HSF: The Respiratory System
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
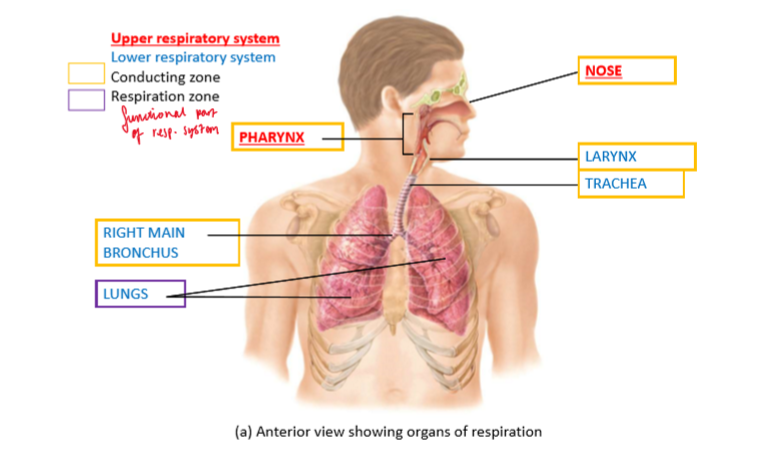
Main structures of respiratory system
Conducting zone:
Nose (U)
Pharynx (U)
Larynx
Trachea
Bronchi
Respiration zone:
Lungs
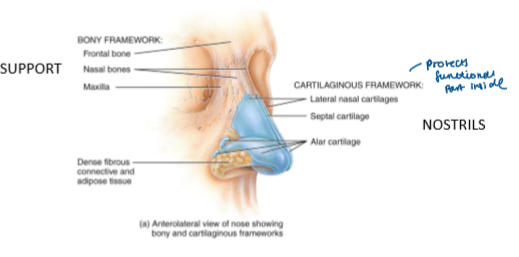
Nose
External portion of nose = cartilage + skin + lined with mucous membrane
protects functional part inside
Bony framework formed by = frontal + nasal + maxillary bones
Internal Structures of Nose
3 functions:
filter air
detect olfactory stimuli
speech
Superior nasal concha = has blood capillaries = warms air up
air enters vestibule
hairs in nostril filter dust (first barrier defence to stop getting into body)
conchae form 3 passages (incr SA)
air warmed by blood capillaries in SNC + mucus from goblet cells trap dust
Cilia move mucus to pharynx (spit or swallow)
Pharynx
Functions as a passageway for air + food
Provides a resonating chamber for speech sounds
Houses tonsils - participate in immunological reactions against foreign invaders
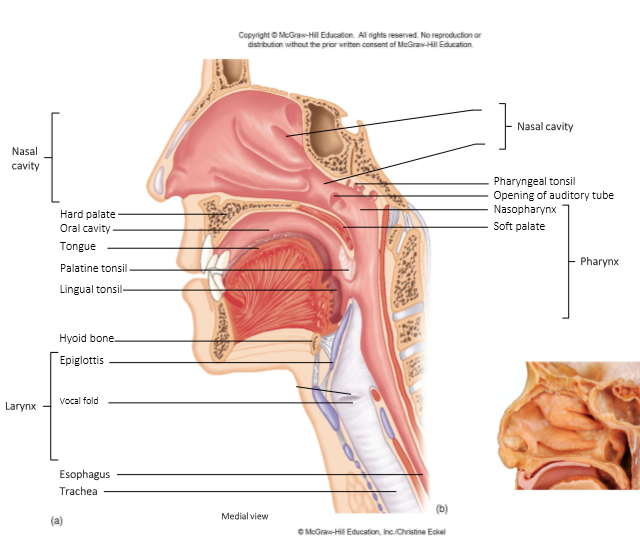
Larynx
AKA voice box
passageway that connects pharynx + trachea
air pressure = controls sound volume
tension of vocal folds = determines pitch

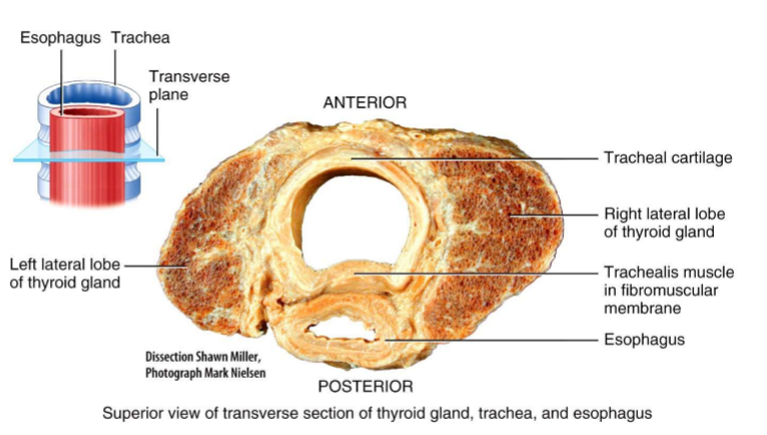
Trachea
Extends from larynx to the primary bronchi
Branches into a right primary bronchus (enters right lung) + a left primary bronchus (enters the left lung)
Lungs = paired organs in the thoracic cavity
Bronchi
