Red Blood Cell Production
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What components make up blood?
red blood cells
white blood cells
monocytes
neutrophils
eosinophils
basophils
lymphocytes
platelets
At 5 years old where does RBC formation occur?
bone marrow in all bones
Between 5-20 years old where does RBC formation occur?
in the bone marrow of the long bones
femur and tibia
At 20+ years where does RBC formation occur?
in the bone marrow of membranous bones
vertebrae, sternum, ribs, and pelvis
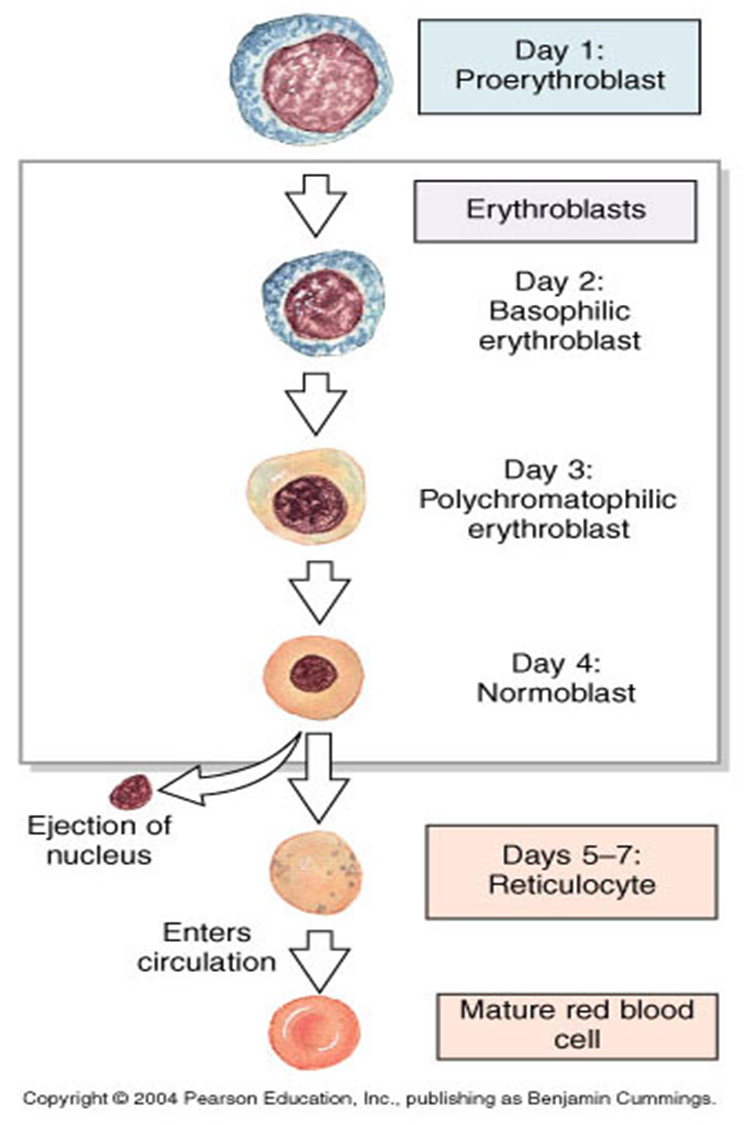
What are the stages of mature RBC formation?
What plasma proteins are part of blood composition?
albumins (60%)
maintains blood volume and transports
globulins (35%)
transports and has immune functions
fibrinogen (4%)
component of clotting system
regulatory proteins (1%)
enzymes, proenzymes and hormones
What are albumins in charge of?
controls osmotic pressure in plasma
transports fatty acids and thyroid hormones
moves bilirubin
What are globulins responsible for?
transport small molecules
serve an immune function
Do RBCs proliferate?
Can RBCs repair themselves?
no
no
How long is a RBC lifecycle?
How do RBCs get ‘killed’?
120 days
90% are engulfed by phagocytes and 10% rupture
What happens to haem group from dead RBC?
phagocyte recognises it so it can be recycled
What charge is membrane of RBC?
negative surface charge due to glycoprotein coat
What is the membrane of RBC made of?
lipid bilayer
outer glycoprotein coat (gives the negative surface charge)
What are RBCs stained with and what does this cause?
stained with eosin which causes the RBC to go red colour (more pigmented around perimeter)
What are the stages of mature RBC formation?
Proerythroblast
first erythrocyte precursor, differentiates from multipotent stem cell due to influence from erythropoietin
Basophilic erythroblast
Smaller than proerythroblast has more ribosomes in cytoplasm though, involved in production of haemoglobin
Polychromatophilic erythroblast
Last precursor cell capable of mitosis, smaller than basophilic erythroblast
Normoblast
Contains a nucleus
Reticulocyte
Still has a slight basophil stain
Erythrocyte
Final product of erythropoiesis and is released from the bone marrow into circulation
What does erythropoietin do?
stimulates proliferation and differentiation of precursor stem cells to produce mature RBCs
What causes blood to agglutinate/ coagulate?
if the blood type has antibodies for the other blood type/ blood antigen, then the antibodies “kill” it by agglutinating
e.g. B+ would agglutinate with anti-A making it useless (dead)