HumanA&P 10: Joints
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
3 Functions of Joints
Enable movement
Provide stability
Allow bones to lengthen
3 Joint Classifications by Motion
Synarthrosis: no movement between bones
Amphiarthrosis: small amount of movement between bones
Diarthrosis: freely moveable within ROM
3 Classifications of Joints by Structure
Fibrous
Joined by dense regular connective tissue
No joint space
Arthroses or amphiarthroses
Cartilaginous
Joined together with cartilage
No space between articulating bones
Arthroses or amphiarthroses
Synovial
Hyaline articular cartilage on bones
Joint space is fluid filled cavity
Diarthrosis joints
3 Types of Fibrous Joints
Sutures
Syndesmoses
Gomphoses
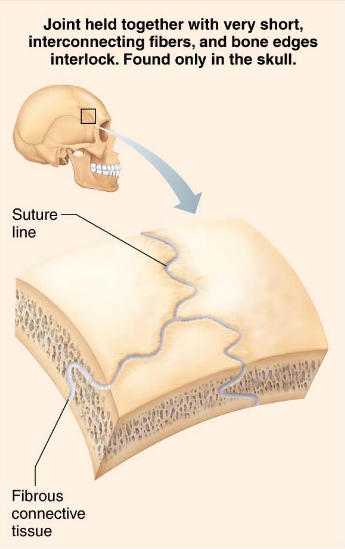
Sutures
Fibrous joints
Joints of skull
Allow for growth during youth
Structures ossify/fuse at middle age
syostoses
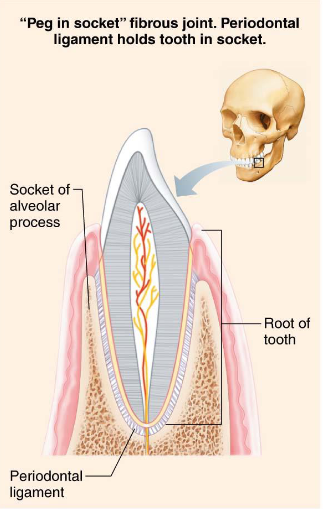
Gomphoses
Fibrous joints
Peg-in-socket
Periodontal ligament is fibrous connection
