essay 2 - Nucleotides – composition and structure. Free nucleotides of biologic significance. Nucleic acids – composition and structure. DNA and RNA. Levels of organization of DNA – nucleosomes and chromosomes. Types of RNA molecules – mRNA, tRNA, rRNA, miRNA.
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
section
nucelotides
function of nucelotides
nucleic acid
dna and rna difference
dna organisation levels
types of rna molecules
nucelotides
made up of: nitrogenous base, pentose group, phosphate group
purine base is either adenine or guanine base
pyrimidine base has either cytosine or thymine or uracil (in RNA)
pentose group is either ribose or deoxyribose
nitrogenous base is bonded to ribose via glycosidic bond
ribose group bonded to phosphate group via phosphodiester bond
function of nucelotides
building blocks on nucleic acid
metabolic role
regulators
allosteric effectors
nucleic acid
nucleic acids are polynucleotides, lots of nucleotides joined together by phosphodiester bonds
phosphodiester bond between 5’ hydroxyl group on one sugar to 3 hydroxyl group on next sugar in chain
phosphodiester bonds found in both dna and rna
direction of nucleic acid is 5’-3’
nucleic acid is read in same 5’-3’ direction
dna and rna difference
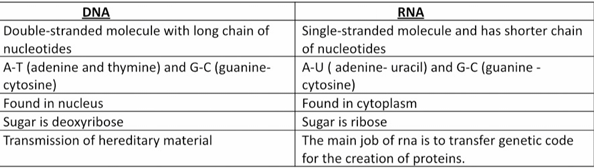
dna organisation level
DNA is a double-stranded helix with antiparallel strands
Held together by hydrogen bonds:
A–T has 2 hydrogen bonds
G–C has 3 hydrogen bonds
Most DNA helices are right-handed, except Z-DNA (left-handed)
DNA is packaged into chromosomes
Chromosomes are made of DNA tightly coiled around histone proteins
Histones are positively charged proteins that bind to negatively charged DNA
DNA + histones form nucleosomes, which help compact DNA into the nucleus
types of rna molecules
mRNA (messenger RNA)
tRNA (transfer RNA)
rRNA (ribsoomal RNA)
miRNA (micro RNA)