Biology CLEP Molecular and Cellular Biology
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Non-reactionary elements
Elements with a full valence shell
Endothermic
Absorb energy
Exothermic
Release energy
Electronegativity
Ability to attract electrons
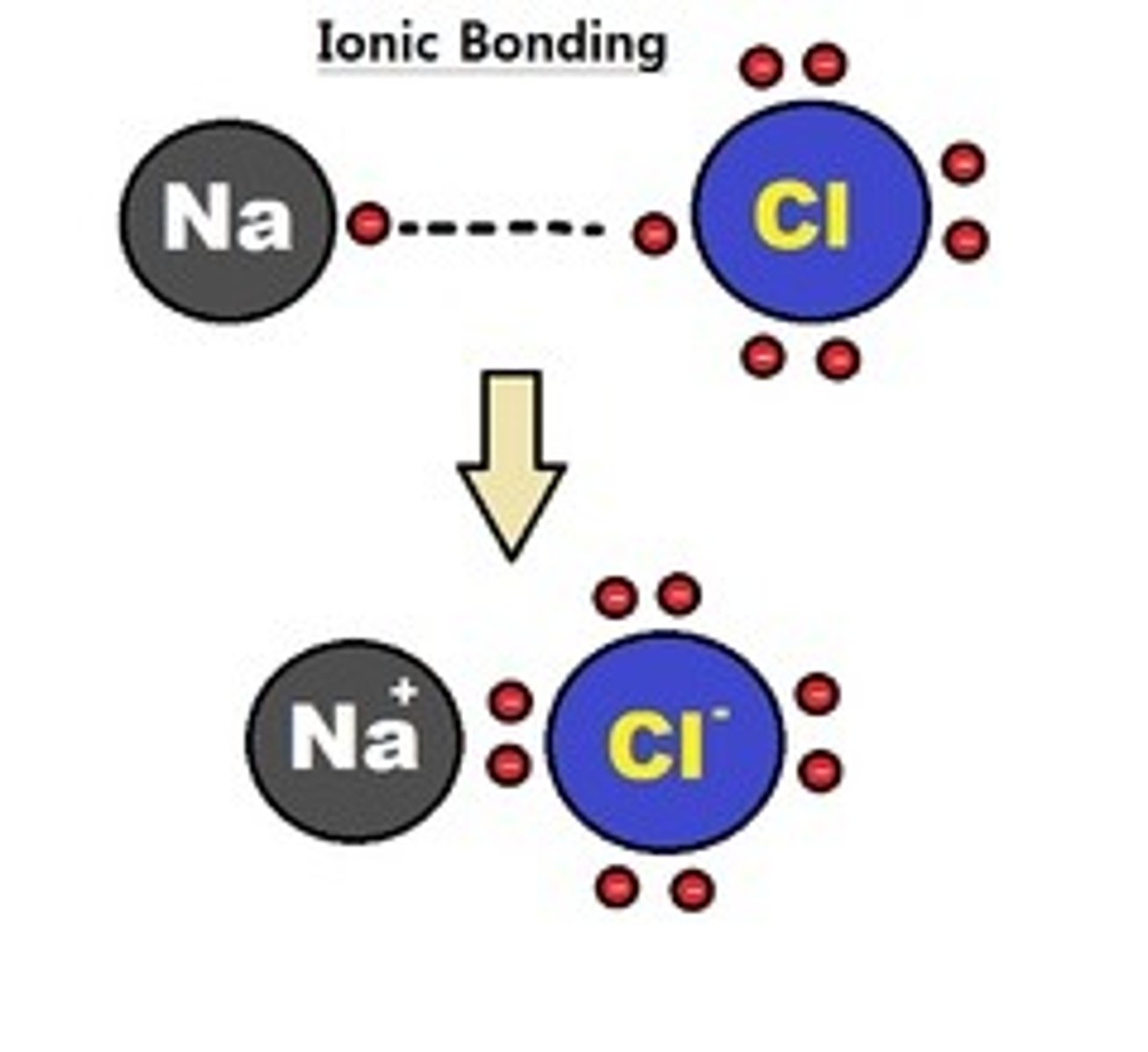
Ionic Bond
-Electrons are transferred completely from one atom to the other in order to complete the valence shell of each atoms
-Electrons transferred (NaCl), high electronegativity between atoms
-Always between metals and non-metals
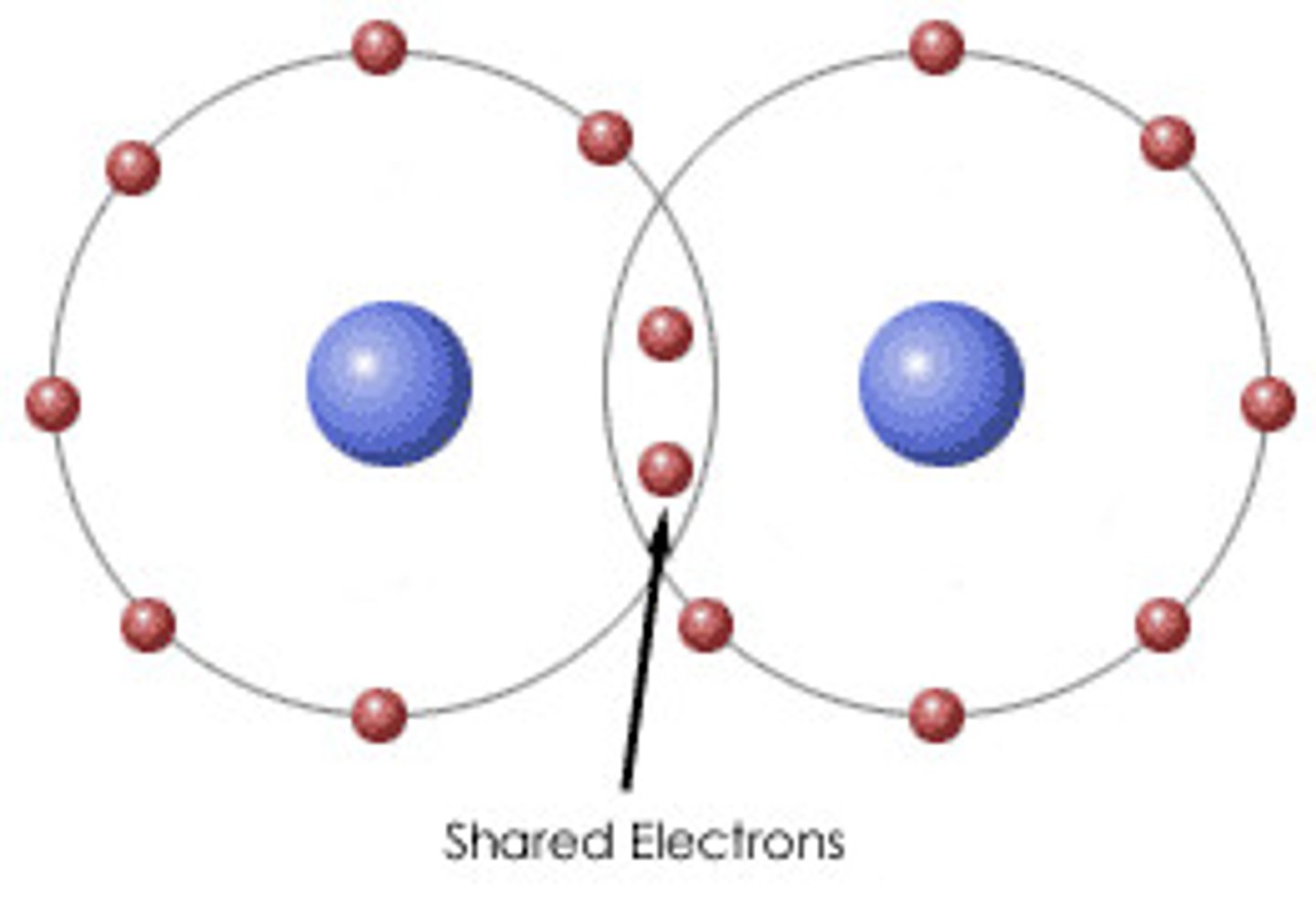
Covalent Bond
-Atoms don't give up their electrons freely, but share them instead.
-Electrons are shared
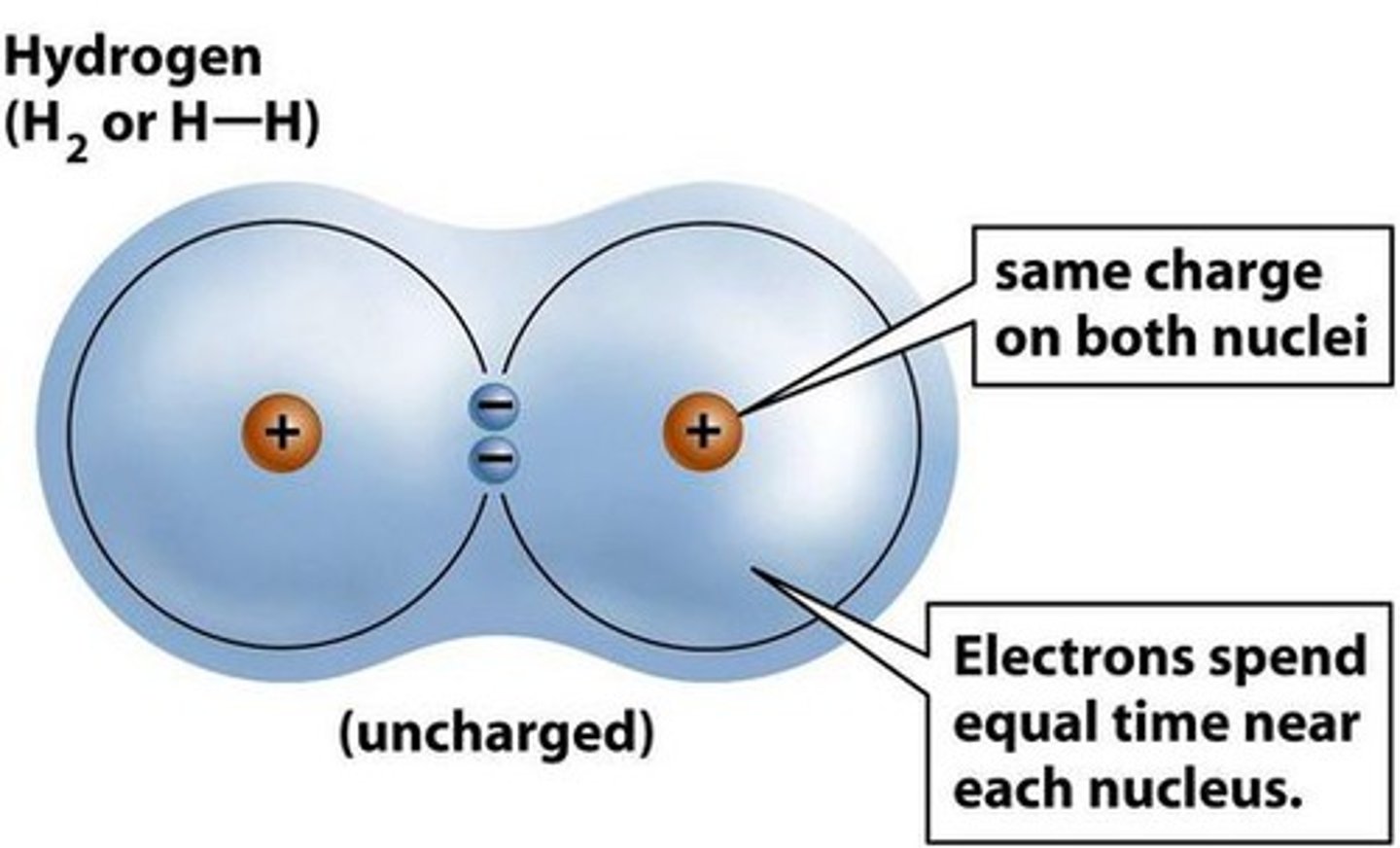
Nonpolar Covalent Bonds
-Electrons shared equally (O2, hydrophobic)
Polar Covalent Bonds
-Electrons shared unequally (H2O, hydrophilic)
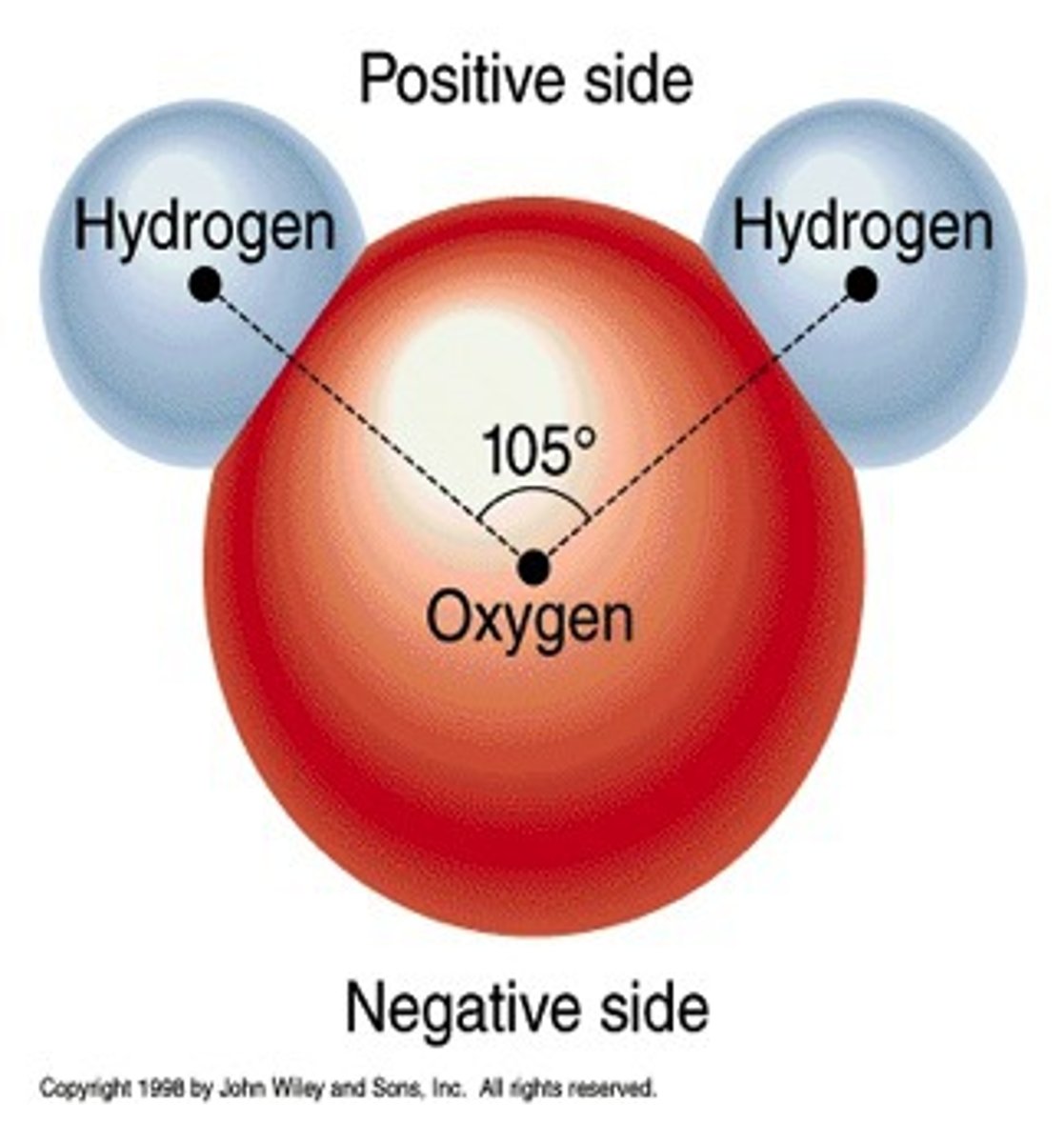
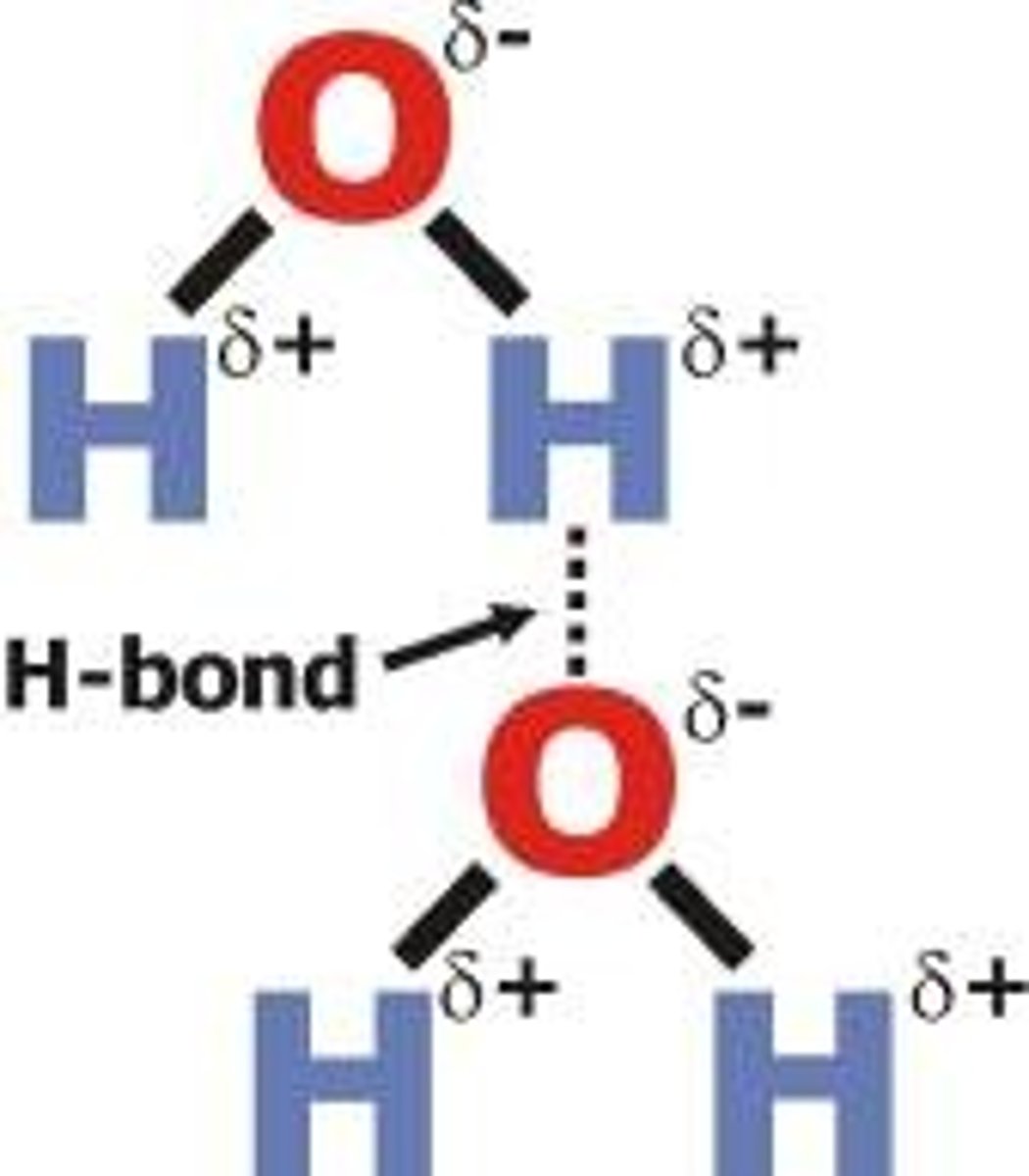
Hydrogen Bonds
-Weak bonds between polar molecules
Chemical Compound
-The result of a chemical bond that takes place when two or more elements come into contact with one another.