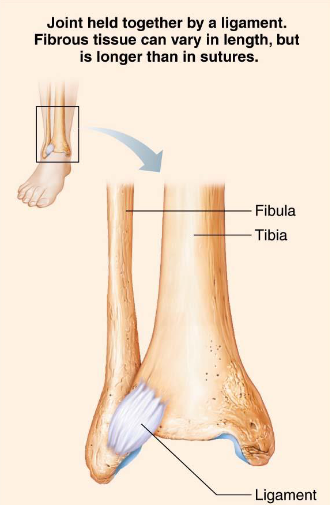
Sydesmoses
Fibrous joints
Fiber length varies
Movement varies
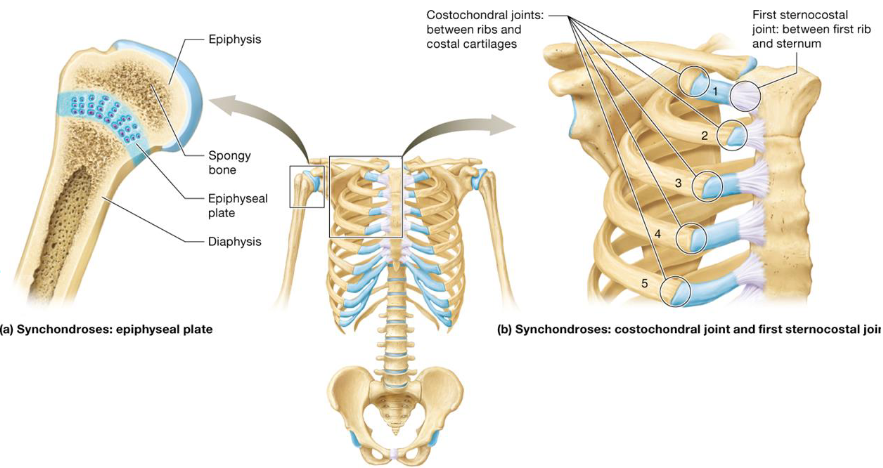
2 Types of Cartilaginous Joints
Synchondroses
Symphyses
Synchondroses
Type of cartilaginous joint
Bones joined together by hyaline cartilage
Immovable joint (synarthrosis)
Ex
Epiphyseal plates
First sternocostal & all costochondral joints
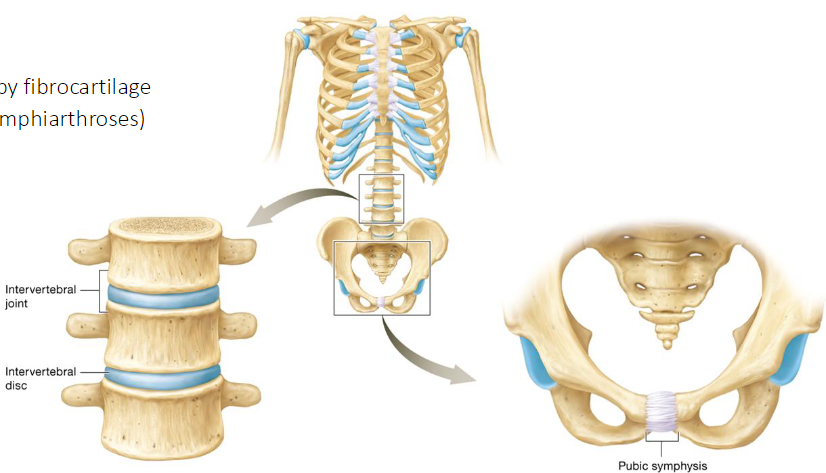
Symphyses
Type of cartilaginous joint
Bones joined by fibrocartilage
Partially moveable joints (amphiarthroses)
Ex
Intervertebral joints
Pubic symphysis
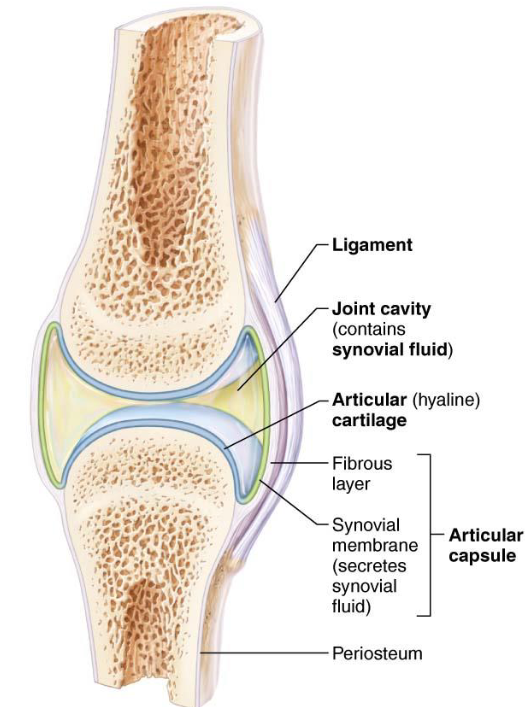
Synovial Joints
Bones separated by fluid-filled joint cavity
Diarthrotic
6 Characteristics
6 General Features of Synovial Joints
Articular Cartilage
hyaline covers ends of bones
Joint Cavity
fluid filled space
Articular Capsule: 2 layers thick
External fibrous layer
Inner synovial membranes: loose connective tissue; makes synovial fluid
Synovial Fluid: viscous, filtrate of plasma & hyaluronic acid
