Sediment Transport
5.0(1)Studied by 2 people
Card Sorting
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 2:28 AM on 2/6/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
1
New cards
Dry mass wasting
* gravitational collapse of slope
* no water/little water
* avalanche
* no water/little water
* avalanche
2
New cards
Sediment entrainment
* sediments enter the fluid
* more energy needed to entrain than keep moving
* more energy needed to entrain than keep moving
3
New cards
parameters for how fluids flow:
* density
* viscosity/resistance to flow
* viscosity/resistance to flow
4
New cards
laminar flow
uniformly in parallel/subparallel sheets
* low velocity water
* lower flow velocity near the bed
* low velocity water
* lower flow velocity near the bed
5
New cards
turbulent flow
unpredictable flow that changes in local pressure and velocity ie eddies (more mixing)
* high velocity water flow
* higher flow velocity near the bed
* high velocity water flow
* higher flow velocity near the bed
6
New cards
What determines if a flow is laminar or turbulent
Reynolds number
*
*
7
New cards
reynolds number is dependant on:
* velocity
* viscosity
* flow boundary roughness
* confinement of flow
* viscosity
* flow boundary roughness
* confinement of flow
8
New cards
froude number
measures how gravity affects fluid flow (shallow water)
* inertia vs shallow wave
* inertia vs shallow wave
9
New cards
subcritical flow
Fr
10
New cards
critical flow
Fr = 1
velocity = wave speed
velocity = wave speed
11
New cards
supercritical flow
Fr>1
most downstream flow
most downstream flow
12
New cards
hydraulic jump
sudden change from supercritical to subcritical flow
13
New cards
bernoullis principle
flow entering and leaving at equal marks must be the same magnitude of pressure and speed
* fluid must be incompressible
* friction by viscous forces = negligible
* this keeps planes up
* fluid must be incompressible
* friction by viscous forces = negligible
* this keeps planes up
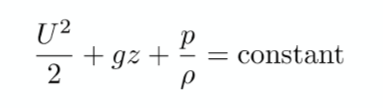
14
New cards
traction
sediment is dragged and rolled along bed surface
* bedload
* bedload
15
New cards
saltation
sediments jump along bed
* bedload
* bedload
16
New cards
suspension
sediments float along with flow
* suspended load
* suspended load
17
New cards
hjulstrom curve
both larger grain and smaller grain sizes need higher velocity to be transported
18
New cards
why does the hjulstrom curve include small grain sizes
* flocculation due to charges of clay platelets to increase diameter
* viscous sublayer at the bed make it difficult to erode
* viscous sublayer at the bed make it difficult to erode
19
New cards
stokes law
predicts settling velocity of sediment for spherical grains, laminar flow, and dilute suspensions
* if density of particle > density of fluid, it will settle
* if density of particle > density of fluid, it will settle
20
New cards
Types of Gravity Flows
* turbidity current
* liquefied flow
* grain flow
* mud/debris flow
* liquefied flow
* grain flow
* mud/debris flow
21
New cards
turbidity currents
gravity flows where sediment is supported by upward turbulence of fluid
* flows down slope due to denser than water
* fining upwards/normal grading due to decrease in energy
* flows down slope due to denser than water
* fining upwards/normal grading due to decrease in energy
22
New cards
liquefied flow
gravity flow via concentrated grains supported by pore space fluids
* flow when force is encountered and lose cohesion = liquefaction
* leads to pipes/fluid escape structures
* flow when force is encountered and lose cohesion = liquefaction
* leads to pipes/fluid escape structures
23
New cards
grain flow
gravity flow via cohesionless sediment moves downslope via gravity (30 degrees under air)
* water/air is present btwn grains but dont propel
* need high slope
* water/air is present btwn grains but dont propel
* need high slope
24
New cards
debris flows
gravity flows through masses of liquified mud that move via gravity with BOULDER-sized clasts
* >10 degree after heavy rains
* inverse graded
* >10 degree after heavy rains
* inverse graded