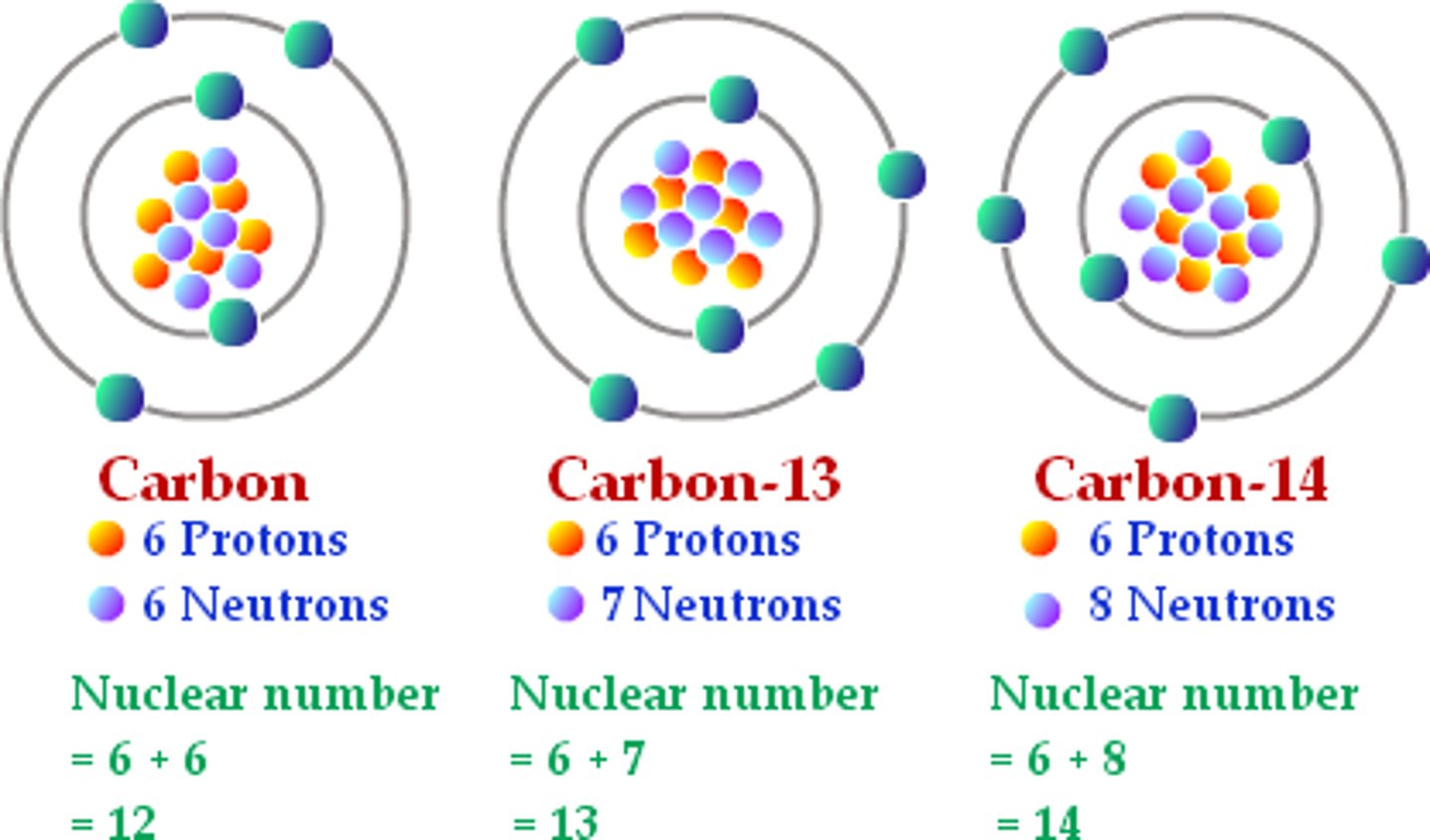
Isotopes
-Variants of a particular chemical element protons/electrons stay the same, neutrons vary
-Carbon 14 has 6 protons, 8 neutrons (6+8=14), 6 electrons
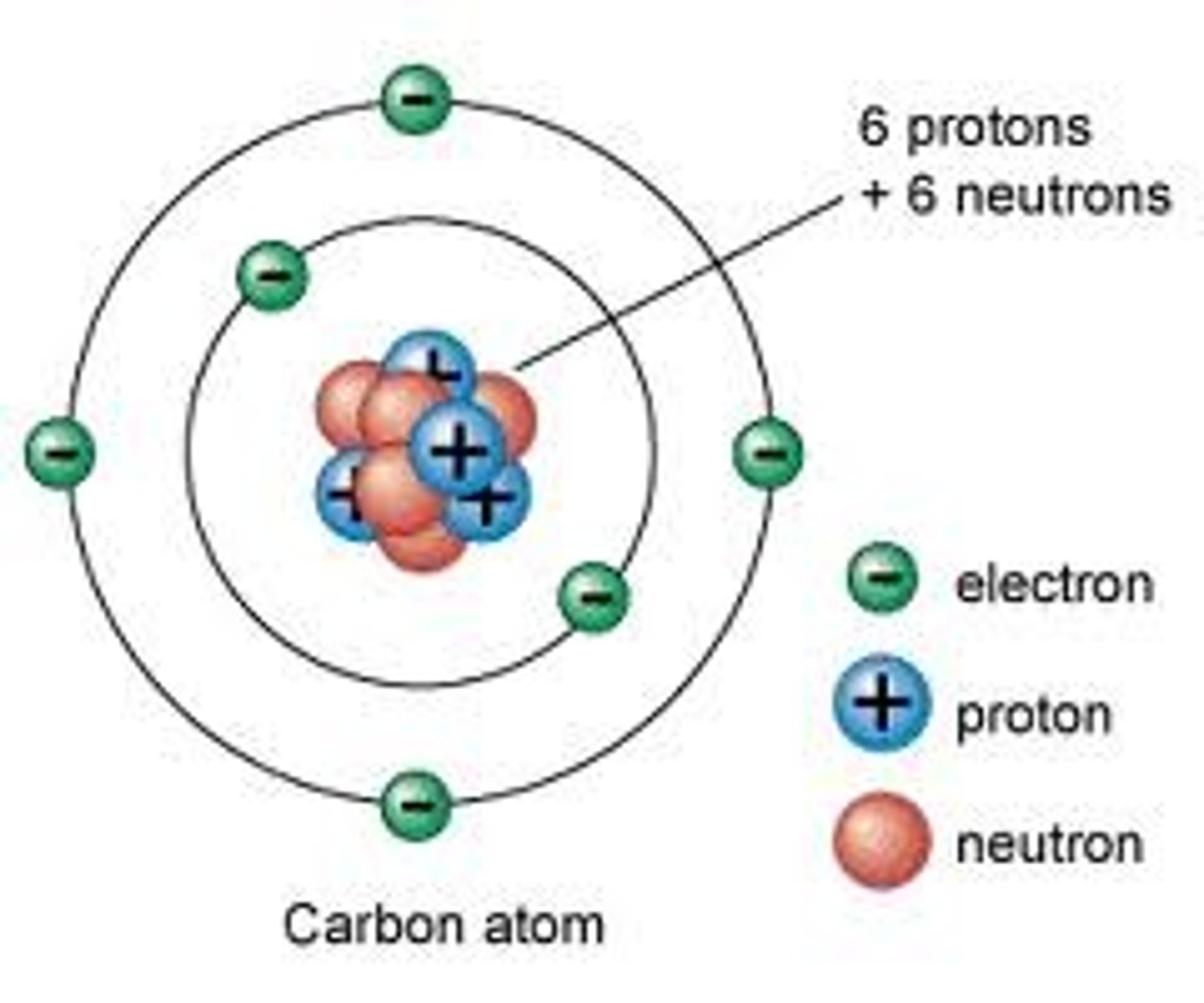
Make up of subatomic particles
Protons, Electrons, & Neutrons
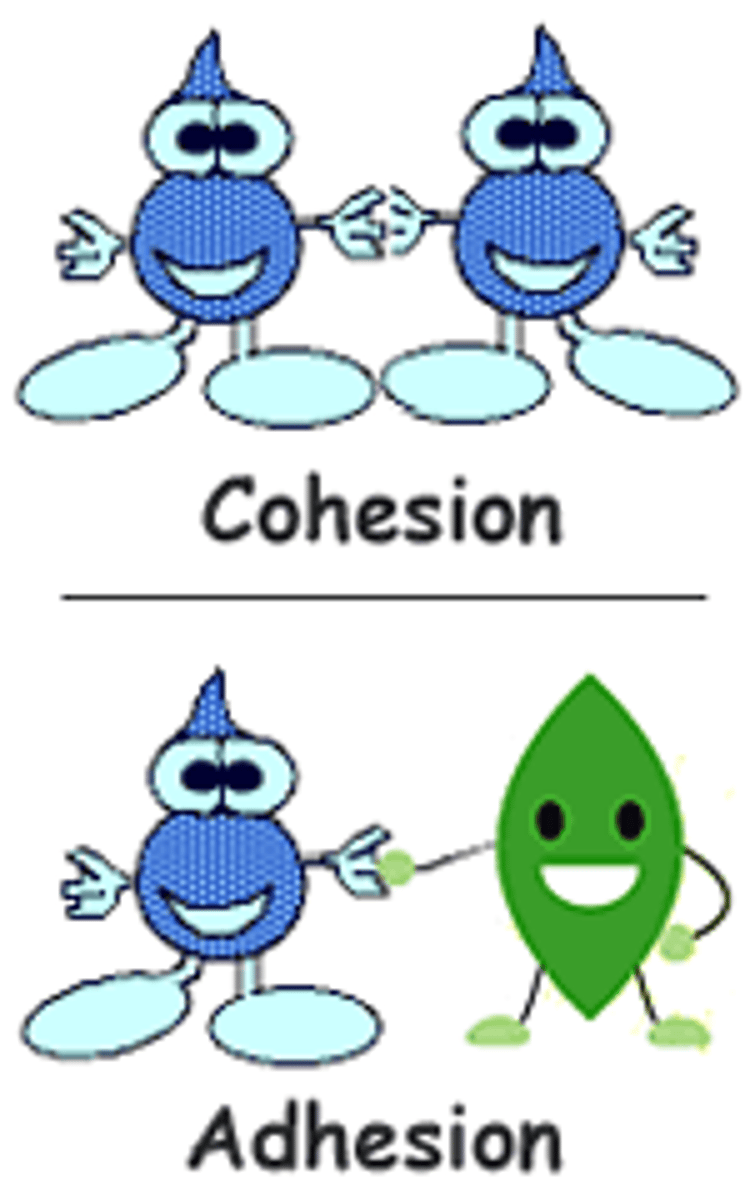
Cohesion
-When atoms stick to themselves like a chain
pH
Logarithmic scale (tenfold)
-Acids (acidic) - pH < 7, release hydrogen ions (H+) in water
=Low pH
-Bases (alkaline) - pH > 7, release hydroxide ions (OH-) in water
=High pH

Properties of Water
-Water is comprised of one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms
-Water contracts until it reaches four degrees Celsius and then expands until it becomes solid
-Solid water is less dense than liquid water
-Ice floats - expands as freezes, less dense
Solvent (water)
-Distinct positive/negative regions (dipolar), separates polar substances into ions
-The reason why water displays nearly universal solvent properties is its hydrogen bonding

Cohesive (water)
Molecules stick together (hydrogen bonds), high surface tension
Adhesive (water)
Molecules stick to other substances, capillary action
Heat capacity (water)
Resists temperature change (stable)
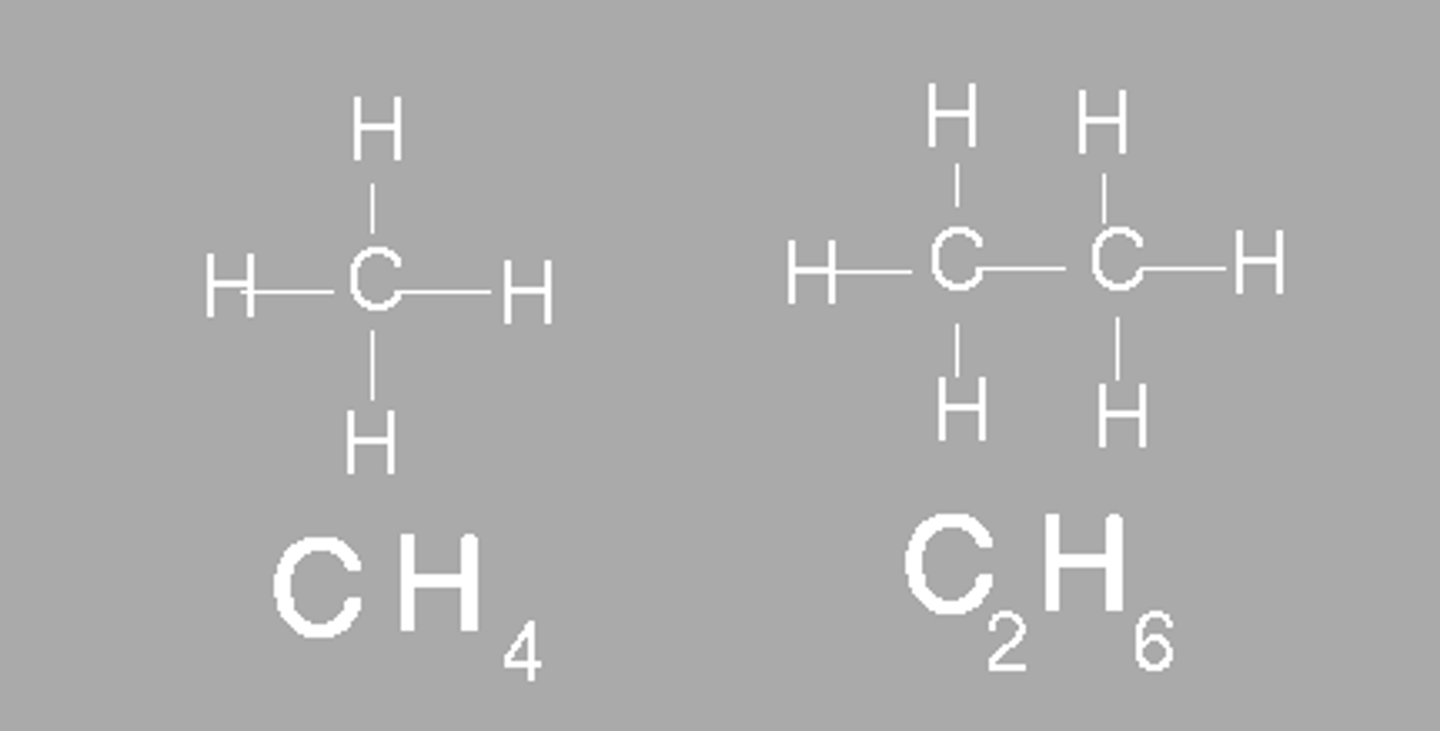
Molecular Formula
-A formula giving the number of atoms of each of the elements present in one molecule of a specific compound.
-For example, for butane, the molecular formula is C4H10.