Different types of ligaments
Capsular
Extracapsular
Intracapsular
Nerves & Blood Vessels:
Nerves detect pain
Capillary beds
Special Features of Synovial Joints
Fatty pads
cushioning between fibrous layer of capsule & synovial membrane/bone
Articular discs
Fibrocartilage separates articular surfaces
3 Factors that Determine Stability of Joints
Shape of articular surface: Shallow surfaces less stable than ball-socket
Ligament number & location
Muscle tone: keeps tendons taught
Synovial Joints Structure: 4 Stabilizing & Supporting Elements
Ligaments
Tendons
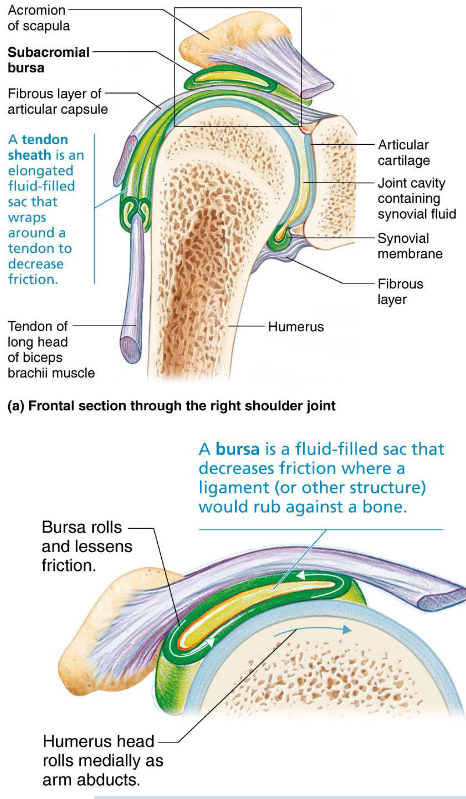
Bursae
Tendon Sheath
Bursae
Bags of synovial fluid that act as lubricating “ball bearing”
Reduce friction where ligaments, muscles, skin, tendons, or bones rub together
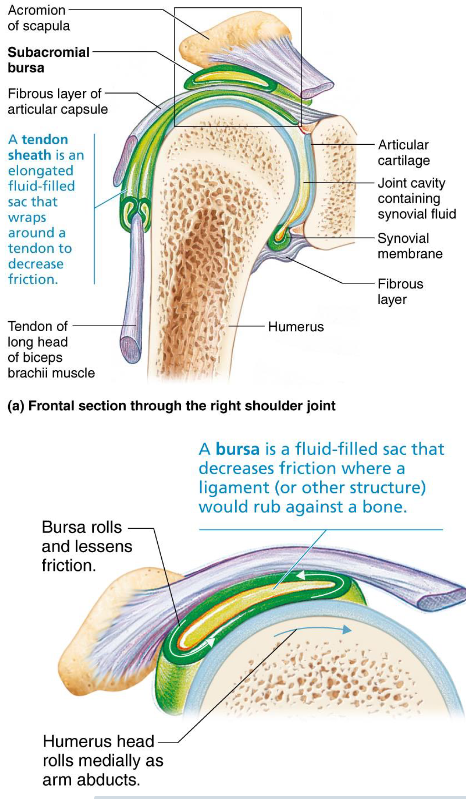
Tendon Sheaths
Elongated bursae wrapped completely around tendons subjected to friction
Muscle Origin
Attachment to immoveable bone
Muscle contraction causes insertion to move toward origin
