Campbell Biology Chapter 28- Protists
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Protists
Mostly unicellular eukaryotes.
___ constitute a paraphyletic group, and ___-a is no longer valid as a kingdom
Photoautotrophs
Contain chloroplasts.
Heterotrophs
Absorb organic molecules or ingest larger food particles.
Mixotrophs
Combine photosynthesis and heterotrophic nutrition.
Endosymbiosis
Mitochondria evolved by endosymbiosis of an aerobic prokaryote.
Plastids evolved by endosymbiosis of a photosynthetic cyanobacterium.
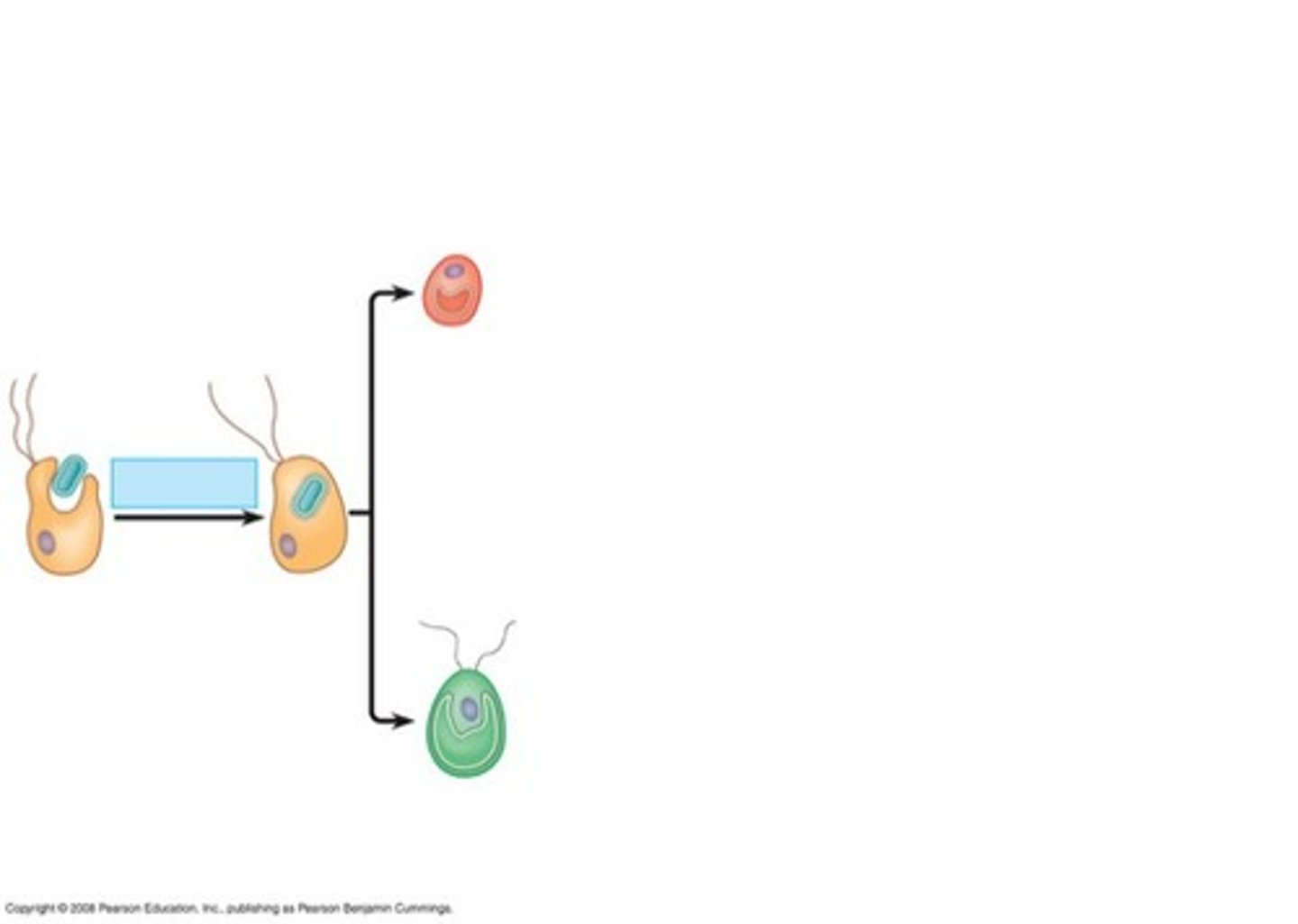
Secondary Endosymbiosis
Occurs when a living cell engulfs another eukaryote cell that has already undergone primary endosymbiosis
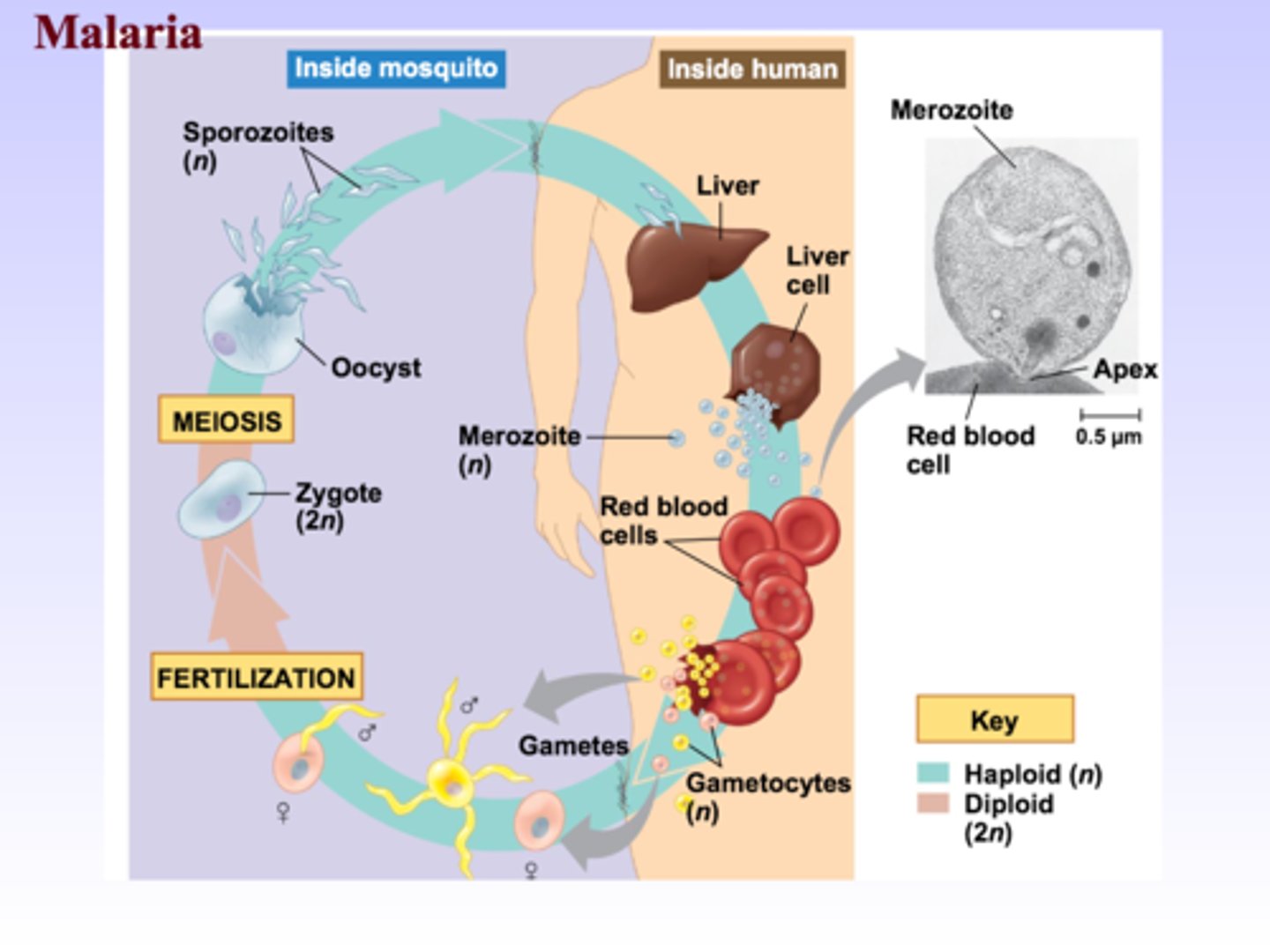
Apicomplexans
Parasites of animals; some cause serious human diseases.
