Coordination Compounds PART ONE
1/176
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Basic Nomenclature, Denticity, yeah that's about it for this one. There is a part two. Check out my other flashcards! Answer mode: Answer with Definition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
177 Terms
What are addition compounds?
When two or more simple salt solutions are mixed and then subjected for crystallization, the crystals which are obtained are called addition compounds.
What are the two types of addition compounds?
Double Salt / Lattice Compound
Coordination / Complex Compound
What are double salts?
The addition compounds that can undergo complete ionisation are called double salts.
What are complex compounds?
Addition compounds that undergo partial ionisation to form a complex ion in aqueous solution are called complex compounds or coordination compounds.
Which sort of addition compounds retain their identity in aqueous solution?
Coordination Compounds
Which sort of addition compounds do not retain their identity in aqueous solution?
Double Salts.
What is central metal ion?
The metal ion which forms complex ion in combination with anions or neutral molecules.
Which type of addition compounds can form ions that can give confirmative tests?
Double Salts?
Which type of addition compounds form ions that cannot give confirmative tests?
Coordination Compounds
What is an ionisation sphere?
The ionisable part of a coordination compound
What is a coordination sphere?
The non-ionisable / complex part of a coordination compound
What are ligands?
They are atoms/ions/molecules that are attached to the metal atom/ion by coordinate bonds
Are ligands Lewis acids or Lewis bases?
Lewis Bases.
What is the oxidation state of the central metal atom?
It is a number which represents the electric charge on the central metal atom of a complex ion
What are unidentate ligands?
Ligands which only have one donor atom of lone pair.
What is the denticity of NH_3?
unidentate
What is the denticity of H_2O?
unidentate
What is the denticity of CO?
unidentate
What is the denticity of NO?
unidentate
What is the denticity of triphenyl phosphine?
unidentate
What is the denticity of (C_6H_5)_3P?
unidentate
What is the denticity of Cl^-?
unidentate
What is the denticity of Br^-?
unidentate
What is the denticity of OH^-?
unidentate
What is the denticity of NO_2^-?
unidentate
What is the denticity of CN^-?
unidentate
What is the denticity of O^{2-} ?
unidentate
What is the denticity of pyridine?
unidentate
What are bidentate ligands?
Ligands which have 2 donor atoms of lone pair
What is the structure of ethylenediamine?

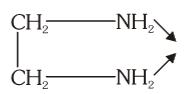
What is this structure called?
ethylenediamine
What is the structure of oxalate?
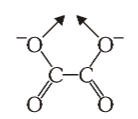
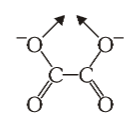
What is this structure called?
oxalate
What is (ox) short for?
oxalate
What is the structure of phenanthroline
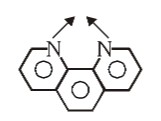

What is this structure called?
phenanthroline
What is the structure of Dimethyl Glyoximato ion?
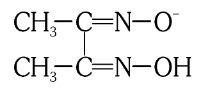

What is this structure called?
Dimethyl Glyoximato ion
What is (DMG) short for?
Dimethyl Glyoximato
What is the structure of Glycinato?
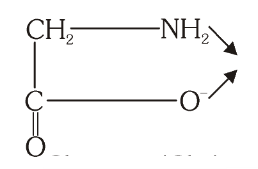
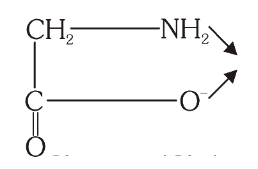
What is this structure called?
Glycinato
What is (Gly) short for?
Glycinato
What is the structure of 2,2-Dipyridyl?
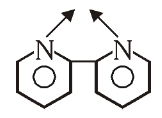
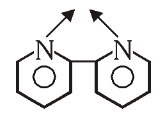
What is this structure called?
2,2-Dipyridyl
What is (Dipy) short for?
2,2-Dipyridyl
What is the structure of Carbonate ion?