Muscle Insertion
Attachment to moveable bone
Muscle contraction causes insertion to move toward origin
4 Ranges of Motion Allowed by Synovial Joints
Nonaxial: slipping only
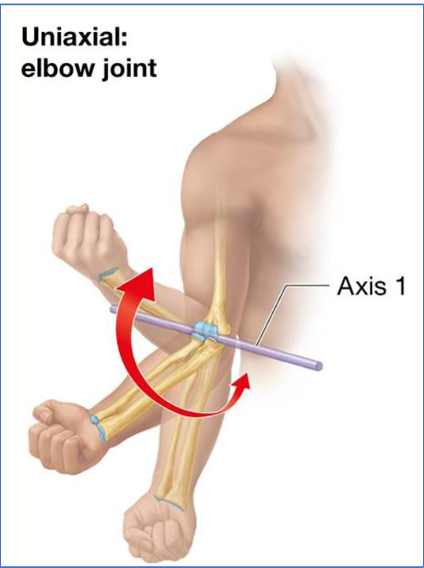
Uniaxial: movement in 1 plane
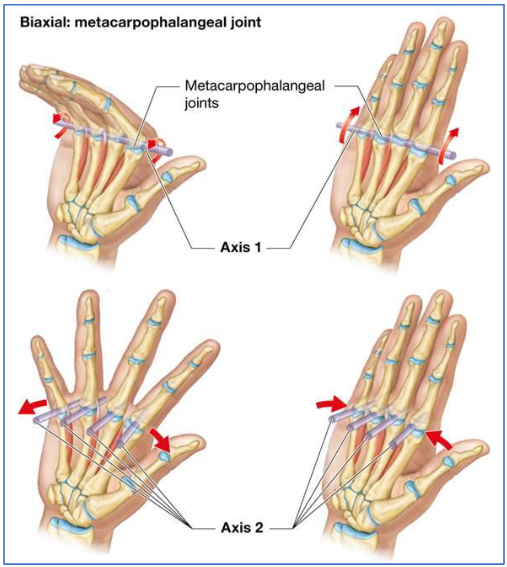
Biaxial: movement in 2 planes
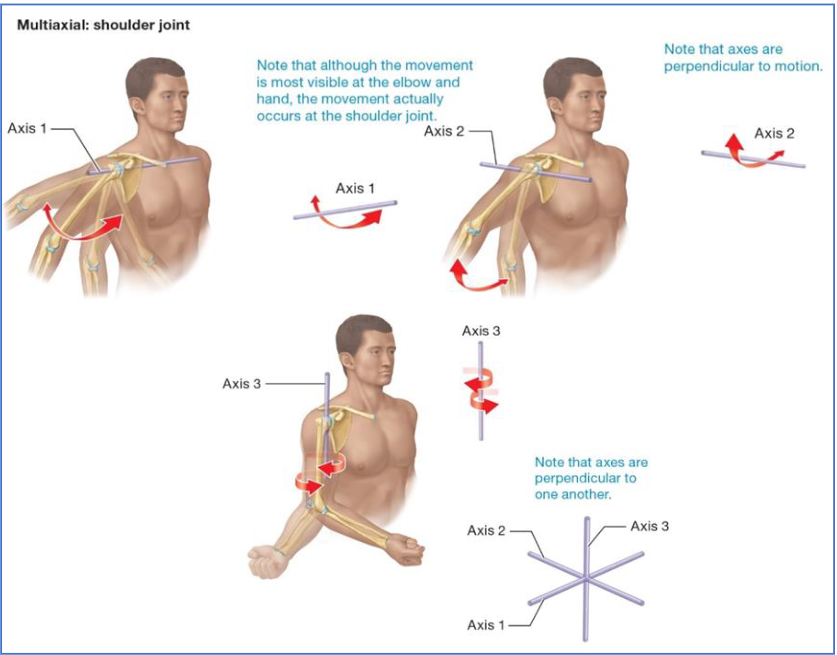
Multiaxial: movement in 3 planes
3 General Types of Movements
Gliding
Angular Movements
Rotation
Uniaxial Joint Example
Biaxial Joint Example
Multiaxial Joint Example
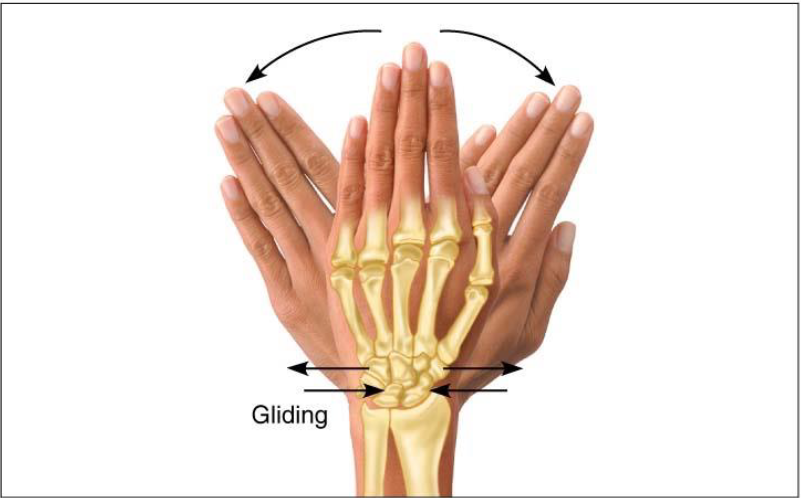
Gliding Movements
Movement permitted by synovial joint
Flat bone surface glides or slips over another similar surface
Angular Movements
Movement permitted by synovial joint
Increase or decrease angle between 2 bones
Flexion: decreases angle
Extension: increases angle
Abduction: away from midline
Adduction: towards midline
Rotation: medial. lateral
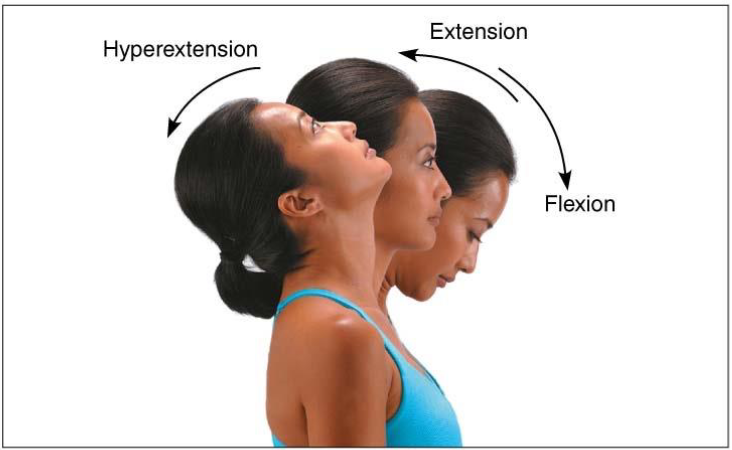
Supination & Pronation
Movement permitted by synovial joint