The apex contains a complex of organelles specialized for penetrating a host
ie. Plasmodium, malaria
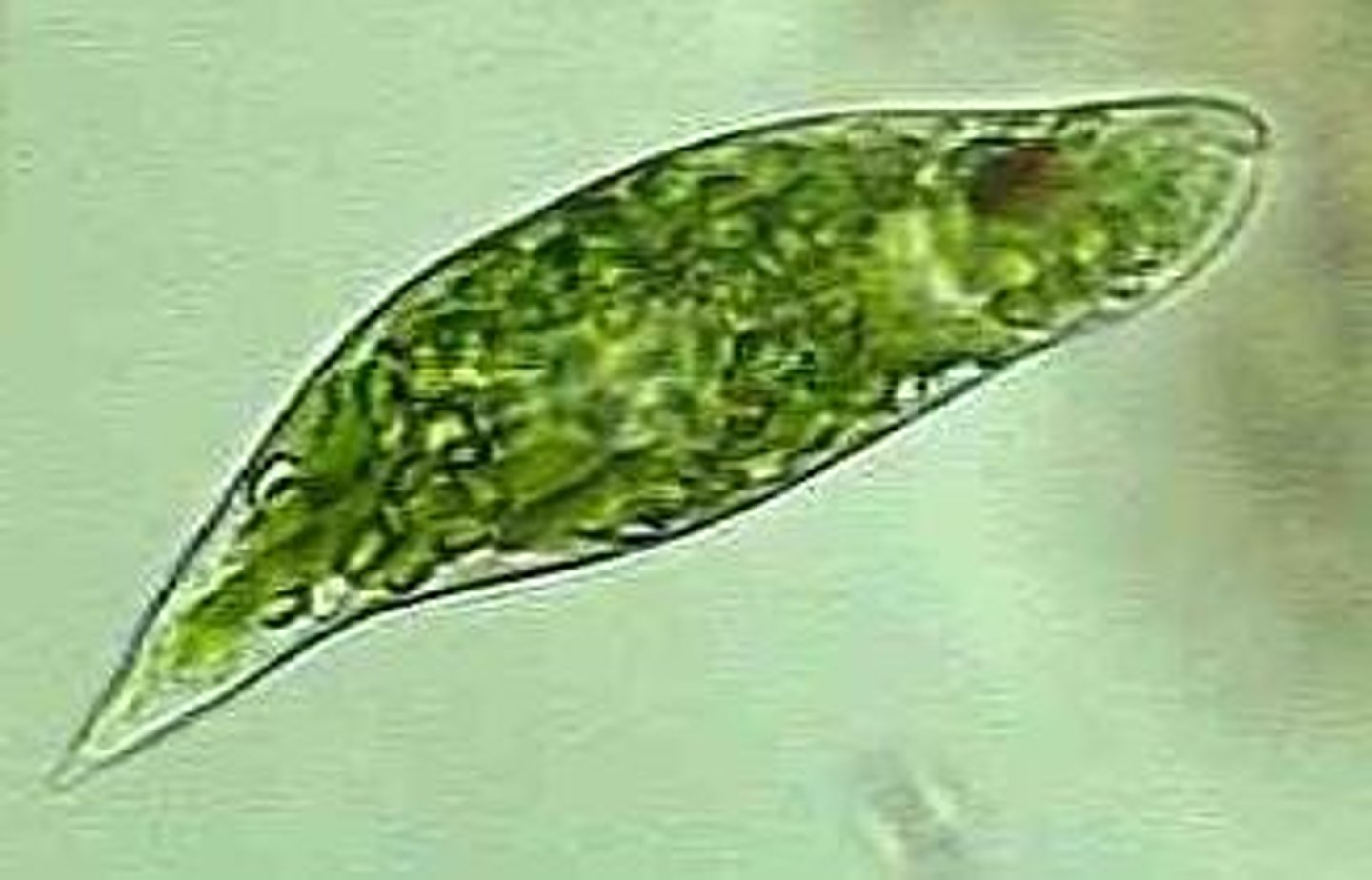
Euglena
Use both photosynthesis and absorb or consume other protists or prokaryotes.
