1.5 Lipids
1/8
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exclusion statement: the molecular structure of specific lipids
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Lipids
class of molecules that do not include true polymers
generally small in size
often not considered to be a macromolecule
nonpolar
hydrophobic
types are fats, phospholipids, steroids, and cholesterol
Fats
provide energy storage
support cell function
provide insulation to keep mammals warm
composed of glycerol and fatty acids
Glycerol
classified as an alcohol (hydroxyl groups)
Fatty acids
long carbon chains(carboxyl group at one end)
3 fatty acids join to a glycerol via ester linkage
bond between a hydroxyl and a carboxyl group
saturated or unsaturated
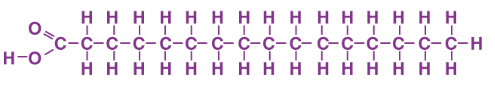
Saturated fatty acid
single bonds between carbons in the carbon chain=more hydrogen
think saturated with hydrogen
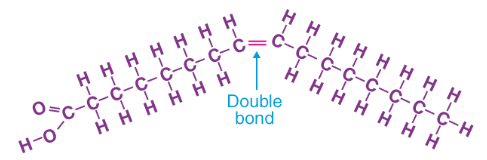
Unsaturated fatty acid
contains one or more double bonds, which causes the carbon chain to kink
the more double bonds in a fatty acid tail, the more unsaturated the lipid becomes
the more unsaturated a lipid is, the more liquid it is at room temperature
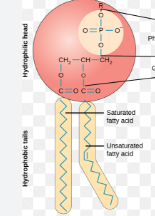
Phospholipids
major component of cell membranes
two fatty acids attached to a glycerol and a phosphate
assemble as a bilayer in H2O
tails are hydrophobic (non polar)
head is hydrophilic(polar)
group together to form the lipid bilayers found in plasma and cell membranes.
Steroids
hormones that support physiological functions like growth and development, energy metabolism, and homeostasis
have 4 fused rings
unique groups attached to the ring determine the type of steroid ex testosterone (not gonna ask about unique groups)
Cholesterol
provides essential structure stability to animal cell membranes