Acids, Bases & Buffers
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Define Bronsted Lowry acid
Proton (H+) doner
Define Bronsted Lowry base
Proton (H+) acceptor
What occurs in a Bronsted Lowry acid-base reaction?
Proton is transferred from acid to base
Define strong acid with 3 examples
acid that completely dissociates
HCl, H2SO4, HNO3
Write the expression for the ionic product of water (kw) and its units
Kw=[H+][OH]
Mol2dm-6
Why does kw value change with temperature?
Dissociation of water is endothermic, increasing temp shifts equilibrium to the right to produce more H+ and OH-
Why is pure water neutral?
[H+]=[OH-]
Write the ionic product of water for pure water
Kw=[H+]²
What happens to [H+] when [OH-] increases?
[H+] will decrease proportionally
Acidic solution in terms of H and OH?
[H+]>[OH-]
Alkaline solution in terms of H and OH?
[OH]>[H+]
Define pH
pH=-log[H+]
Useful re-arrangement of pH?
[H+]=10^-pH
Define monoprotic acid
One mole of acid dissociates to give one mole of H+
Define diprotic acid
One mole of acid dissociates to give two moles of H+
Define weak acid
Acid that partially ionises/dissociates
Write an expression for the acid dissociation constant for the weak acid HA
Ka=[H+][A]/[HA]
What are the units for Ka?
Moldm-3
Write the simplified expression for Ka for a weak acid with nothing added
Ka=[H+]²/[HA]
State the two assumptions used to simplify the Ka expression for a weak acid with nothing added
[H+]=[A-]
[HA] does not alter significantly after dissociation
Define pKa
pKa=-logKa
Useful re-arrangement of pKa?
Ka=10^-pKa
Stronger the weak acid the ___ the value of Ka and the ___ the value of pKa
Higher
Lower
Describe a method to be used to continuously measure the pH change of a solution during ma titration
Use a pH probe and reader and place it in the conical flask
Add acid/base from a burette in small intervals and record the pH reading
Strong/weak acid/base titration curves
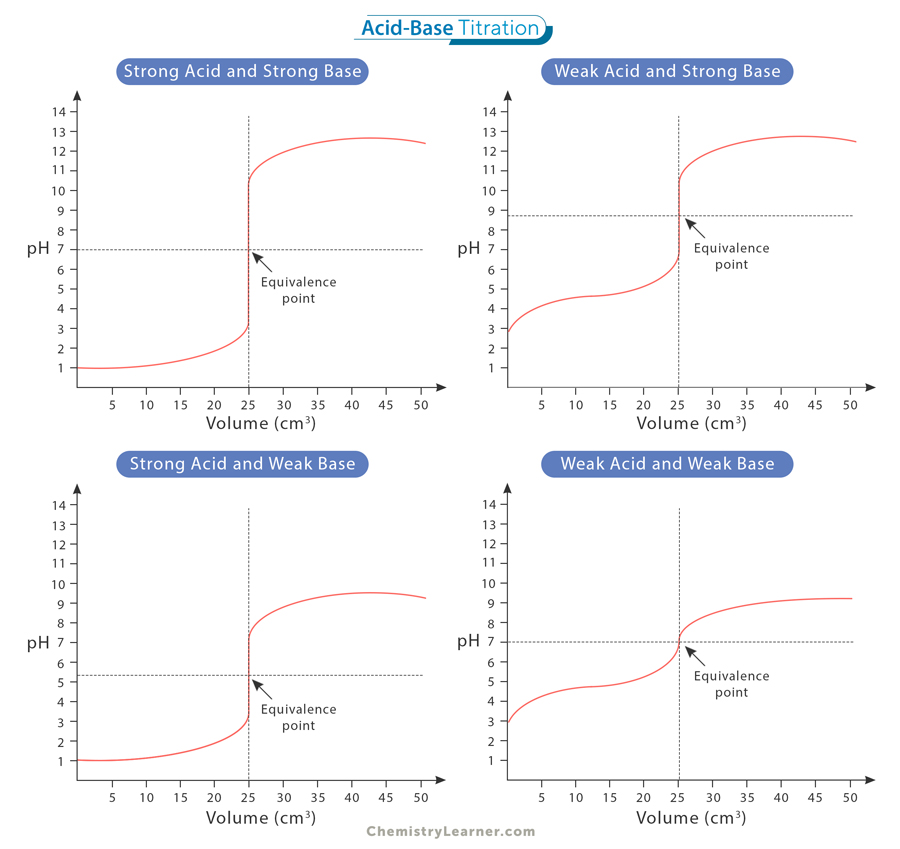
Define equivalence point in a titration. Where is it found on the titration curve?
When moles of H+ = moles of OH- in the conical flask. Found at central point of the vertical section on the graph
Define end point of titration
Point where indicator changes colour
How can you find a suitable indicator for an acid-base titration using a titration curve?
pH range over which indicator changes colour lies within pH range of vertical section of the titration curve
Where is half neutralisation point on a pH curve and why is it useful?
Half the volume needed to reach the equivalence point
pKa of weak acid= pH of solution in conical flask
Define buffer solution
Solution that minimises changes to pH upon the addition of small amounts of acid/alkali
State 2 methods of producing an acidic buffer
Mix weak acid with salt of weak acid
Mix an excess of weak acid with a strong base
What happens to a buffer solution when a little acid is added? (Terms of HA and A-)
[A-] decreases and [HA] increases
[HA]/[A-]»[H+]
What happens to a buffer solution when a little base is added? (Terms of HA and A-)
[HA] decreases and [A-] increases
[HA]/[A-]»[H+]
General overall equation for reaction of a strong acid with strong base?
H+ + OH- —>H2O
General overall equation for the reaction of a weak acid with a strong base?
HA + OH- —> A- + H2O