A Level CIE Biology: 13 Photosynthesis
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
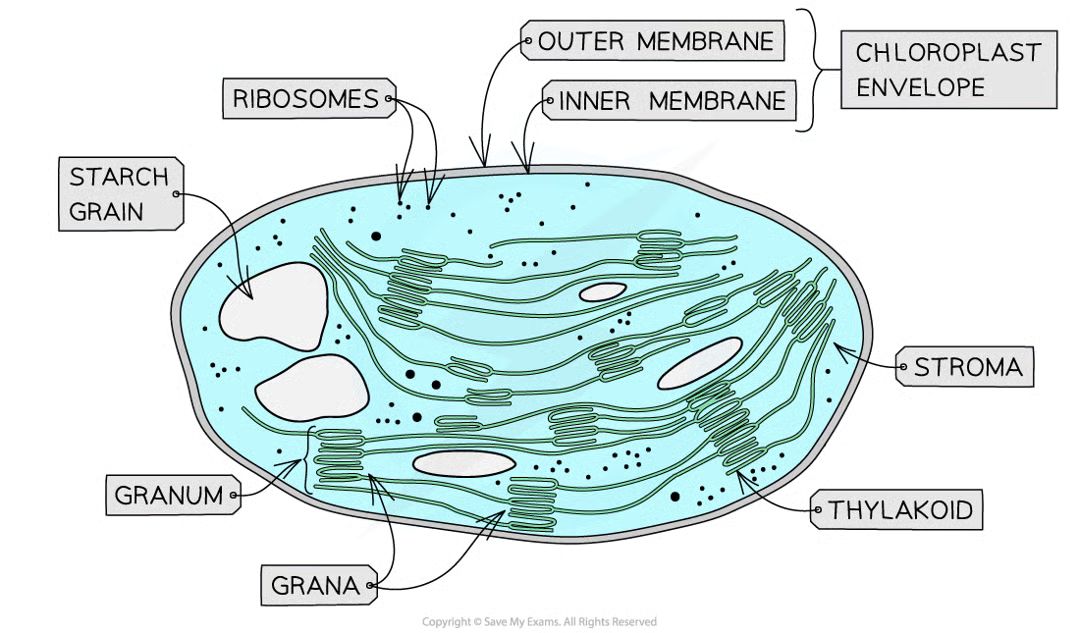
what are chloroplasts
organelles in plant cells where photosynthesis occurs where each chloroplast is surrounded by double-membrane envelope [phospholipid bilayer]
what are chloroplasts filled with and what is the function
stroma, site of light-independent stage of photosynthesis
what is found in the stroma
system of membranes where the light-dependent stage of photosynthesis is carried out
what do the membranes in the stroma contain
pigments, enzymes, electron carriers required for light dependent reactions
where and what are thylakoids
in the membrane series, series of flattened, fluid filledsacs
what do thylakoids stack up to form
grana/granum
what are grana connected by and why
membranous channels called stroma lamellae. ensure stacks of sacs are connected but distanced from each other
what do the membranes of grana create
create a large surface area to increase the number of light-dependent reactions that can occur
why is the membrane system necessary
provides large number of pigment molecules in an arrangement that ensures as much light as necessary is captured
what 3 things the stroma also contain and why
small 70s ribosomes - where proteins coded for by this loop of chloroplast dna are produced
loop of dna - codes for some chloroplast proteins [other done by dna in plant cell nucleus ]
starch grains - sugars formed during photosynthesis is stored as starch in here
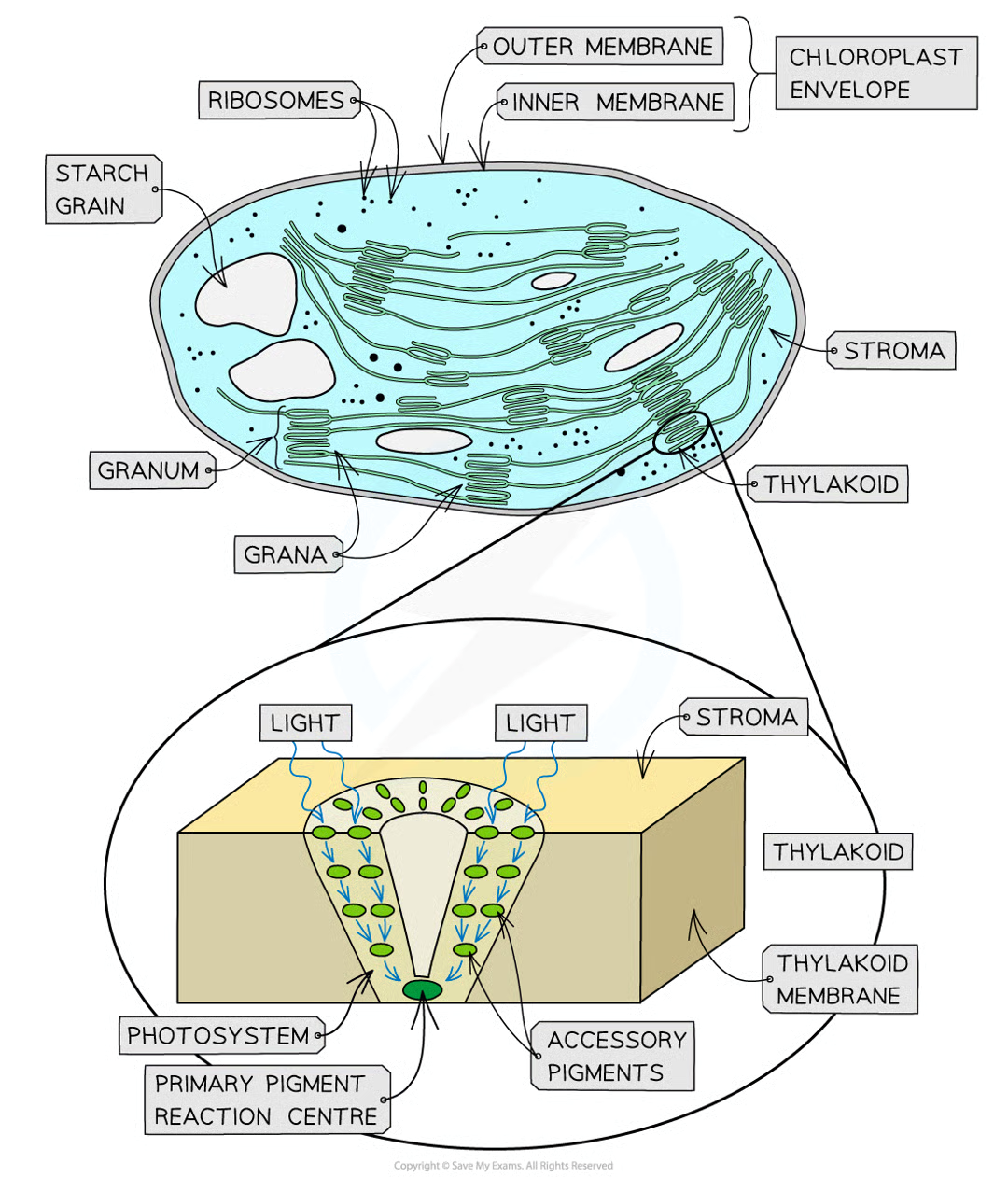
chloroplast structure parts 7
ribosomes
chloroplast envelope - outer memb, inner memb
starch grain
stroma
thylakoid
granum
grana
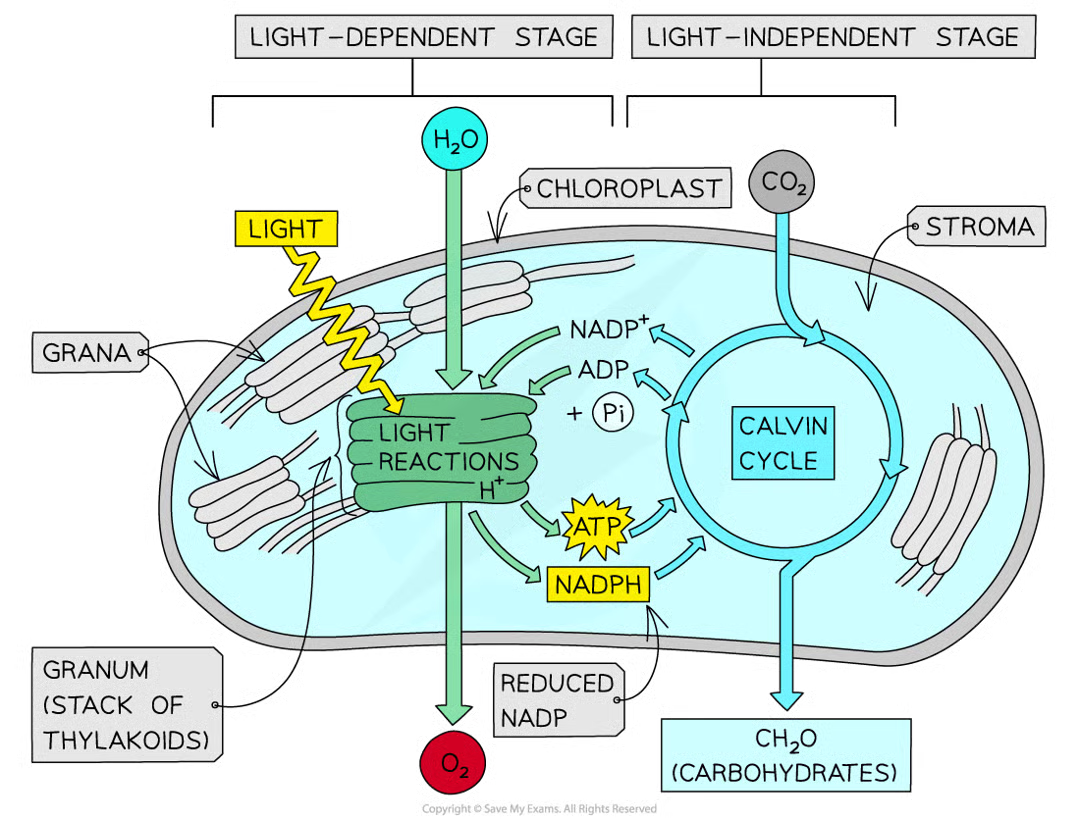
two stags of photosynthesis + where
light-dependent stage (thylakoids)
light-independent stage (stroma)
light dependent stage summary
nadh produced when h+ combines w/ carrier molecule NADP using e- from photolysis of water
atp produced in photophosphorylation (uses H+ gradient generated by photolysis of water
energy from atp and h from nadph are passed from ld stage to li stage of photosynthesis
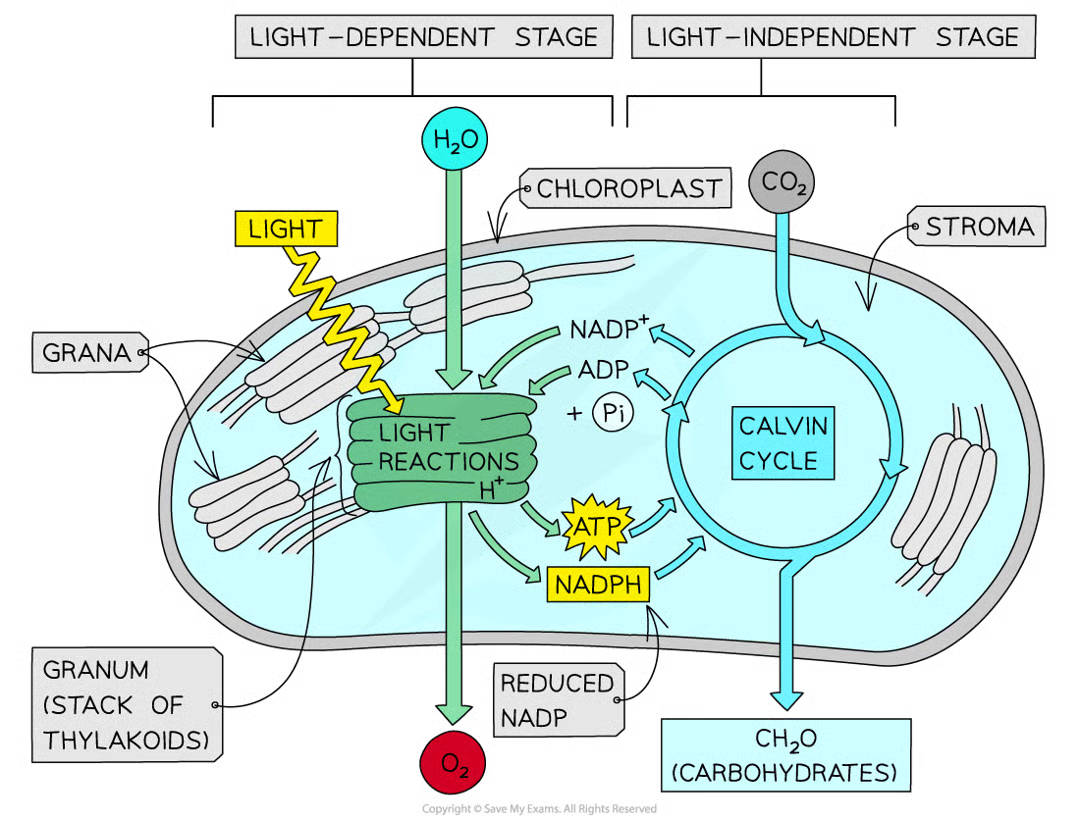
light independent stage summary
energy and h from ld stage used
takes place in calvin cycle