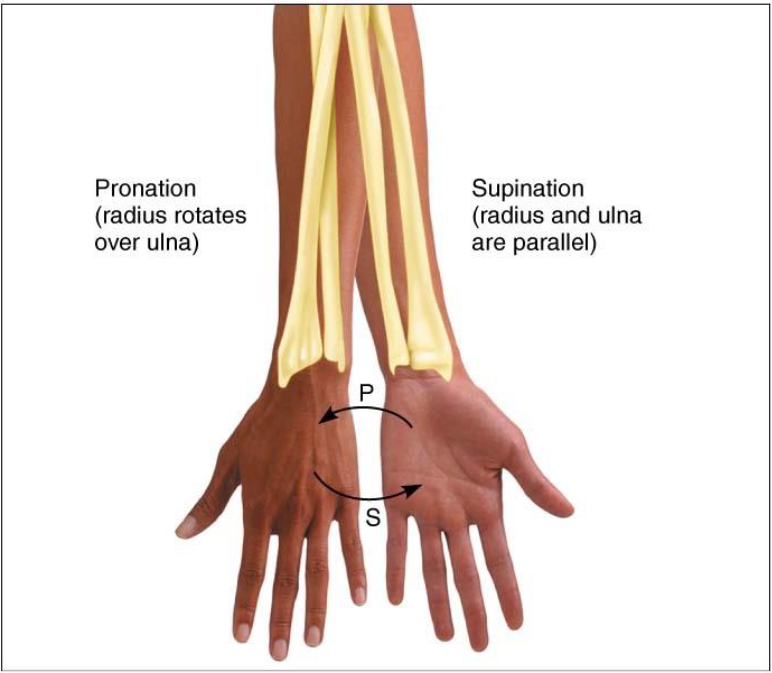
Dorsiflexion & Plantar Flexion
Movement permitted by synovial joint
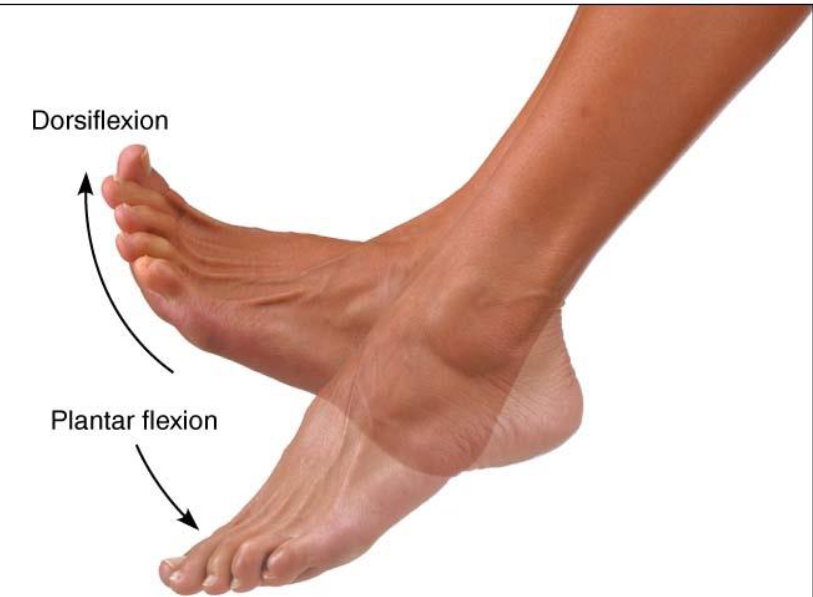
Inversion & Eversion
Movement permitted by synovial joint
Protraction & Retraction
Movement permitted by synovial joint
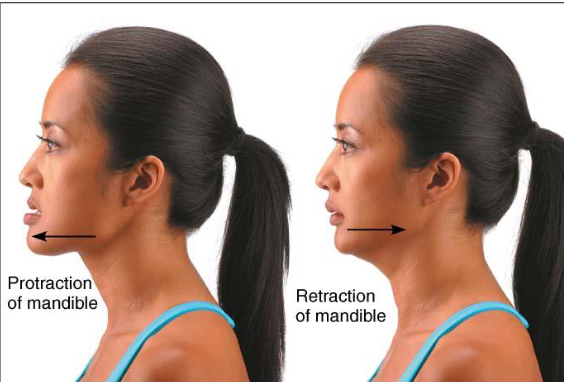
Elevation & Depression
Movement permitted by synovial joint
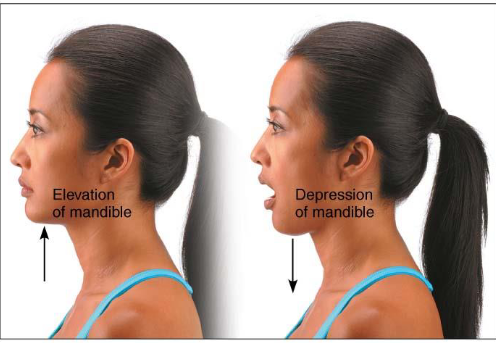
Opposition
Movement of thumb
Permitted by synovial joint
6 Types of Synovial Joints
Plane
Hinge
Pivot
Condylar
Saddle
Ball & Socket
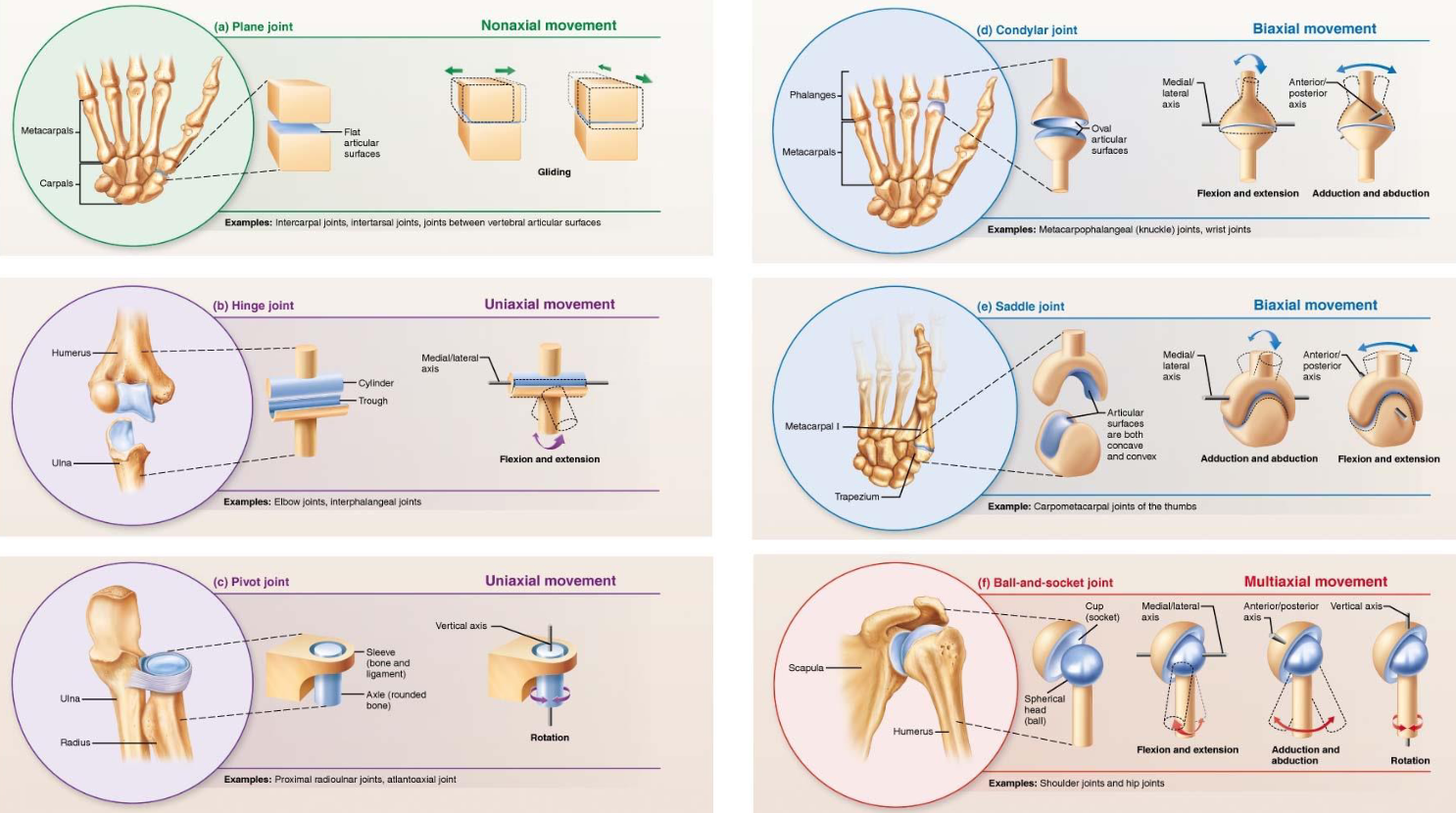
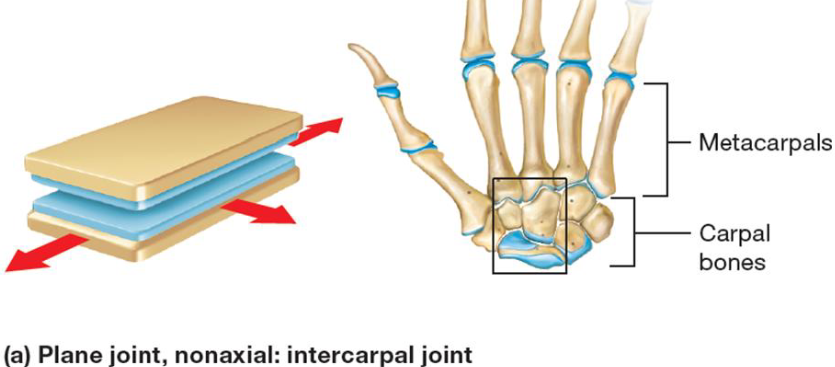
Plane Joint
Synovial joint
Least mobile
Between 2 flat surfaces
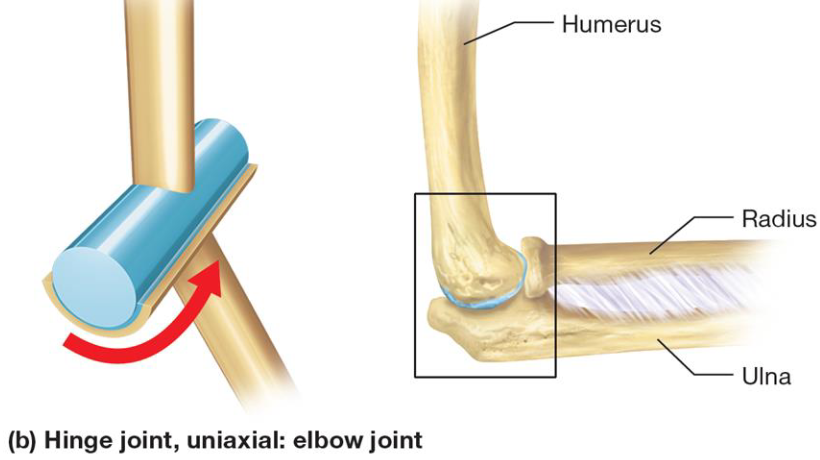
Hinge Joint
Synovial joint
Convex articular surface of one bone interacts with concave depression of second bone
Uniaxial movement
Pivot Joint
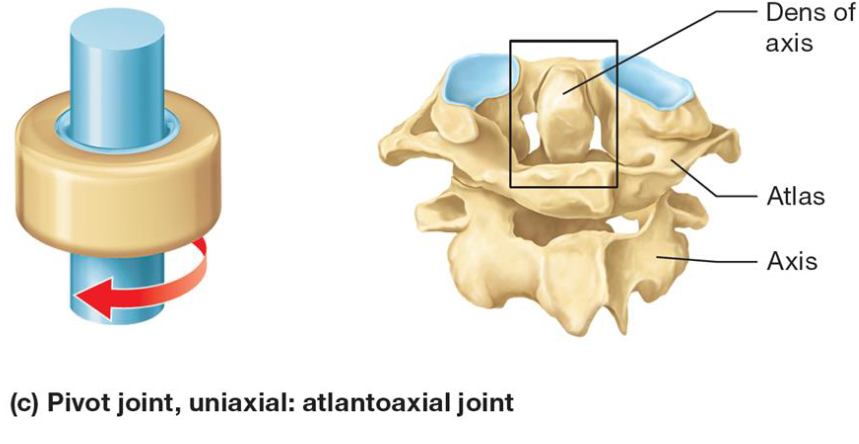
Synovial joint
Rounded end surface of bone fits into groove on surface of other bone
