Sampling and Data Collection
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
probability sampling
the probability of being chosen for each individual in the population is known
non-probability sampling
the probability of being chosen for each individual in the population is unknown
simple random sampling
every member in the population has an equal chance of being chosen for the sample
stratified random sampling
the population is divided into subgroups (strata) and simple random sampling is used to choose individuals from each subgroup (stratum)
cluster sampling
identify and sample clusters of individuals in a population
probability sampling advantages and disadvantages
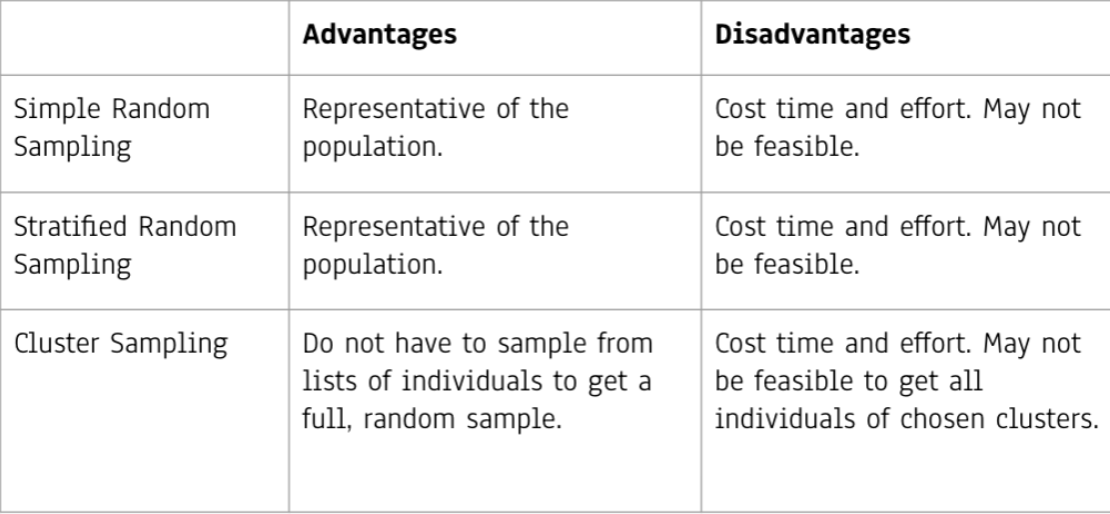
non-probability sampling
the probability of being chosen for each individual in the population is unknown
Very common in psychological research
May not be representative of the population at interest
Some are more representative than others
In some studies, may not be a big concern
convenient/haphazard sampling
recruiting from wherever feasible
quota sampling
choose a sample that reflects the composition of subgroups in a population. Use haphazard sampling to achieve this sample
Data collection
instructions
clear
allow participants to ask questions
whether to inform participants about the hypotheses of the study?
placebo effect
demanding characteristics
whether to inform experimenters about the hypotheses of the study?
experimenter bias
single-blind experiment
the participants are unaware of which condition (experimental or control) they’re in
double-blind experiment
the participants and experimenters are unaware of which condition (experimental or control) each participant is in
measure (and manipulaion) of IVs and DVs
Reliability and validity
Multiple DVs
Sensitivity of measures
Ceiling effect
Floor effect
Strength of manipulation (ex: length, dosage)
Manipulation check
debriefing
ethical for participants to know the aims and hypotheses about the study
Learn about participants’ thoughts and feelings, which can be helpful for interpreting results
pilot studies
a trial run with a small number of participants
Do participants understand your instruction?
How long does it take?
Is the age group appropriate?
Do you have floor/ceiling effects?