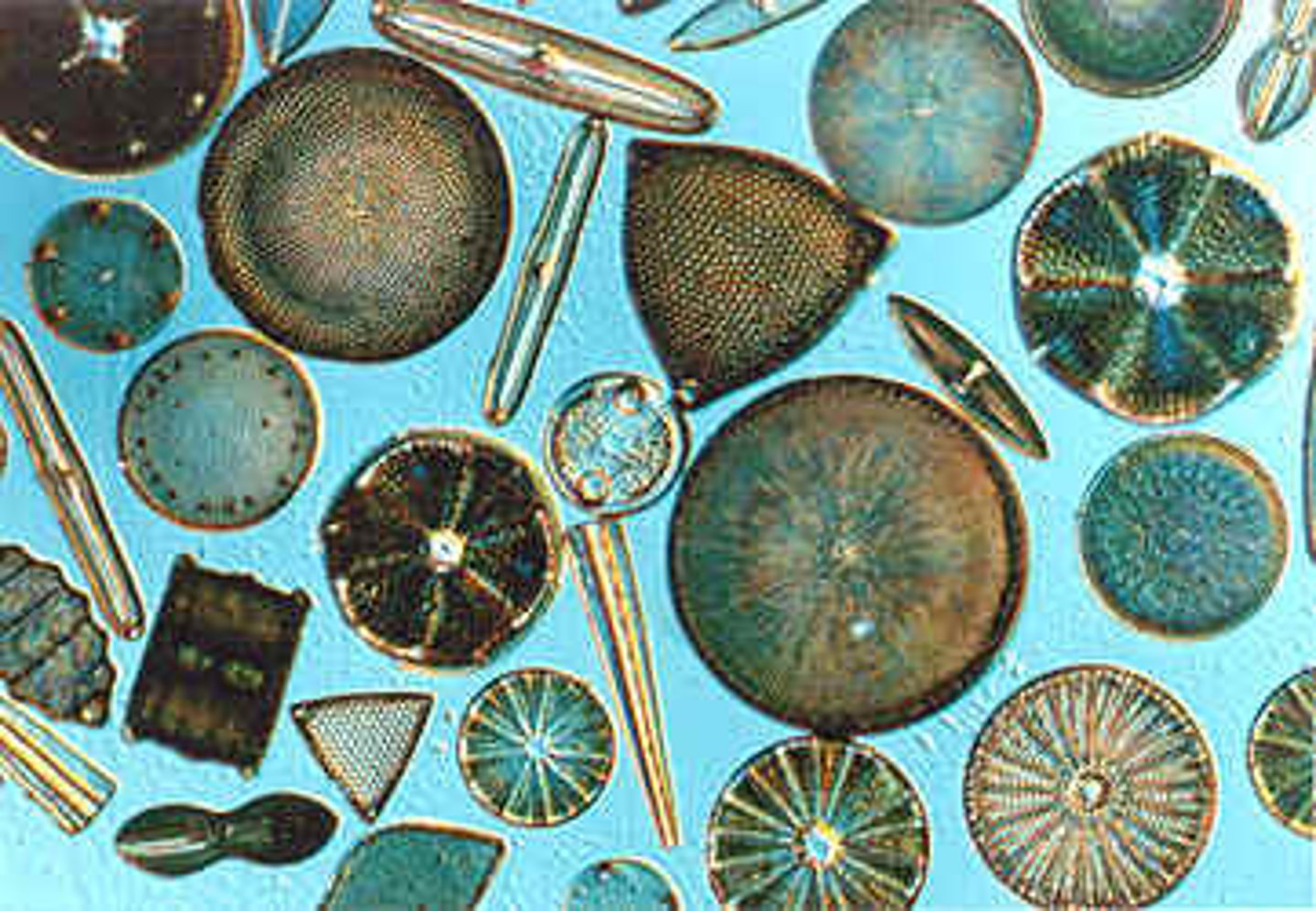
Diatoms
Unicellular algae with a unique two-part, glass-like wall of hydrated silica.