Carbohydrates
-Are made up of:
-Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (1:2:1)
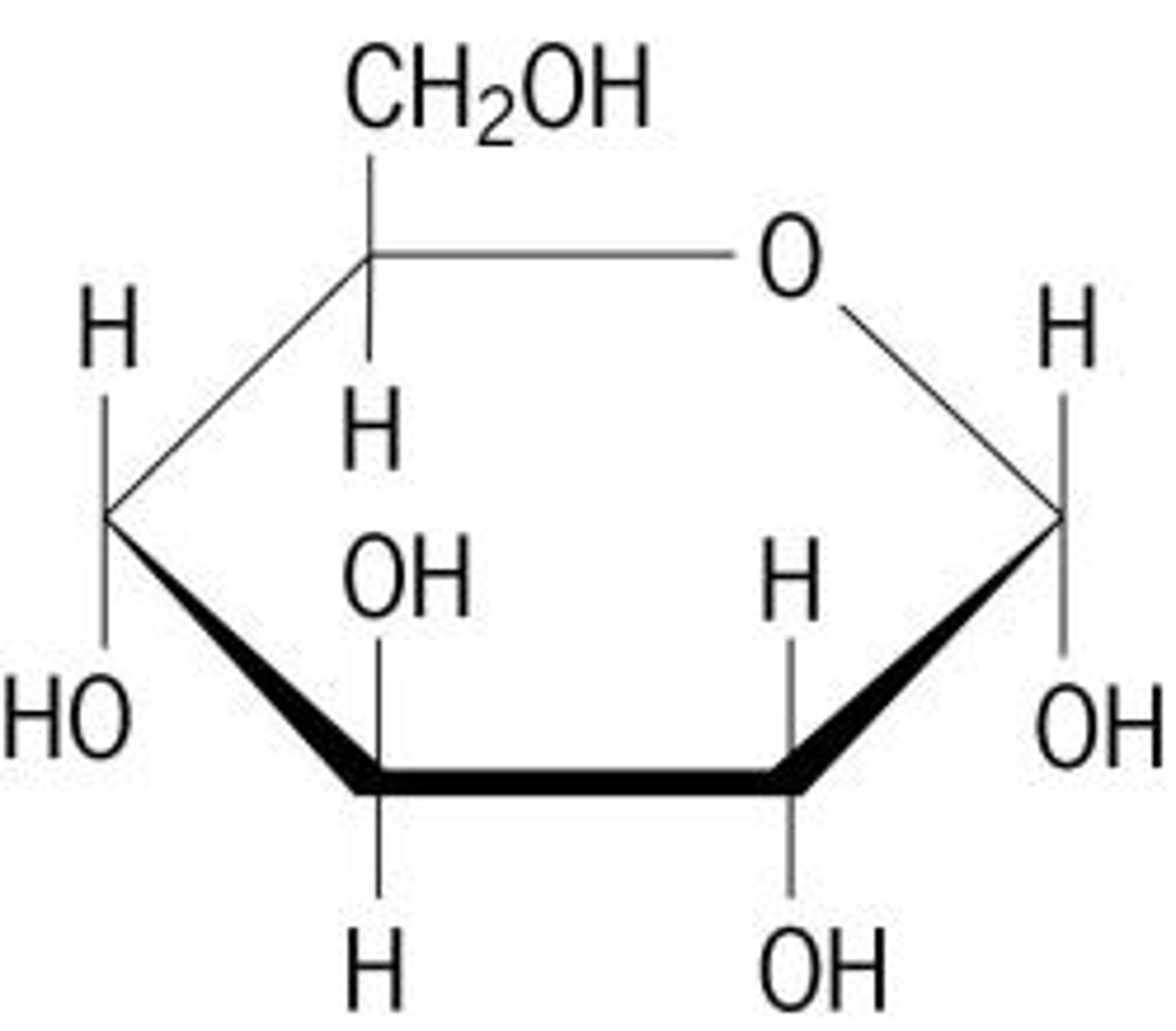
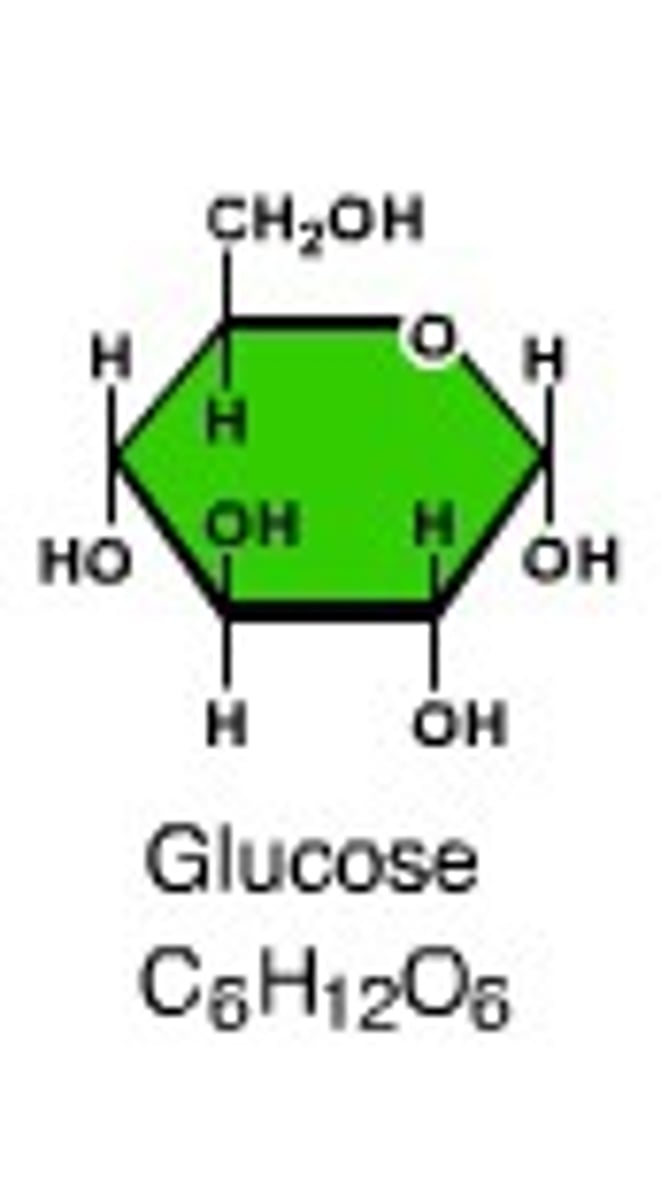
Monosaccharide
-A carbohydrate comprised of one molecule
-Energy source for cells (glucose, fructose)
-Linear or ring structure
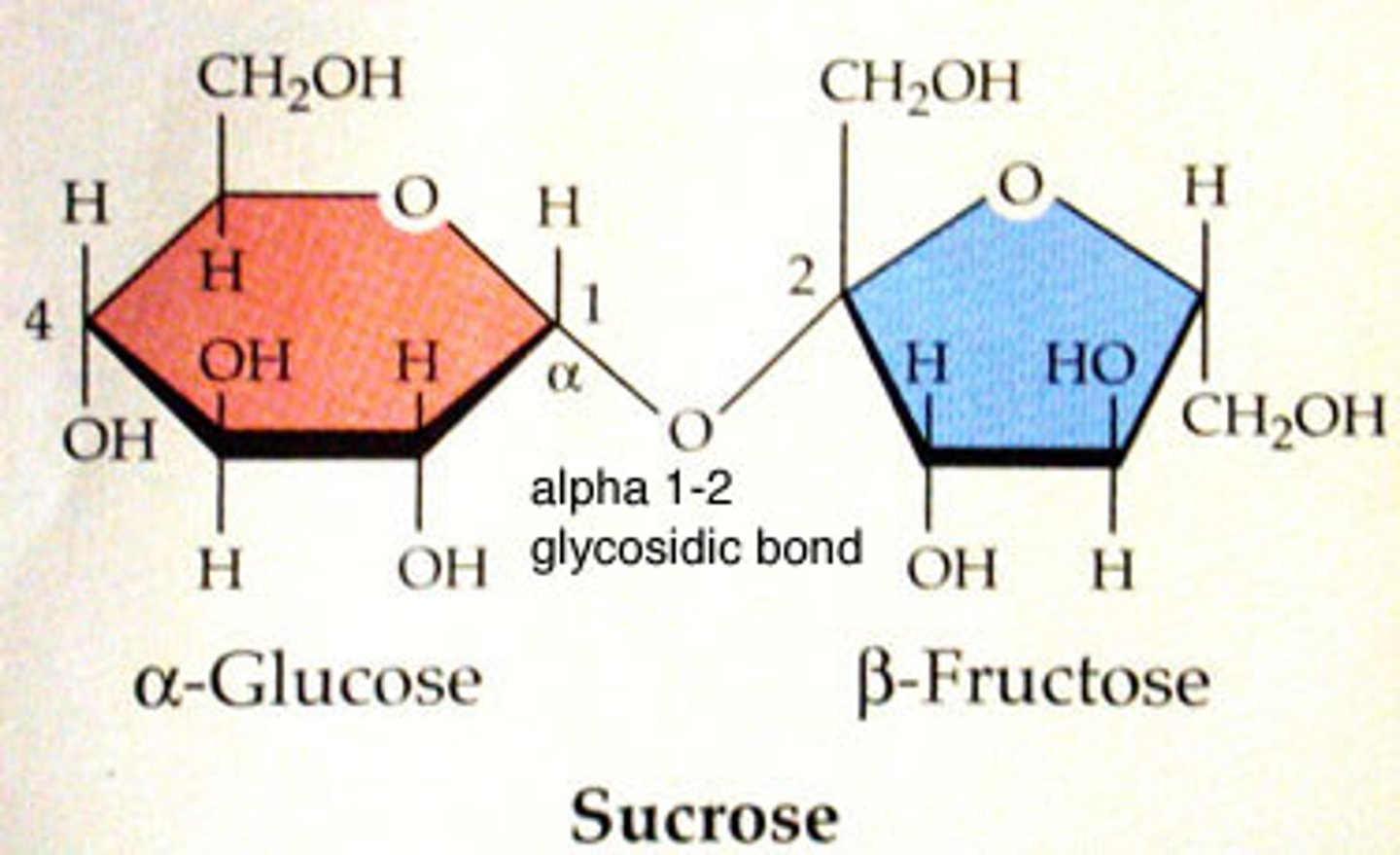
Disaccharide
-A carbohydrate comprised of two molecules
-(maltose, sucrose, lactose)
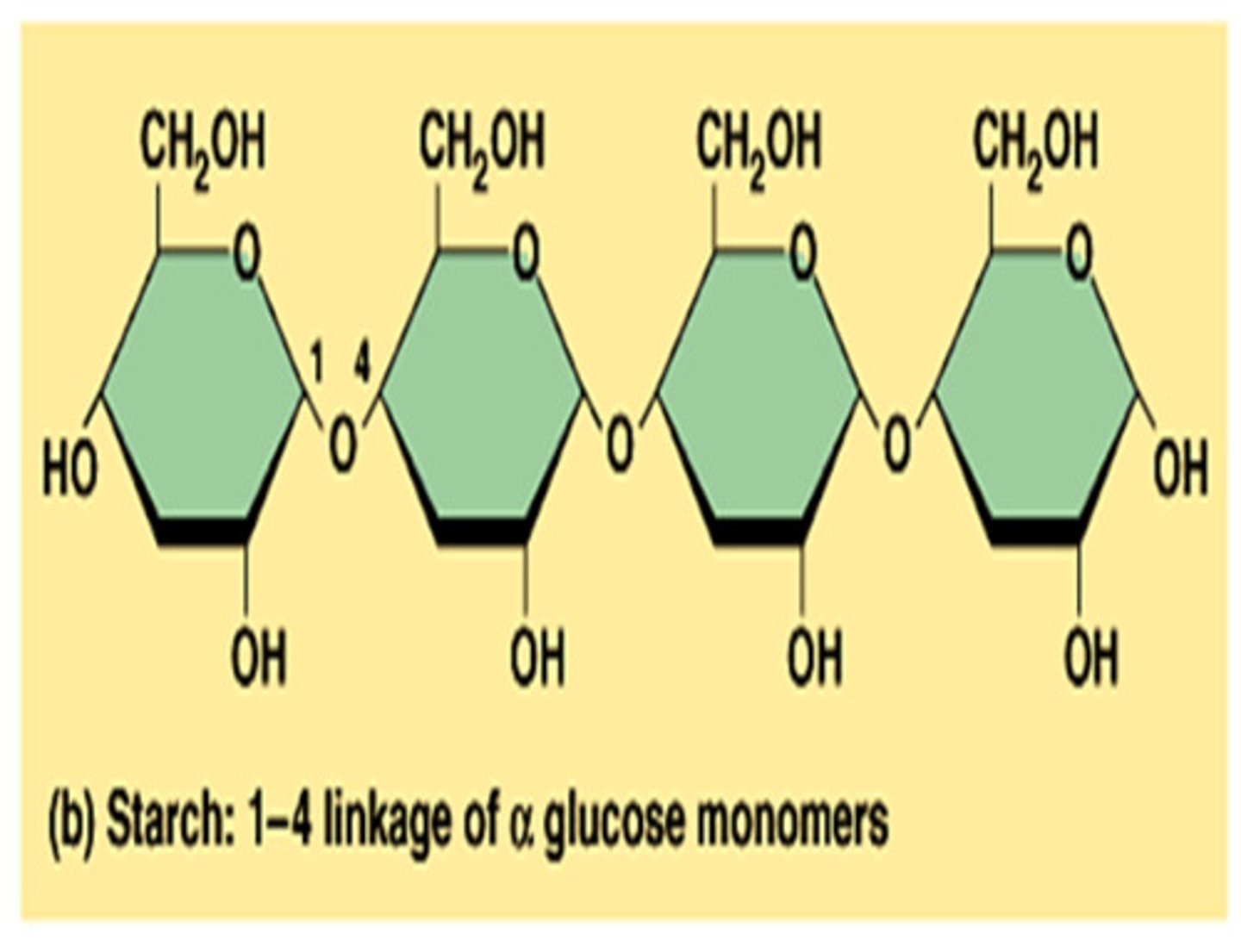
Polysaccharide
-A carbohydrate comprised of three or more molecules
-Polymer, glucose storage, or structure
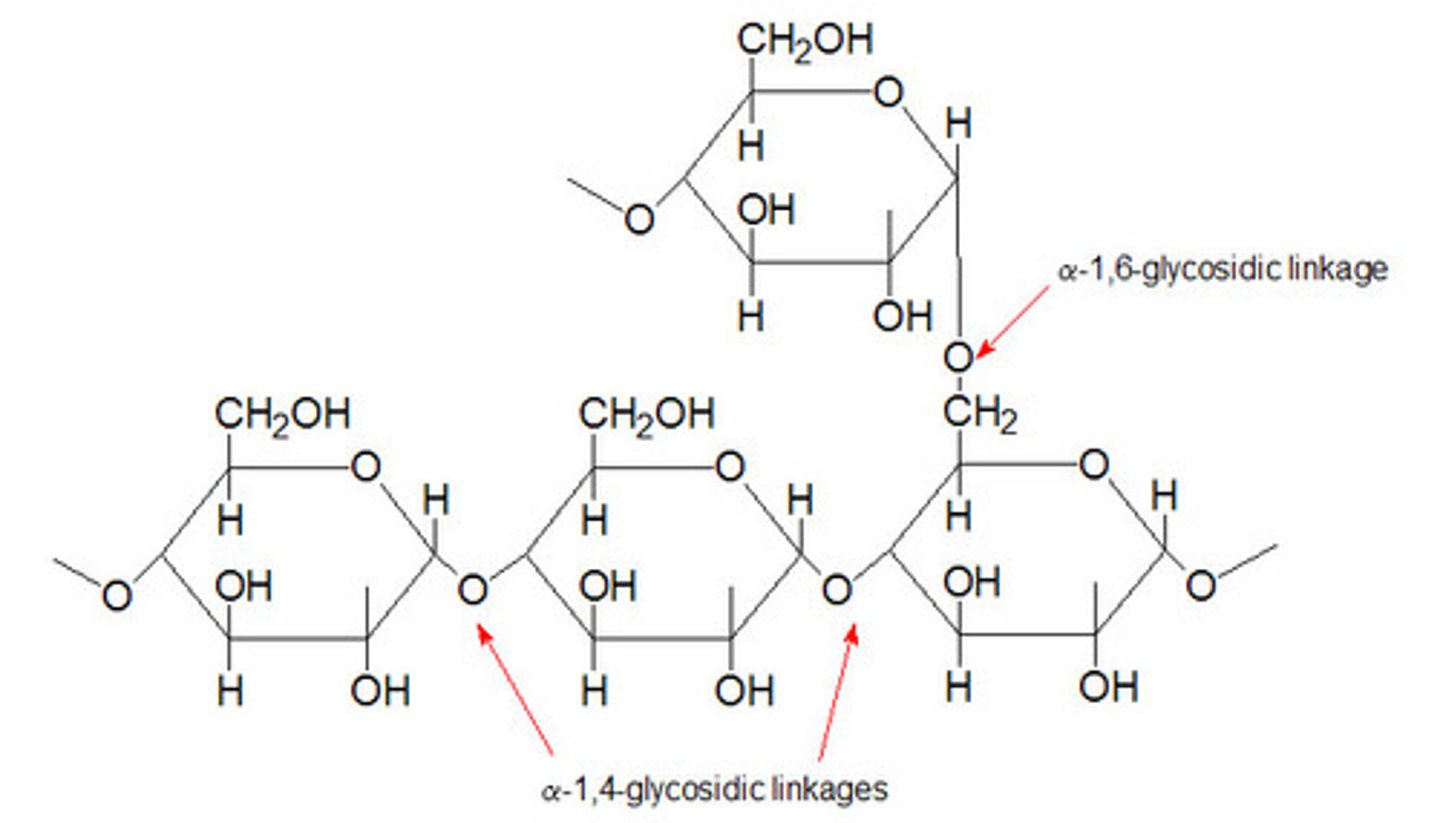
Glycosidic Linkage
-Hydrogen from one sugar combines with the hydroxyl group of another
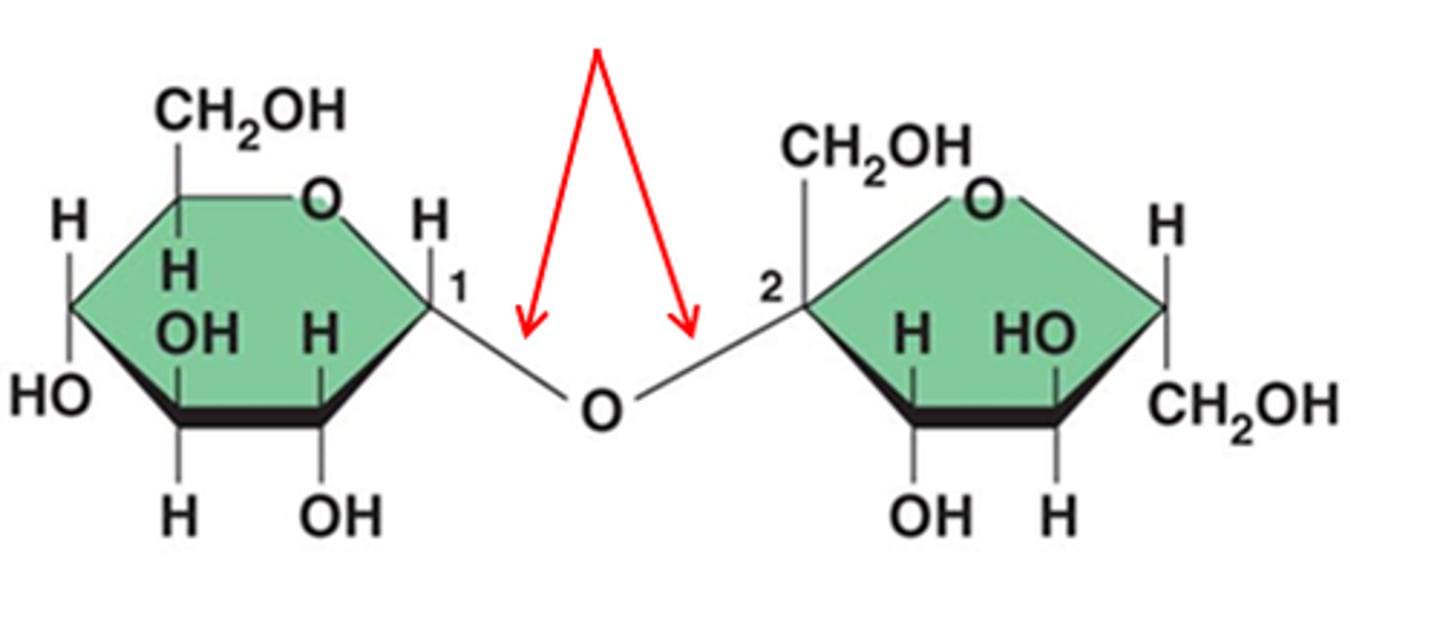
Hydrolysis
-Add H2O to break bonds
-Chemical reaction where the molecule is split into two molecules. The breaking of this bond requires breaking a water molecule.