Upon entering lungs - primary bronchi divide to form smaller branches
The terminal bronchioles are the end of the conducting zone
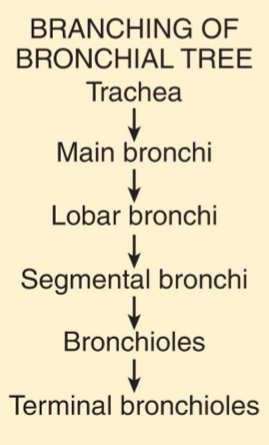
Branching of Bronchial Tree
Trachea
Main Bronchi
Lobar Bronchi
Segmental Bronchi
Bronchioles
Terminal Bronchioles
Branching of Bronchial Tree
Alveoli
When the conducting zone ends at the terminal bronchioles = the respiratory zone begins
The respiratory zone = terminates at the alveoli
Alveoli = ‘air sacs’ found within the lungs
Sighing
a long drawn-out deep inhalation
followed by a shorter, forceful exhalation
Crying
an inhalation followed by many short exhalations
vocal cords remain open + vibrate
Coughing
long-drawn, deep inhalation
full closure of vocal cords
causing a strong exhalation which sends out a blast of air
maybe caused by blockage of windpipe
Lung Volume and Capacities: IMAGE
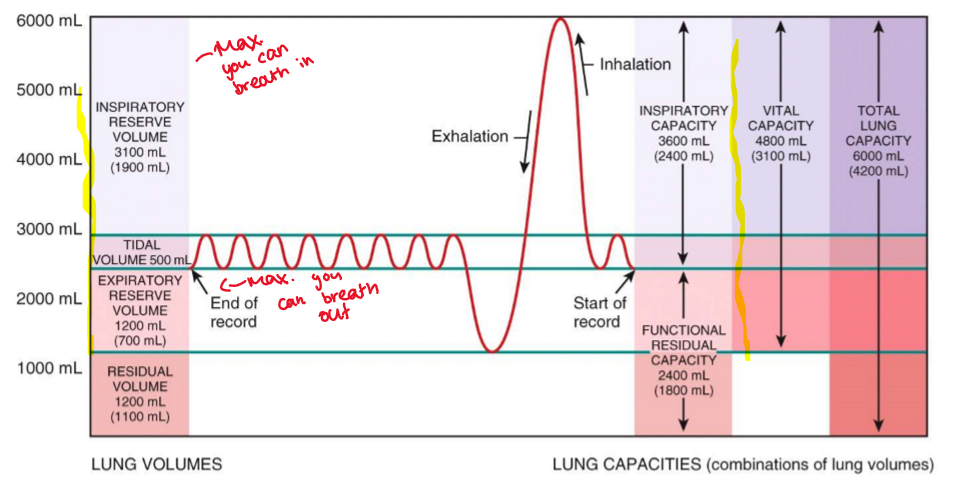
Lung Volume and Capacities: TIDAL VOLUME
Amount of air passing in / out of lungs during each cycle
Lung Volume and Capacities: INSPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME
Extra volume of air that can be inspired during maximum inspiration
Lung Volume and Capacities: INSPIRATORY CAPACITY
Amount of air that can be inspired at max effort (TV + IRV)
Lung Volume and Capacities: FUNCTIONAL RESIDUAL CAPACITY
Air remaining in air passages + alveoli after quiet expiration
Lung Volume and Capacities: EXPIRATORY RESERVE VOLUME
maximum volume of air that can be exhaled after a normal, quiet exhalation.
