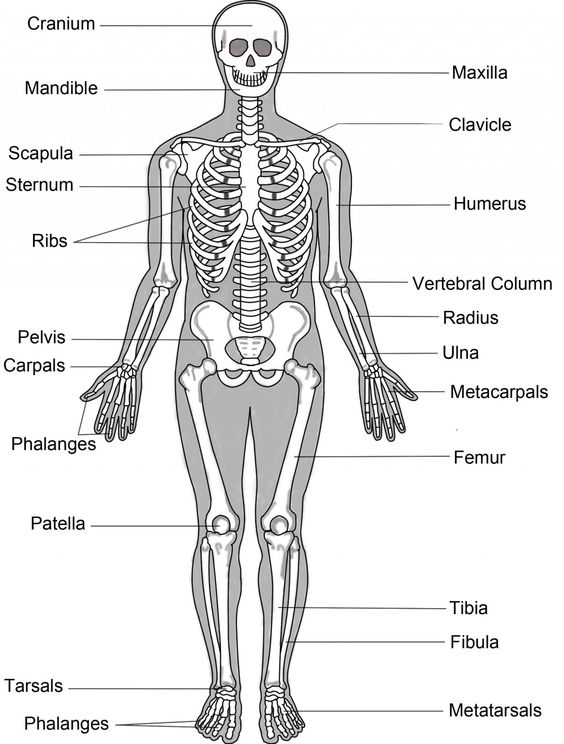
the skeletal system
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
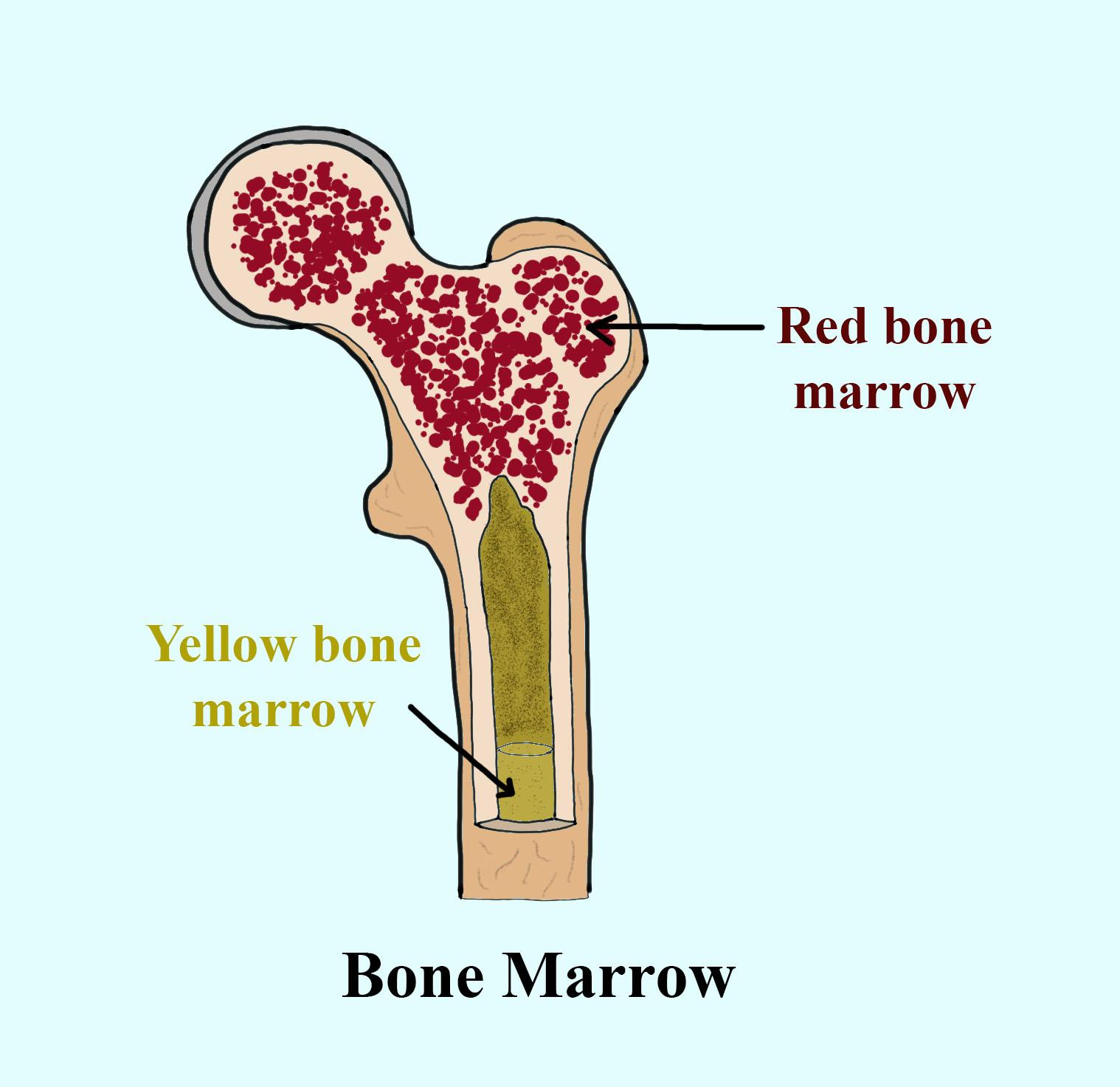
