Biology Chapter 3 - The Biosphere
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
ecology
the study of interactions among organisms & their physical environment
6 levels of organization (small to big)
SPaCE BB
1. species
2. population
3. community
4. ecosystem
5. biome
6. biosphere
species
a group of similar organisms that can breed and produce offspring
population
a group of a particular species living in the same area
community
different populations living in the same area
ecosystem
all the living and nonliving factors combined in one area
biome
a group of ecosystems with the same climate
biosphere
all life on earth & all parts of the Earth in which life exists (living and non-living)
ex. land, water, temperature
3 methods to conduct ecological research
1. observing
2. experimenting
3. modeling
observing
qualitative (behaviors) and quantitative (numbers) observations
ex. #'s of koalas
experimenting
used to test hypotheses; artificial environments and manipulative conditions
ex. growing plants using different fertilizers in a greenhouse
modeling
models made to study events that happened over large periods of time or are large in scale
ex. illustrating a food web to shoe feeding relationships in an ecosystem
primary producers (autotrophs)
first producers of energy-rich compounds which are to be used by other organisms
- captures energy from sunlight to chemicals and converts it to forms that living things can use during photosynthesis (makes own food)
example of an autotroph would be grass
photosynthesis
When a cell captures energy in the sunlight and uses it to make food
chemosynthesis
process in which chemical energy is used to produce carbohydrates
photosynthesis v.s chemosynthesis
- both get/make carbs
- chemosynthesis produces sulfur
- photosynthesis makes oxygen
- photosynthesis = sunlight
- chemosynthesis = chemicals
consumers/heterotrophs
an organism that gets its energy by eating other organisms
- all organisms expect for autotrophs
- energy indirectly form the sun
6 types of consumers
1. carnivores - meat eaters; sharks
2. herbivores - eat plant matter; deer
3. omnivores - eat meat and plants; people
4. scavengers - do not hunt and eat the big dead things they find; vultures
5. decomposers - break down organic matter (dead plants and animals) to produce detritus; mushrooms, bacteria