Glucose
-The energy used in all living things
-Dominant product of photosynthesis
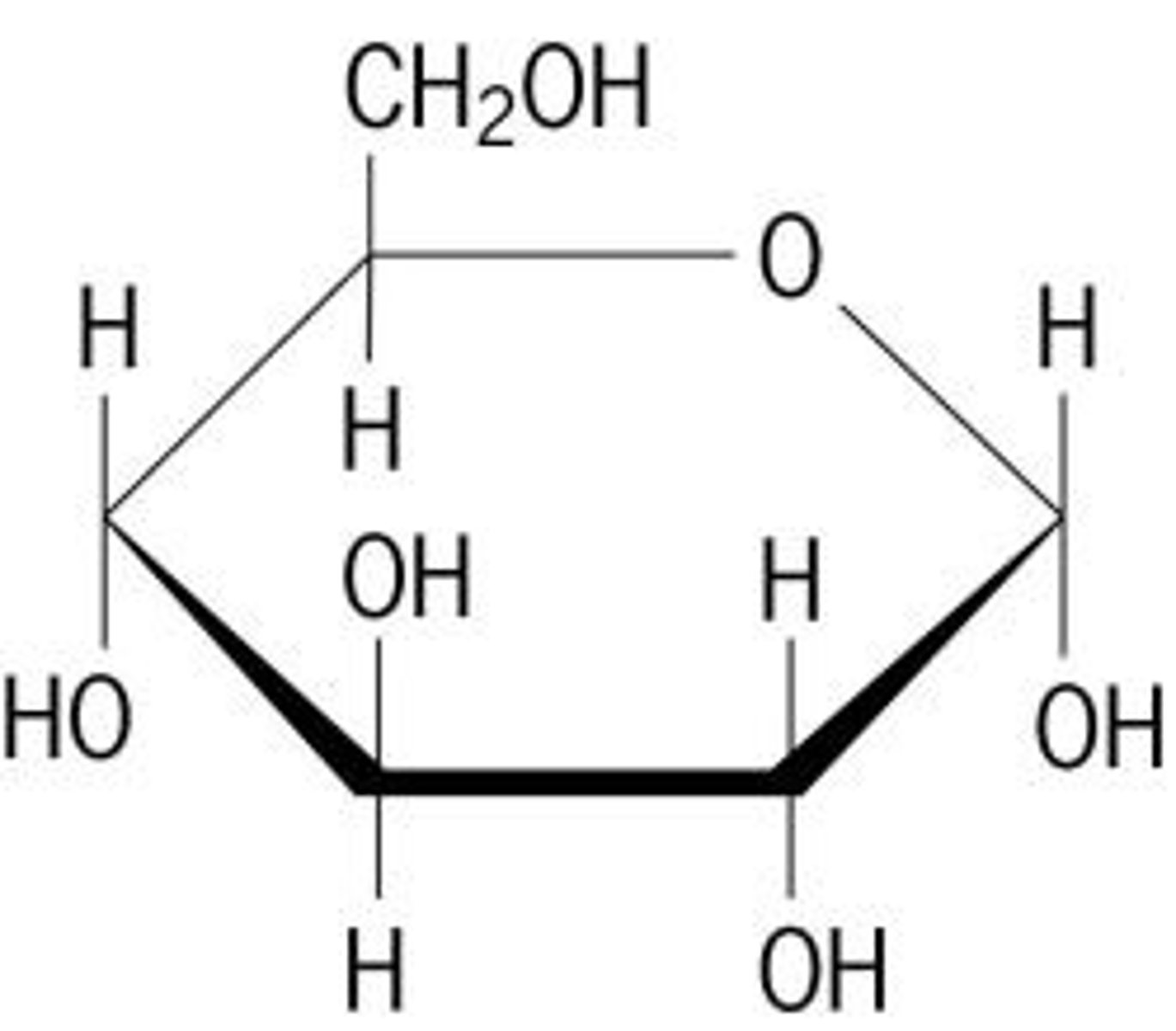
Starch (α-glucose)
-Plant storage (plastids)
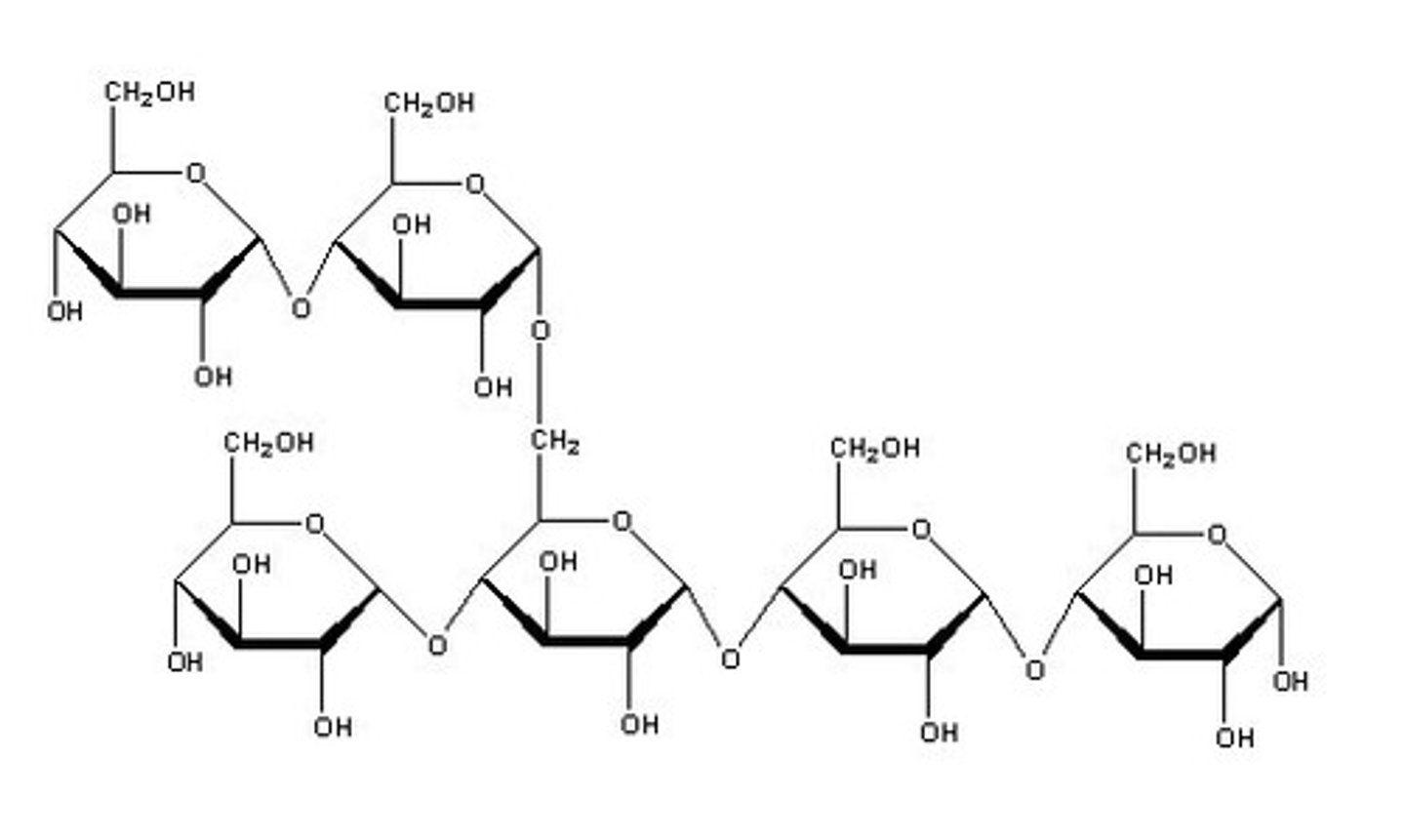
Glycogen (α-glucose)
-Animal storage (liver/muscle cells)
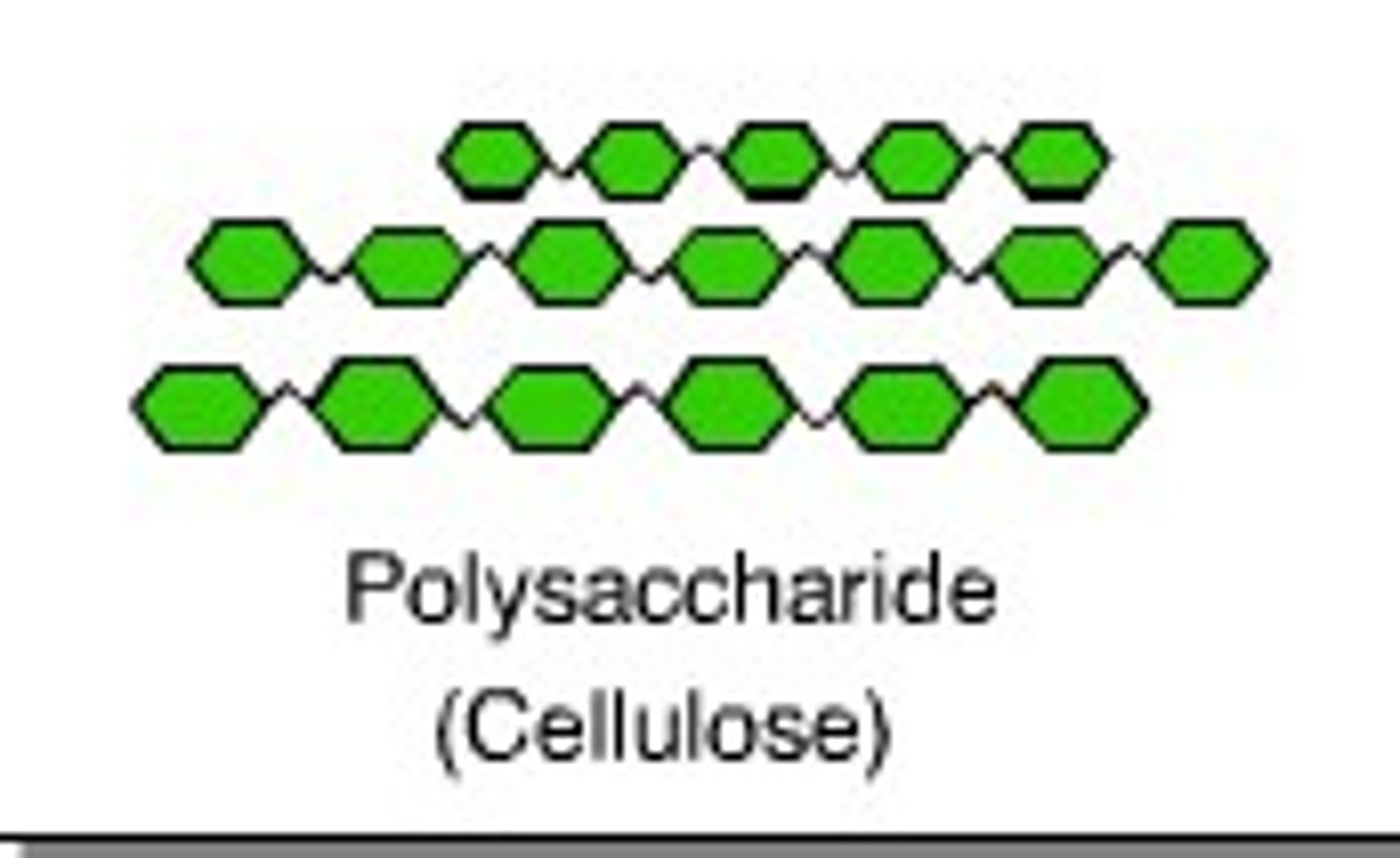
Cellulose (β-glucose)
-Plant structure (cell walls)
Chitin (β-glucose)
-Fungus/arthropod structure
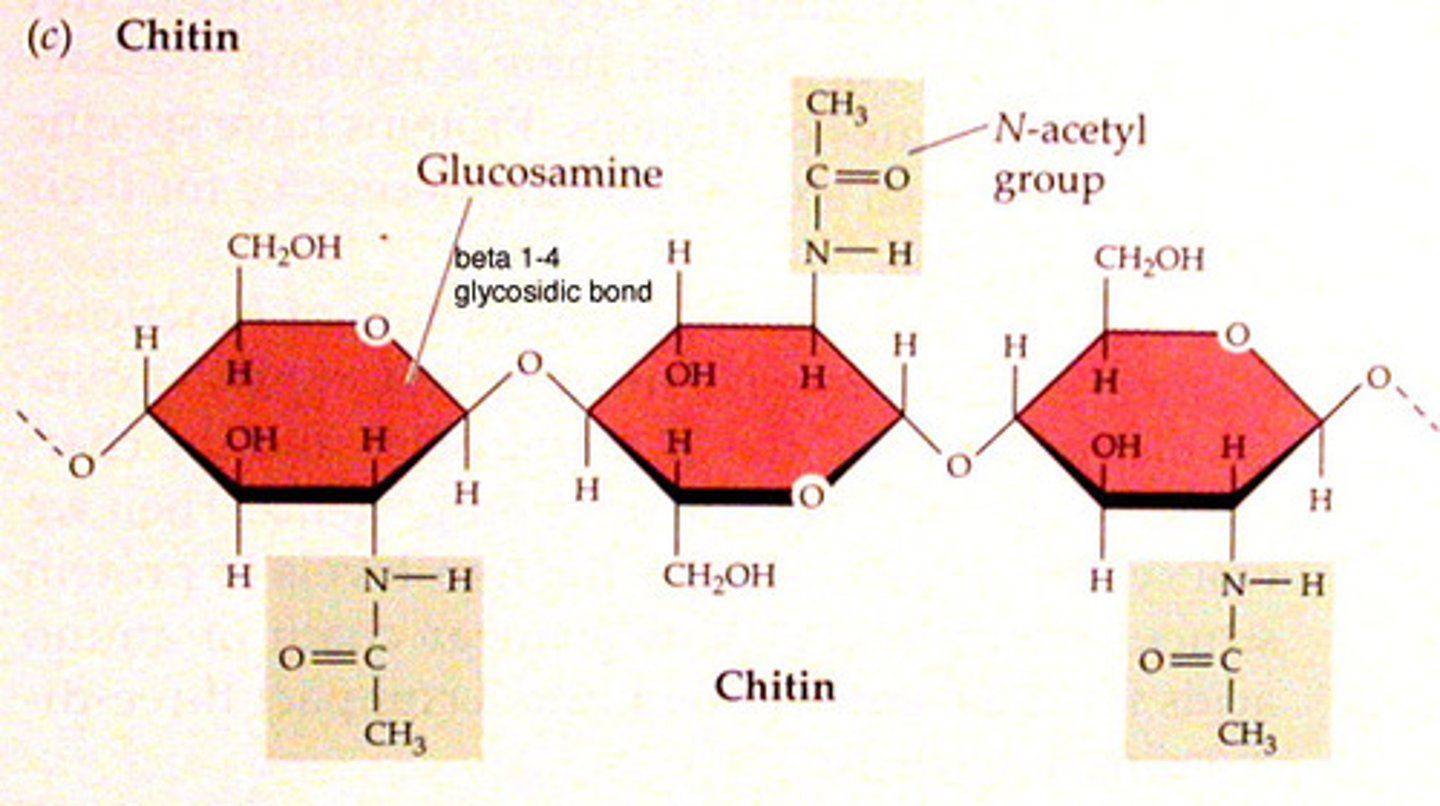
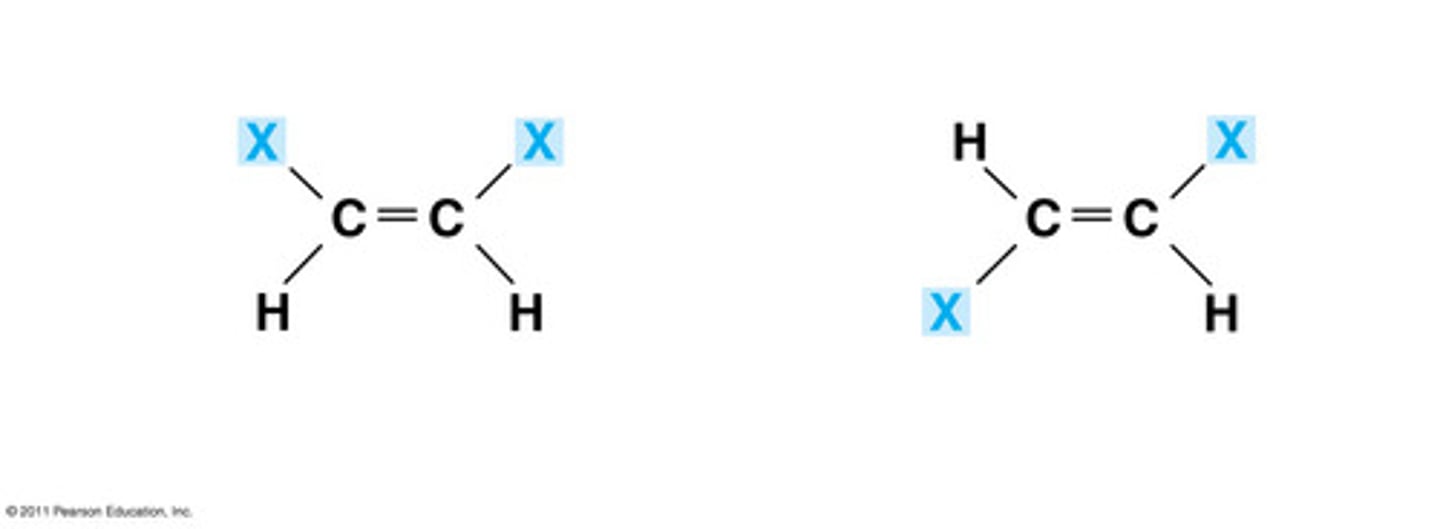
Isomer-
-Common molecular formula, molecular structure differ
-Isomers contain the same number of atoms of each element, but have different arrangements of their atoms.