complex organic mols produced including and not limited to carbs e.g. starch for storage, sucrose for translocation around plant and cellulose for cell walls
where does ld stage of photosyn occur
thylakoid membranes and thylakoid spaces
what do thylakoid membranes contain
pigments, enzymes and electron carriers
why and how is there a large sa
membranes of grana, to increase no. ld reactions
photosystems
pigment molecules arranged in light harvesting clusters known as photosystems
what does membrane system provide to ensure as much light as necessary is captured
large no. pigment mols
arrangement in photosystem
diff pigment mols arranged in funnel-like structures the thylakoid membrane (each pig mol passes energy down to next pig mol in cluster until reaches primary pigment reaction centre)
what is dissolved in stroma fluid
co2, sugars, enzymes and other mols
what is stroma
fluid that fills chloroplasts and surrounds thylakoids and site of li stage of photosyn
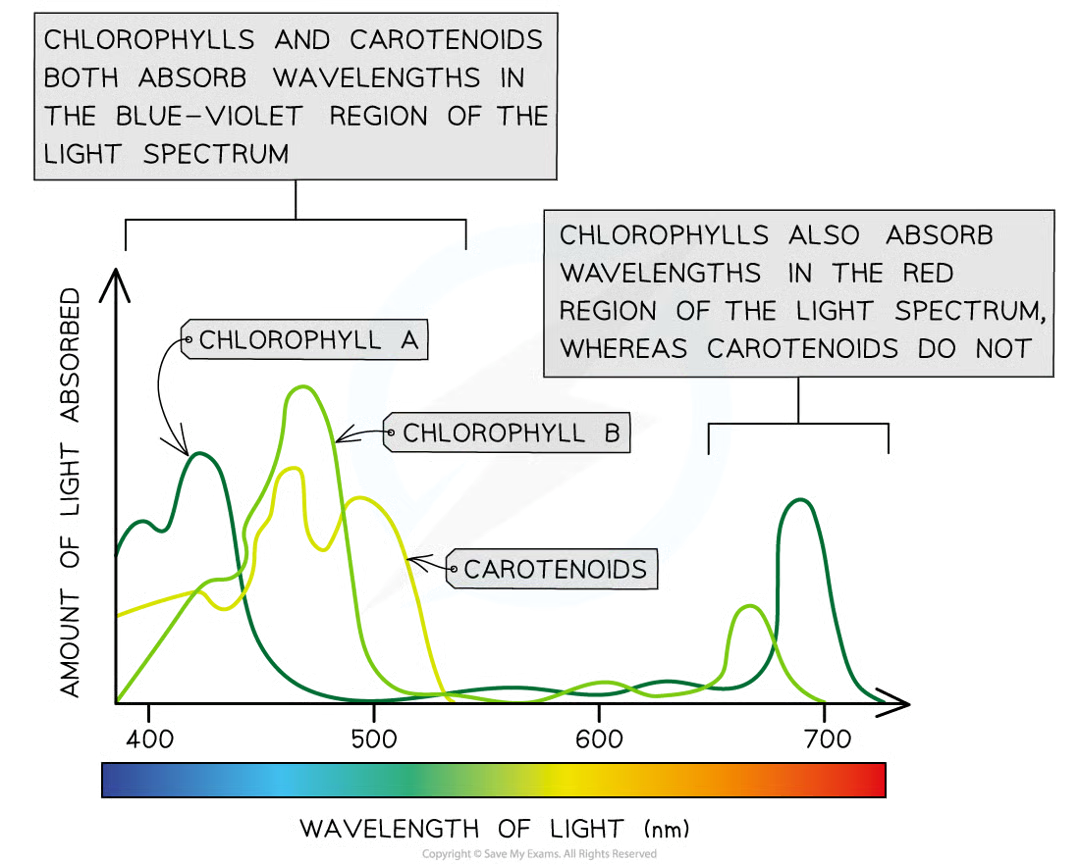
diff photosynthetic pigments within thylakoids absorb diff…
wl of light
chlorophylls name of pigment and colour of pigment
chlorophyll a and b, light green and dark green
pigment groups
chlorophylls, carotenoids
carotenoids name of pigment and colour of pigment
beta carotene and xanthophyll, orange and yellow
chlorophylls absorb what wl
blue-violet and red regions of light spectrum and reflect green light = plants green
carotenoids absorb what wl of light
blue-violet region of spectrum mainly
absorption spectrum
graph that shows absorbance of diff wl of light by particular pigment
action spectrum
graph that shows rate of photosyn at diff wl of light
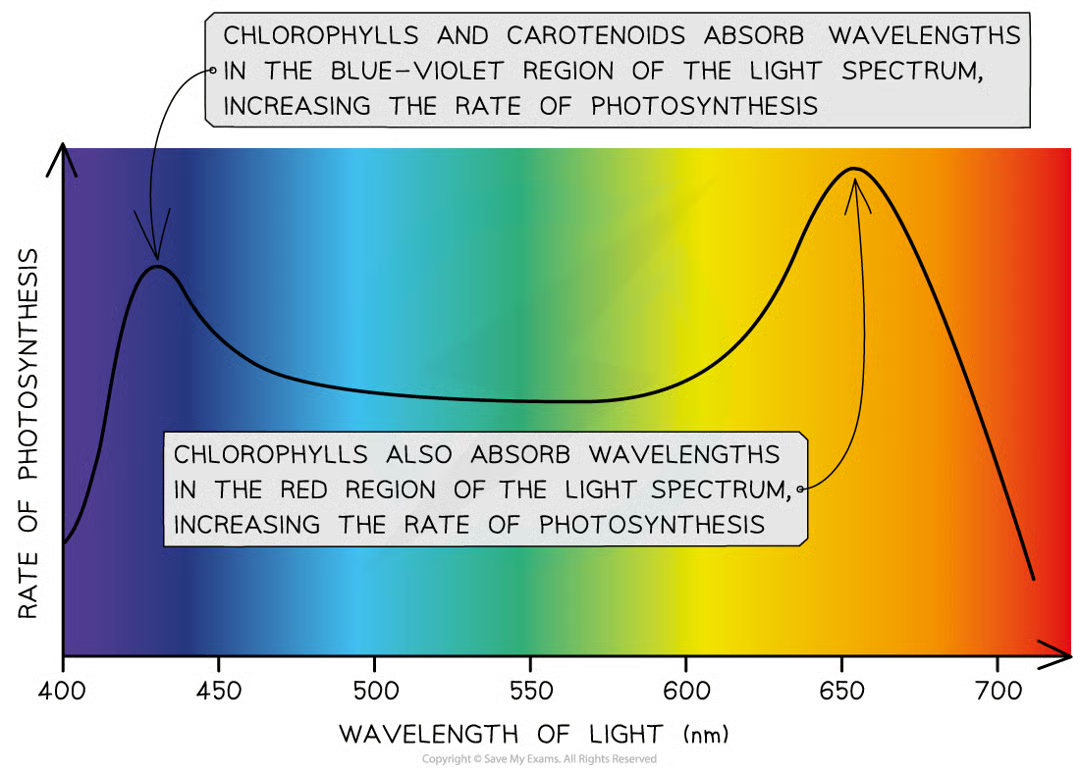
when is rate of photosyn highest
at blue-violet and red regions of light spectrum as these are wl of light that plants can absorb
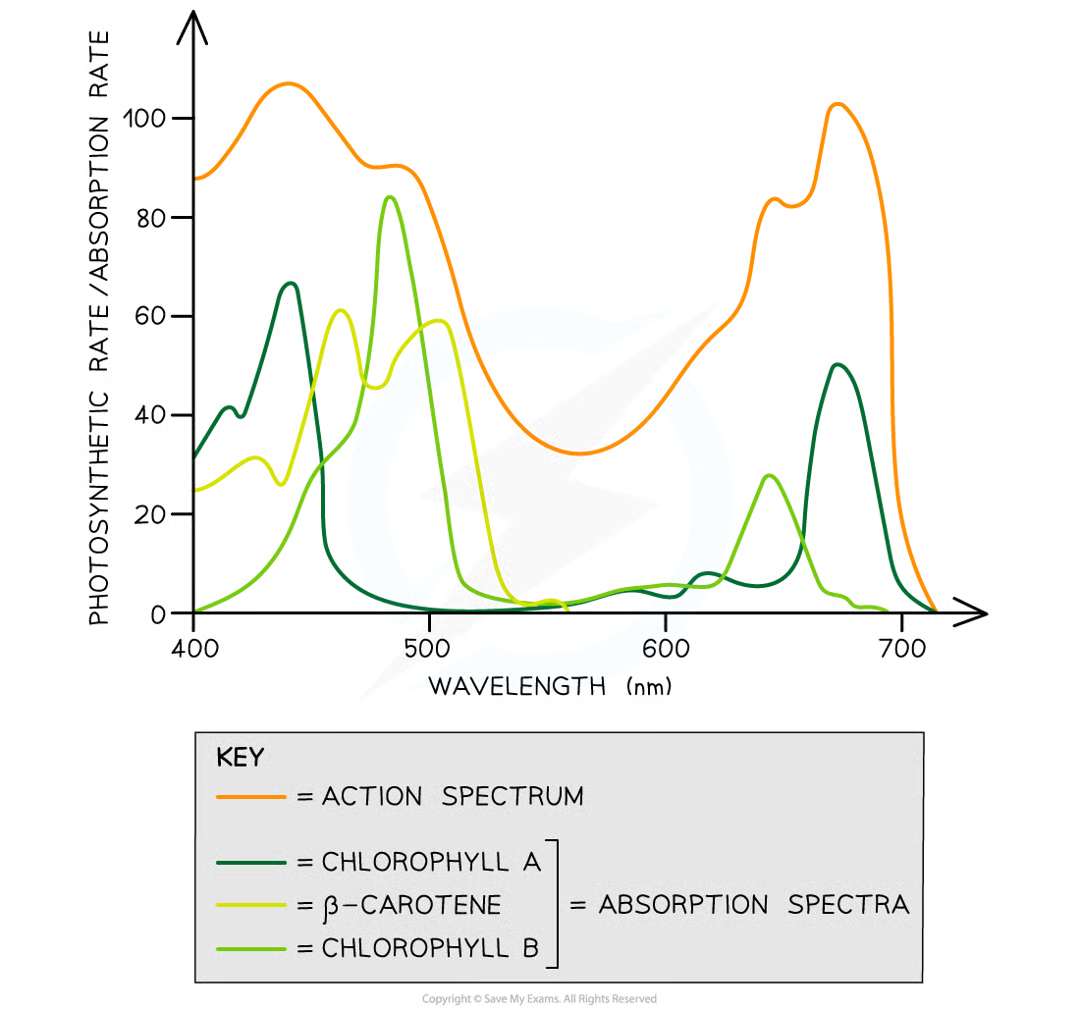
how is there a strong correlation between cumulative absorption spectra of all pigments and action spectrum
both graphs have 2 main peaks at blue-violet region and red region of light spectrum
both graphs have trough in green-yellow region of light spectrum
chromatography
experimental technique that is used to separate mixtures
chromatography process
