Lecture 2-COMMUNICATION VARIABLES & COLLABORATIVE PRACTICES
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
JOHARI Window Model
Developed in 1955 by Joseph Luft and Harry Ingham
Purpose
Demonstrate the importance of open communication and self-disclosure
Goal of the Model
is to increase the Open Self by sharing information about yourself and being receptive to feedback
Helps To learn things about ourselves
To build trust with others by disclosing information about oneself
From feedback from others, we learn about ourselves and how to improve one’s skills, deal with issues
Always give constructive feedback
do not get personal or offensive
be sensitive to the individual’s feelings
The four quadrant grid of JOHARI Window Model
Known to self
Open Self
Hidden Self
Not Known to self
Blind Self
Unknown Self

Open Self (known to self)
Information about you that others and you know
(Knowledge, skills, attitude, personal or family history)
involves self-disclosure
disclosing your thoughts, feelings, goals
without disclosing information that is personnel
builds trust
The more people know about each other, the more cooperative and effective they are when working together
People with large “Open Self” are
easy to talk to
communicate honestly and openly
work well as a team
Benefits of Open self
helps with feedback and by being open
accepting feedback
one improves one’s skills and knowledge
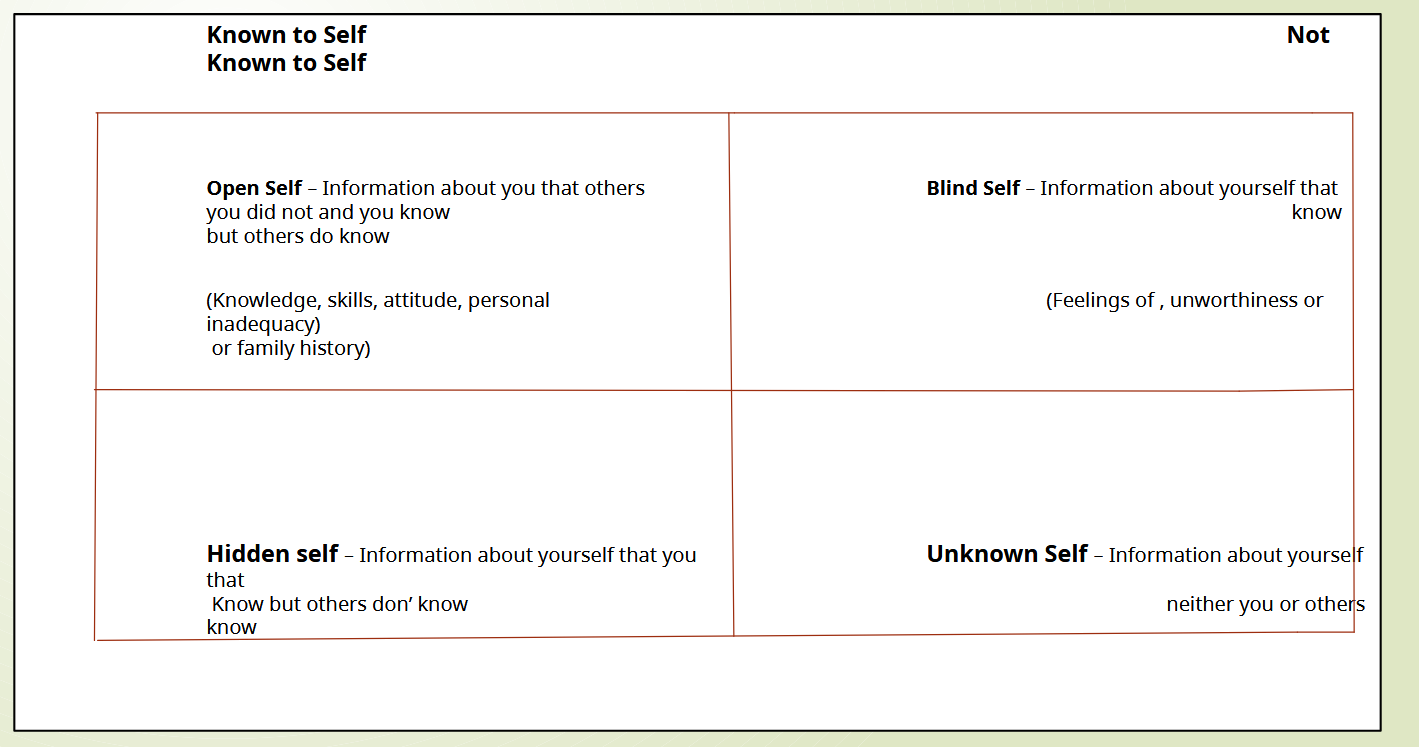
Hidden Self (known to self)
Information about yourself that you Know but others don' know
Blind Self
Information about yourself that you did not know but others do know
(Feelings of , unworthiness or inadequacy)
Causes
one not to take feedback well
No improvement of skills and knowledge
Unknown Self
Information about yourself that neither you or others know
Self Disclosure (part of open self; to increase awarness)
Reveals information about oneself, disclosing things/events about yourself to others, who previously were not aware of this information
Revealing information about yourself
when you need help
what you do well
articulating your aspirations/goals
Benefits of self disclosure
Enhances communication and relationships
by being open and gaining trust
Formalize relationships
- Get support/help in improving
technical skills or managing problems
Gain new perspective and understanding
of yourself based on feedback from
others
Disadvantage of self disclosure
Personal risk, in competitive environments,
you reveal information that others can use against you
Relationship risk
where personal information may result in rejection
Professional risk,
where inappropriate comments about
management or colleagues
the organization
can result in a disciplinary letter or termination
Interaction with Others (part of open self; to increase awarness)
Accepting feedback
listening and incorporating the information to further develop your communication skills
Seek Information about yourself
Ask for feedback for work you done or in your communication with colleague
Know yourself
Perceptions
are formed based on our perspective
shaped by own experiences, knowledge, prejudices,
how we see the situation or the people we interact.
Based on how one communicates verbally, non-verbally, how one behaves, dresses and how one comes across to others.
Art and skill of communication is to be able to understand and manage the impressions you give to others