6. detritivores - eat very small dead remains; worms, mites
biotic
living parts of the environment
- fungi, puppies, people, bacteria
abiotic
nonliving parts of the environment
- water, wind, sunlight, cars, rocks, temperature
primary producer
plants, algae, and bacteria that capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and convert it into forms that living cells can use in the process of photosynthesis
also known as autotrophs
primary consumer
eats primary producers (plants/heterotrophs)
- bunny to plant
secondary consumer
an animal that feeds on primary consumers
- fox to bunny
tertiary consumer
An organism that eats secondary consumers
nutrients
chemical substance needed to sustain life
- builds tissue and carries out essential life functions
- food chains continually recycle nutrients
6 essential nutrients
1. carbs, 2. protein, and 3. fats (macronutrients
4. water
5. vitamins, 6. mineral (micronutrients)
food chain
a series of feeding steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten

the main source of energy
the sun
trophic levels
each step in a food chain that shows the transfer of energy (there are never more organisms than there is energy to support)
- energy only flows away from the sun
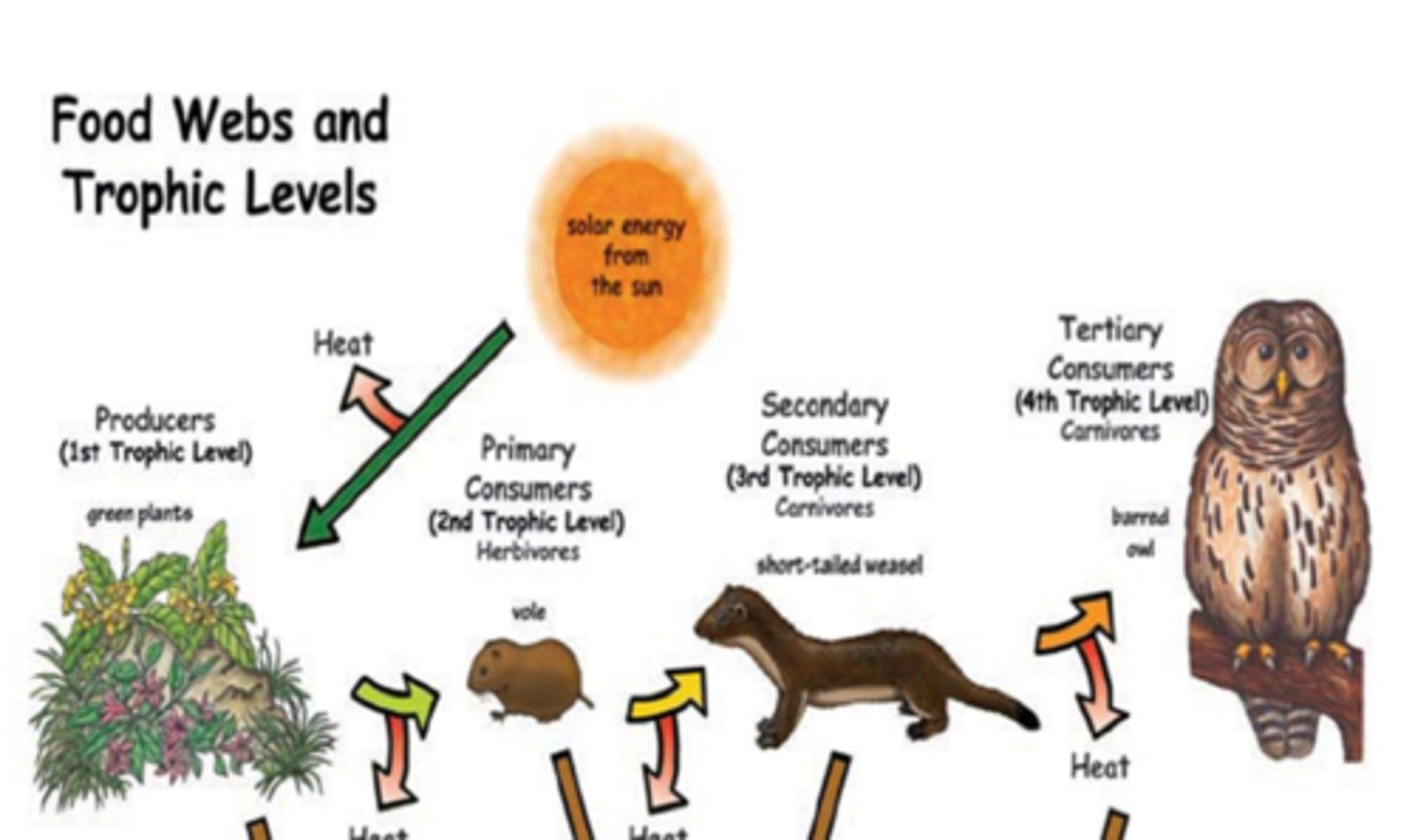
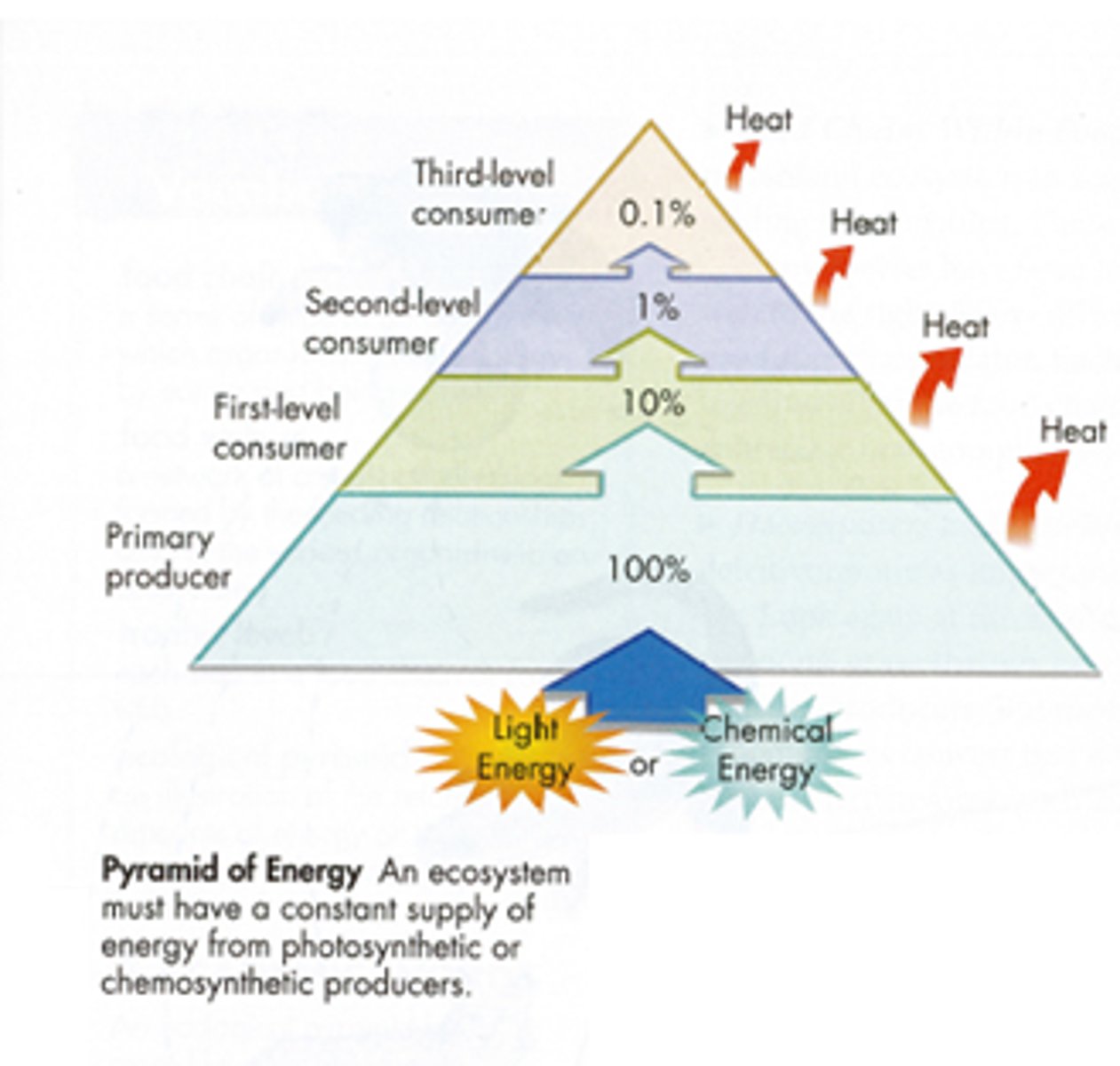
10% rule
only 10% of the energy stored in an organism is passed to the next generation on the next level
- the rest is eliminated as heat
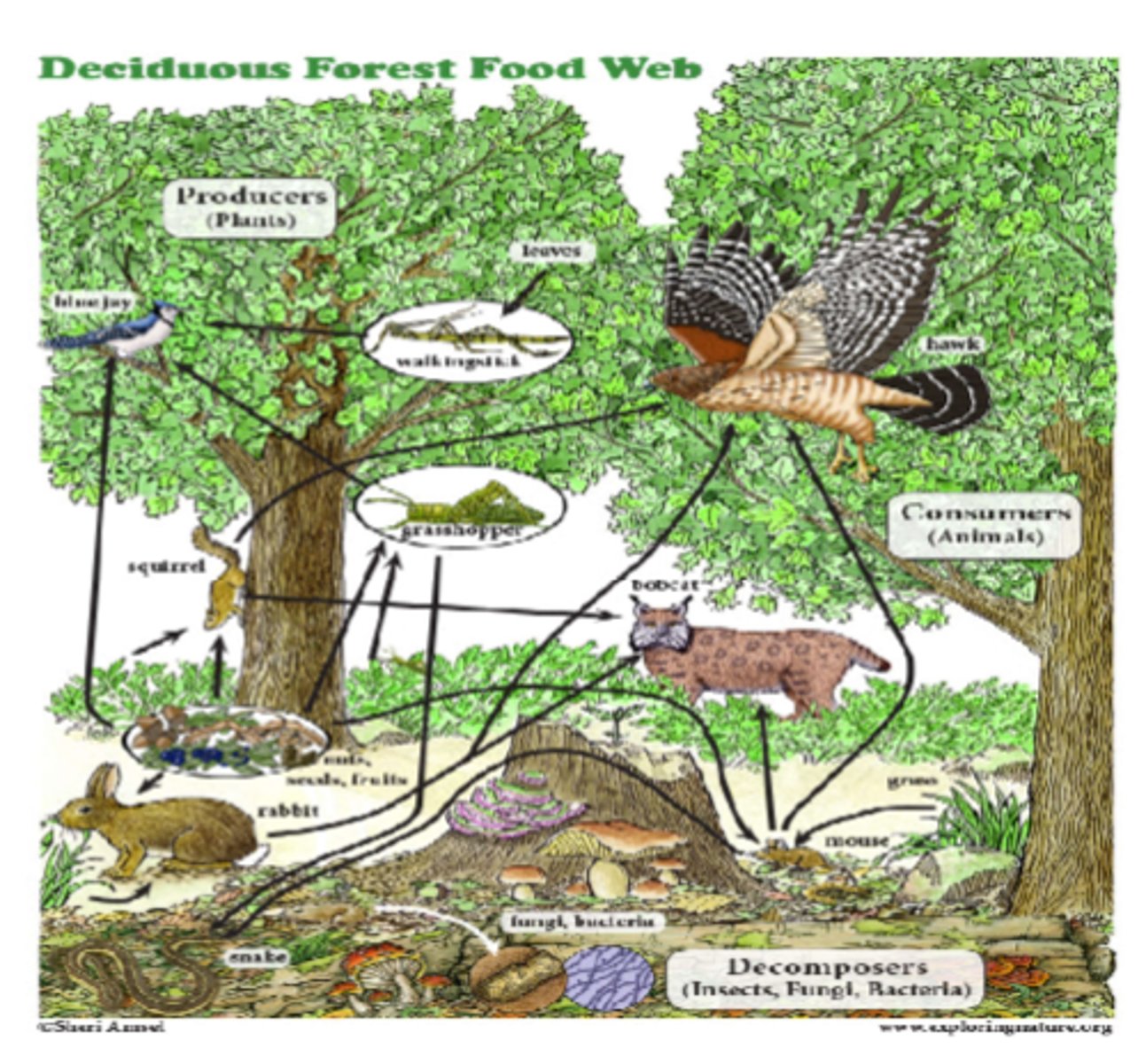
food webs
