The Lungs
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
The Lungs
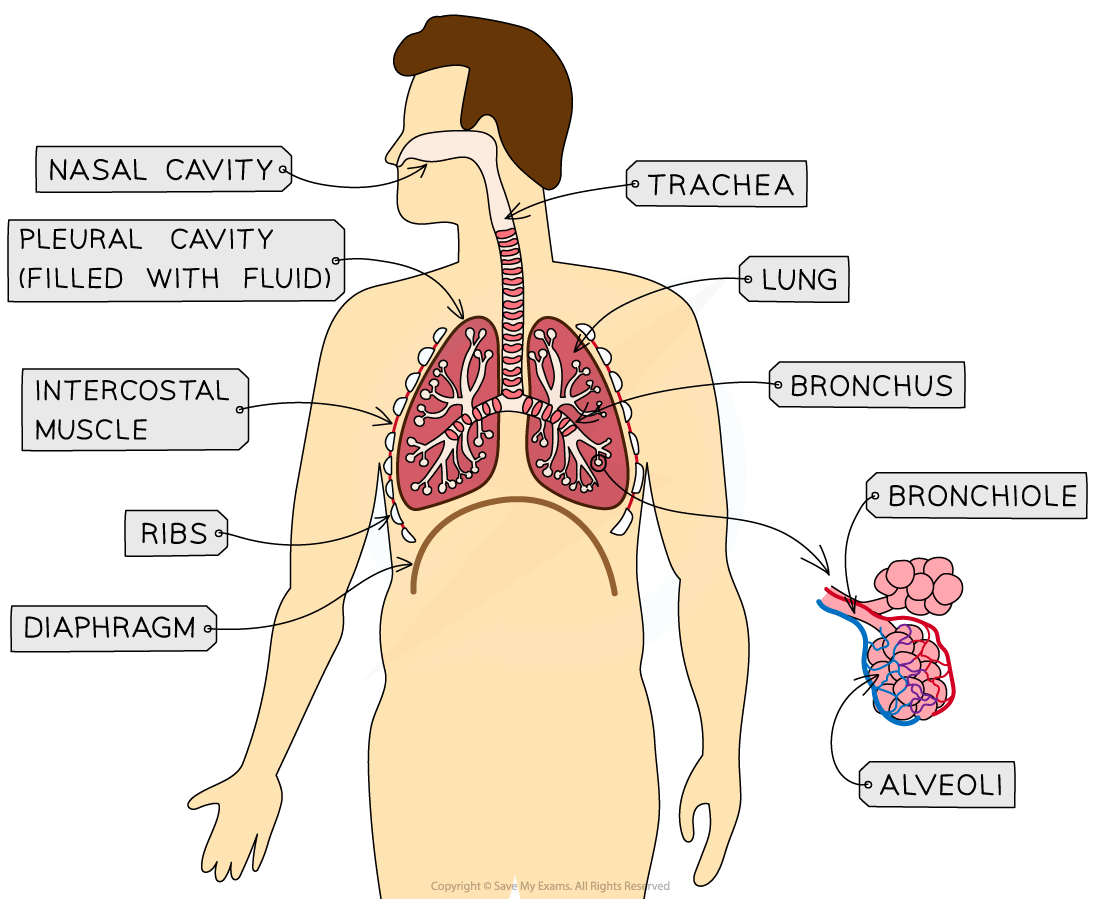
Key Adaptions for Gas Exchange:
presence of surfactant
high surface area
diaphragm and intercostal muscles
thin respiratory membrane
What are alveoli covered with?
A thin layer of pulmonary surfactant (a protein/lipid liquid)
What is the role of pulmonary surfactant in the alveoli?
It reduces surface tension in the alveoli, making it easier for oxygen and carbon dioxide to diffuse in and out of the lungs.
How does high surface area contribute to gas exchange?
A high surface area provided by many bronchioles and extensive capillary beds increases the efficiency of gas exchange.
What does the diaphragm and intercostal muscles control?
The movement of air expanding and contracting to create pressure gradients
How thick are the respiratory membranes lining the alveoli and capillaries?
One cell thick to enhance gas exchange
Antagonistic muscle pairs
When one muscle contracts, the other relaxes
What happens during inspiration?
The pressure in the chest is less than the atmospheric pressure, causing air to move into the lungs.
What occurs during expiration?
The pressure in the chest is greater than the atmospheric pressure, resulting in air moving out of the lungs.
Inhalation
Diaphragm
External intercostal muscles
Volume of the lungs
Pressure of the lungs
Air
Diaphragm - contracts
External intercostal muscles - contract
Volume of the lungs - increases
Pressure of the lungs - decreases
Air - enters
Exhalation
Diaphragm
External intercostal muscles
Volume of the lungs
Pressure of the lungs
Air
Diaphragm - relaxes
External intercostal muscles - relaxes
Volume of the lungs - decreases
Pressure of the lungs - increases
Air - leaves
When to the internal intercostal muscles also contract?
During long or forced exhalations
What contracts to push the diaphragm upward?
Additional abdominal muscles
Techniques for measuring ventilation rate or lung tidal volume:
observation
chest belt and pressure meter
spirometer
Observation
Count the number of breaths per second
Chest belt and pressure meter
Recording the rise and fall of the chest
Spirometer
Records the volume of gas expelled per breath
Inhalation + exhalation
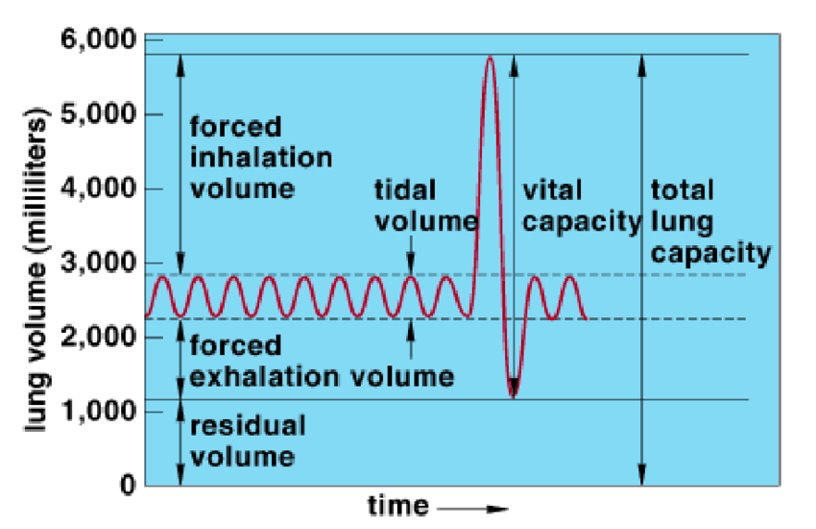
What is ventilation rate?
The number of breaths per minute
What allows for more continuous gas exchange?
Greater frequency of breaths
What is tidal volume?
The total volume of air that moves in or out of the lungs with each breath.
What allows more gas exchange?
Deeper breaths
What is vital capacity?
The maximum amount of air you can inhale and exhale in one breath.
Expiratory reserve
Extra air you breath in or out after normal inhalation or exhalation
Total lung capacity
The maximum volume of air your lungs can hold
Residual volume
The volume of air that remains in your lungs after exhalaing
How does exercise affect ventilation?
Increases ventilation rate
Increases tidal volume
Over time enhance vital capacity and expiratory reserve.