Uniaxial movement
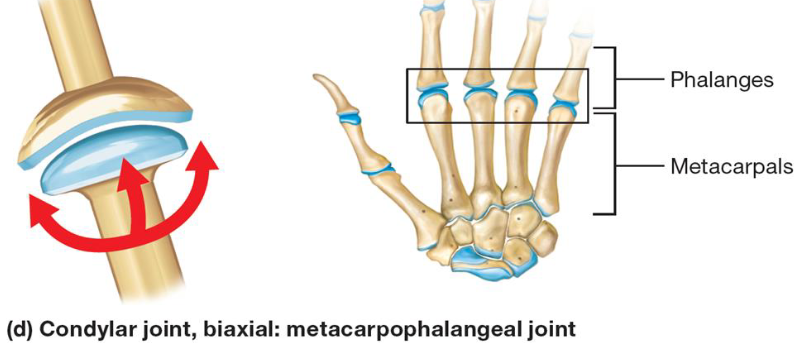
Condylar Joint
Synovial joint
Oval, convex surface of bone fits into shallow concave articular surface of other bone
Biaxial movement
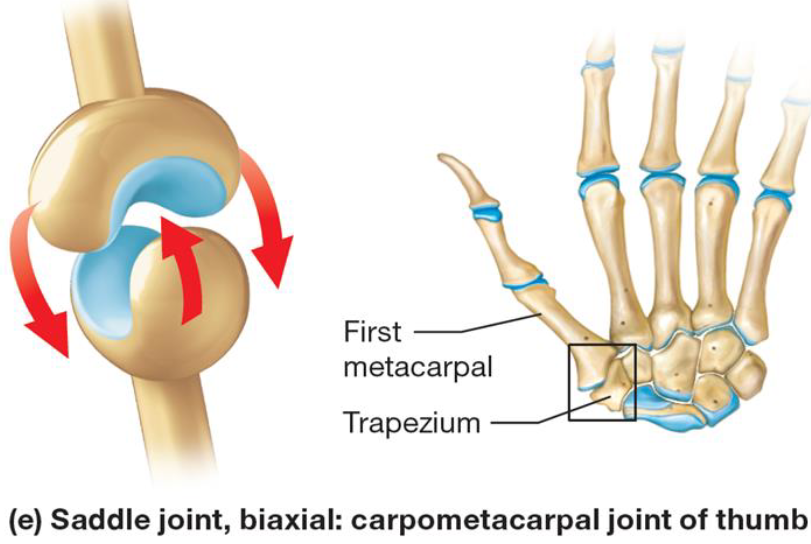
Saddle Joint
Synovial joint
Each bone has concave & convex region
Biaxial movement
Ball & Socket Joint
Synovial joint
Articulating surface is spherical, fits into cup-shaped depression in other bone
Multiaxial movement
Specific Hinge Joints: The Elbow
2 Articulations:
Humerolunar joint: trochlea of humerus & trochlear notch of ulna
Humeroradial joint: capitulum of humerus & head of radius
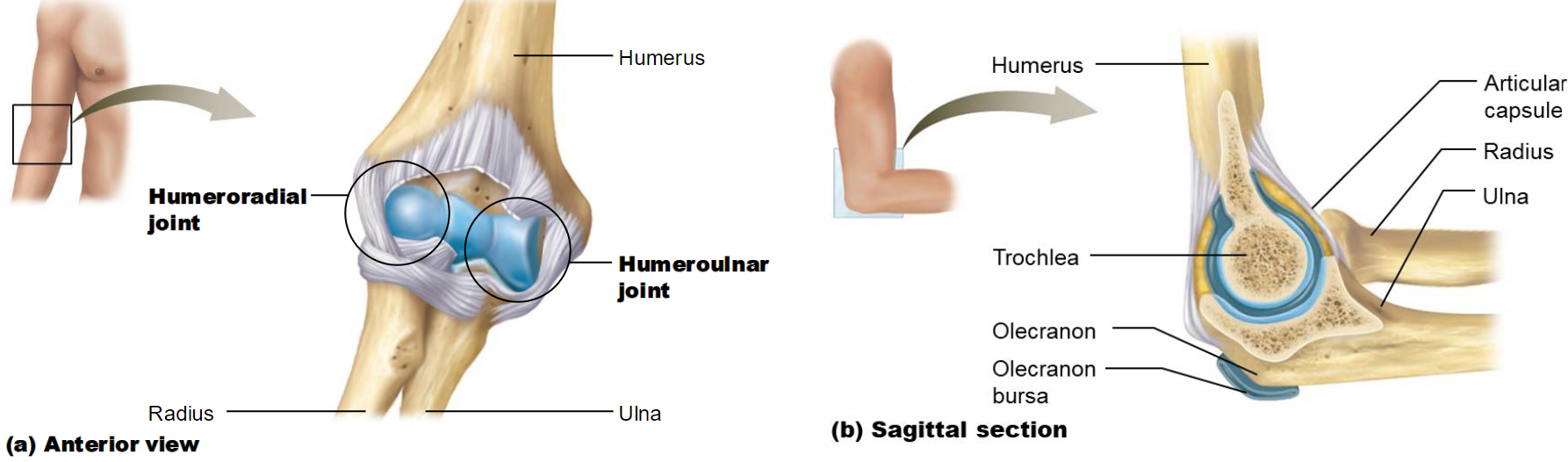
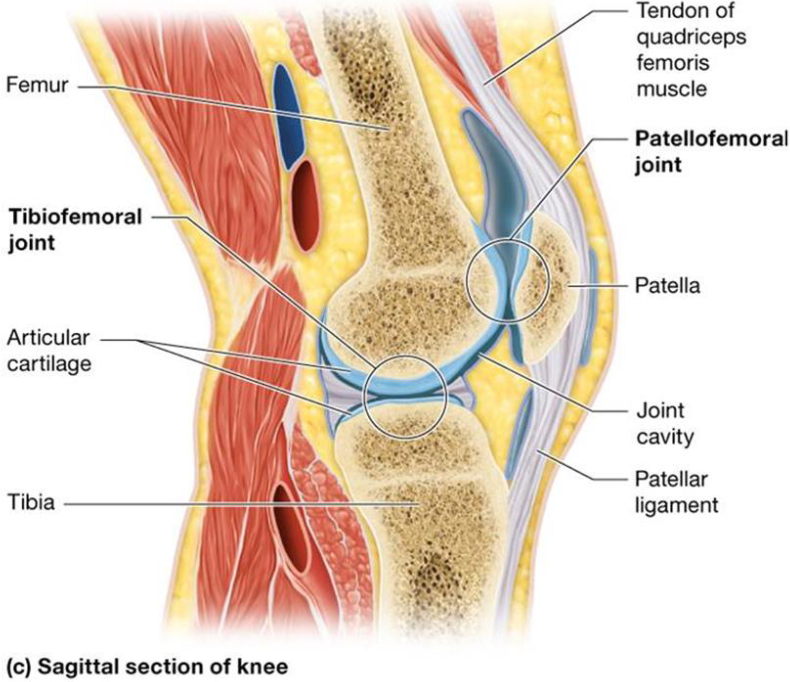
Specific Hinge Joints: The Knee
2 articulation
Tibiofemoral joint: condyles of femur & tibia
Patellofemoral joint: posterior & patellar surface of femur
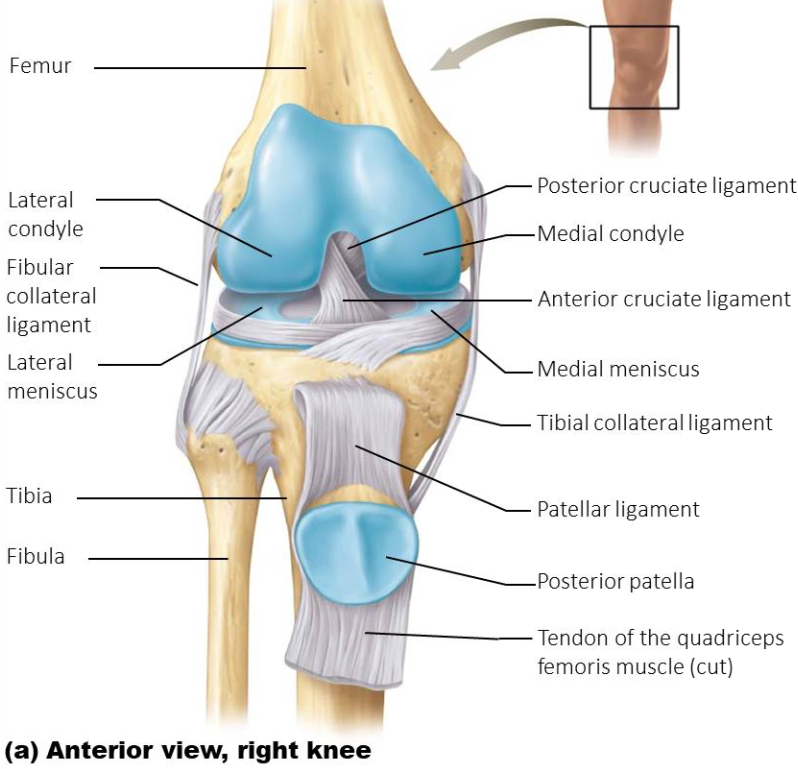
6 Primary Supporting Structures of the Knee
Patellar ligament: distal continuation of quad tendon.
