CH.8 JOINTS (ANATOMY)
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
Articulation
joint
Joints are classified based on:
Function (range of motion) and structure (makeup of the joint)
Joints can be classified based on their range of....
Motion (function)
Synarthrosis
immovable joint
Synarthrosis joints are found where?
Bones of the skull
Amphiarthrosis joints
slightly movable joint
Amphiarthrosis joints are found where in the body?
Intervertebral discs and pubic symphysis
Synovial (diarthrosis) joints
freely movable joint
Synovial (diarthrosis) joints are found where in the body?
Ends of long bones
(Shoulder, Knee, Hip, Elbow, Wrist, Ankle, Fingers and toes)
Synovial joint
Monaxial
movement in one plane
Biaxial
movement in two planes
Triaxial
movement in three planes
What are the 6 characteristics of synovial joints?
-Articular cartilage
-Joint (synovial) cavity
-Articular capsule
-Synovial fluid
-Reinforcing ligaments
-Nerves and blood vessels
Articular cartilage
Smooth cartilage covers the ends of bones to reduce friction and absorb shock.
Joint (synovial) cavity
A space between bones that contains synovial fluid
Articular capsule
A double-layered capsule enclosing the joint
Synovial fluid
Lubricates the joint and nourishes the cartilage.
Reinforcing ligaments
Strengthen and support the joint.
Nerves and blood vessels
Help with joint movement, pain sensing, and nourishment.
Menisci (articular discs)
fibrocartilaginous pads in the knee
Fat Pads
Packing material for joint, fill spaces when bones move
Synovial tendon sheaths
surround tendons where they pass over bone to reduce friction or pressure
Bursae
small, fluid filled pockets of connective tissue
CIRCUMDUCTIONLinear Movements
two bones gliding past each other
Where do Linear Movements occur?
- Carpal/carpal
- Tarsal/tarsal
- Clavicle/sternum
Angular Movements
- Abduction/adduction
- Flexion/extension
Abduction
Movement away from the longitudinal axis of the bodyin the frontal plane.
Adduction
The opposite motion—moving it back to center
TRUE OR FALSE
Abduction and adduction always refer to movements of the appendicular skeleton.
True
1 multiple choice option
Flexion
Movement in the anterior-posterior plane that decreases the angle between the bones of the joint
Extension
In the same plane, but it increases the angle between the bones of the joint.
Hyperextension
a limb is extended beyond its normal limits
Circumduction
Moving the arm in a circle
What is an example of circumduction?
when drawing a large circle on a chalkboard in one continuous motion.
What are the 3 types of rotation?
- Internal/Medial Rotation
- External/ Lateral Rotation
- Left or Right Rotation
Internal/Medial Rotation
anterior surface of the limb rotates inward, toward the anterior surface of the body.
External/ Lateral Rotation
rotation in the transverse plane away from the midline of the body
Left or Right Rotation
rotation of head
Supination
movement that turns the palm up
Eversion & Inversion
moving the sole of the foot outward or inward
Dorsiflexion & Plantar Flexion
up and down movement of the foot
Lateral Flexion
Side-bending left or right
Protraction & Retraction
anterior to posterior movement of scapula or mandible
Eversion
motion of the foot that turns the sole outward.
Inversion
The opposite movement (turning the sole inward.)
Dorsiflexion
Elevates the distal portion of the foot and the toes
Dorsiflexion example
walking on heels
Plantar Flexion
elevates the heel and the proximal portion of the foot
Plantar Flexion example
standing on tiptoe
Lateral Flexion
vertebral column bends to the side.
Protraction
Moving a part of the body anteriorly in the horizontal plane
Retraction
moving a part backward
Opposition
pad-to-pad contact of the thumb with the palm or any other finger.
Reposition
the opposite movement that returns the thumb and fingers to their normal position.
Rotational Movements are...
Pronation/supination
Circumduction Movements are...
