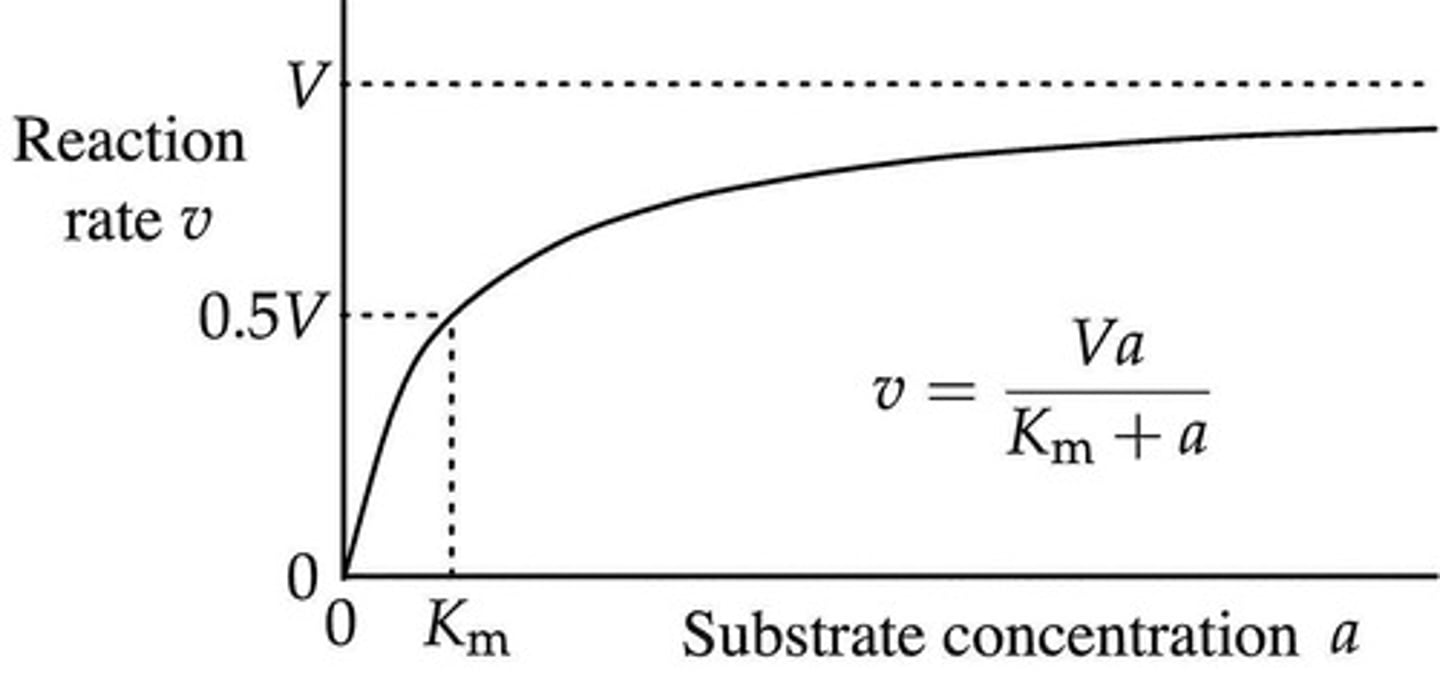
What does the Michaelis-Menten equation describe?
The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions as a function of substrate concentration.
What is the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation used for?
To calculate pH based on the ratio of acid and base concentrations.
What happens to blood plasma concentrations of metabolites during starvation?
Glucose drops, fatty acids and glycerol rise, leading to increased ketone bodies for brain fuel.