interconnected food chains that show all feeding relationships in an ecosystem
phytoplankton
plant-like aquatic microorganisms found in fresh and marine water
- primary producers in water (first level on the food chain)
- releases oxygen
zooplankton
animal-like aquatic organisms and the larval stages of other life forms
- primary or secondary consumers
- consumes oxygen
energy flow pyramids
flow of energy (amount) decreases as you go higher in the pyramid
energy pyramid
shows relative amounts of energy available at each trophic level
- heat/energy of organisms
- 10% rule
biomass pyramid
shows the relative or total amount of living organic matter at each trophic level
- mass of organisms
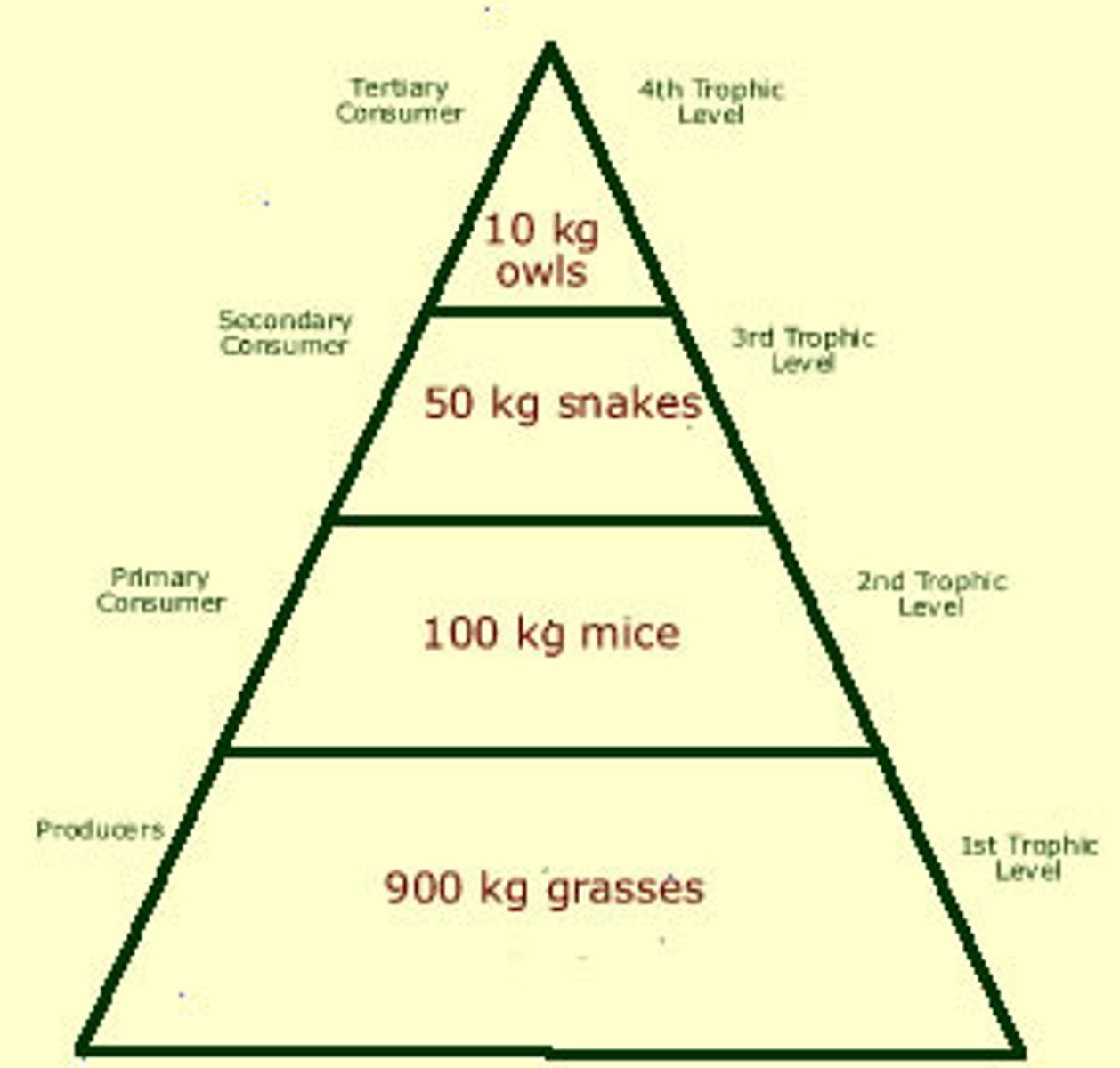
pyramid of numbers
shows the relative number of individuals living at each trophic level