Lipids
-Are made up of- carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
-Contain less oxygen than carbohydrates
-Cell membrane structure, insulation, energy storage
-3 types
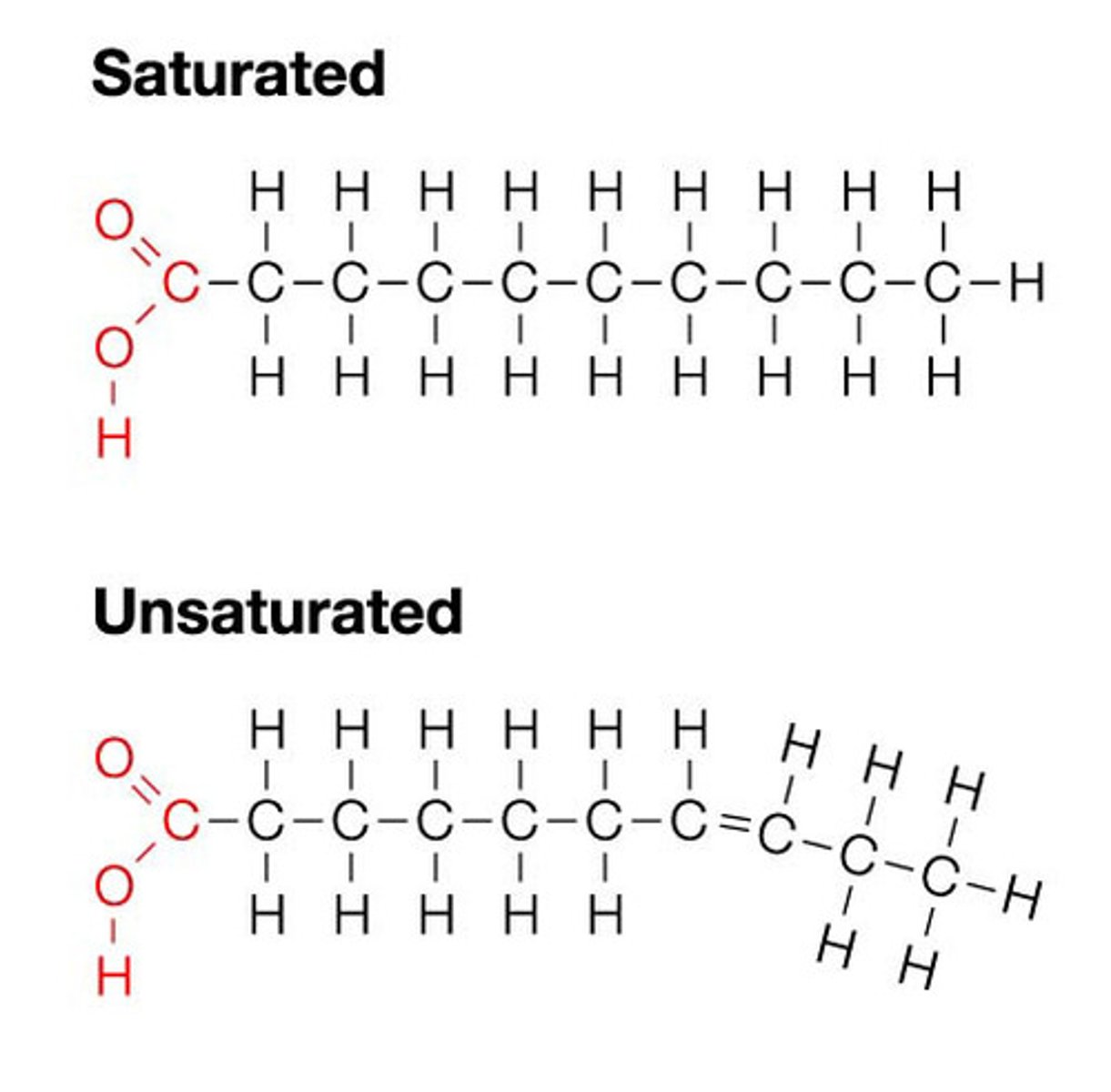
Simple Lipids
-Fats and oils
-Compound lipids
Glycolipids and phospholipids
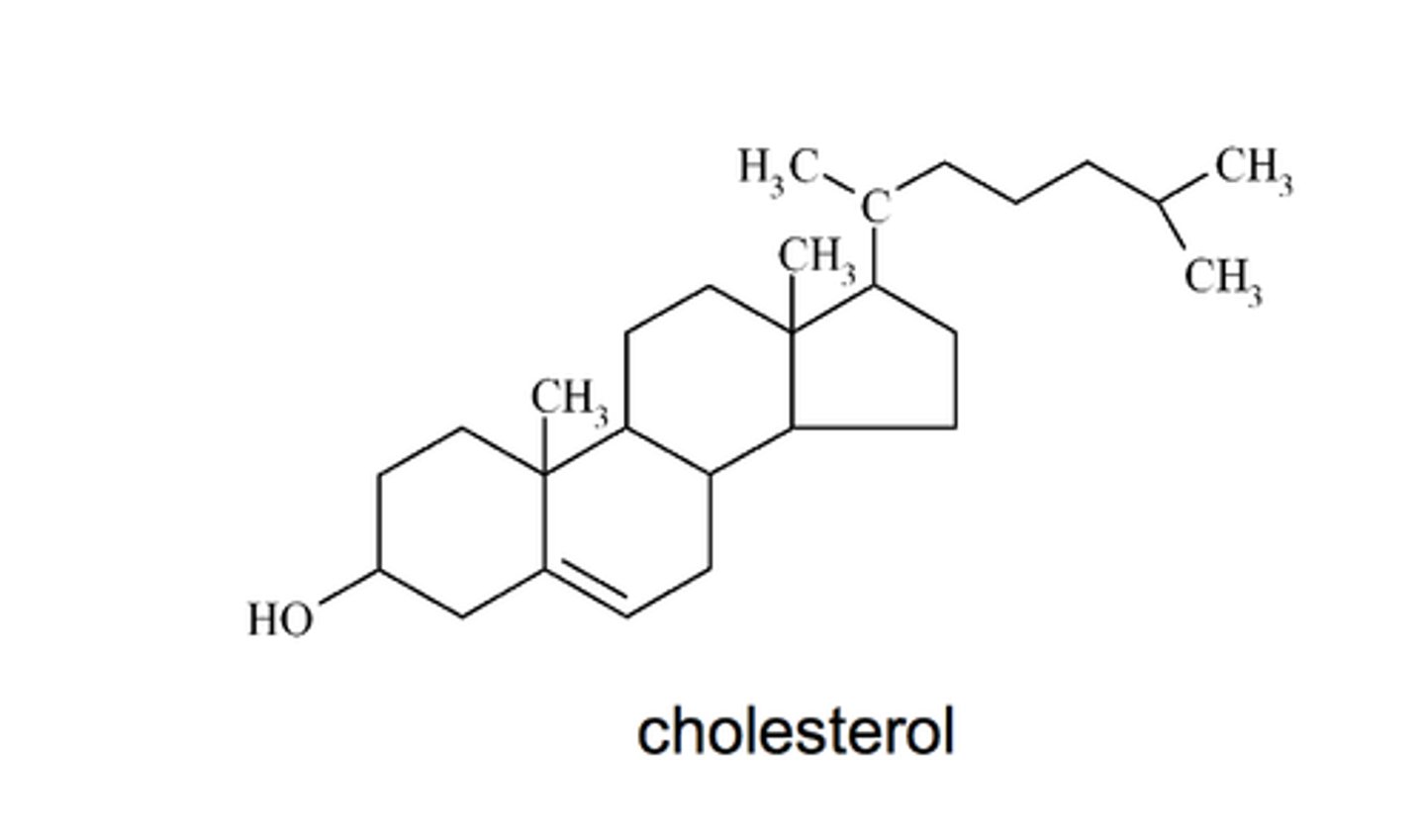
-Derived lipids
Steroids
-4 linked carbon rings
-(cholesterol, vitamin D, sex hormones)
...
...
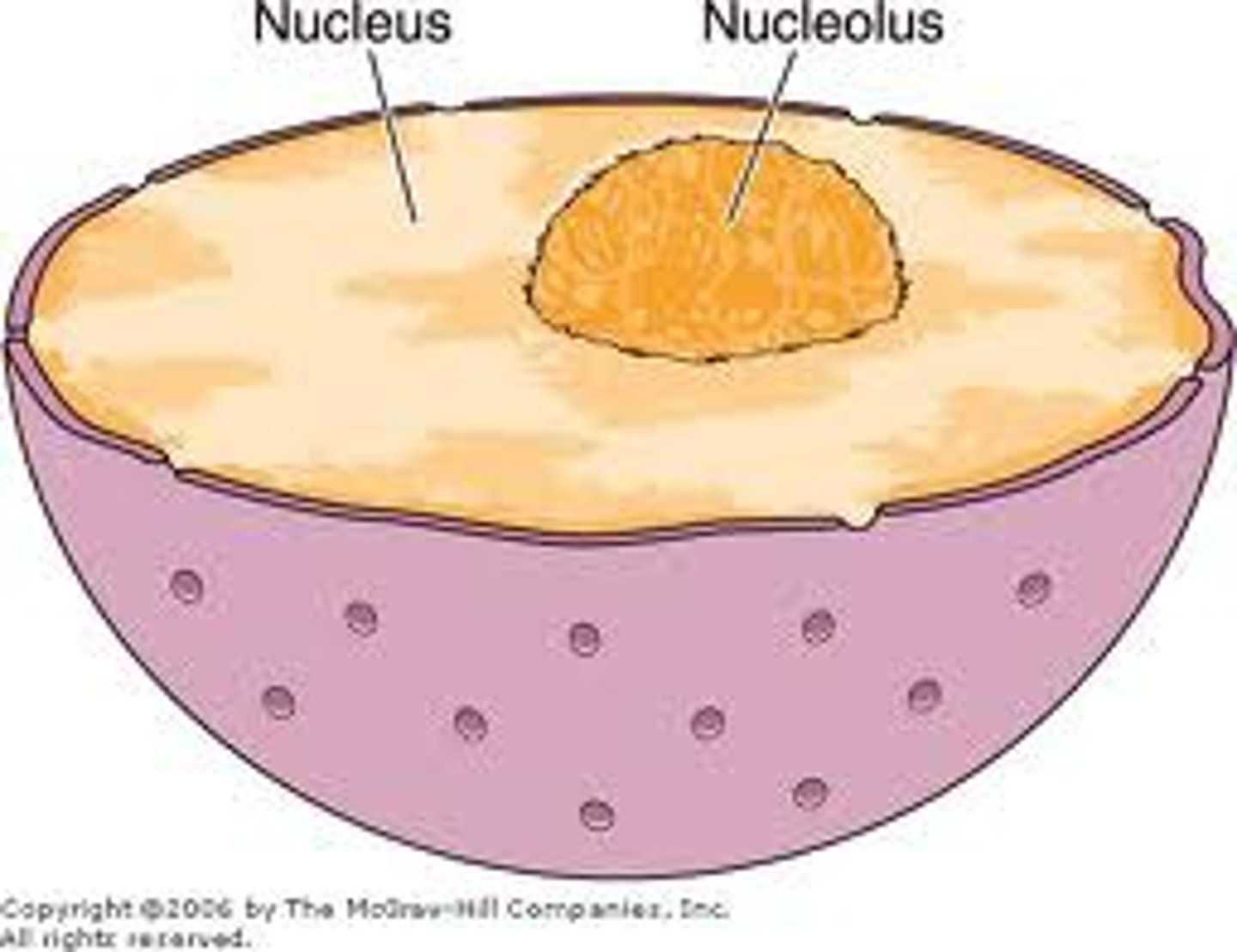
Nucleus
-Control center
-Cell reproduction
-Nuclear envelope- phospholipid bilayer
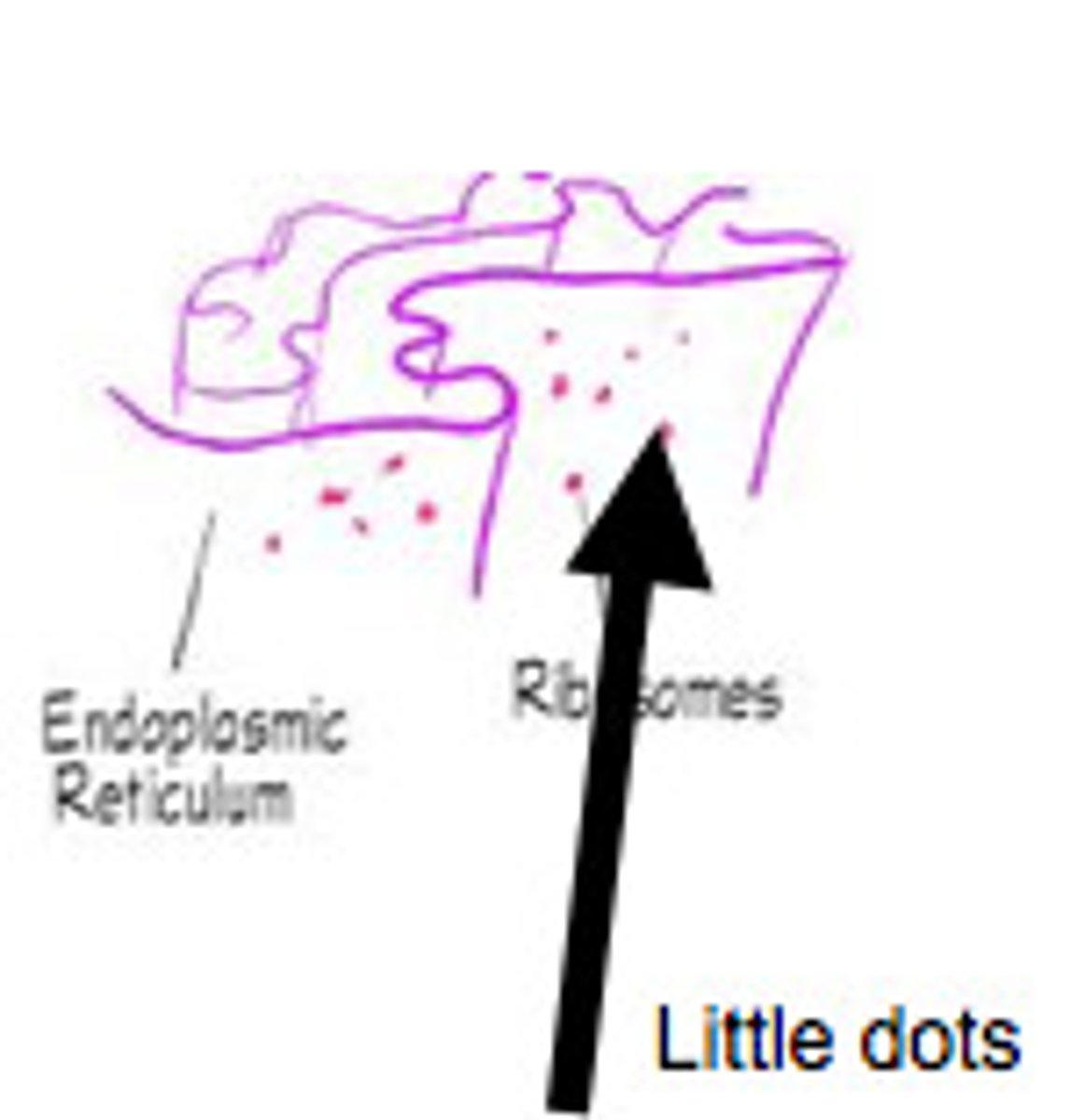
Ribosomes
-Protein synthesis in cytoplasm (amino acids -> polypeptide chains -> proteins)
-No membrane
-RNA + proteins
-3 binding sites (mRNA, tRNA + polypeptide chain, tRNA + amino acid)
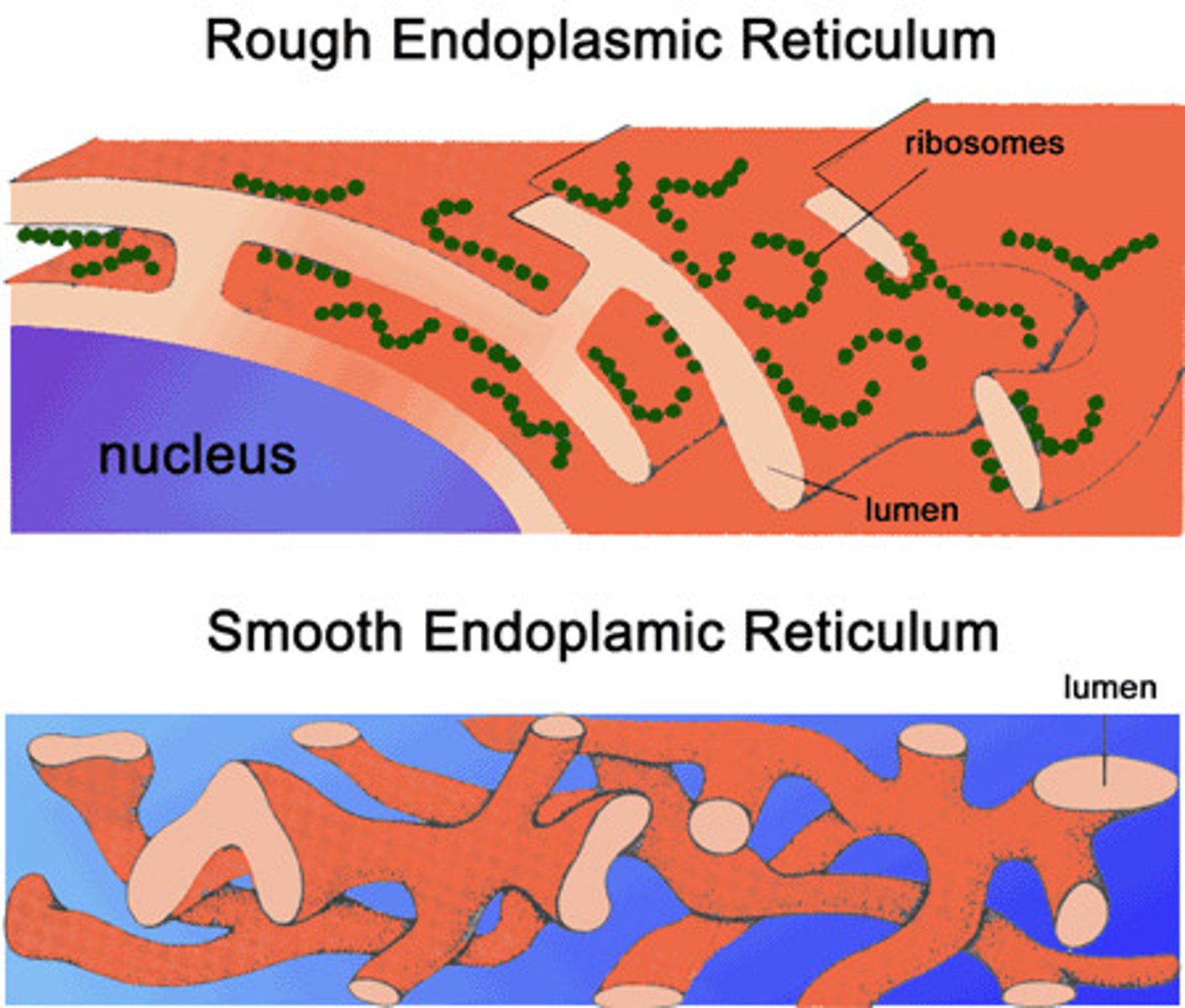
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Maze-like channels associated with nucleus
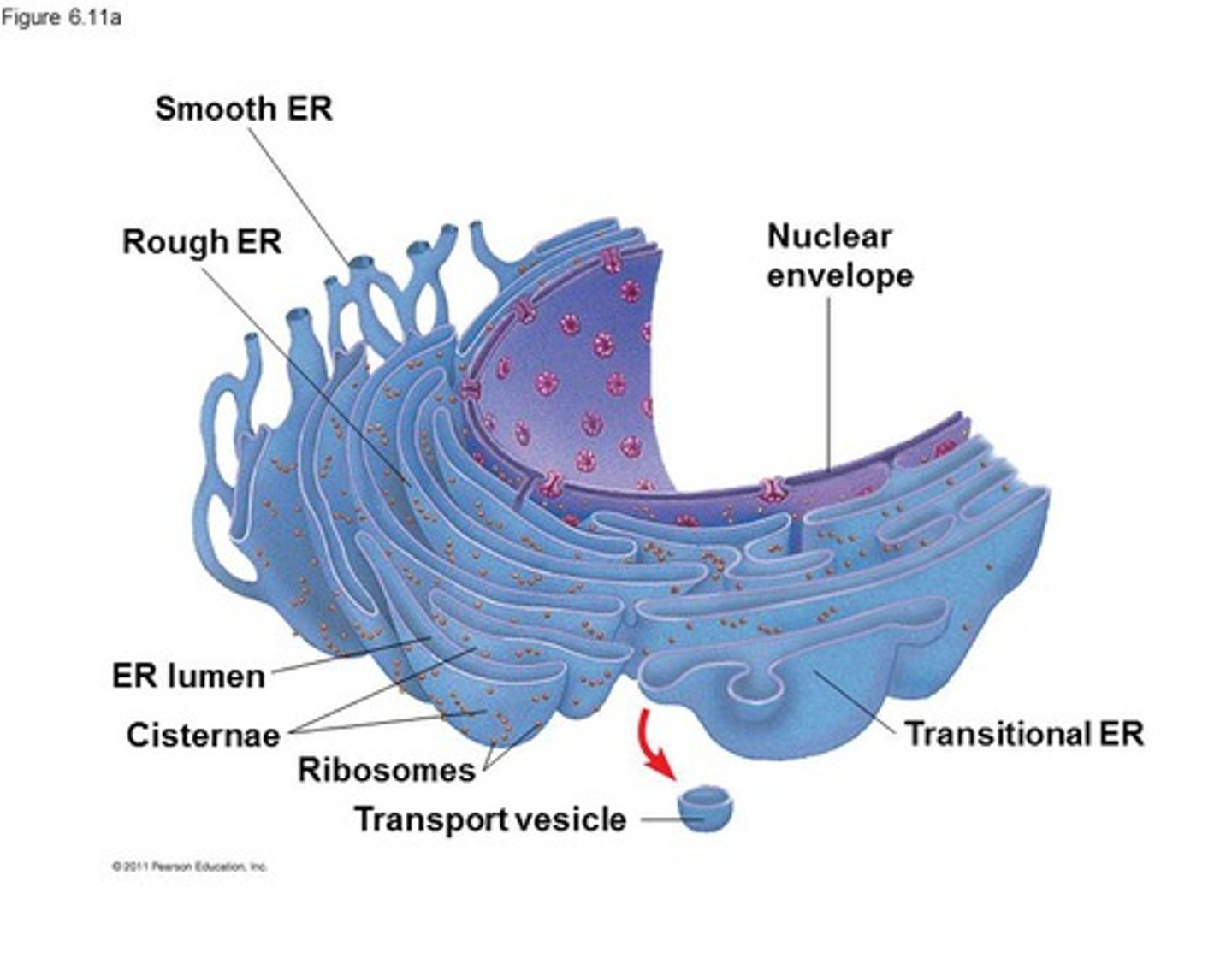
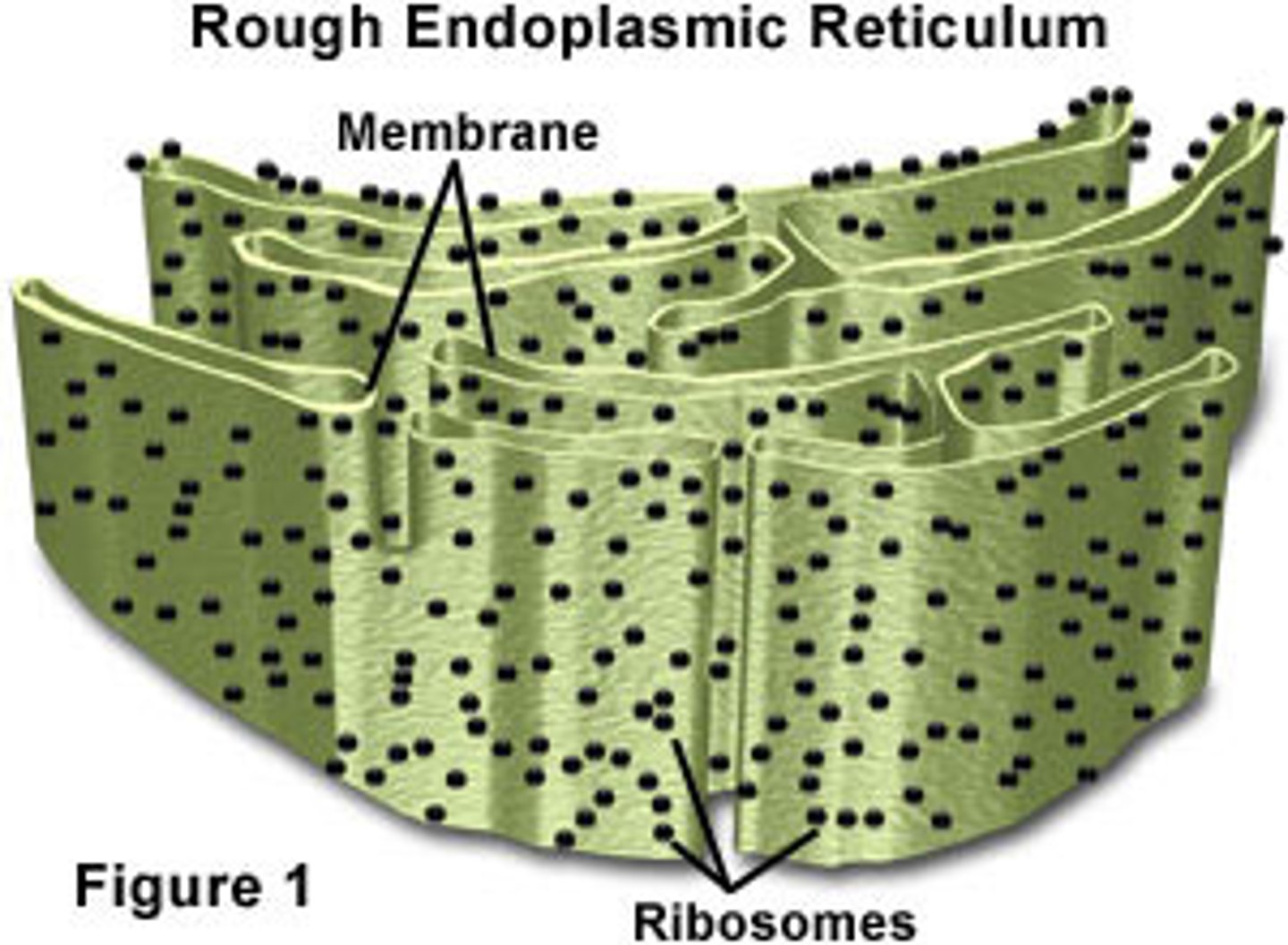
Rough ER (Ribosomes)
Make glycoproteins for external transport (via Golgi body), become membrane proteins
Smooth ER
Enzymes that produce lipids/hormones, breakdown of toxic cellular byproducts
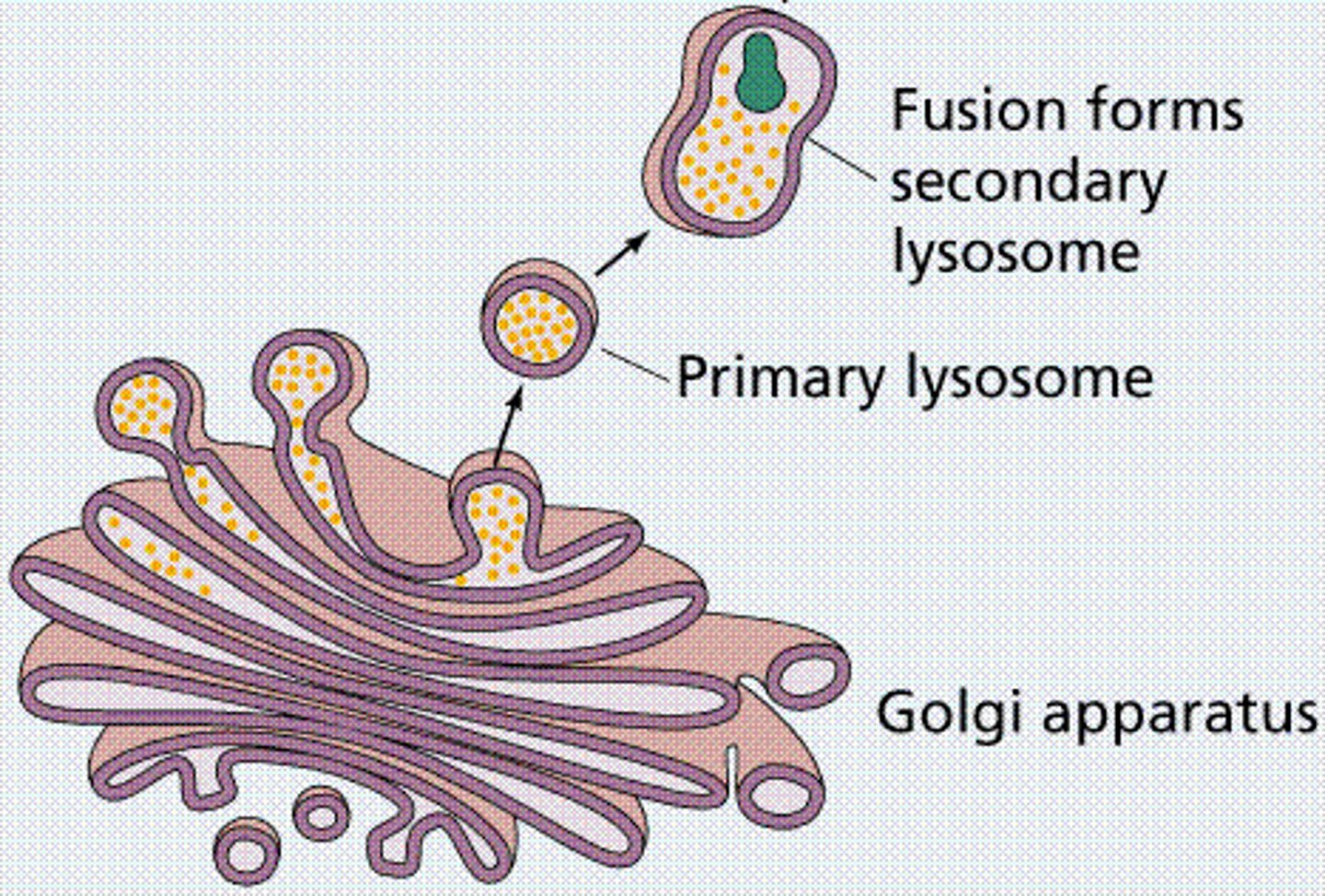
Golgi Apparatus