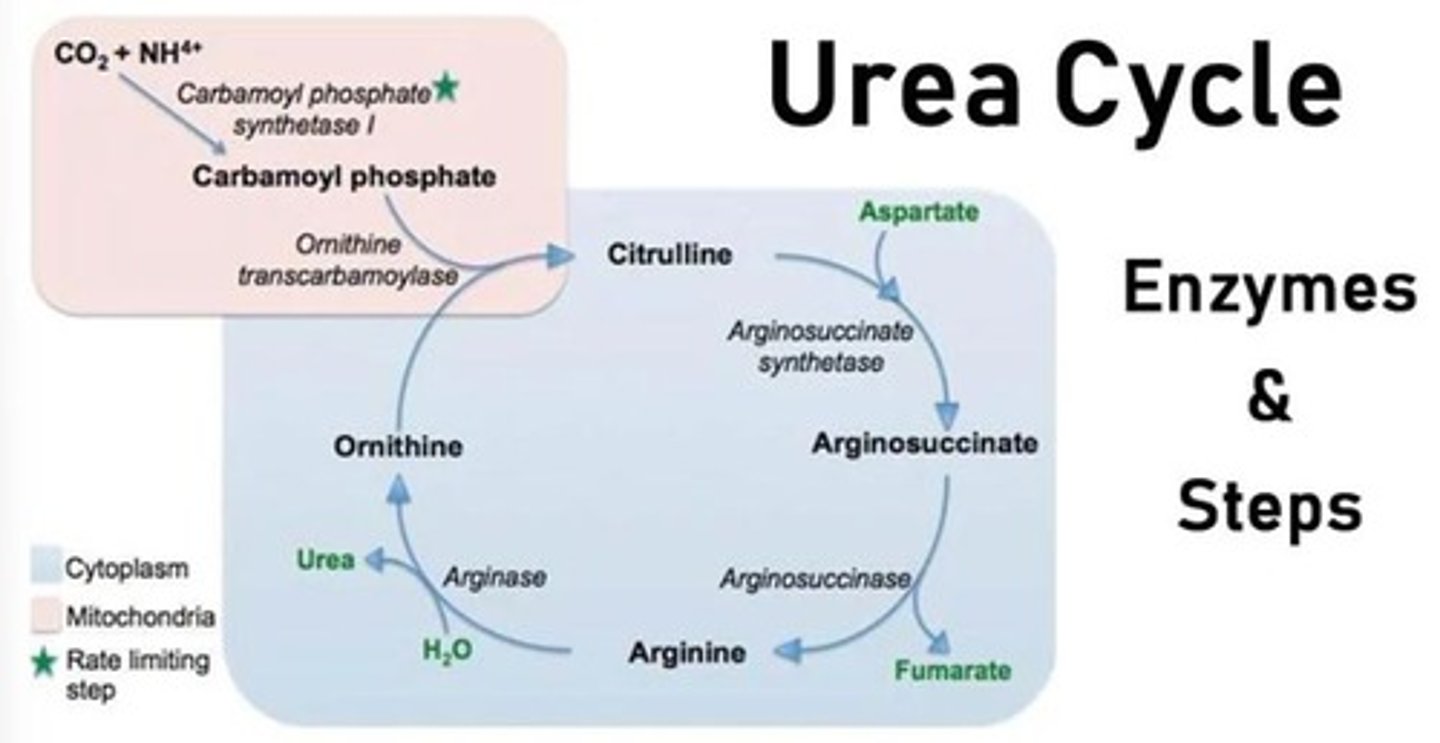
What is the Urea Cycle's main function?
To convert toxic ammonia into non-toxic urea for excretion.
What are lipoproteins?
Particles made of fats and proteins that transport fats to cells for energy or storage.
What is transamination in amino acid metabolism?
The transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid.