mixture dissolved in fluid/solvent called mobile phase and dissolved mixture passes through static material called stationary phase
diff components within mix travel thru material at diff speeds
diff components separate
retardation factor (Rf) can be calc for each comp of mixture
Rf
distance travelled by comp/dist travelled by solvent
two most common techniques for separating photosynthetic pigments:
paper chromatography - mix of pigments passed through paper/cellulose
thin layer chromatography - mix of pigments passed through thin layer of adsorbent (e.g. silica gel) through whicb mix travels faster and separates more distinctly
what does rf value show
how far dissolved pigment travels through stationary phase (smaller rf = pigment less soluble and larger)
how can chromatography be used with a leaf
separate and identify chloroplast pigments that have been extracted from leaf as each pigment has unique rf value
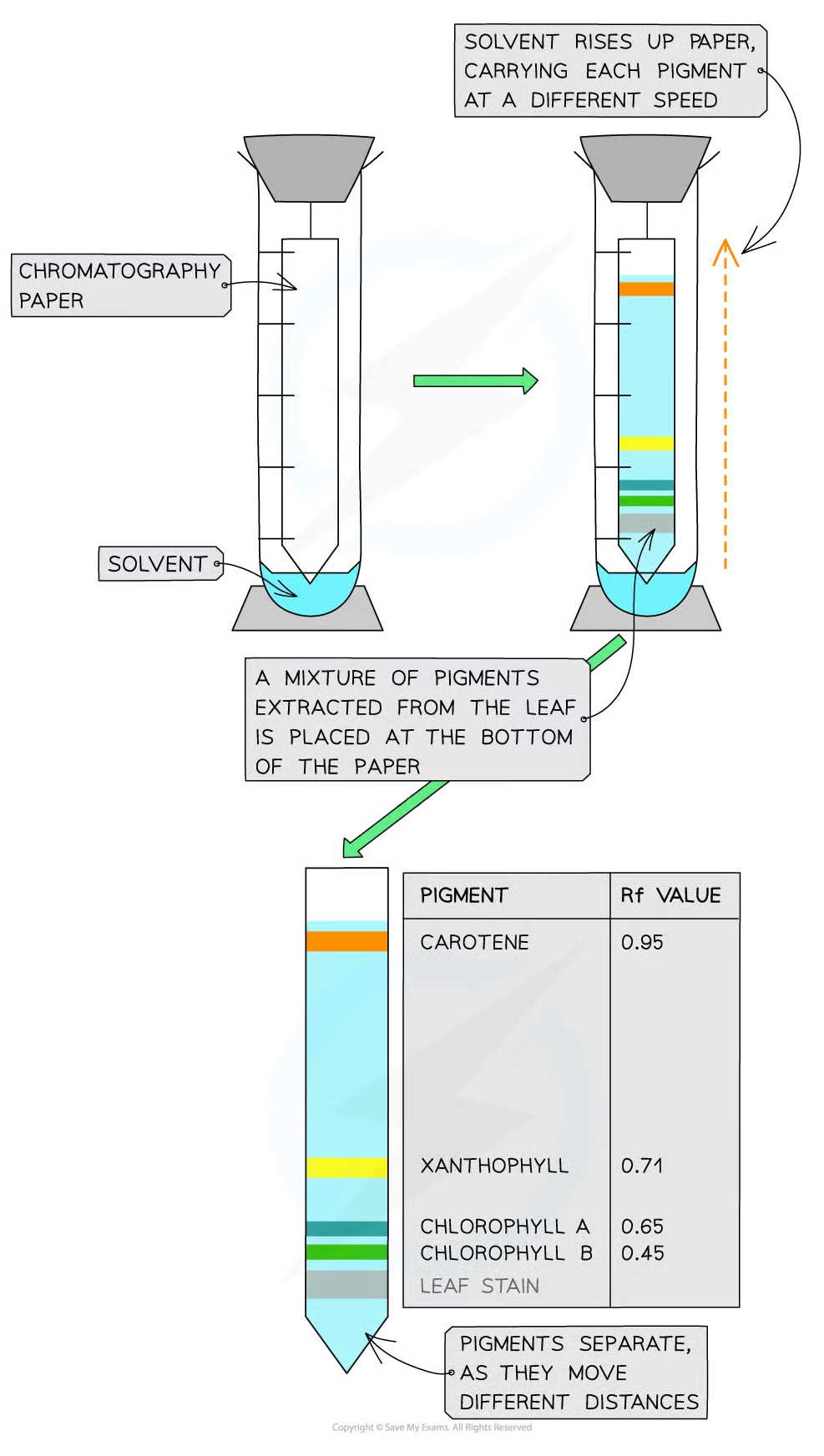
rf values depend on solvent but generally: 4
carotenoids have highest rf values close to 1
chlorophyll b has must lower rf value
chlorophyll a has rf value somewhere between carotenoids and chlor b
small rf values indicate less soluble and larger pigment
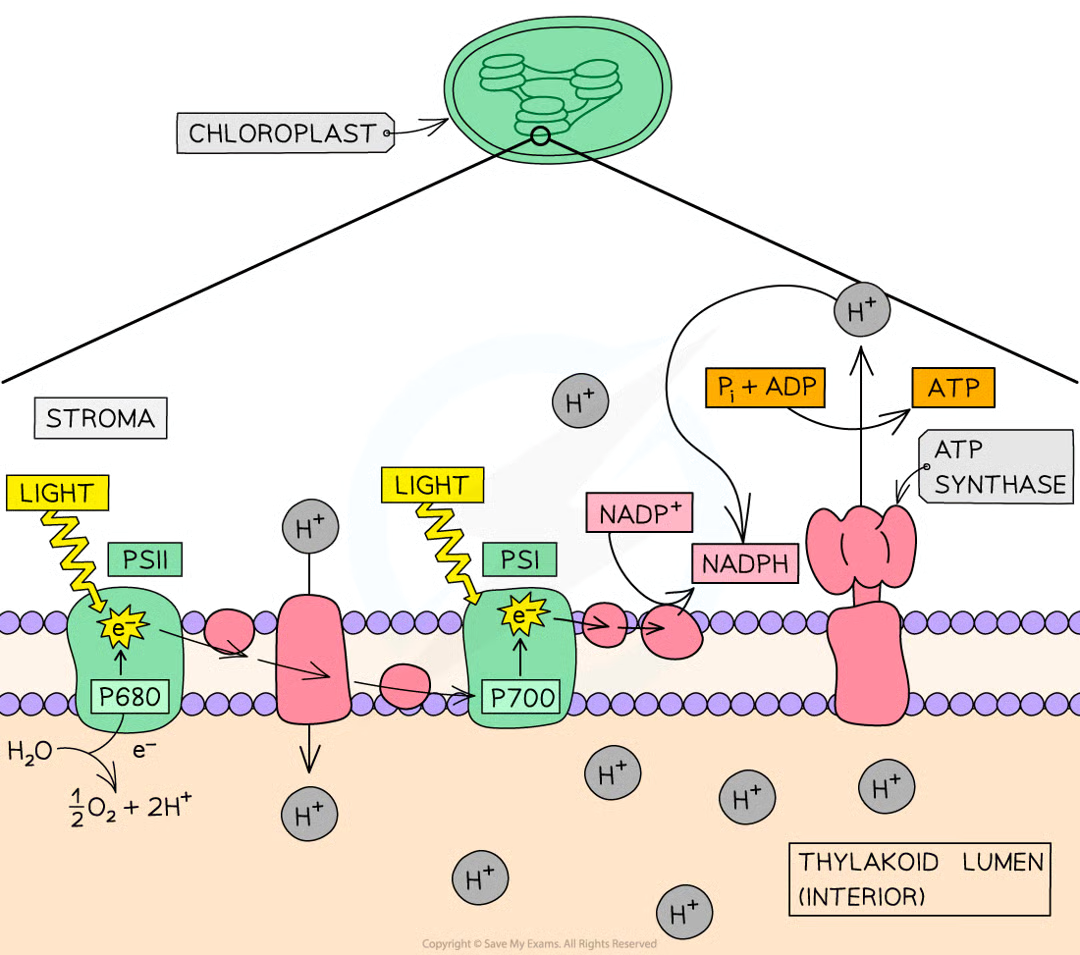
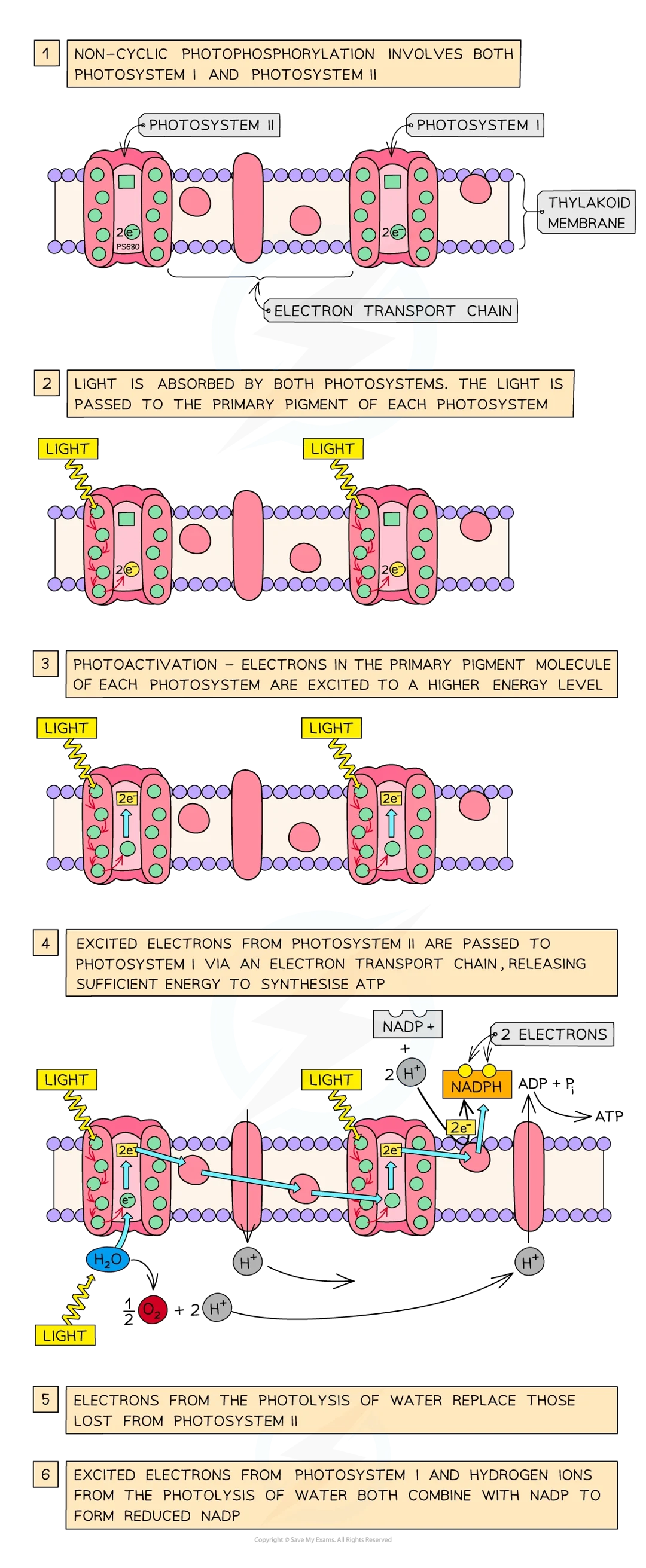
during ld stage of photosyn
light energy used to break down water (photolysis) to produce H+, e- and oxygen in thylakoid lumen
proton gradient formed due to photolysis of water, resulting in high conc of H+ in thylakoid lumen
e- travel through etc of proteins within memb
nadph is produced when h+ ions in stroma nad e- from etc combine w/ carrier molecule nadp
atp is produced during process known as photophosphorylation (adp+pi → atp) using proton gradient between thylakoid lumen and stroma to drive enzyme atp synthase
photophosphorylation of adp to atp can be ___ or ____ how
cyclic, non-cylic depending on pattern of e- flow in photosystem I or photosystem II or both
in cyclic photophosphorylation…
only photosystem I involved
in non-cyclic photophosphorylation…
both photosystem I and photosystem II are involved
photosystems
collections of photosynthetic pigments that absorb light energy and transfer the energy onto e-, each contains primary pigment
photosystem II primary pigment + location