Moving the joint in a circular manner
Inversion/eversion involves
ankles
Dorsiflexion involves
ankles
Plantar flexion involves
tippy toes
Lateral flexion involves
the spine
Protraction/retraction involves
temporomandibular joint and shoulders
Depression/elevation involves
shoulder moving up and down
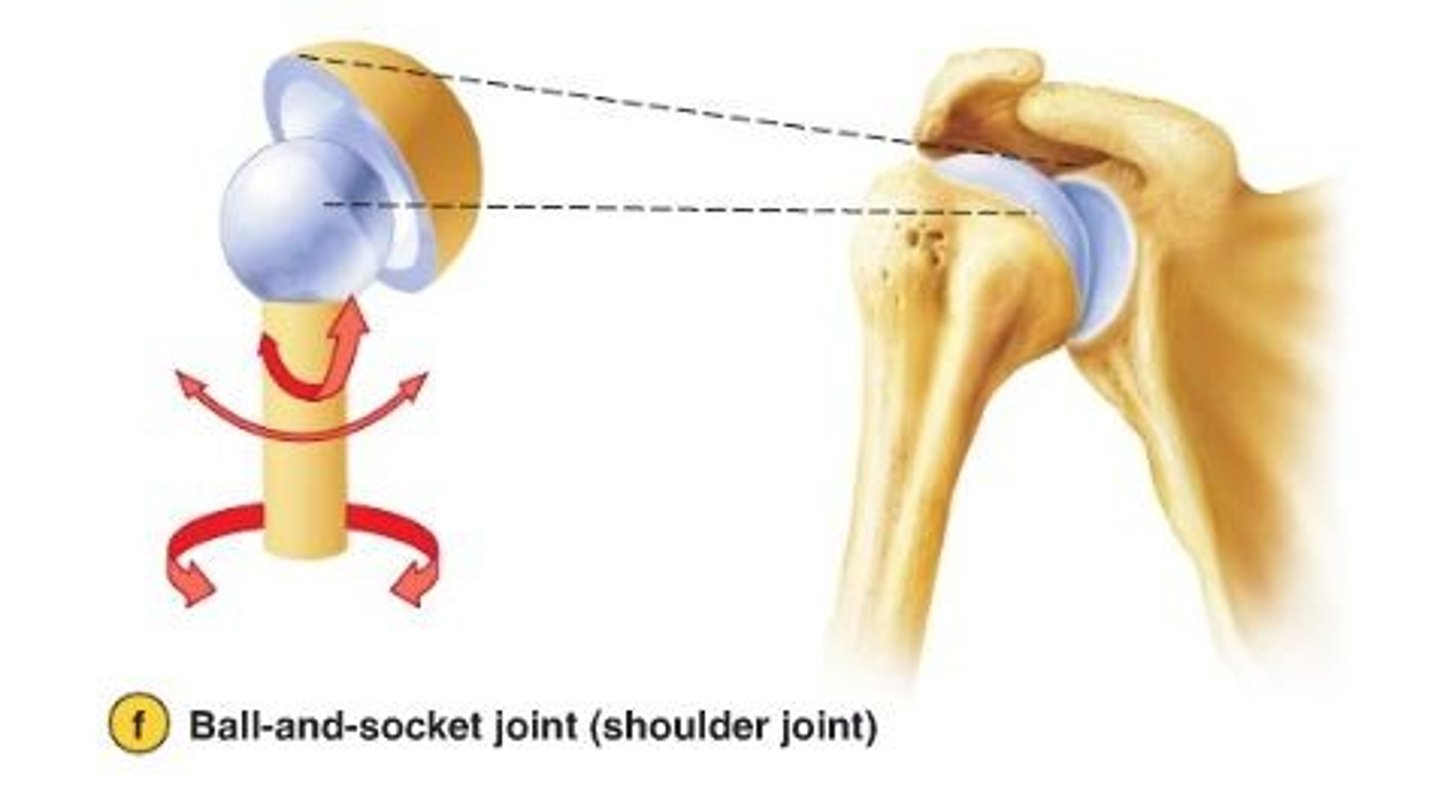
Ball-and-socket joint
hip and shoulder joints
Hinge joint
elbow and knee
Pivot joint
the joint at C1 and C2
Saddle joint
carpometacarpal joint
Ellipsoid joint
metacarpophalangeal joint
Gliding joint
clavicle and manubrium