Packaging/distribution in vesicles for transport out of cells
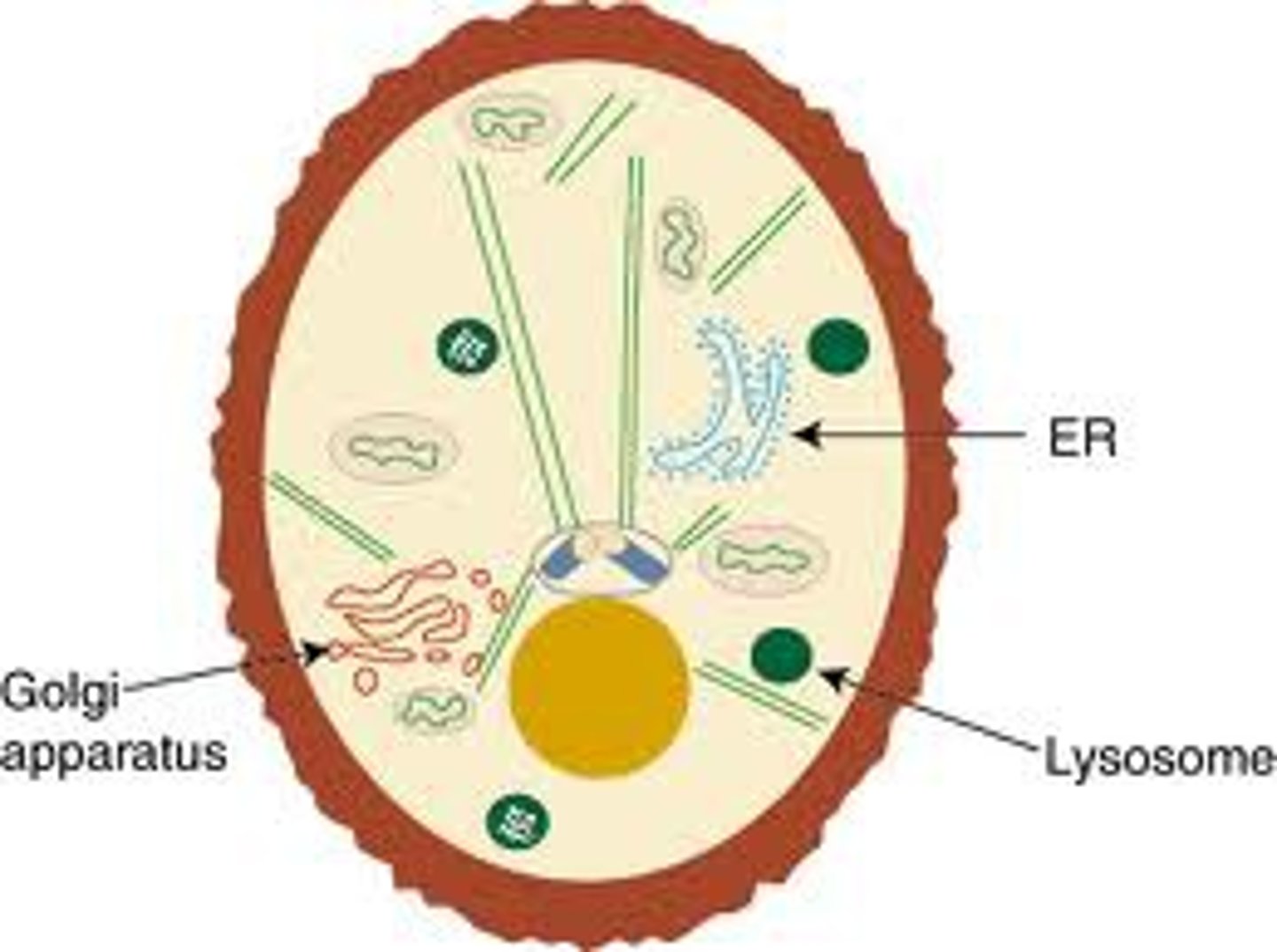
Lysosomes
-Vesicles from Golgi bodies, digestion via enzymes (low pH), recycling
-Rarely in plant cells
Peroxisomes
-Break down toxins (liver, kidneys) with H2O2 byproduct, break down H2O2
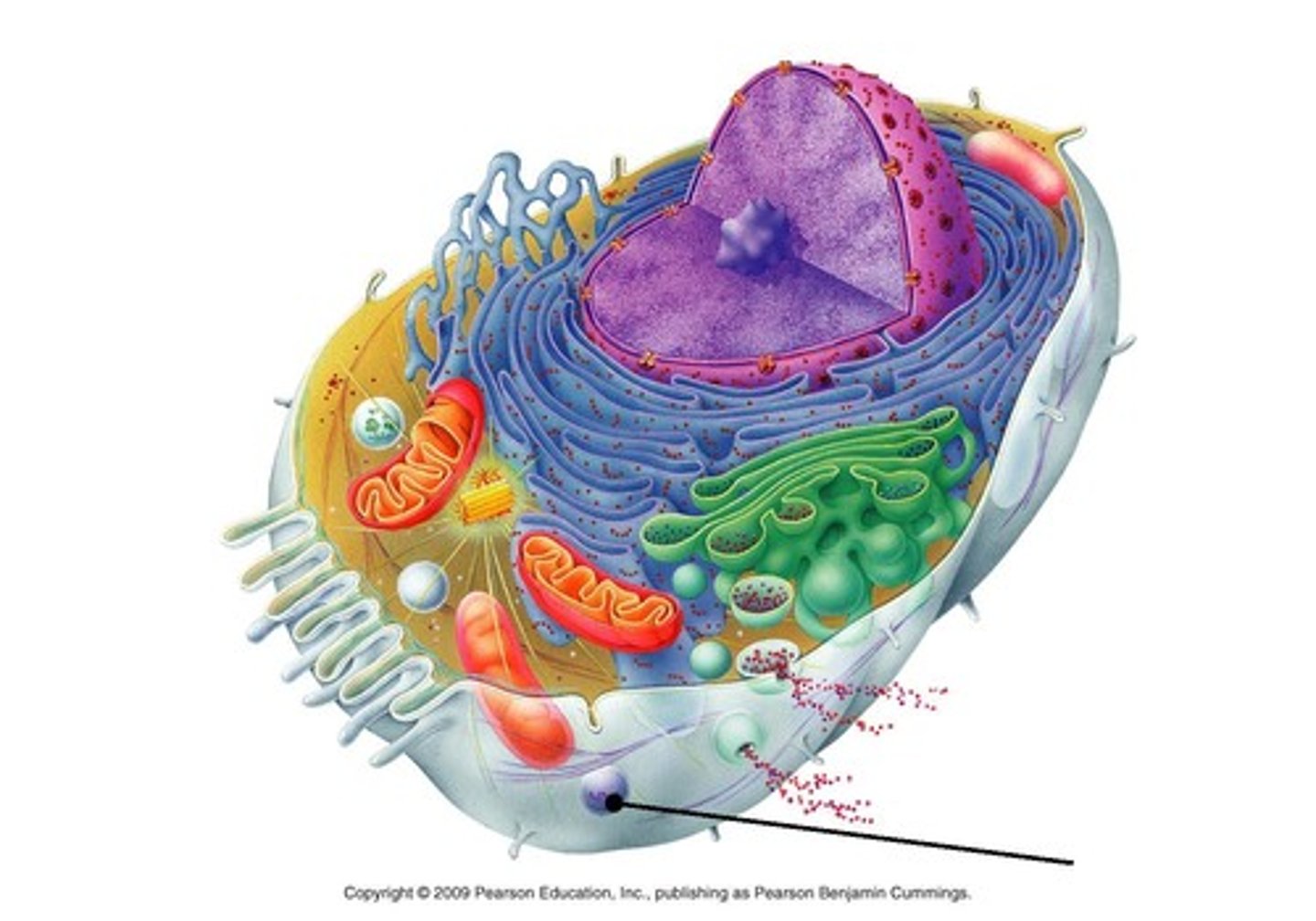
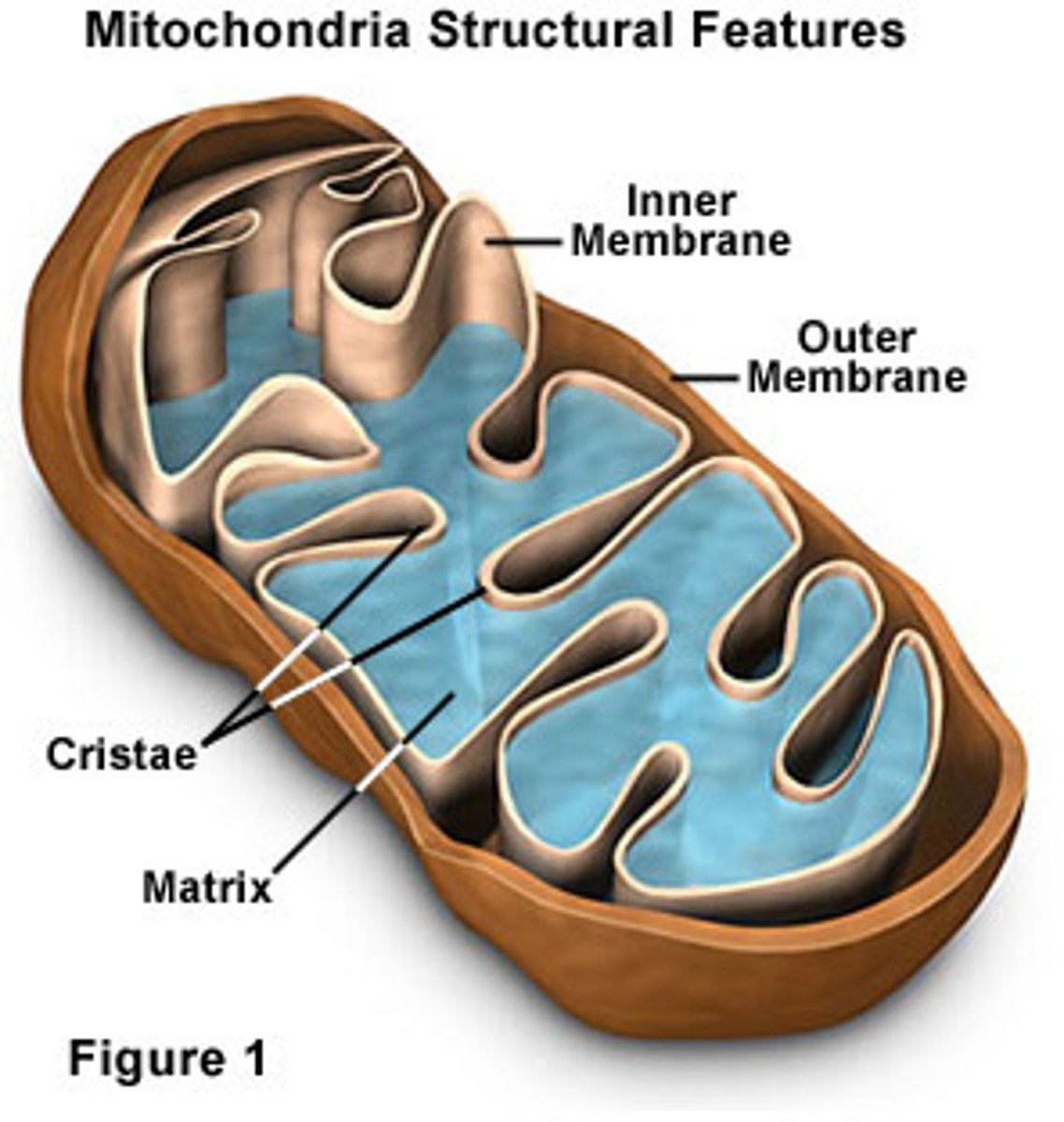
Mitochondria
-Convert energy to ATP (cellular respiration)
-Outer membrane - phospholipid bilayer
-Intermembrane space - H+ ions accumulate here
-Inner membrane (cristae) - oxidative phosphorylation, protein complexes, ATP synthase
-Matrix - Krebs cycle, pyruvate to acetyl coA
-Found in cells that require a lot of energy (muscles)
Centrioles/basal bodies (granules)
-Paired structures enclosed in centrosomes
-Microtubule organizing centers (MTOCs), produce microtubules
-Involved in the development of spindle fibers in cell division.
...
...
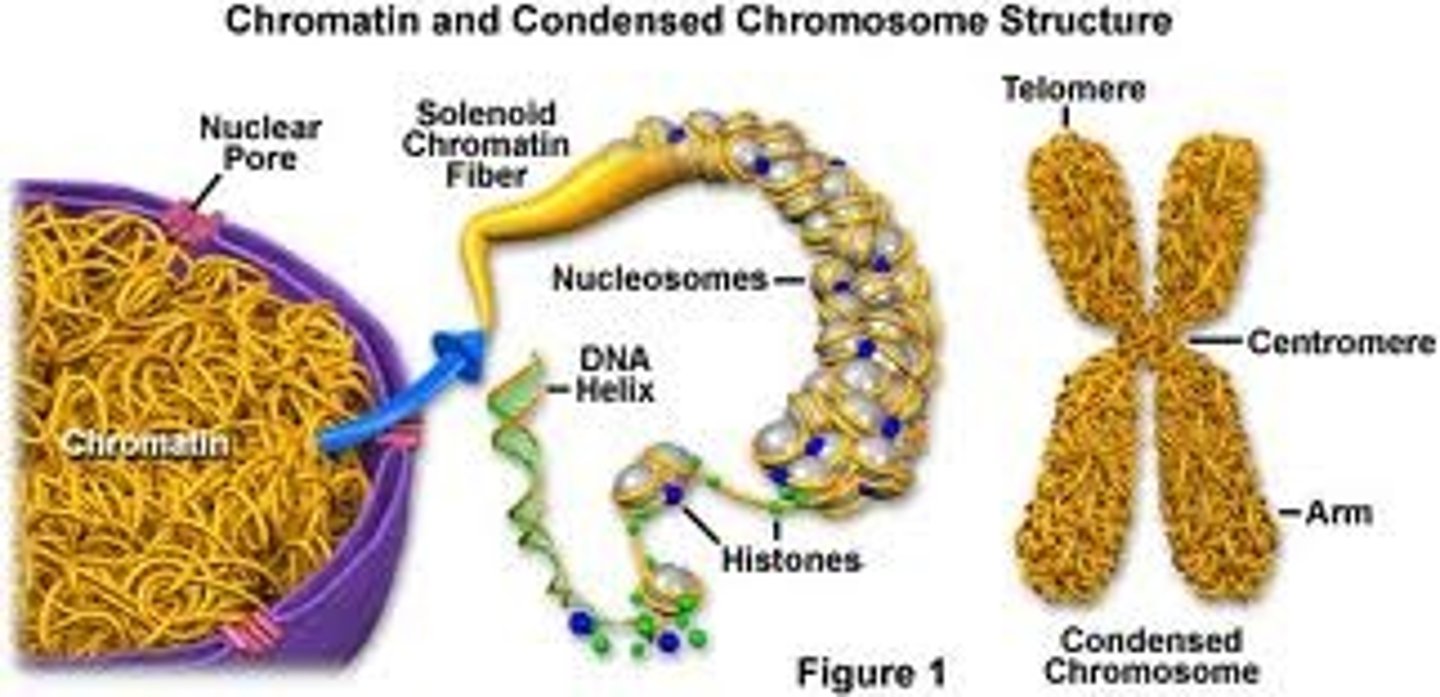
Chromatin
-Genetic material, unraveled DNA coils around histones (protein cores)
-Contained in chromosomes
-The complex of DNA and proteins making up chromosomes.
-A complex for 40% DNA and 60% protein, which contains the determiners of heredity.
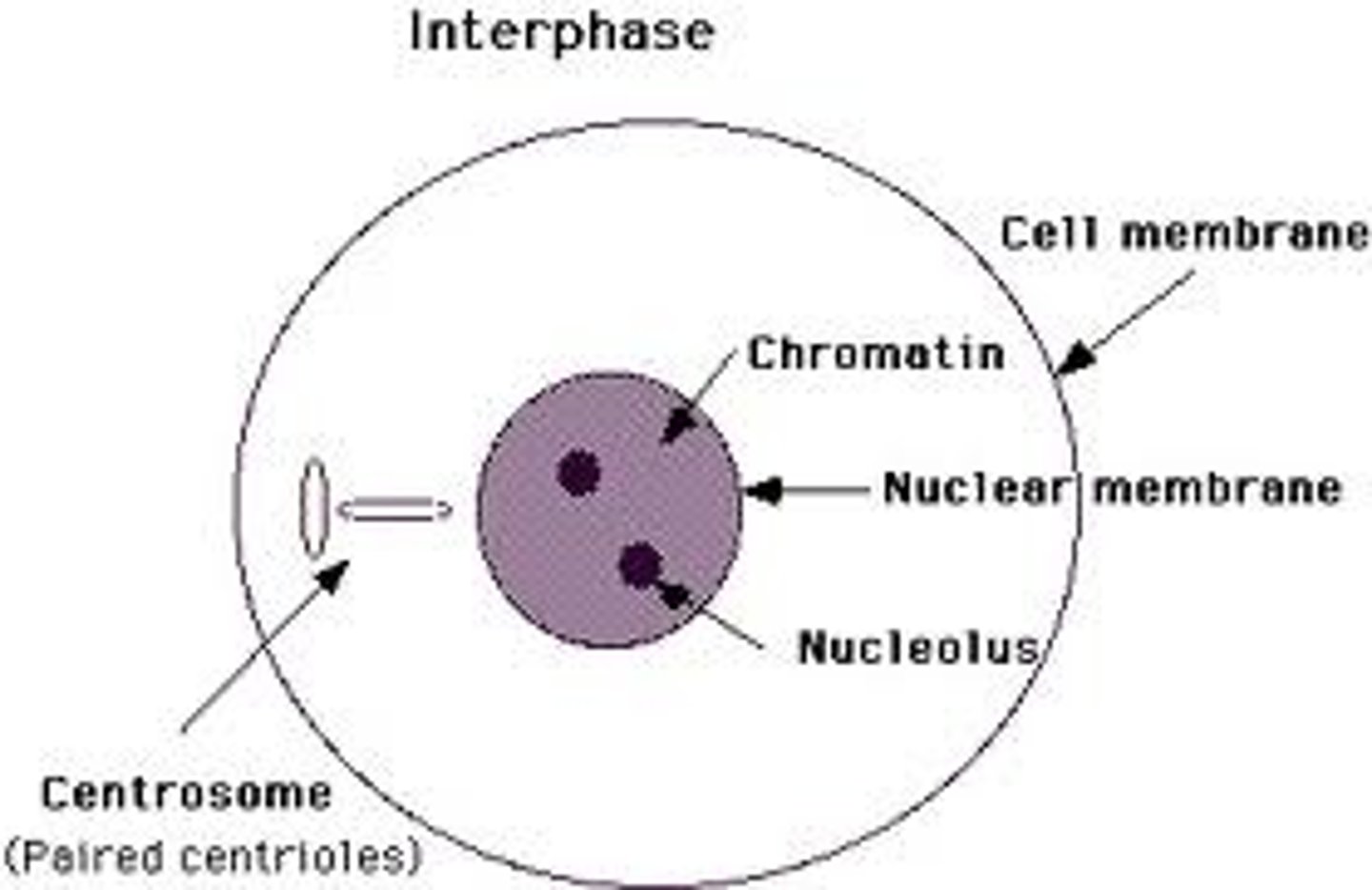
