Test 4 SPRING 2023
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/134
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Audio Fundamentals
Last updated 5:51 PM on 5/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
1
New cards
Balanced Cable
Considered Low impedance or Low Z
2
New cards
Unbalanced cable
Considered high impedance or high Z
3
New cards
What provides common mode rejection (CMR)
Balanced inputs
4
New cards
What does common mode rejection mean
Interference (noise) picked up by the cable will be rejected by the input
5
New cards
What is the PIN side of an XLR connector (male)
The output
6
New cards
What is the socket side of an XLR connector (female)
The input
7
New cards
Male XLR connector (output)
\

8
New cards
Female XLR connector (input)
\

9
New cards
1/4 inch phone plug is considered a
Guitar Jack
10
New cards
What does a tip sleeve TS mean
Mono unbalanced
11
New cards
What does a tip ring sleeve TRS mean
Mono balanced
12
New cards
Stereo unbalanced
Headphone jack
13
New cards
The tip is
\+ (or left)
14
New cards
The ring is
\- (or right)
15
New cards
The sleeve is
Shield (ground)
16
New cards
1/4 in TS - tip sleeve

17
New cards
1/4 inch TRS - tip ring sleeve

18
New cards
What is smaller than the 1/4 “ connector
The Bantam or TT(tiny telephone)
19
New cards
The Bantam / TT(tiny telephone)

20
New cards
What does RCA phone stand for
Radio Corporation of America
21
New cards
What is a unbalanced mono and consumer audio connector
RCA phono
22
New cards
RCA connector

23
New cards
3\.5 mm (1/8”) Mini I I-connectors
24
New cards
Speakon connector

25
New cards
Audio electrical signal is
Analog
26
New cards
Audio signal that is interpreted as ones and zeros
Digital
27
New cards
Computer-based mixer (program)
DAW
28
New cards
Tactile controller for computer-based mixer
DAW with a control surface
29
New cards
Full analog console with added features to control a computer-based mixer
Analog with DAW control
30
New cards
Console inputs and outputs
32x24x2
32 inputs
24 outputs
2 program outputs
32 inputs
24 outputs
2 program outputs
31
New cards
What is the icon for an amplifier

32
New cards
What is the icon for trim
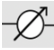
33
New cards
What is considered as level control
Trim
34
New cards
Where are trims usually found
Online level inputs and are used to set a course level well the fader sets the fine level
35
New cards
What is the icon for a fader

36
New cards
What are faders
These are variable resistors (potentiometers) or digital encoders
37
New cards
In what systems does the fader adjust the control voltage or control signal which in turn adjusts the audio game
VCA (voltage control amplifiers) and DCA (digital control attenuators)
38
New cards
What processors do larger analog systems include
Dynamic processors
39
New cards
Which is the switches icon
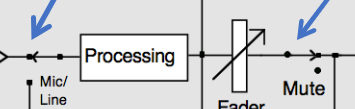
40
New cards
Which is the pan icon
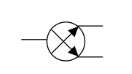
41
New cards
What are panners or panpots
These are panoramic potentiometers (analog)
42
New cards
What are the three different types of solar systems out there
PFL, AFL, and IPL
43
New cards
What are the monosolo systems
Pfl and AFL
44
New cards
What does pfl stand for
Pre fader listen
45
New cards
What does AFL stand for
After fader listen
46
New cards
What does IPL stand for
In place solo or sip (Solo in place)
47
New cards
AUX Master icon
48
New cards
The parts of a meter