Flashcard: Bone Marrow
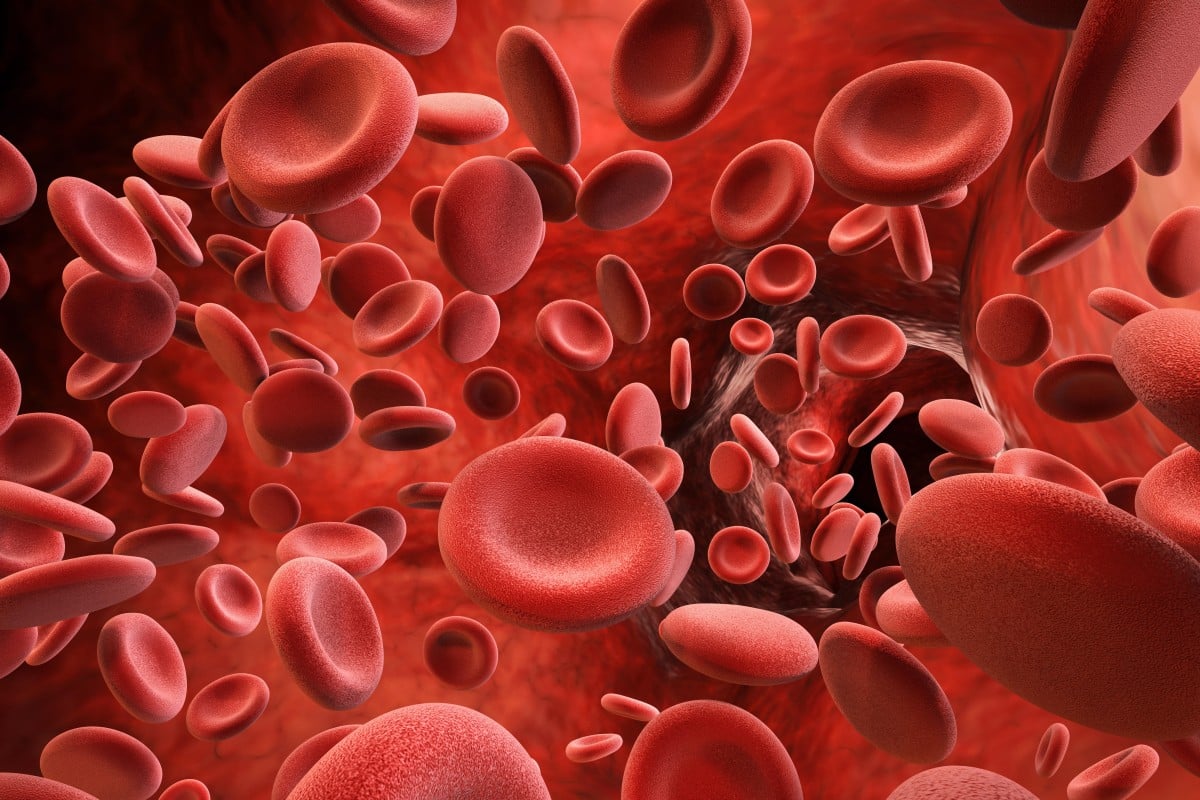
blood cells
die rapidly; made mostly in our bones. formed by the process of hematopoiesis.