beginning of etc where photolysis of water takes place. primary pigment p680 bc absorbs light at wl 680nm
photosystem I primary pigment and location
middle of etc, primary pigment p700 bc absorbs light at wl 700nm
energy carried by atp is used…
during li reactions of photosyn
what does cyclic photophosphorylation involve
photosystem I (PSI) only
cyclic psi photophosphorylation process
light absorbed by psi located in thylakoid memb and passed to psi primary pigment p700
e- in primary pig mol (chlorophyll) is excited to higher energy level and emitted from chlorophyll mol in photoactivation
excited e- captured by e- acceptor and transported via chain of e- carriers (etc) before passing back to chlorophyll mol in psi
as e- pass thru etc they provide energy to transport H+ from stroma to thylakoid lumen via proton pump
buildup of protons in thylakoid lumen drives synthesis of atp from adp and an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) thru chemiosmosis
then atp passes to li reactions
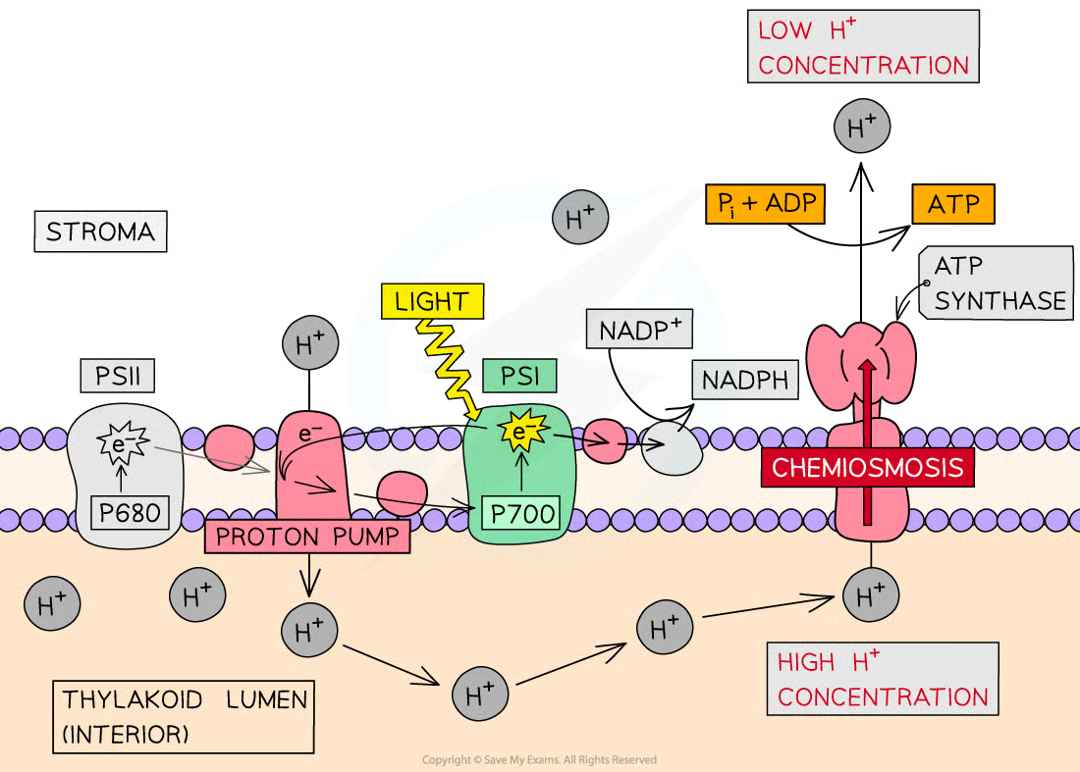
chemiosmosis
movement of chemicals/protons down conc grad, energy released from this can be used by atp synthase to synthesise atp
what does non cyclic photophosphorylation involve
psi and psii
where is light asborbed by psii
thylakoid memb and passed to psii primary pigment p680
non cyclic process (psii)
e- in primary pig mol excited to higher energy level and is emitted from chlorophyll mol in photoactivation
excited e- passed down chain of e- carriers (etc) before being passed on to psi
during this atp is synthesised from adp and an inorganic phosphate group (Pi) by process of chemiosmosis
atp then passes to li reactions
psii contains water splitting enz called oxygen evolving complex which catalyses breakdown (photolysis) of water by light: 2H2O → 4H+ + 4e- + O2
as excited e- leave primary pig of psii and are passed on to psi, they are replaced by e- from photolysis of water
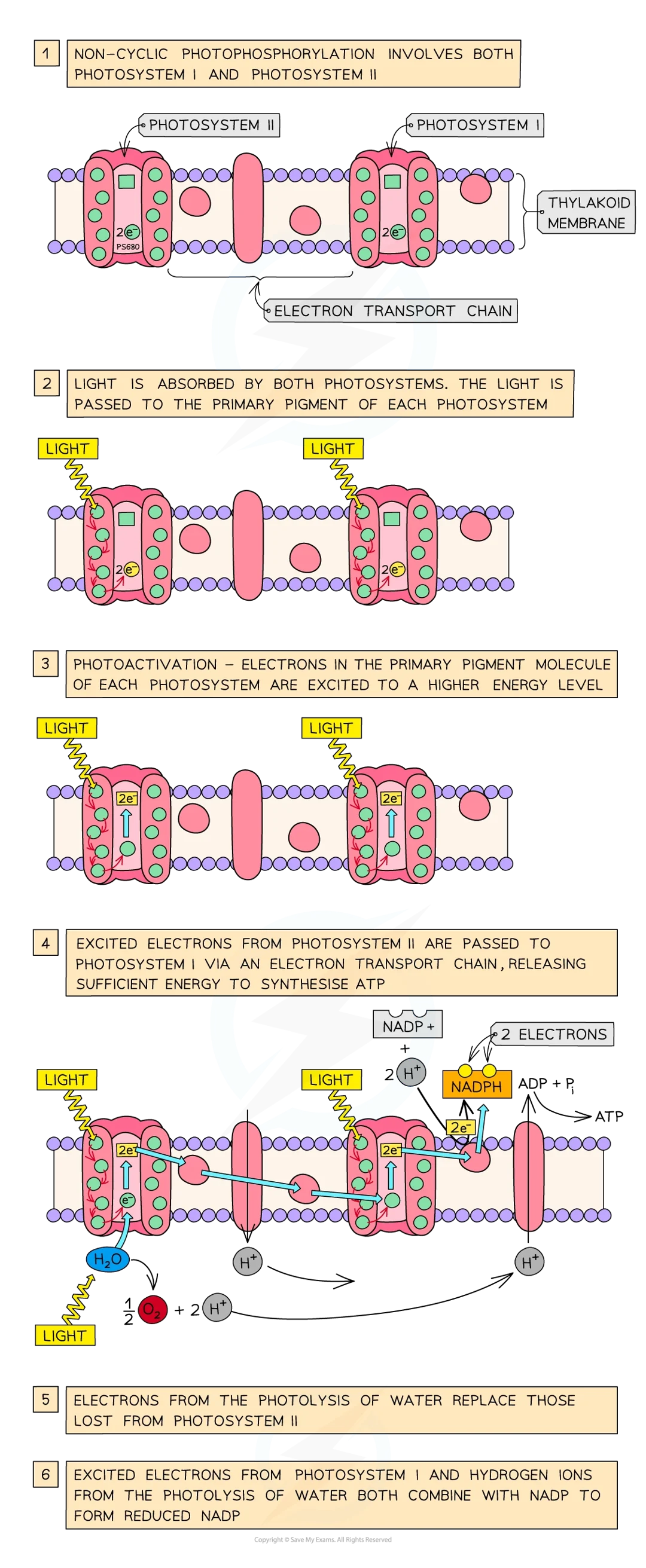
non cyclic psi process
at same time as photoactivation of e- in psii, e- in psi also undergo photoactivation
excited e- from psi also pass along etec
e- combine w/ h+ produced by photolysis of water and the carrier mol nadp to give nadph: 2H+ + 2e- + NADP → reduced NADP
nadph then passes to li reactions to be used in synth of carbs