____ usually reproduce asexually, and occasionally sexually

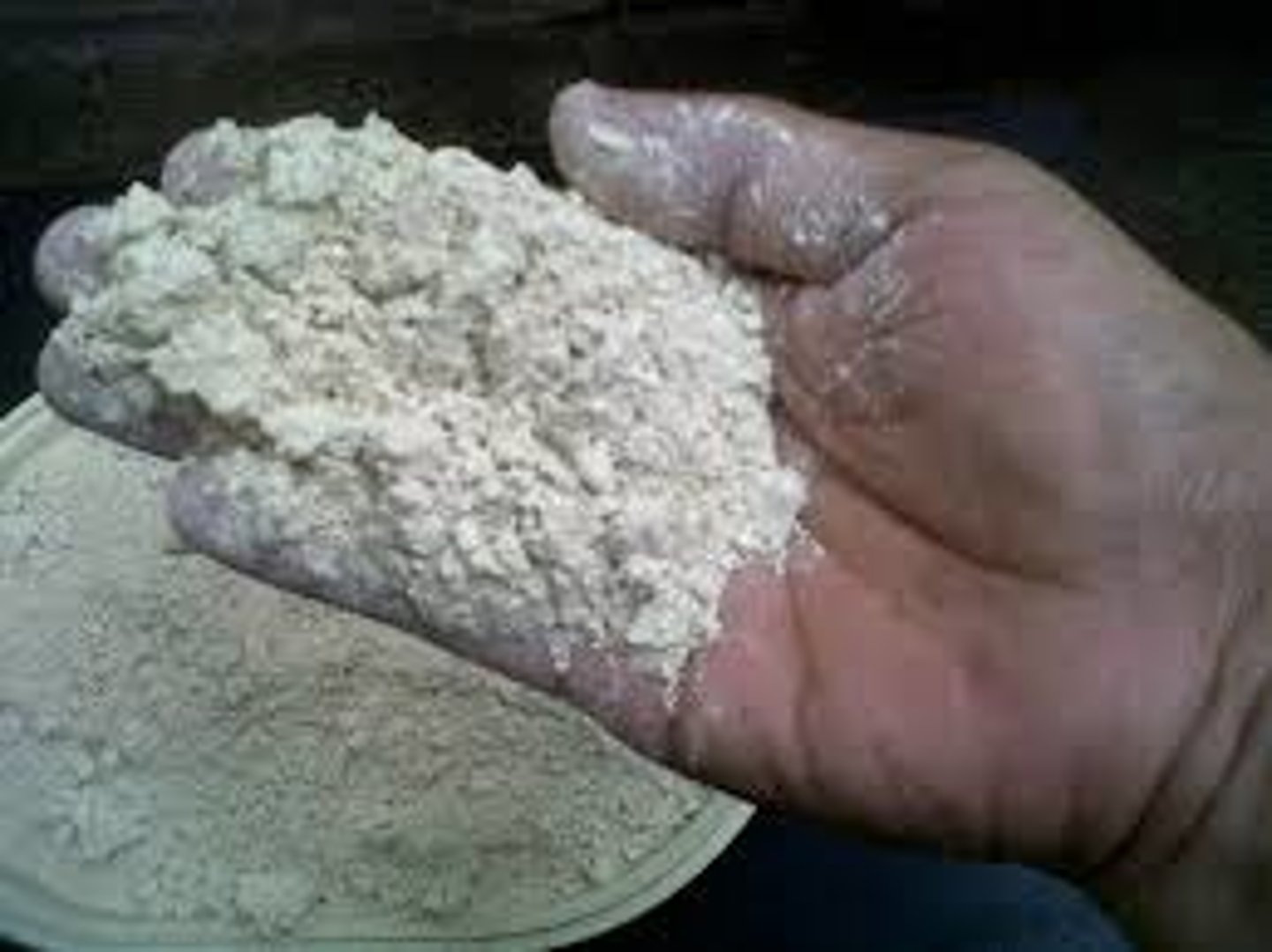
Diatomaceous Earth
A soft, crumbly, porous sedimentary deposit formed from the fossil remains of diatoms.

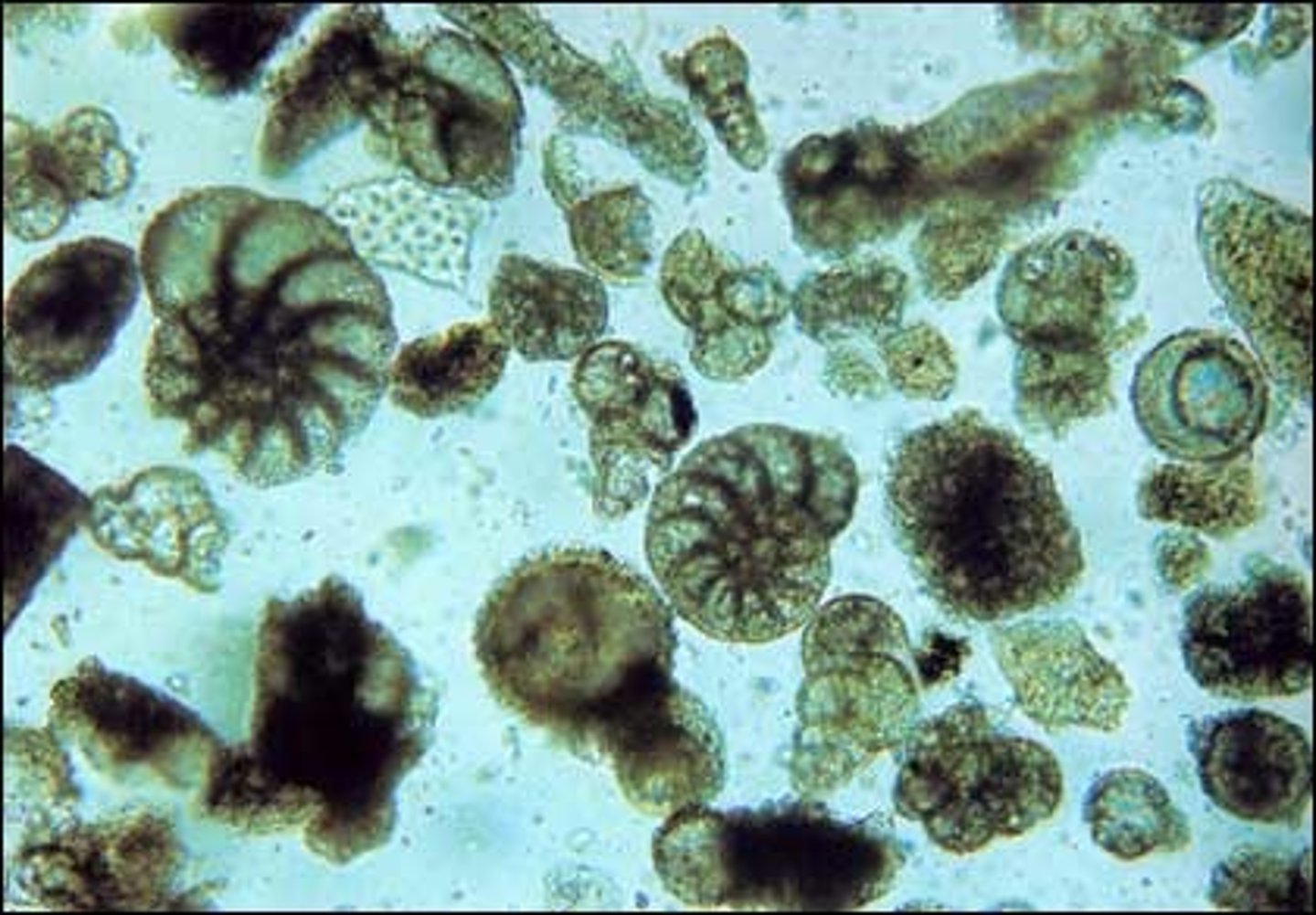
Foraminiferans
A single-celled planktonic animal with a perforated chalky shell through which slender protrusions of protoplasm extend. Most kinds are marine, and when they die, their shells form thick ocean-floor sediments.
Dinoflagellates
a single-celled organism with two flagella, occurring in large numbers in marine plankton and also found in fresh water.
Cause of red tides.
Nourish coral polyps that build reefs
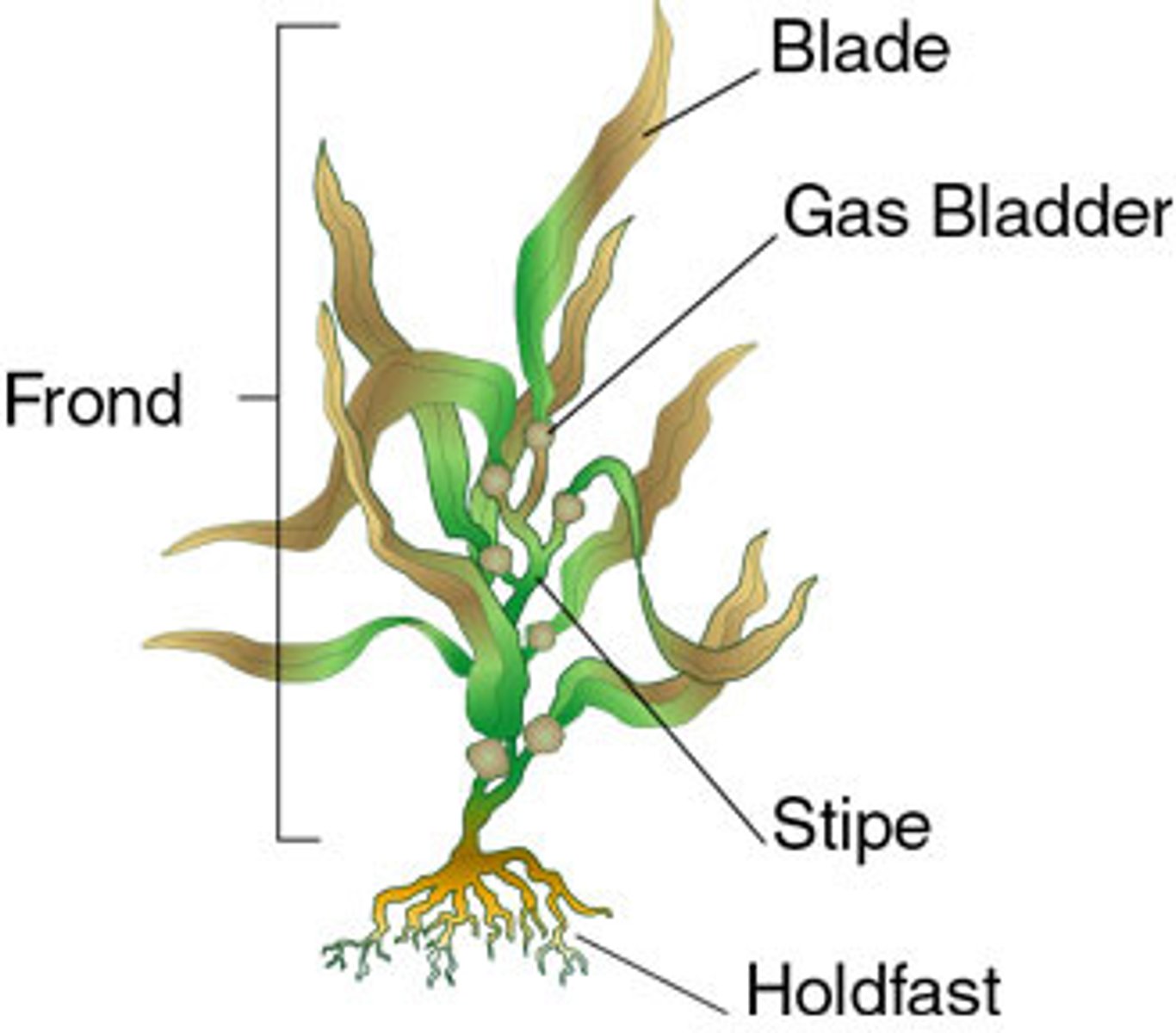
Brown Algea
The largest and most complex algae. "Seaweed"
Algal body is plantlike but lacks true roots, stems, and leaves.
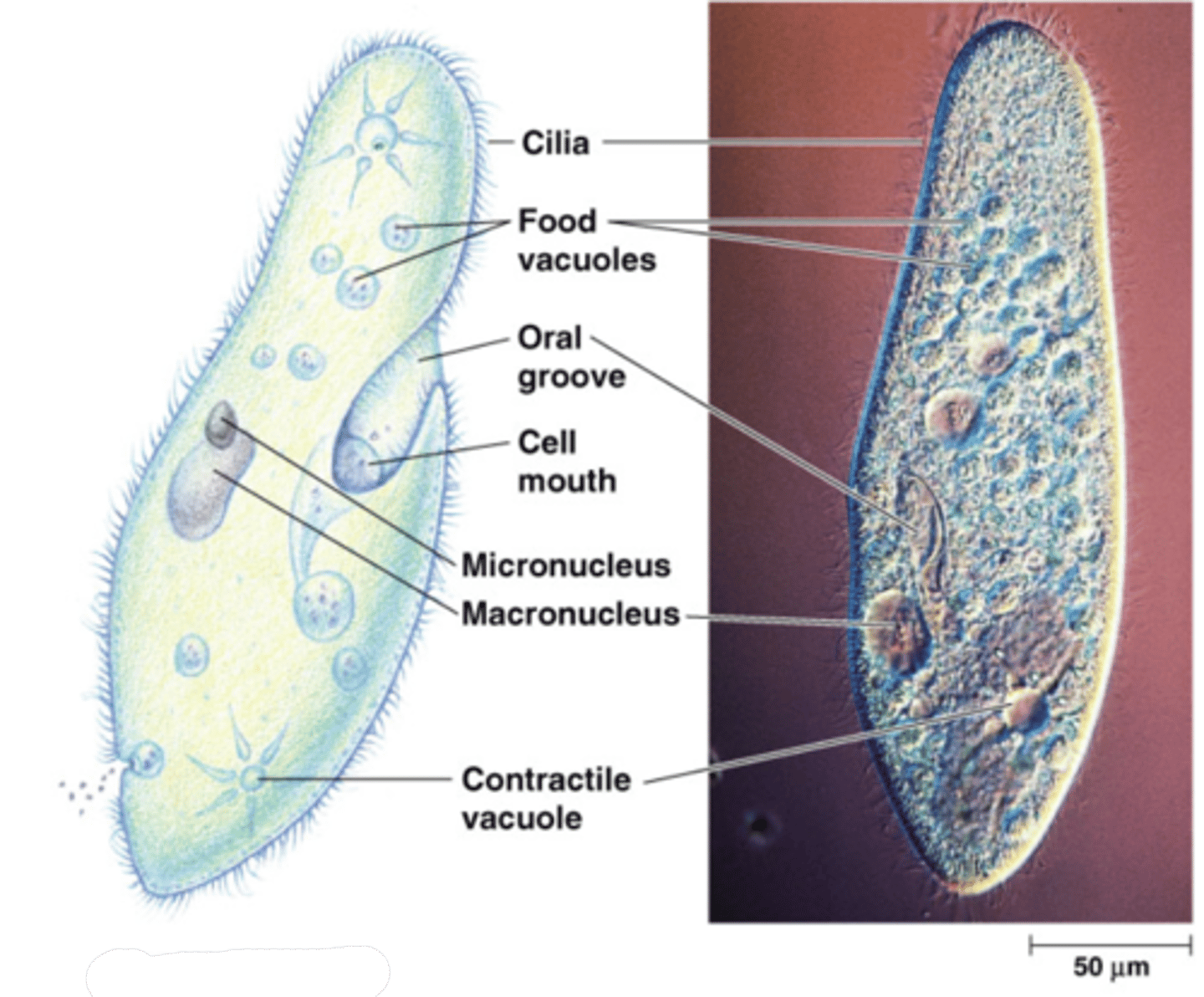
Ciliates
Use of cilia to move and feed
ie. Paramecium.