Lung Volume and Capacities: RESIDUAL VOLUME
Volume of air that can be expired during max. expiration
Lung Volume and Capacities: VITAL CAPACITY
max volume of air that can be moved into and out of lungs
Control of Respiration
Cortical influences:
Allow conscious control of respiration that may be needed to avoid inhaling noxious gases or water
Chemoreceptor:
Central + peripheral chemoreceptors monitor levels of O2 + CO2 = provide input to the respiratory center
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder (COPD)
Symptoms:
Shortness of breath
Persistent cough
Wheezing
Increased Phlegm / sputum
COPD
Caused by inhalation of toxic gases + particulate matter into the lungs
Damage to lung tissue:
more prevalent in smokers (not all lead to COPD)
inflammatory response = release of plasma + immune cells into bronchi
Forced Expired Volume in 1 sec (FEV1) / forced vital capacity (FEV)
GOLD criteria: <70% = indicative of COPD
GOLD = Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease
basc usually in 1st second = 75-85% of air is out so if its less than 70% = COPD sign
Global initiative for chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD): CRITERIA (severity)
GOLD 1 - mild
FEV > 80% predicted
GOLD 2 - moderate
50% < FEV1 < 80% predicted
GOLD 3 - severe
30% < FEV1 < 50%
GOLD 4 - very severe
FEV1 < 30%
COPD: What causes the symptoms?
Follow as flowchart: (1)
Long expiration time
Stimulus to take breath = occurs before lung returned to previous resting level of inflation
Hyperinflation of lungs during exercise
Hyperinflation of lungs during rest
Long expiration time
(2)
Long expiration time
Increased intrathoracic pressure
Increased pulmonary vascular pressure
If alveolar pressure > pleural pressure
Pulmonary hypertension