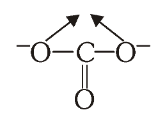
What is this structure called?
Carbonate ion
What is the structure of acetylacetonato (acac)?
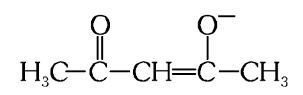
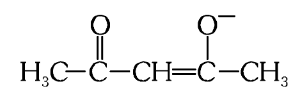
What is this structure called?
acetylacetonato (acac)
What is the structure of Trimethylene diamine?
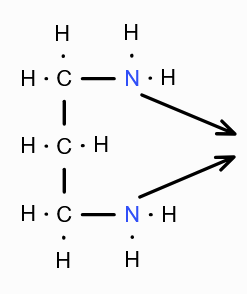
What is (en) short for?
Ethylene diamine
What is (tn) short for?
Trimethylene diamine
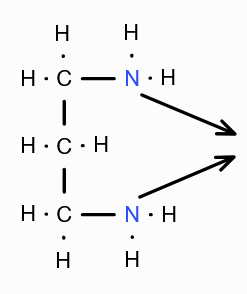
What is this structure called?
Trimethyl diamine
What are tridentate ligands?
Ligands which have 3 donor atoms of lone pair.
What is the structure of Diethylene Triamine (dien)?
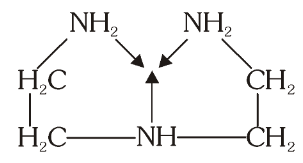
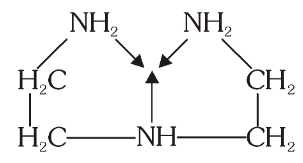
What is this structure called?
Diethylene Triamine
What is (dien) short for?
Diethylene Triamine
What is the structure of 2,2’,2’’-Terpyridine (Terpy)
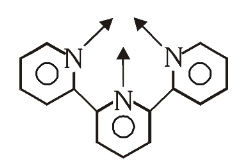
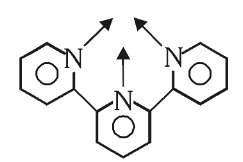
What is this structure called?
2,2’,2’’-Terpyridine
What is (Terpy) short for?
2,2’,2’’-Terpyridine
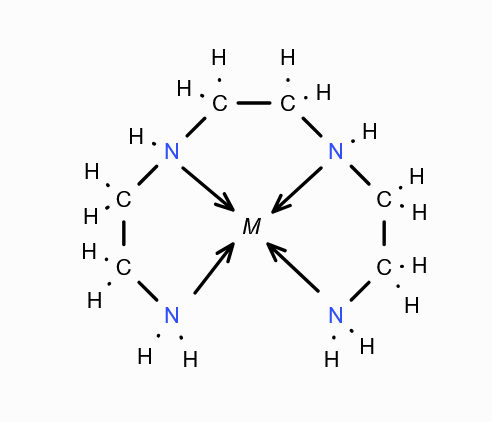
What is this structure called?
Triethylene Tetraamine (trien)
What is the structure of Triethylene Tetraamine (trien)?

What is (trien) short for?
Triethylene Tetraamine
What is the structure of Nitriloacetato?
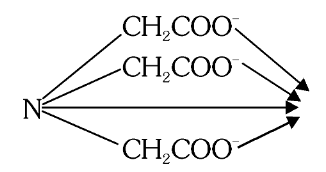
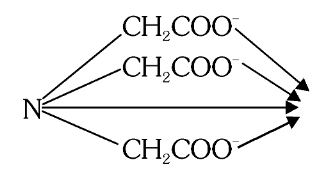
What is this structure called?
Nitriloacetato
What is the structure of (EDTA)-3 ?
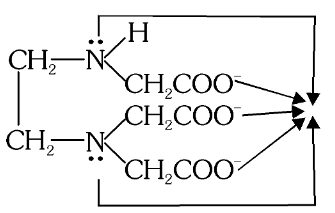

What is this structure called?
(EDTA)-3
What is the full form of EDTA-3?
Ethylenediaminetriacetate
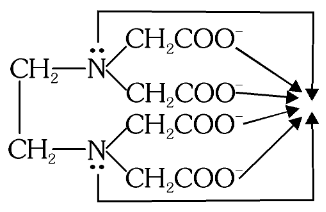
What is this structure called?
(EDTA)-4
What is the structure of (EDTA)-4
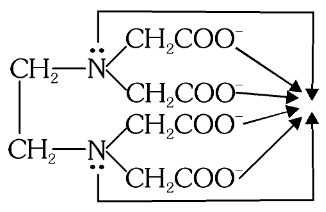
What is (EDTA)-4 the short form of?
Ethylenediaminetetraacetate
What is the denticity of Ethylene diamine?
bidentate
What are the donor atoms in Ethylene diamine?
N
What is the denticity of Trimethylene diamine?
bidentate
What is the donor atom in Trimethylene diamine?
N
What is the denticity of oxalate?
bidentate
What is the donor atom in oxalate?
O
What is the denticity of phenanthroline?
bidentate
What is the donor atom in phenanthroline?
N
What is the denticity of carbonate ion?
bidentate
What is the donor atom in carbonate ion?
O
What is the denticity of (acac)?
bidentate
What is the donor atom in (acac)?
O
What is the denticity of Dimethyl Glyoximate?
bidentate
What are the donor atoms in Dimethyl Glyoximate?
O,N
What is the denticity of glycinate?
bidentate
What are the donor atoms in glycinate?
O,N
What is the denticity of Diethylene Triamine?
tridentate
What is the donor atom in Diethylene Triamine?
N
What is the denticity of Terpyridine?
tridentate
What is the donor atom in Terpyridine?
N
What is the denticity of Triethylene Tetraamine?
tetradentate
What are the donor atoms in Triethylene Tetraamine?
N
What is the denticity of (EDTA)-4?
hexadentate
What are the donor atoms of (EDTA)-4?
four O and two N
What is the denticity of (EDTA)-3?
pentadentate
What are the donor atoms in (EDTA)-3?
three O and twoN.
What are ambidentate ligands?
These are monodentate ligands that have two or more different donor atoms.
What is the structure of N-Nitrito?
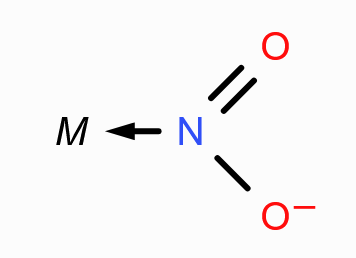
What is the donor atom in N-Nitrito?
N