Interphase
-Consists of 3 phases:
-G1, S, G2
-During which the cell grows and replicates its DNA
G1 Phase
-Growth
-The primary growth phase
-(G = Gap)
-Gap between completion of mitosis and the beginning of S phase (DNA synthesis)
-Protein synthesis occurs and the cell grows to about double its original size. More organelles are produced, increasing the volume of the cytoplasm
-Diploid cell produces enzymes for DNA replication (DNA helicase, polymerase, ligase)
S Phase
-The replication phase
-DNA synthesis, diploid cell with 2x DNA linked as sister chromatids
-DNA is replicated to produce exactly two identical chromosomes. At the end of S phase, all of the chromosomes have been replicated; the amount of DNA in the cell has therefore effectively doubled. Typically, in a population of cells, about 30% will be in S phase at any one time.
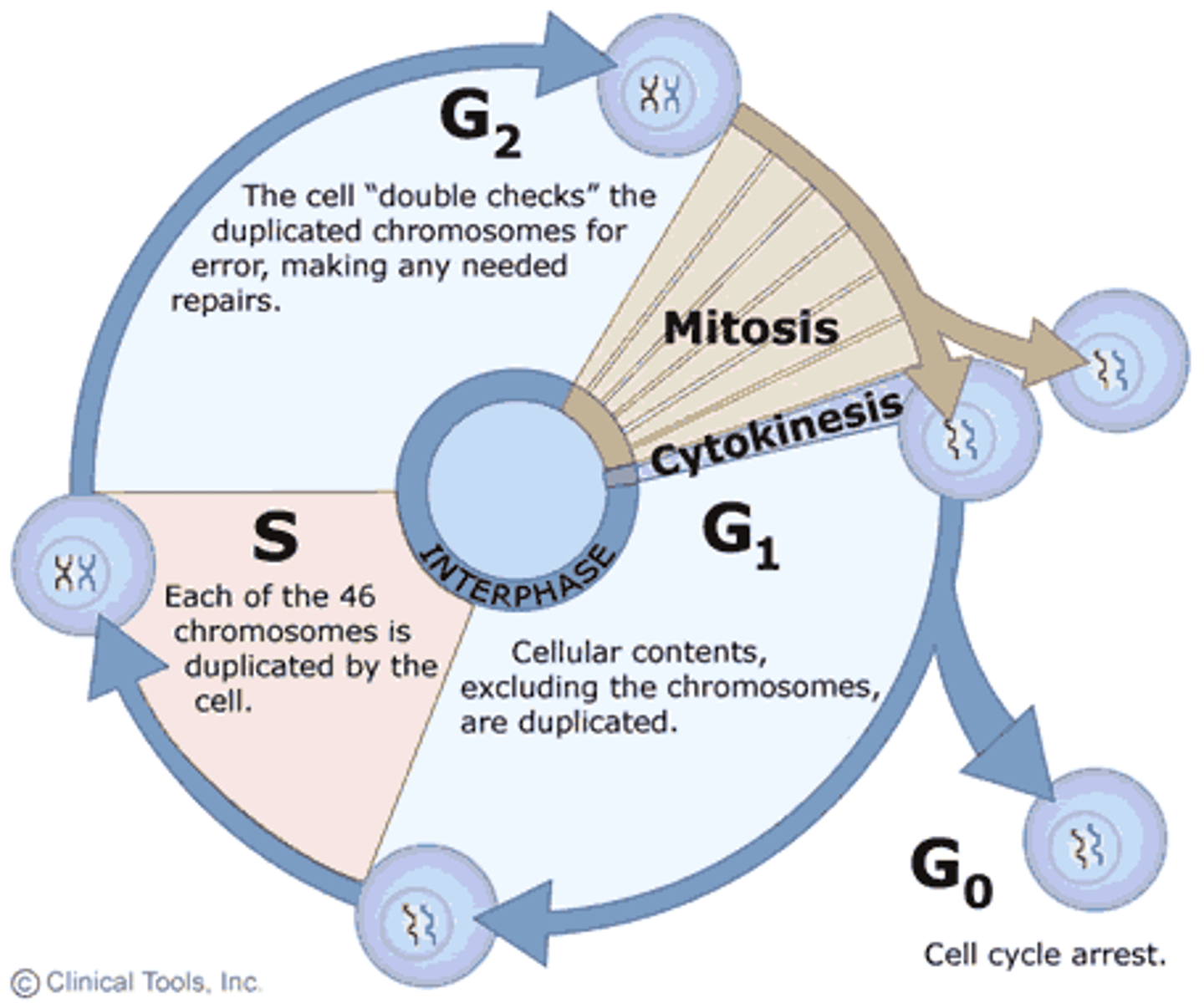
G2 Phase
-Rapid growth, construction of microtubules, preparation for division
-Second growth phase
-Lasts until the cell enters mitosis.
-Here, the cell undergoes significant biosynthesis to ensure necessary cell growth and production of microtubules required for mitosis. Inhibition of protein synthesis during G2 phase prevents the cell from undergoing mitosis.