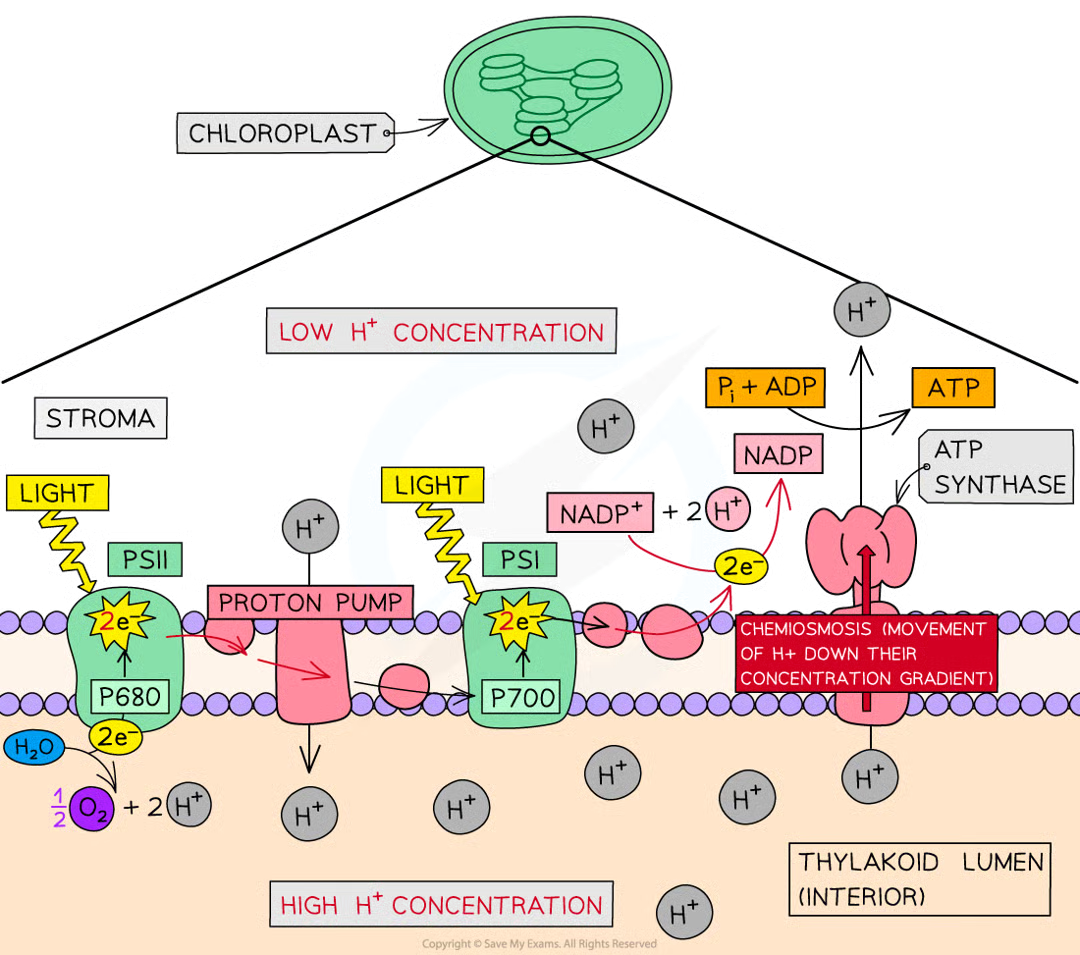
phosphorylation and chemiosmosis
during photophosphorylation, energetic e- captured by e- acceptor in thylakoid memb
energetic e- passed along chain of etc
e- carriers are alternately reduced as they gain e- and then oxidised as they lose e- by passing to next carrier
excited e- gradually release energy as they pass thru etc
released energy usedd to actively transport h+ across thylakoid memb from stroma (fluid within chloroplasts) to thylakoid lumen
proton pump transports protons across thylakoid memb from the stroma to thylakoid lumen
creates a proton grad w high conc of protons in thylakoid lumen and low conc in stroma
protons then return to stroma moving down proton conc grad by facil diffusion thru transmembrane atp synthase enz in chemiosmosis
process provides energy needed to synthesise atp by adding an inorganic phosphate group Pi to ADP (ADP + Pi → ATP)
whole process known as photophosphorylation as light provides the intial energy source of atp synth
after being passed down etc de energised e- from psii are taken up by psi
what is passed from the ld stage to the li stage of photosyn
energy from atp and hydrogen from nadph
what is the eneryg and hydrogen used during
li reactions/calvin cycle to produce complex organic molecules including but not limited to carbs e.g. starch,sucrose, cellulose
why cant the calvin cycle continue indefinitely indarkness
inputs run out bc even tho photosyn doesnt in itself need energy from li and can take place in light or darkness, it requires inputs of atp and nadph from ld stage
3 main steps within calvin cycle
rubisco catalyses the fixation of carbon dioxide by combination w molecule of ribulose bisphosphate (RuBP) a 5C compound to yield 2 mols of glycerate 3-phosphate (GP) a 3C compound
gp reduced to triose phosphate (tp) in reaction involving nadph and atp
RuBP is regenerated from tp in reactions that use ATP
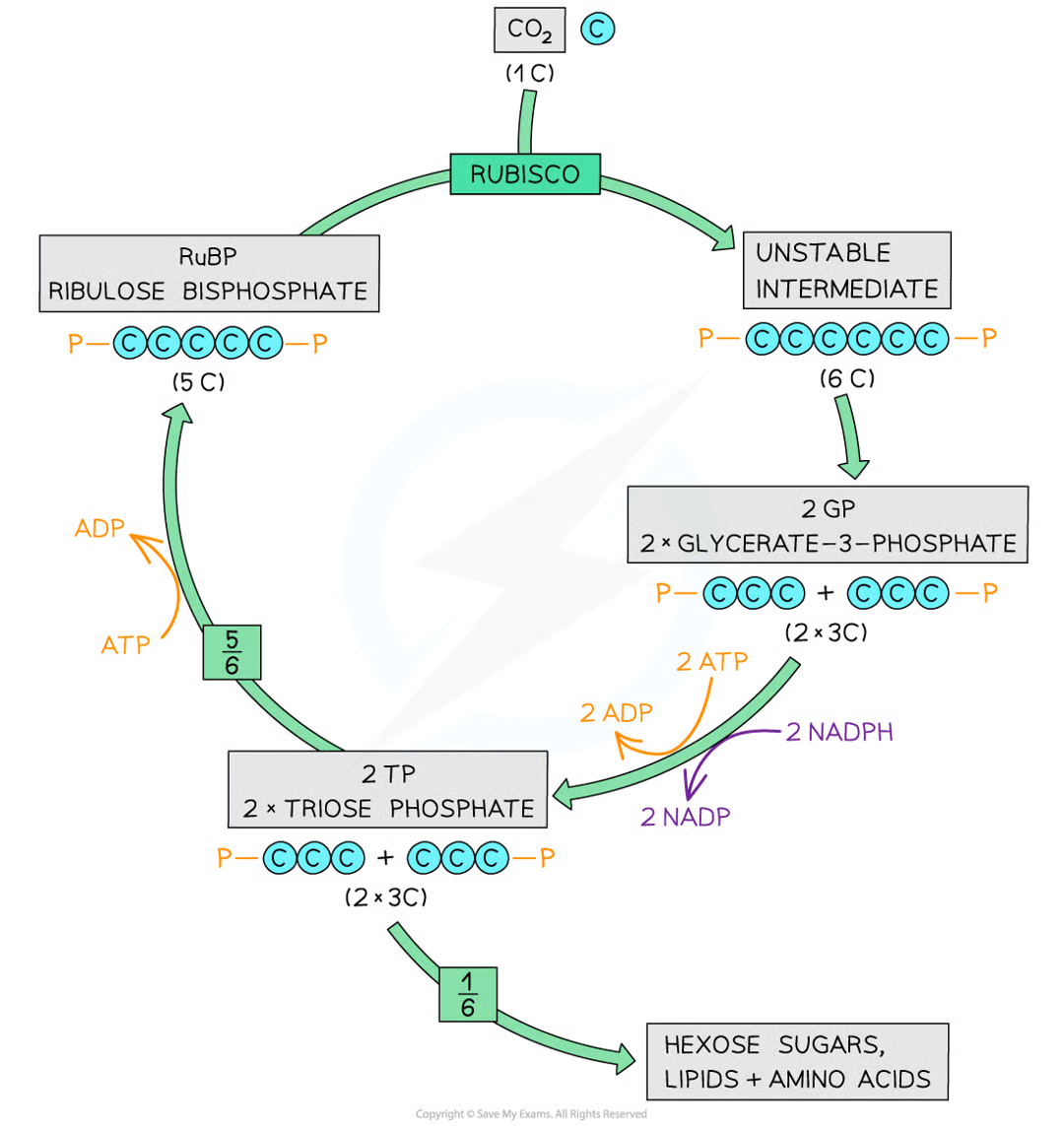
how does carbon fixation occur
co2 combines w/ 5c ribulose bisphosphate (rubp)
enzyme aclled rubisco (ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase) catalyses reaction
resulting 6c compound unstable and slpits into 2 3c compounds = glycerate 3-phosphate (gp)