Connects patella to anterior tibiaTibial (medial) collateral ligament: connects femur to tibia
(medial joint stabilization)Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament: connects femur to
fibula (lateral joint stabilization)Anterior Cruciate Ligament: connects anterior tibia to
posterior femur (prevents tibia from sliding anteriorly,
prevents hyperextension)Posterior Cruciate Ligament: connects posterior tibia to
anterior femur (prevents tibia from sliding backward)Medial and lateral meniscus: C-shaped fibrocartilage pads
between the femoral and tibial condyles (provide extra
stability and shock absorption)
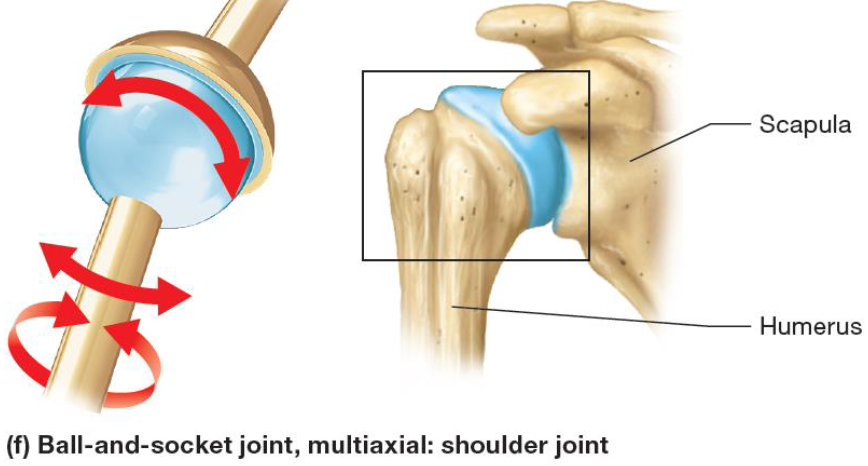
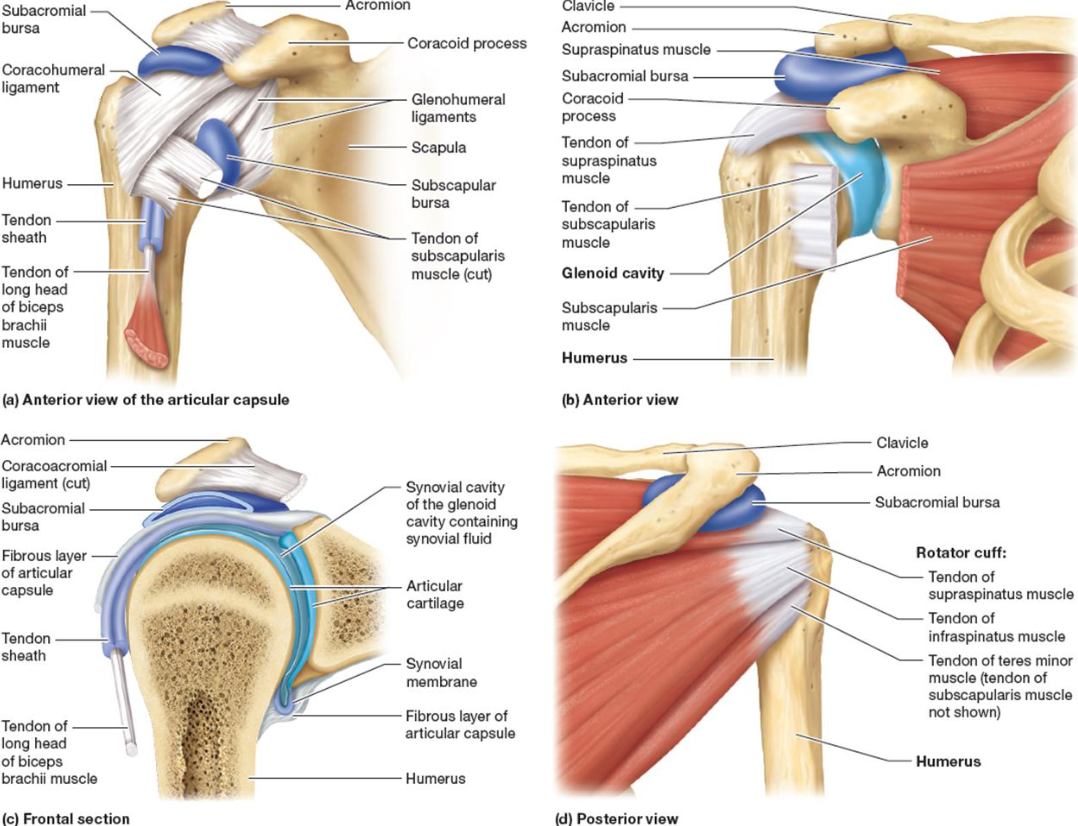
Specific Ball & Socket Joints: The Shoulder
Glenohumeral Joint
Head of humerus with glenoid cavity of scapula
Biceps brachii tendon: keeps head of humerus in joint
4 rotator cuff muscles
supraspinatus,
infraspinatus, subscapularis,
Teres minor
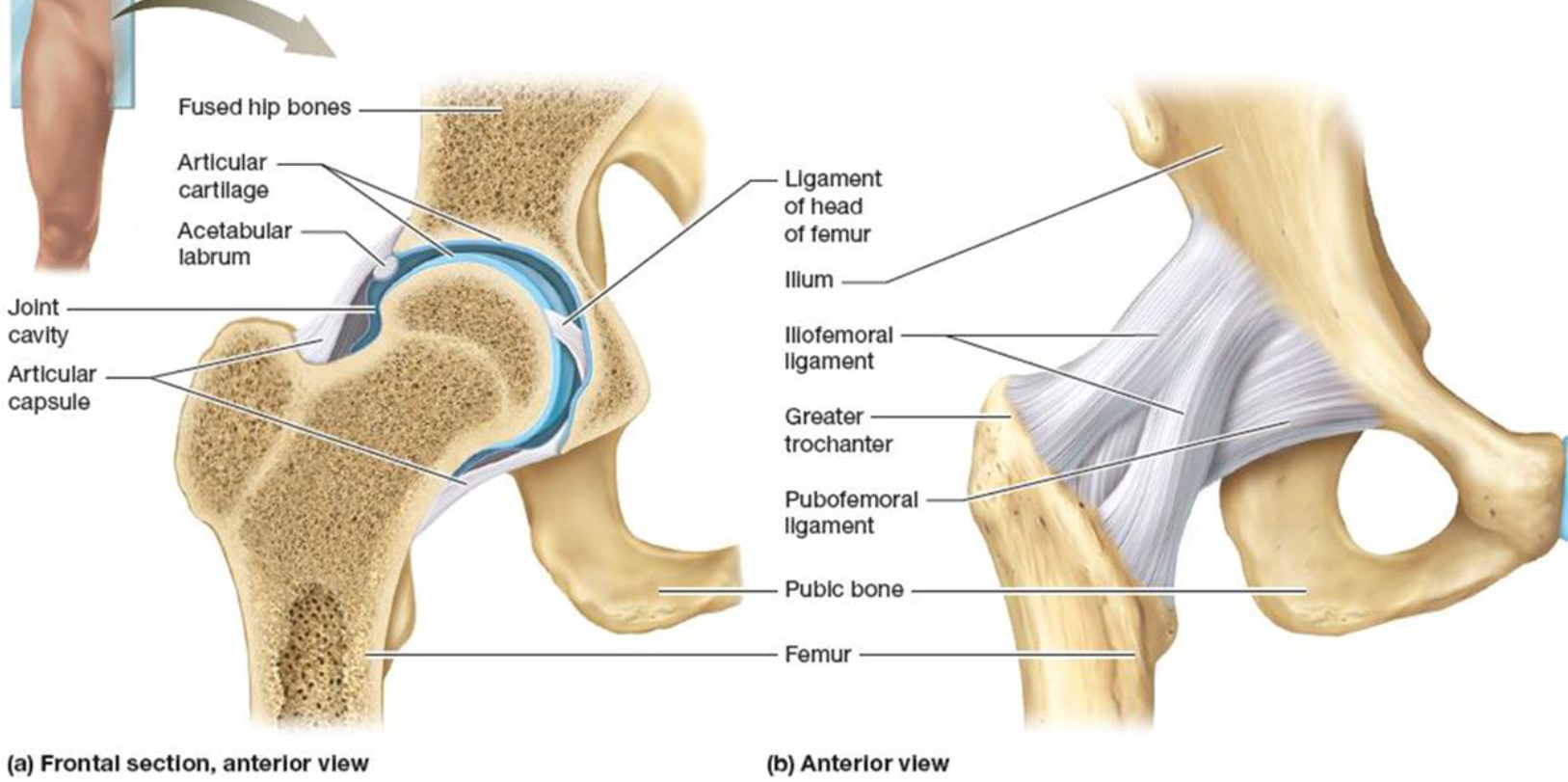
Specific Ball & Socket Joints: The Hip
Articulation between acetabulum & femur
Main supporting structures:
Iliofemoral ligament: connects
ilium to femurIschiofemoral ligament: connects
ischium to femurPubofemoral ligament: connects
pubis to femurLigament of the head of femur:
found within joint
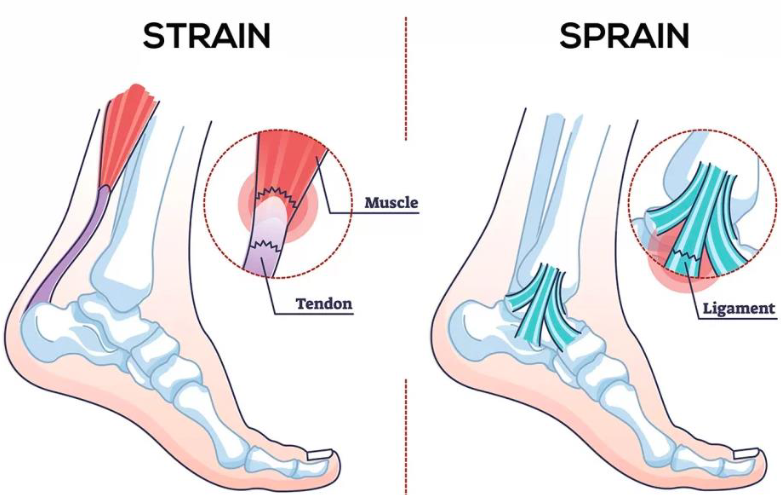
Sprain
Common joint injury
Reinforcing ligaments are stretched or torn
Partial tears are repair slow due to poor vascularization
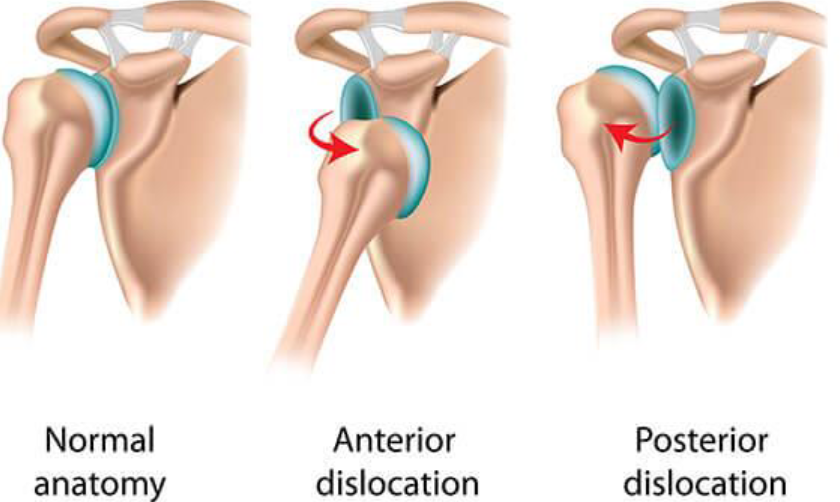
Dislocations
Common joint injury