-Preparation for division
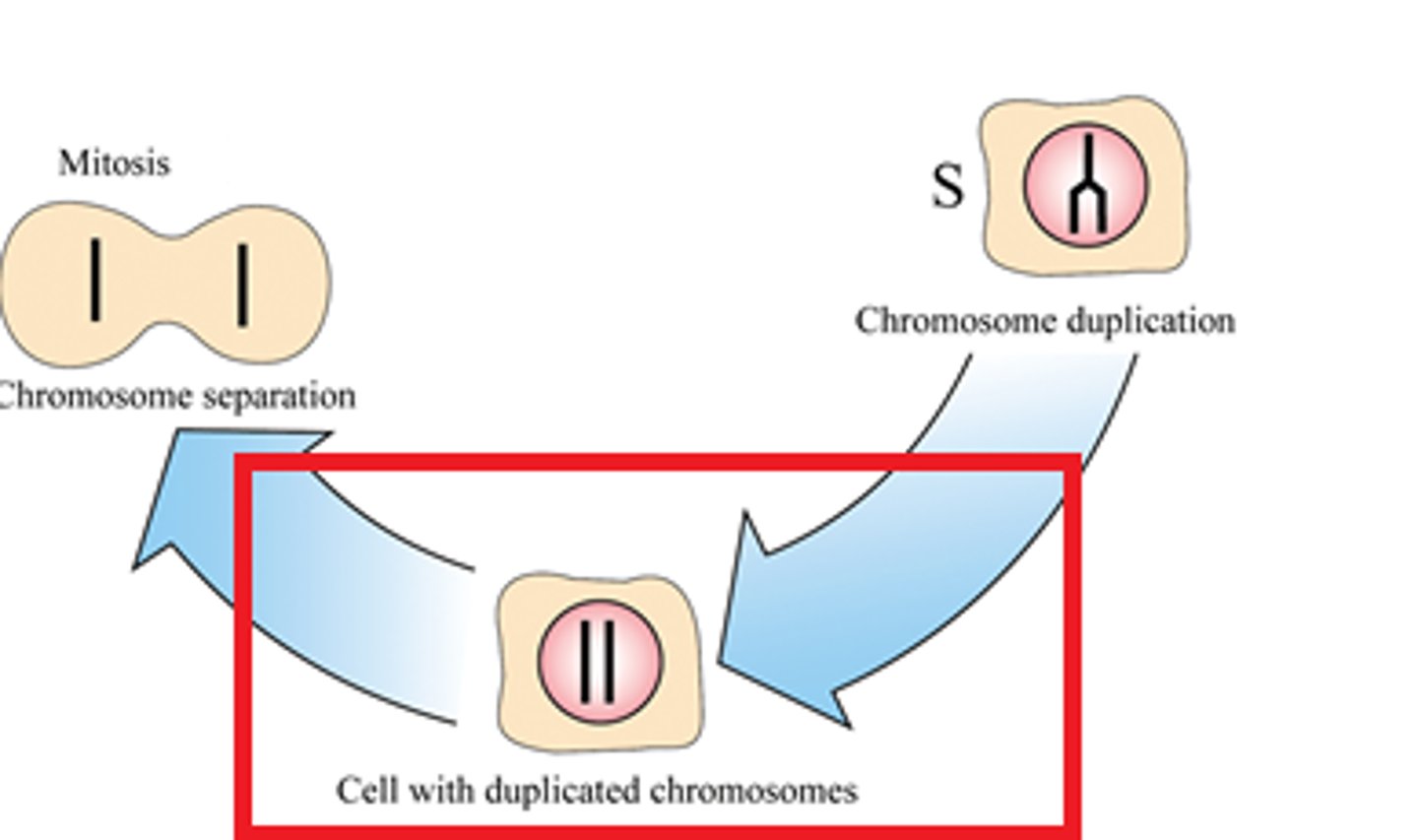
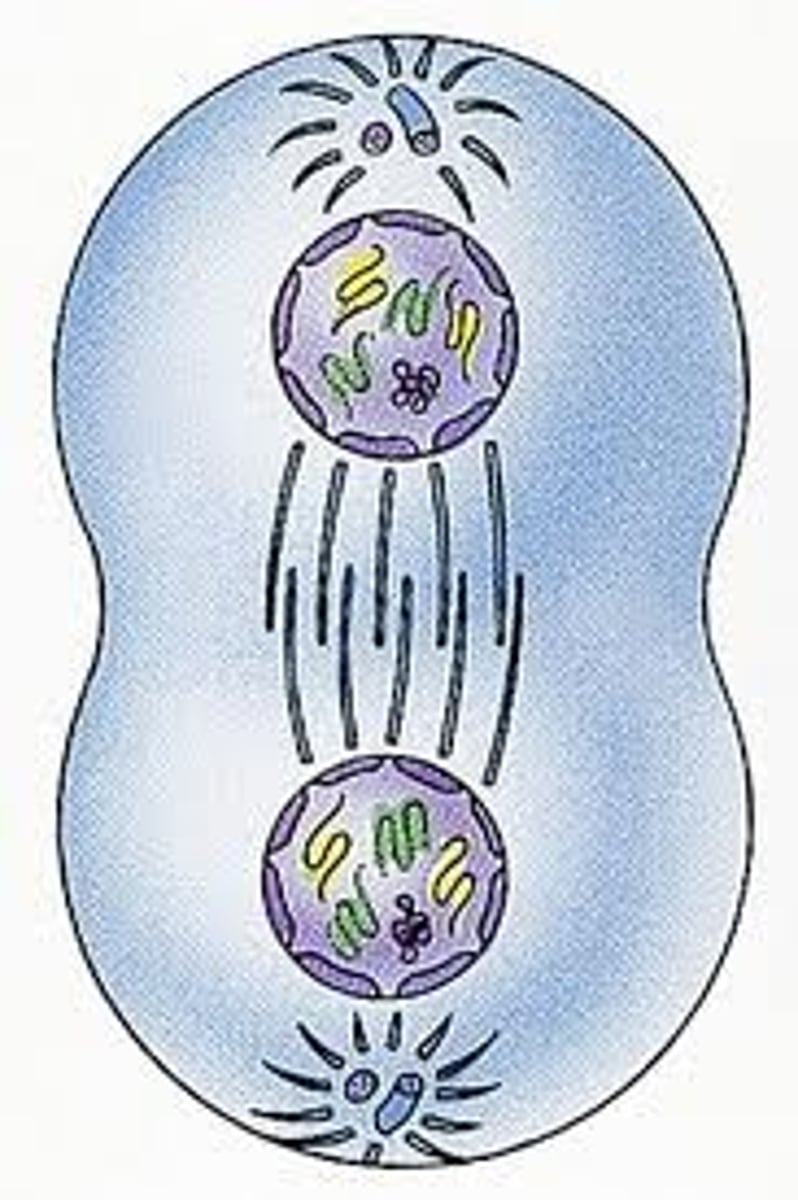
Mitosis
-The division of the nucleus during the four phases of cell division to form two identical daughter cells.
-Produces daughter cells identical to parent cells, maintains # of chromosomes, somatic cells
-Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
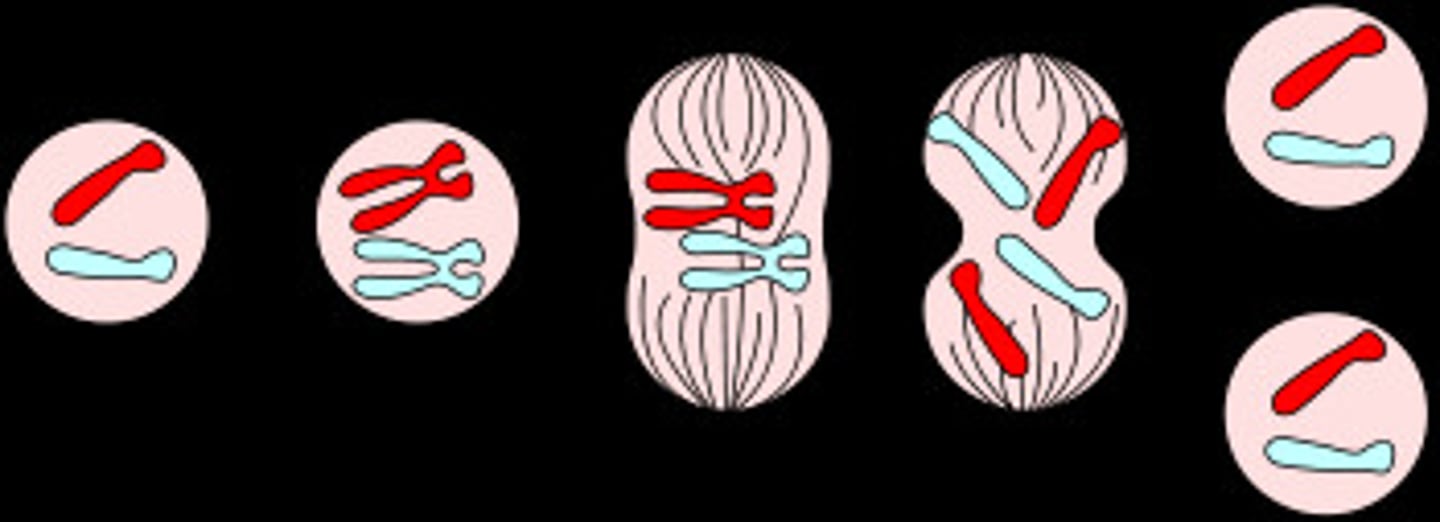
Prophase
-There is a shortening and tight coiling of the DNA into rod-shaped chromosomes. The two copies of each chromosome (called chromatids) stay connected to each other by the centromere.
-Nucleoli disappear, chromatin condenses into chromosomes
-Each chromosome has duplicated during the preceding S phase and consists of two sister chromatids. Towards the end of prophase, the cytoplasmic microtubules disassemble and the mitotic spindle begins to form.

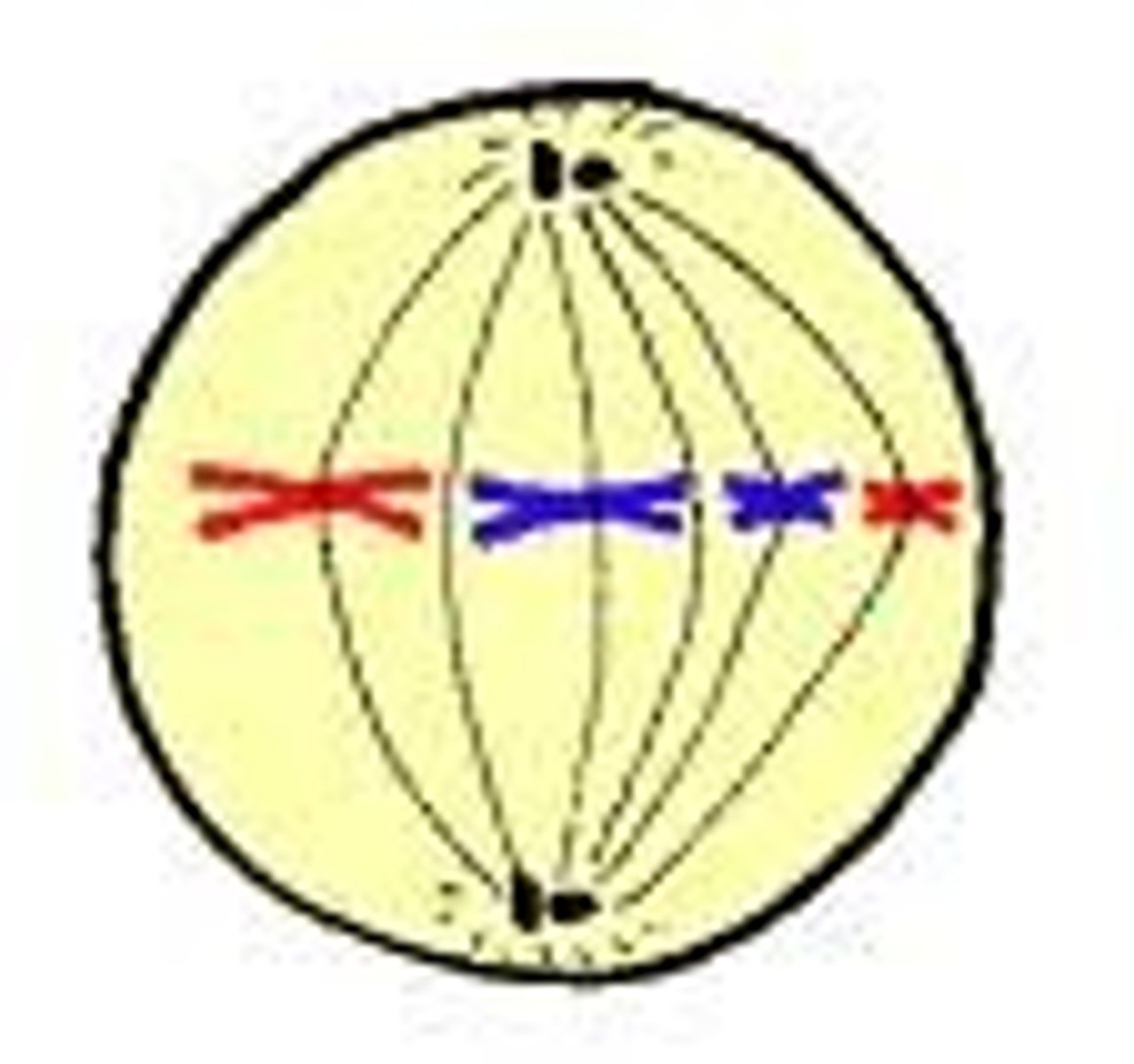
Metaphase
-Starts abruptly with breakdown of the nuclear envelope (prometaphase).
-Specialized protein complexes called kinetochores attach to some of the spindle microtubules, which are then called kinetochore microtubules. These structures are responsible for aligning the chromosomes in one plane between the poles of the cell. This is called the metaphase plate.
-Kinetochore fibers move the chromosomes to the center of the dividing cell and hold them in place there along a perceived metaphase plate at the equator of the cell.
Anaphase
-The shortest but most beautiful stage. Starts when all the chromosomes divide simultaneously. Then the two chromatids of each chromosome separate at the centromere and slowly move toward the opposite poles where their kinetochores are attached.
-Microtubules shorten, separate chromosomes to opposite poles
-Triggered by a specific signal, begins as the chromosomes are pulled to opposite ends of cell. The kinetochore microtubules shorten as the chromosomes approach the poles. This typically occurs at around a distance of 1 µm per minute.
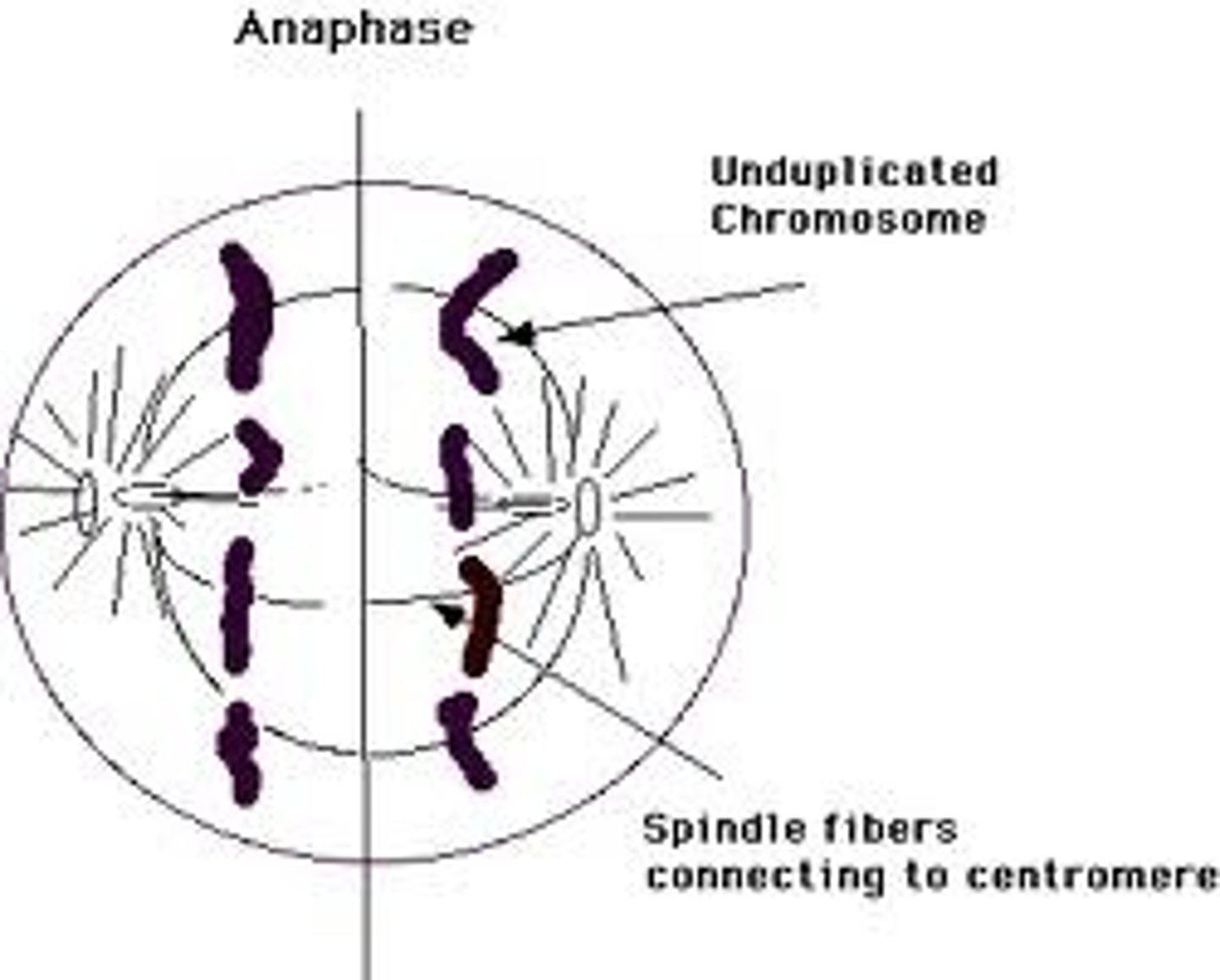
Telophase
-Spindle fibers disappear.
-Microtubules break down to be re-used to construct the cytoskeletons of the daughter cells.
-Nuclear envelope forms around each set of chromosomes and the chromosomes begin to uncoil to permit gene expression.
-Nuclear envelope develops around each pole (2 nuclei)
-Chromosomes disperse into chromatin, nucleoli reappear