co2 has been fixed (removed from ext env and become part of organic matter of plant cell)
gp not carb but next step in calvin cycle converts it into one
how does reduction of gp occur
energy from atp and h from nadph both produce during ld stage of photosyn are used to reduce gp to phosphorylated three-carbon 3c sugar known as triose phosphate (tp)
1/6 of those tp mols used to produce useful roganic molecules needed by plant:
tp can condense to become hexose phosphates 6c which can be used to make starch, sucrose or cellulose
tp can be converted to glycerol and glycerate 3-phosphates to fatty acids which join to form lipids for cell membranes
tp can be used in prod of aas for protein synth
regeneration of ribulose bisphophate
5/6 of tp mols used to regen RuBP
requires atp
calvin cycle intermediates
intermediate mols of calvin cycle such as gp and tp are used to produce other mols
gp is used to produce some aas
tp is used to produce
hexose phosphates (6c) whihc can be used to produce starch, succrose or cellulose
lipids for cell membs
aas for protein synth
5 factors plant for photosynthesis
the presence of photosynthetic pigments
a supply of co2
a supply h2o
light energy
suitable temperature
if there is a shortage of factors…/below opt rate for plant
photosynthesis cannot occur at its maximum possible rate
3 main ext factors that affect the rate of photosyn (limiting factors of photosyn)
light intensity
co2 conc
temp
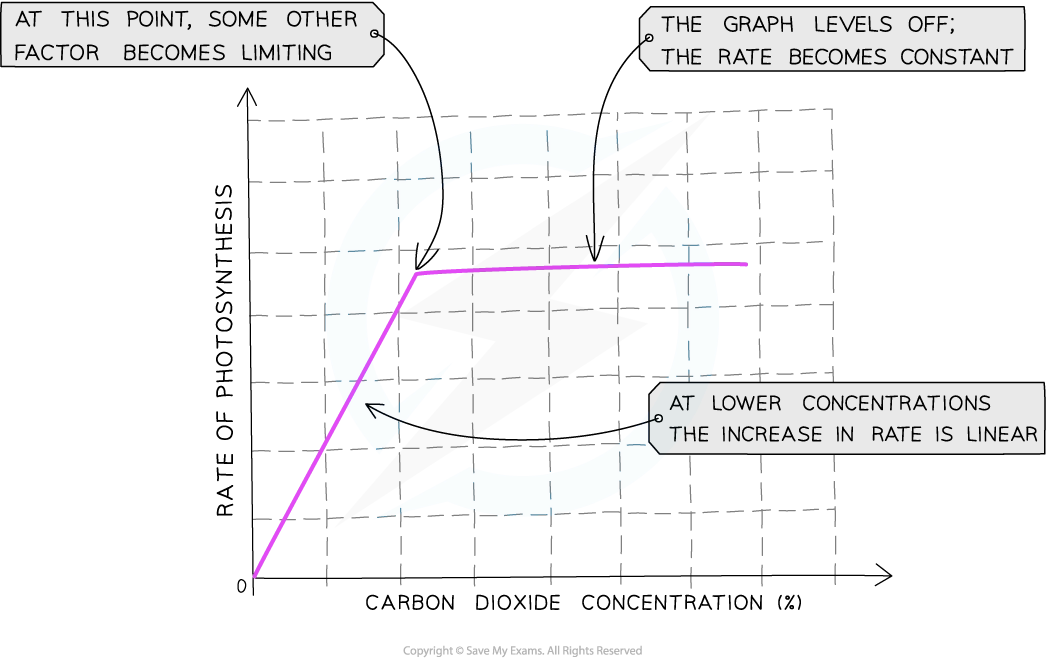
when temp and co2 conc are constant what affects rop
changes in light intensity rate of
why does rop increases as light intens increases
greater light intensity, more eneryg supplied to plant so faster ld stage of photosyn occurs
produces more atp and nadph for calvin cycle (li stage) which can also occur at greater rate
then light intesity will become limiting factor
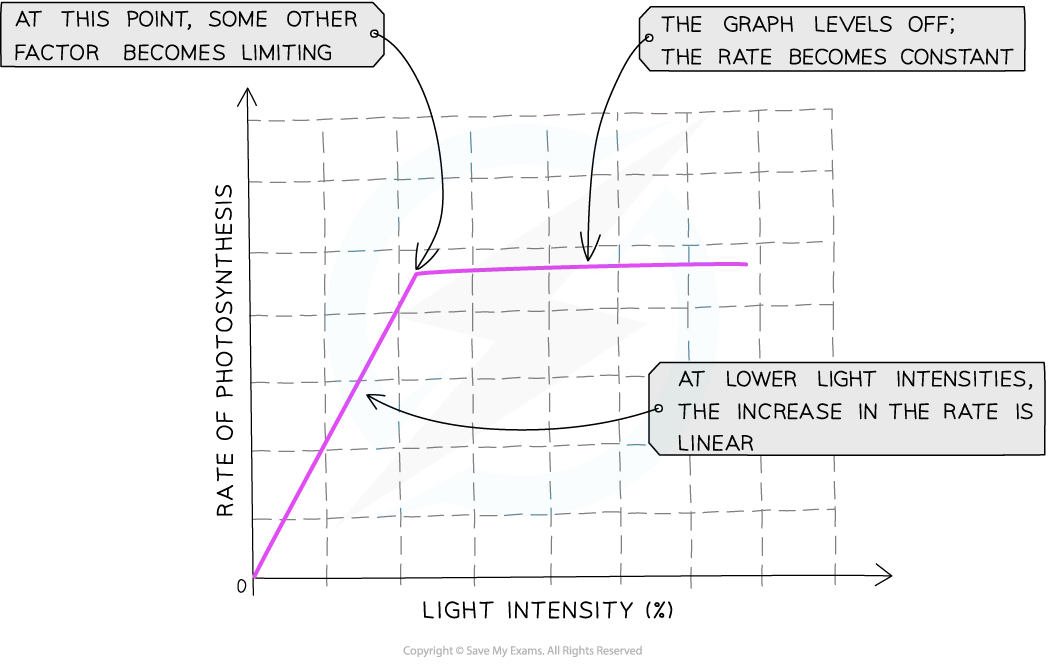
what happens if light intesity continues to increase
relationship above will no longer apply and rop will reach plateau
li no longer limiting factor of photosyn so another factor will become the limitiing
factosr which could be limitng rate when line on graph is horizontal include temp being too low or too high or not enough co2
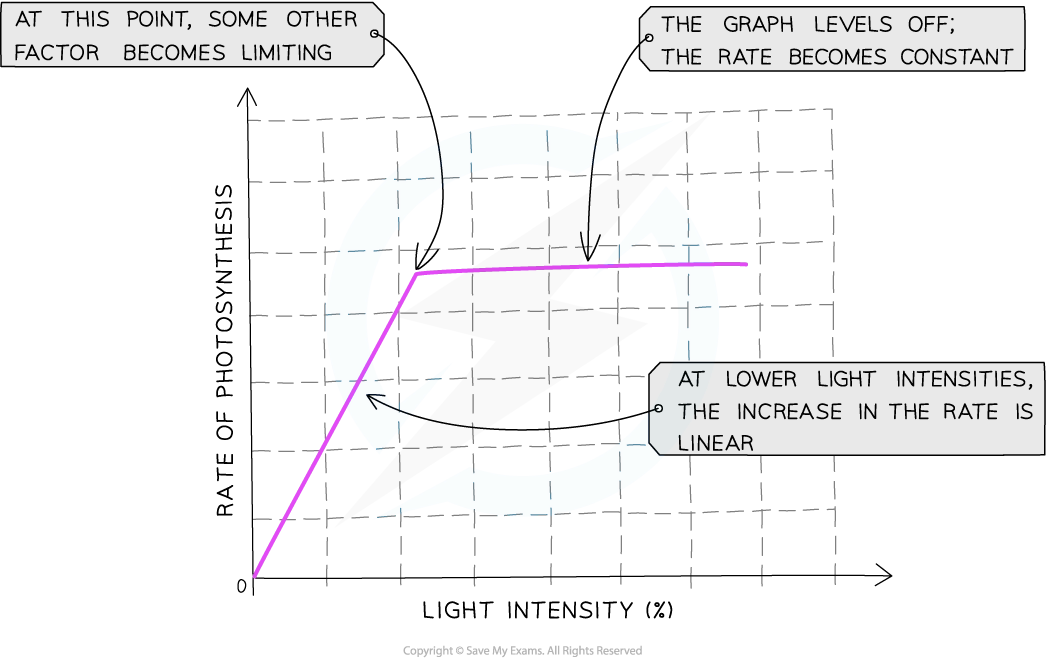
why rop increases as co2 increases