COPD: Pathology (IMAGE)
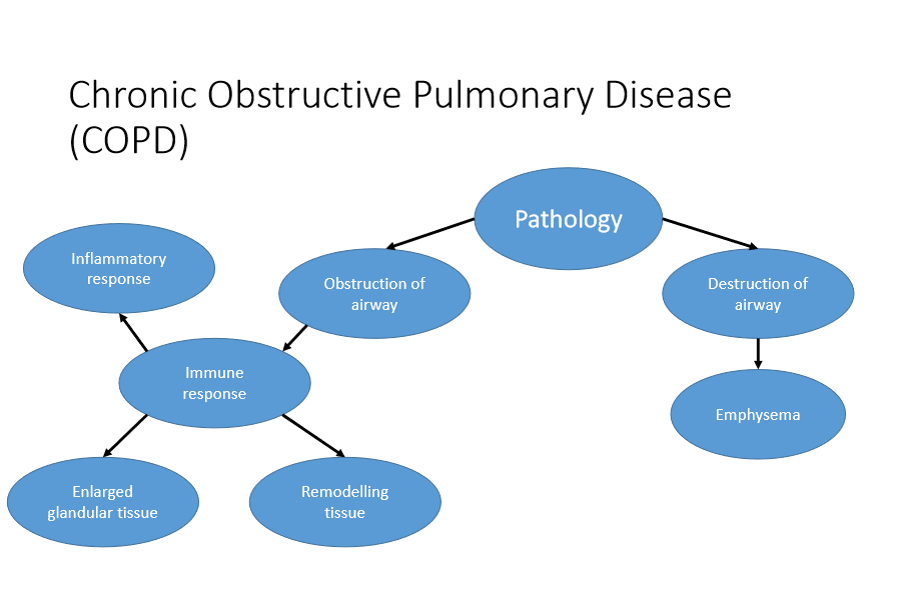
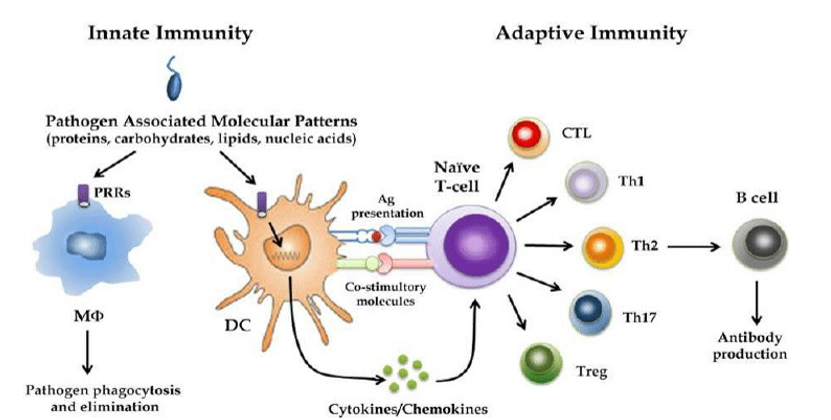
COPD: Immune Response (1)
The innate immune response = primarily functions to maintain the sterile environment in the lungs
Mucous clearance apparatus = clear out lower respiratory tract = into lymphatic system
toxic materials inhaled
tightly joined epithelial cells = detect foreign material on surface
COPD: Immune Response (2)
innate immune system = also functions to increase no. of plasma cells + circulating effector cells to the site of tissue damage
Steps:
Inflammatory response
Increase in chemokines + cytokines
e.g. IL-8 interacts with receptors = to increase polymorphonuclear neutrophil (PMN) infiltration of damaged tissue
Activation of PMN, monocytes, basophils, T-lymphocytes
Infiltration by PMN, macrophages, NK cells, dendritic cells, CD-4, CD-8 + B Cells
Accumulation of dendritic cells = adaptive immune response
Immune response: Dendritic cells
DCs transport antigen to lymph node where they are presented to lymphocytes
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic cough + sputum on most days
for 3 months in 2 consecutive years
Size of mucus gland increases
Caused by:
inhalation of toxins
inflammatory response
enlargement of mucus glands
tissue remodeling
COPD: Bronchioles
Small bronchi + bronchioles (<2mm diameter) = main obstruction sites for COPD
Airflow limitation:
Thickening walls
Reduction lumen
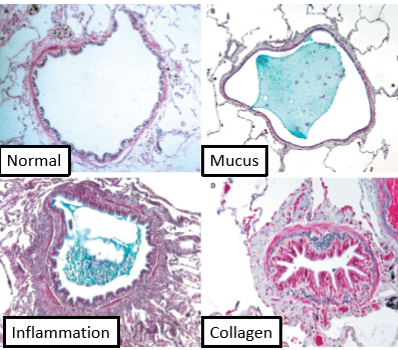
Summary
The respiratory system has roles in the control of:
gas exchange
immune defence
detect olfactory stimuli
speech
Gas exchange occurs in the lungs in specially adapted structures called alveoli
Obstruction or destruction of airways can cause respiratory problems