Bones forced out of alignment
Subluxation: partial dislocation
Bursitis
Inflammation of bursa
Treated with rest, ice, NSAIDs
Tendonitis
Inflammation of tendon sheaths
Symptoms & treatments similar to bursitis
Arthritis
>100 different types of inflammatory or degenerative diseases that damage joints
Symptoms: pain, stiffness, and swelling of joint
Acute forms: caused by bacteria, treated with antibiotics
Chronic forms: osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gouty arthritis
Osteoarthritis
Most common type of arthritis
Irreversible
Usually normal part of aging process
Treatment: moderate activity, mild pain relievers, capsaicin creams

Rheumatoid Arthritis
Chronic, inflammatory, autoimmune disease of unknown cause
Immune system attacks own cells
Inflamed synovial membrane thickens into abnormal pannus tissue that clings to articular cartilage
Treatment includes steroidal and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to decrease pain and inflammation
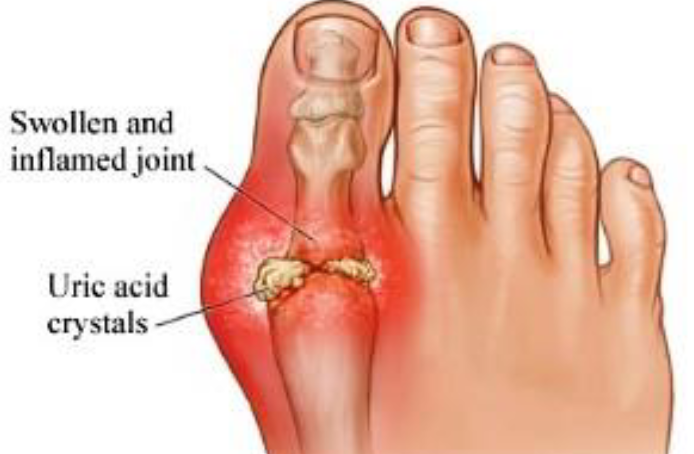
Gouty Arthritis
Deposition of uric acid crystals in joints and soft tissues
More common in men
Typically affects joint at base of great toe
In untreated gouty arthritis, bone ends fuse and immobilize join
Treatment: drugs, plenty of water, avoidance of alcohol and foods high in
purines, such as liver, kidneys, and sardines
Lyme Disease
Bacteria transmitted from tick bites
Symptoms: skin rash, flu-like symptoms, and foggy thinking
May lead to joint pain and arthritis
Treatment: long course of antibiotics