co2 one of the raw mats required for photosyn
required for li stage of photosyn when co2 is combined w/ 5c RuBP
the more co2 present the faster the calvin cycle can occur and faster overall rop
continues until other factor required for photosyn rpevents rate of increasing further bc in short supply
factors could be limiting the rate when line on graph horizontal include temp being too low/high or not enough light
as temp increases…
rop increasess as reaction is controlled by enzymes
this trend only continues up to a ceratin temp beyond which enz begin to denature and the rate of reaction decreases
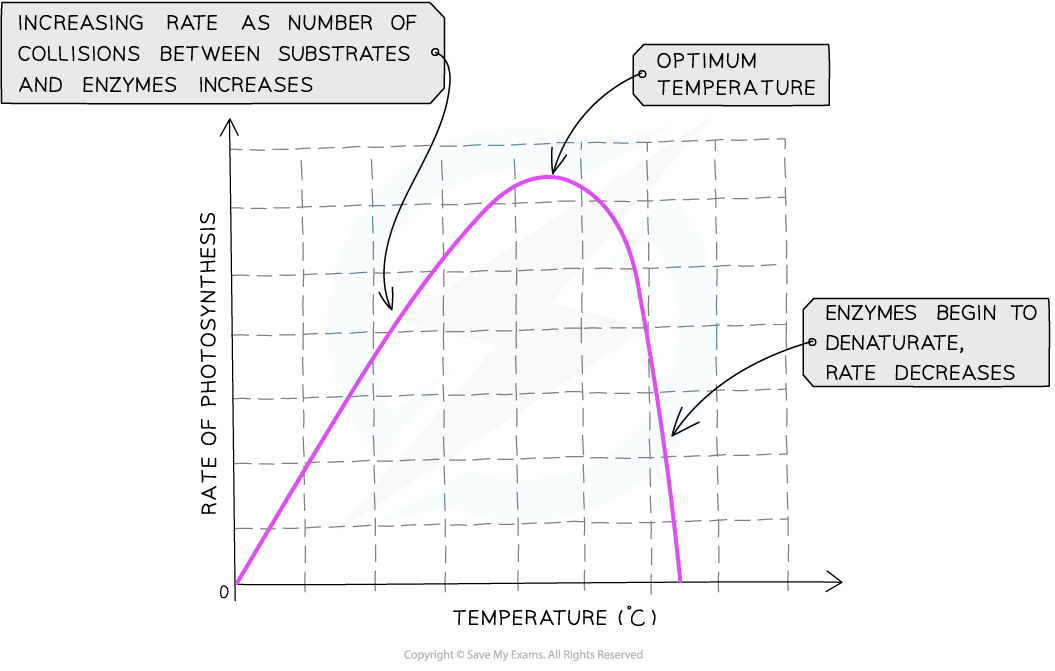
why is calvin cycle a affected by temp
temp has large effect on ror for metabolic reactions
for photosyn, temp has little significant effect on ld reactions as these r driven by energy from light rather than k.e. of reacting mols
however calvin cycle affected by temp as li reactions are enz controlled reactions e.g. rubisco catalyses the reaction between co2 and the 5c RuBP
why does dcpip and methylene blue change colour during photosyn 8
ld reactions of photosyn take place in thylakoid memb and involve the release high energy e- from chlorophyll a mols
mols picked up e- acceptors and then passed down etc
if redox indicator present the indicator takes up the e- instead
dcpip: oxidised (blue) → accepts e- → reduced (colorless)
methylene blue: oxidised (blue) → accepts e- → reduced (colorless)
may appear green bc chlorophyll green color
rate at which redox indicator cahnges color from oxidised state to reduced can be used as measure of rop
when light is at high intens or at more preferable light wls the rop of e- faster so roreduction of indicator is faster
Investigating the Rate of Photosynthesis: Redox Indicators method 4 + extra
leaves crushed in liquid called isolation medium
produces concentrated leaf extract that contains suspension of intact and functional chloroplast
medium must have same water potential as leaf cells so chloroplasts dont shrivel/burst and contain buffer for constant pH
should also be ice cold to avoid damaging chlor and maintain memb structure
small tubes set up w diff intensities or diff colours/wls of light shining
diff intensities must all be same wl
diff wl must all be smame intensity