- number of organisms
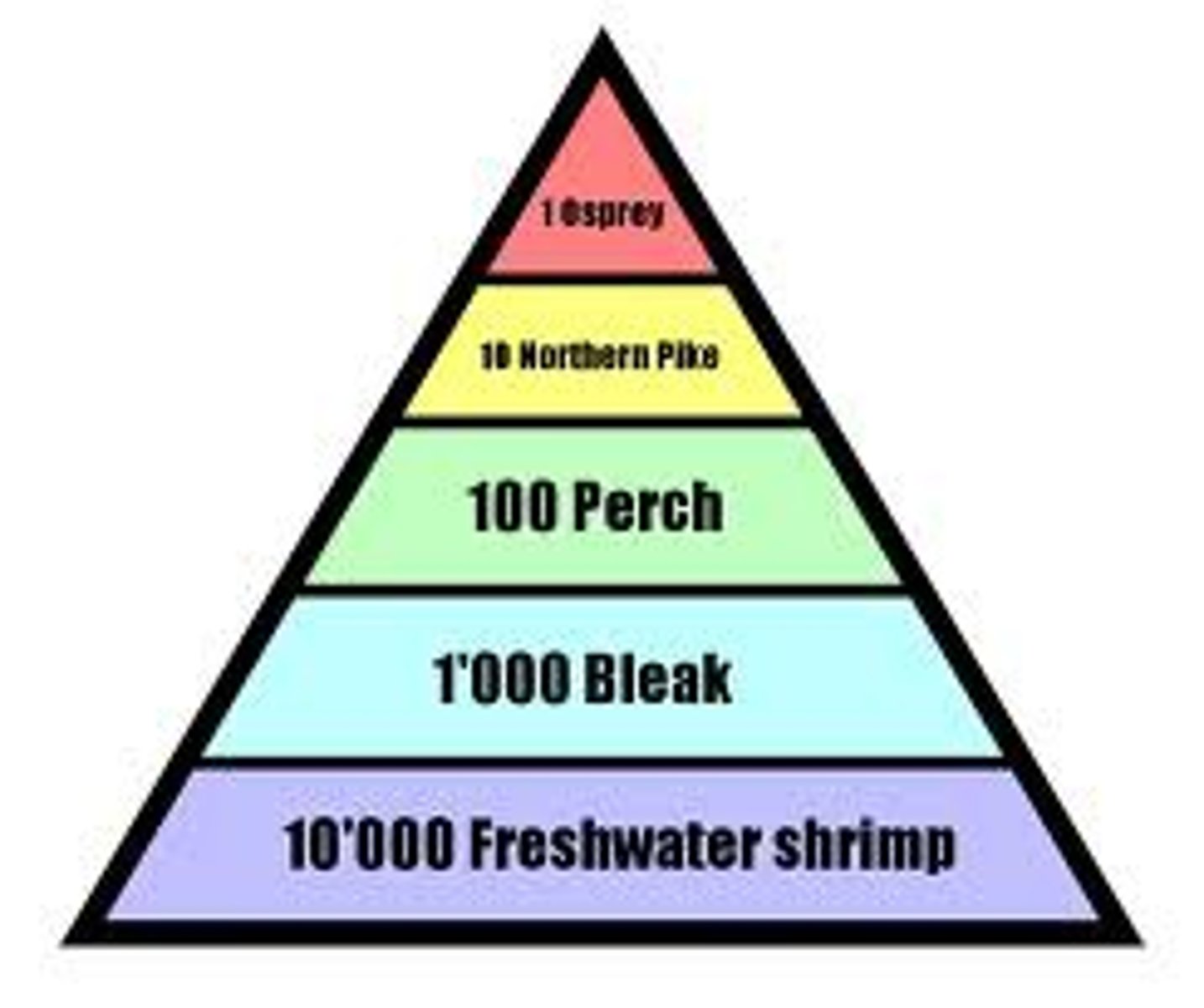
Energy flow rule
because only 10 percent of energy is passed, there will not be an equal amount of creatures at the next level
ecological pyramids
show the relative amount of biomass, numbers or energy contained within each trophic level in a food chain/web
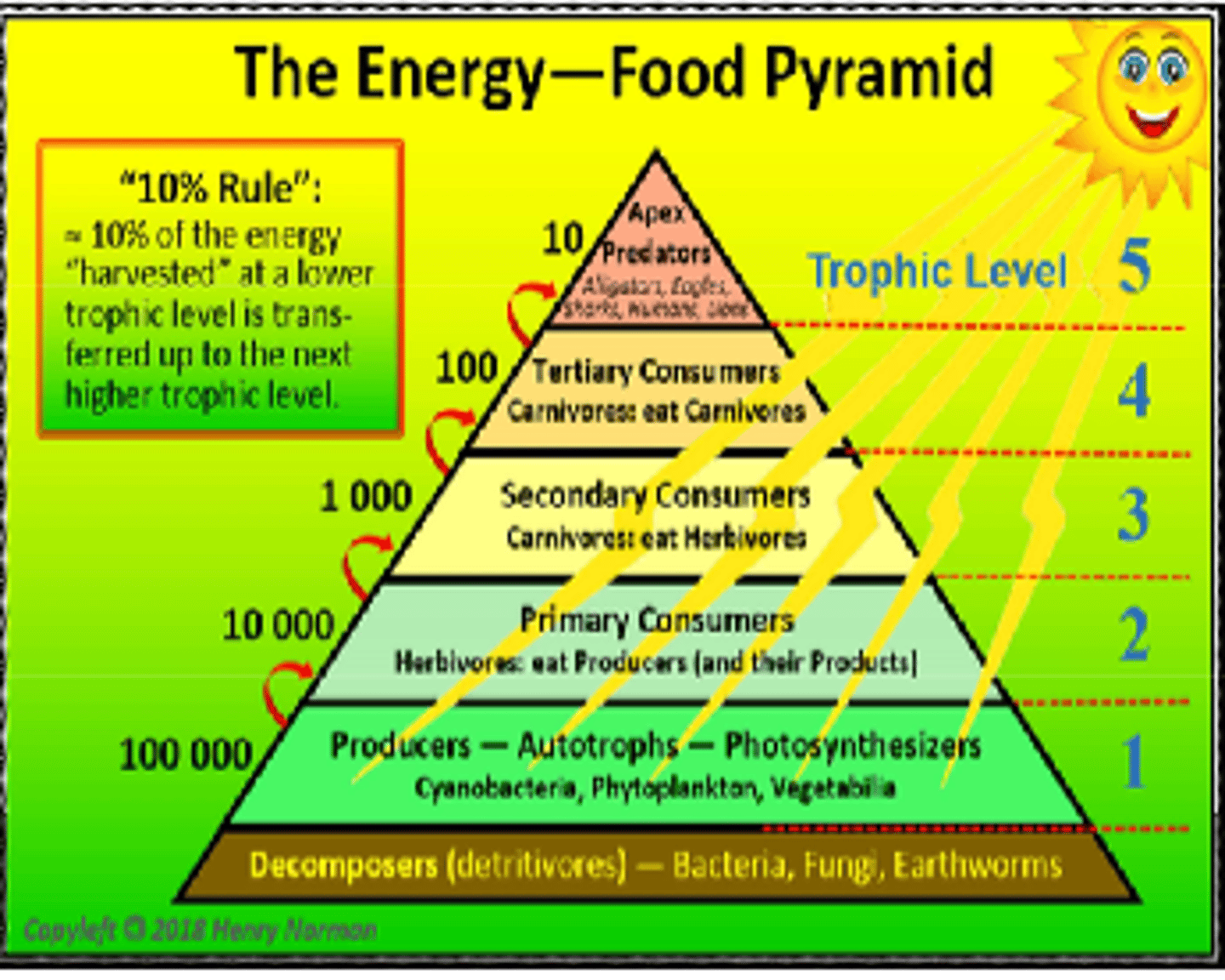
what is the role of decomposers in a food web/ food chain
(benefits it provides)
feed on the remains of the other animals. by decomposers digesting dead matter they put nutrients back into the soil, making them available to producers
what is the 10% rule?
10% of the energy stored in an organism is passed to the next organism on the next trophic level; the rest of the energy is eliminated as HEAT