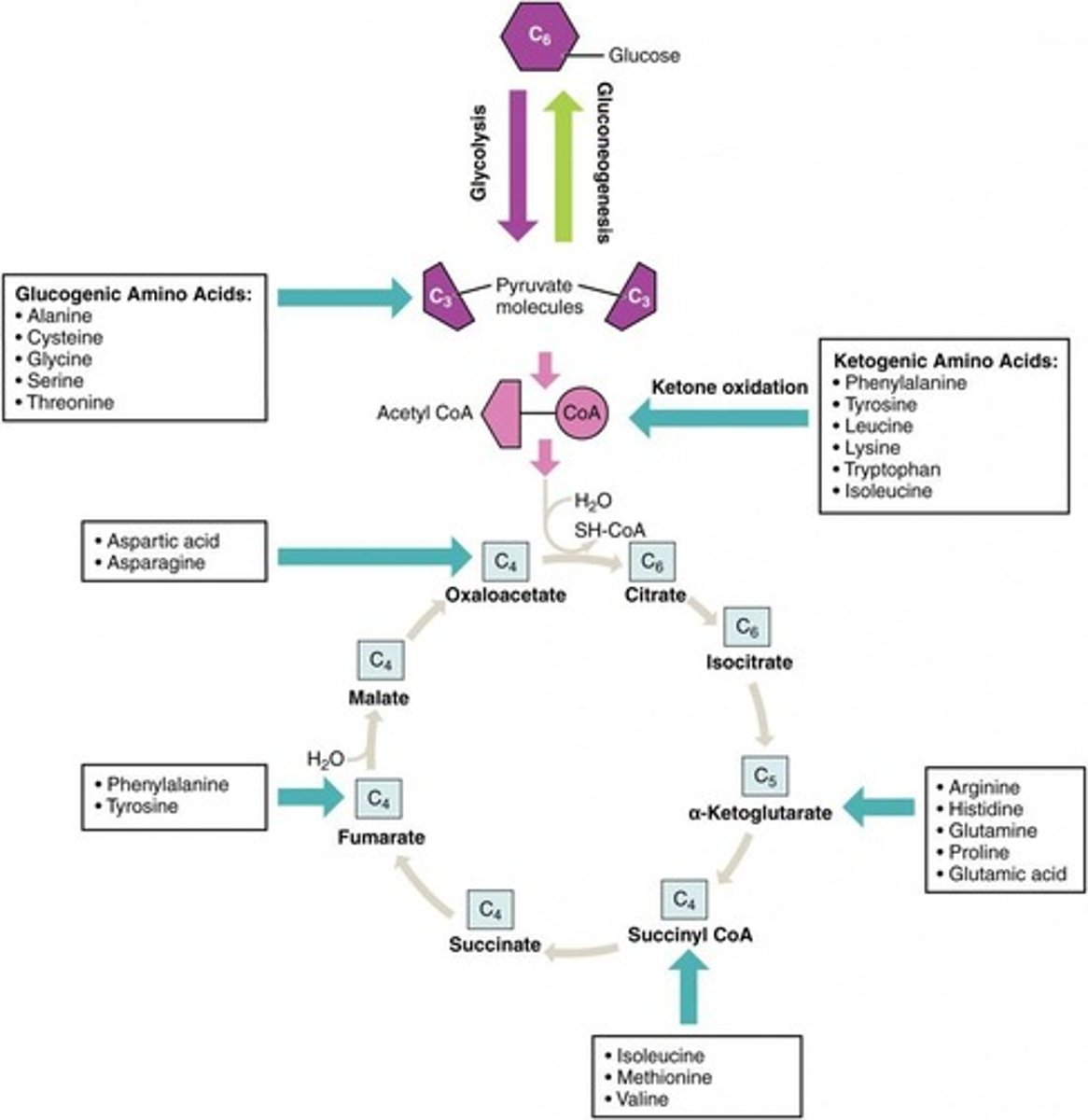
What are glucogenic amino acids?
Amino acids whose carbon skeletons can be converted to glucose precursors.
What are ketogenic amino acids?
Amino acids that can be converted to acetyl-CoA or acetoacetyl-CoA.
What is the role of beta-oxidation?
To break down fatty acids into acetyl-CoA, which fuels the citric acid cycle.
What does the term 'backflux' refer to in the citric acid cycle?
The regeneration of intermediates like fumarate or malate within the cycle.
What is the significance of Complex II in the electron transport chain?
It is inhibited by oxaloacetate, modulating mitochondrial respiration.
What are the symptoms of Type 1 Diabetes?
Frequent urination, intense thirst/hunger, fatigue, and blurry vision.
What is the primary role of NADPH produced in the Pentose Phosphate Pathway?
It is used for lipid synthesis and as an antioxidant.
What is the function of citrate in the citric acid cycle?
It is formed by the reaction of acetyl-CoA and oxaloacetate.
What is the effect of dysfunctional fat in metabolic syndrome?
It disrupts normal metabolism, hormone balance, and inflammation.
What is the importance of the amino acid glutamate?
It is involved in transamination and can be converted to other amino acids.
What is the role of glucagon in glycogen breakdown?
It signals the activation of glycogen breakdown to maintain blood glucose levels.
What does the term 'reciprocal regulation' refer to in metabolism?
The process that prevents wasteful cycling between opposing metabolic pathways.