dcpip or methylene blue added to each tube as well as small vol of leaf extract
time taken for redox indic to go colorless recorded = rop
how can effecft of limiting factors on rop be investigated with aquatic plants e.g. elodea or cabomba (pondweed)
light intensity - change distance of source from plant (light intens = 1.d²)
co2 conc - add diff qts of sodium hydrogencarbonate to water surrounding plant which dissolves to prod co2
temp of solutoin surrounding plant - boiling tube w. submerged plant in water baths of diff temps
while changing one of these factors during investigation as described below ensure other two remain constant e.g. light intens on rop needs glass tank between lamp and boiling tube containing pondweed to asborb heat from lamp so no temp change
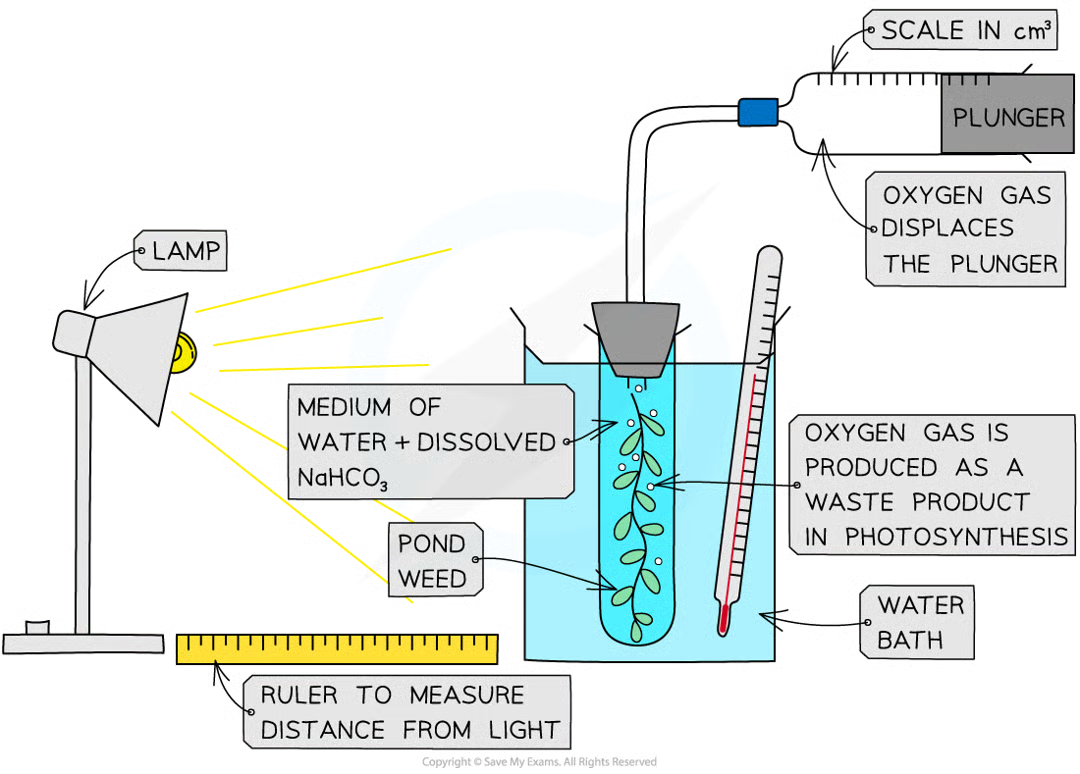
Investigating the Rate of Photosynthesis: Aquatic Plants method
Ensure water is well aerated before by bubbling air through so oxygen gas given off by the plant during the investigation forms bubbles and does not dissolve in the water
Ensure that the plant has been well illuminated before starting the experiment
This will ensure that the plant contains all the enzymes required for photosynthesis and that any changes in rate are due to the independent variable rather than an increase in enzyme activity
Cut the stem of the pondweed cleanly just before placing it into the boiling tube
Cutting the stem at an angle provides a larger surface area from which bubbles can form
Set up the apparatus (as shown below) in a darkened room
This ensures that the lamp is the only light source and so allows light intensity to be controlled
Ensure that the pondweed is fully submerged in sodium hydrogencarbonate solution (1%); this ensures that the pondweed has a controlled supply of carbon dioxide for photosynthesis
Measure the volume of gas collected in the gas syringe in a set period of time, e.g. 5 minutes
Repeat step 5 at least twice more
Change the independent variable and repeat step 5 again
The independent variable could be the light intensity, carbon dioxide concentration or temperature depending on which limiting factor you are investigating
Record the results in a table and plot a graph of the volume of oxygen produced per minute against the independent variable