Alternation of Generations
The alternation of multicellular haploid and diploid forms.
Heteromorphic
Generations are structurally different.
Isomorphic
Generations look similar.
Oomycetes
Include water molds, white rusts, and downy mildews.
Decomposers or parasites.
Phytophthora infestans causing potato blig
Archaeplastida
A supergroup used by some scientists and includes red algae, green algae, and land plants.
Red Algae
Reddish in color due to an accessory pigment call phycoerythrin.
Green Algae
Plants are descended from Green Algae. 2 types: chlorophytes and charophyceans
Chlorophytes
Green Algae; lives in freshwater or marine environments. unicellular such as Chlamydamonas.
Charophyceans
Green Algae; live in damp soil, as lichens or in snow.
Unikonta
Supergroup includes animals, fungi, and some protists.
2 clades: amoebozoans and the opisthokonts
Amoebozoans
includes amoebas with lobe or tube shapes pseudopodia (Tublinids), slime molds (cellular and Plasmodial) and entanameobas (primarily parasites)
Slime Molds
"Mycetozoans"; were once thought to be fungi.
Clade- Amoebozoa
Entamoebas
Parasites of vertebrates and some invertebrates.
ie. Entamoeba histolytica causes amebic dysentery in humans
Opisthokonts
Include animals, fungi, and several groups of protists.
Hypermastigotes
Digest cellulose in the gut of termites.
The SAR clade contains:
Stemenopiles, Alveolates, and Rhizaria
Stremenopiles include:
Diatoms, Golden Algae and Brown Alea.
Alveolates include:
Dinoflagellates, Apicomplexins, and ciliates
Rhizaria Include:
Radiolorians (delicate silika structures, heterotrophic, feed kinda like jellyfish), Forams (pouros shells called tests:both heterotrophic and photosynthetic, marker for age of sedimentary rock), and Cercozoans (kinda boring, flagellates, amoeboid, heterotropic),
Excavates include:
Diplomonads, parabasilids and Euglenozoans
Archeaplastida includes:
Red algae and green algae
Unikonts include
ameabozoans and opisthokonts
Hedrogenozomes belong to
parabasilids
Mitosomes belong to
diplomonads
kinetoplastids
have a large mitochondrian that contains organized mass of DNA called a kinetoplast. cause trypanosoma wich is a neourological sleaping disseas. Part of euglenozoans wich are excavates
Euglenids:
a euglenid has a pocket at one end of the cell from which one or two flagalla emerge. Mixotrophic.
Golden Algea
Cells are typically biflagellated with flagella attached near eachother, components of freshwater and marine plankton
Brown Algae:
the largest and most complex algae, all are multicellular, most are marine, "seeweeds"
Alveolates:
have membrane enclosed sacs: roughly half are purely heterotrophic.
Apicocomplexins:
nearly all are parasites to animals: spread through host as "sporosoites"
Ciliates:
Have ciliated body either all over or in one condensed location