49
New cards
What is a device that only attenuates certain bands of frequencies
A filter
50
New cards
What are the three types of basic filters
Low-cut / High Pass
High-cut / low pass
Notch filter
High-cut / low pass
Notch filter
51
New cards
Where is the cutoff frequency
It is 3 DB down from nominal (flat) level
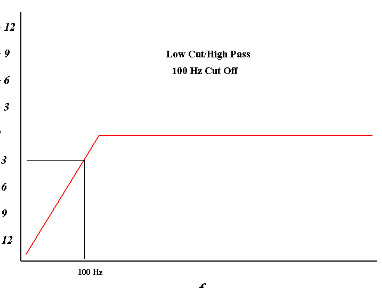
52
New cards
What are considered as tone controls
Shelving equalizers
53
New cards
Bass and treble control is also referred as
Tone control
54
New cards
Image of a shelving EQ
55
New cards
Image of a bell EQ
56
New cards
Which EQ offers the most Equalization control over a signal
A parametric EQ
57
New cards
What type of equalizer is cause phase shift
All analog equalizers
58
New cards
What factors affect the amount of phase shift
The amount of boost or cut, filter slope and slash or Q
59
New cards
What are compressors
Amplifiers whose gain decreases as the input level increases
60
New cards
What are limiters
Compressors whose output level remains constant regardless of the input level
61
New cards
What is a threshold
The input level at which the compressor turns on and gain is reduced
62
New cards
What happens to signals below the threshold
The signals passed through the compressor unchanged this is called unity game
63
New cards
What determines the amount of gain reduction above the threshold
The compression ratio
64
New cards
What is the compression ratio a ratio of
Db in to DB out
65
New cards
What is attack time
The speed with which the processor reacts after the signal goes over the threshold
66
New cards
What is the hold time
The amount of time the gain reduction is maintained
67
New cards
What is the release time
The speed with which the processor stops reacting after the signal Falls below the threshold
68
New cards
What amplifiers game goes down as the input level goes down
And expander
69
New cards
What is the purpose of an expander
To reduce low-level noise (Noise gate)
70
New cards
What is Decay time
The time it takes for the reflected signal to reduce by 60 DB SPL (rt60)
71
New cards
What does a mix of wet and dry signal mean
The closer you are to the source the louder the direct sound and the less you hear the reverberation
72
New cards
What does Decay time Define
Hard surfaces cause the sound to bounce around the room for a longer period of time
73
New cards
What three heads do analog tape machines have
Erase, record and reproduce
74
New cards
What is the creation of flanging represent
The creation of a shifting comb filter using a shifting time delay
75
New cards
What is the creation of pitch shifting
This is varying the playback speed tape provided the ability to raise or lower the pitch of recorded sound
76
New cards
Voltage:
The amount of work required in moving one \n electric charge from one point to the other. Volt is the \n unit.
77
New cards
Current
The amount of charge passing through the \n circuit in unit time. Ampere is the unit.
78
New cards
Resistance
The opposition offered by the flow of \n current in the circuit. Ohms is the units
79
New cards
Power
The product of work done and the number of \n electrons passing through the circuit in unit time. Watt \n is the unit.
80
New cards
the 4 basic units of electricity are
volts, \n amps, ohms, and watts.
81
New cards
Power (watts)
Work Created \n heat, light, amplification, etc.
82
New cards
A doubling of power (watts) yields a
3 dB \n increase
83
New cards
A double of voltage (pressure) yields a
6 dB \n increase.
84
New cards
Inverse Square Law-Doubling the distance
decreases the Sound Pressure Level by 6 dB
85
New cards
Inverse Square Law- Halving the distance
increases the Sound Pressure Level by 6 dB
86
New cards
When a standardized reference power, voltage or \n pressure are used
a specific “kind” of dB is created
87
New cards
The most common types of dB for audio production \n are:
dB-SPL (also A, B, & C weightings) \n • Sound Pressure Level (.00002 Pascals) \n • dBm (1 milliWatt) \n • dBu (0.775 volts) \n • dBFS (0 \= Full Scale (max) in digital) \n • dBV \= (1 volt)
88
New cards
What is sampling like?
This is like “taking shapshots” of the voltage \n level or amplitude at specific intervals
89
New cards
What is the time interval know as
sampling frequency (fs), sampling rate, or Nyquist rate
90
New cards
Nyquist frequency \= ½ of the Nyquist rate \=
the highest audio frequency we can digitize \n accurately (the analog sound that we hear)
91
New cards
Nyquist rate \= sampling frequency
sampling rate (how often we sample or “take a picture” of \n the analog sound)
92
New cards
Violation of Nyquist’s law
(having audio frequencies above ½ the sampling frequency) \n results in the creation of alias waves.
93
New cards
After Sample & Hold
94
New cards
Quantizaing
95
New cards
In digital quality the sampling frequency determines what?
Bandwidth
96
New cards
What does bit depth determine
The dynamic range
97
New cards
How can I find the bit rate?
by multiplying the bit depth by the \n sampling frequency
98
New cards
What is a dither
To prevent quantization error on this a very low \n level noise is sometimes added to the audio (This will increase the dynamic range)
99
New cards
How do you De-Sample
Using a Sample & Hold Circuit
100
New cards
What is an output low pass filter called
anti-imaging filter