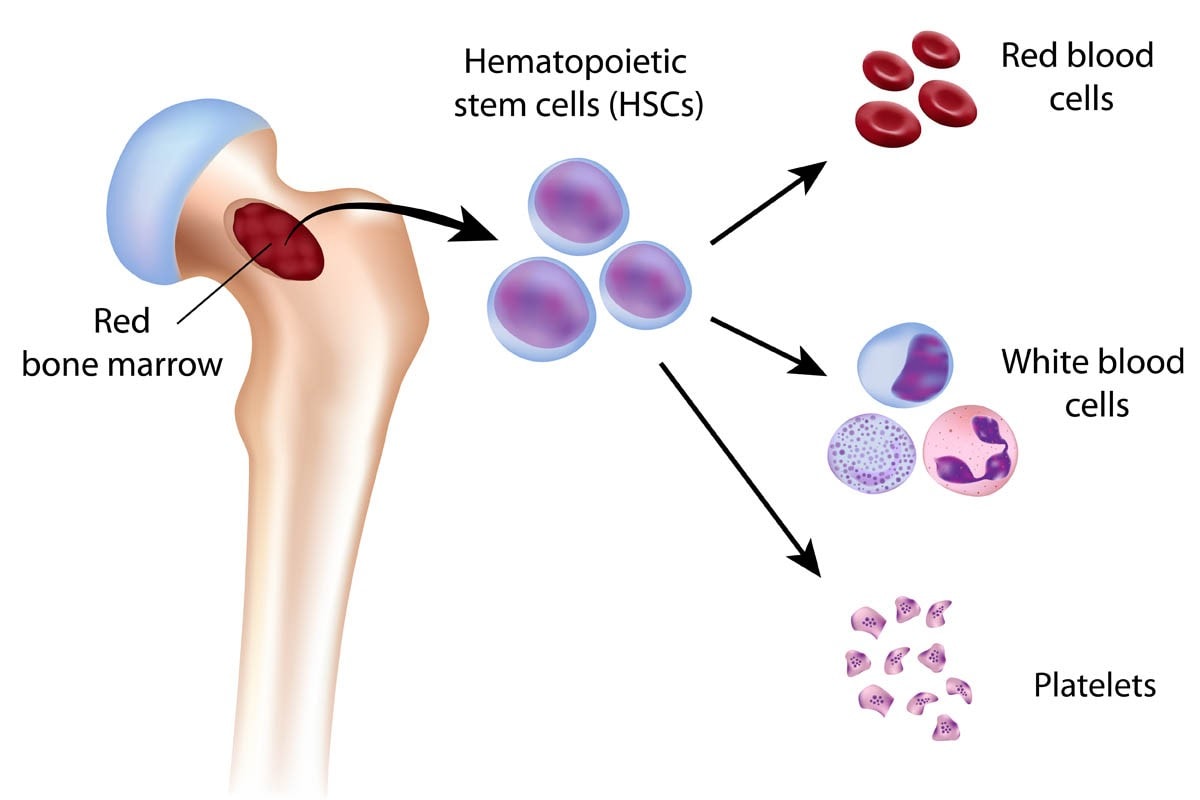
form blood cells
Hematopoiesis
connective tissue
bones consist mostly of __ tissue.
where is blood cell-making bone marrow or fat stored?
medullary
epiphysis
the rounded broader end of a long bone
sesamoid bones
Embedded inside tendons and are found where tendons pass over joints are
cartilage
what covers joint surfaces and makes joints move smoothly?
medullary cavity
in the diaphysis of the long bone the ____is found
periosteum
the outer layer of bone is made of tough connective tissue called ___
compact bone
beneath the periosteum you can find____
spongy bone layer
at the end of long bones, beneath compact bone is where the ___ is found
cylinders, osteons
compact bone is arranged in ___ called __
these lamellae surround a __ or __ that contains blood vessels
central canal, haversion
35% osteoid, which provides flexibility and tensile strength.
bone is composed of
bone to bone
appendicular skeleton consists of what parts of the body?
pectoral, pelvic girdle, bones of the arms, legs, pelvis, and shoulders
convex
sacrum
convex
coccyx (tail bone)
fibrous(cranium), cartilaginous (ribs to your sternum), and synovial (elbows and knees
what are the three structural types of joints?
joint cavity
synovial membrane and articular cartilage line what cavity?