Strategies to achieve desired impression:
Reliable, enthusiastic, eye contact, facial expressions
b) Credibility
demonstrating competence
education background
Suppress or manage negative attitudes/behaviours
such as
raising one’s voice
blaming others
withdrawing from others
Empathy
To feel what others feel
To see the world as others see it
enhances relationship.
Empathy IS
A two way competition
Encourage the speaker to express him/herself
do not interrupt, provide your undivided attention
Strive to be objective
Thinking empathetically
express an understanding of what the patient is saying or going through
Feeling Empathy
Ability to feel what others feel.
Confirmation
Acknowledging the presence of a person who joins a
group or who speaks or does something.
done by greeting a patient or a colleague,
asking how he/she is feeling
Answering the telephone
or responding to a page
Disconfirmation
Ignoring someone’s presence as well as their
communication.
When disconfirmation happens, intentionally or not it
translates as
the person does not exist
what they have to say is not important or worth attention
Trust
Cornerstone of an effective relationship between patient and health professional
critical when one is ill or vulnerable
highly correlated with patient satisfaction
Culture
Beliefs, code of behaviors, traditions, values.
transmitted from one generation to another through communication, observations or rules
permeates all communication, messages effective in one culture may prove totally ineffective in another culture
influences what you say, how you say it and the topics you talk about
Technology and media
are influencing cultural changes and perhaps and are decreasing intercultural differences
Hospitals use interpreters who have multiple roles:
Translators of language
Culture broker
Patient advocate to convey expectations and concerns
High-Context Culture
What Is Said and How or Where It Is Said Are Significant
1) Asia
2) Latin America
3) Middle East
Long lasting relationships
Importance of context
Spoken agreements
Insiders and outsiders are clearly distinguished
Cultural patterns are ingrained and slow to change
Low-Context Cultures
What is Said is more Important Than How or Where It Is Said
1) USA
2) Canada
3) Germany
4) Britain
Shorter relationships
Less dependent on context
Written agreements
Insiders and outsiders are less clearly distinguished
Cultural patterns change faster
Gender
Depending on culture, there is a belief or understanding that boys and girls have different
attitudes, behaviors and values.
not related to biological differences.
Today, the gender roles have changed and there is equality between men and women.
Importance of Culture
Demographic changes
healthcare need to understand how different cultures
communicate illness/procedures
preventative medicine
medications
Culture Diversity:
Communicating healthcare issues with sensitivity
Collaboration Model
between Compete and Avoid
Commonly Used Elements
Communication
Openness
Learning
Listening
Respect
Trust
Inquiry
Negotiation
Less Frequently Used
Assertive
Belief
Optimistic
Acceptance
Objectivity

Communication Essentials (by CMLTO)
Most communication problems resolved around perception
Perception is based on a perspective which is shaped and judged by
our previous experience
prejudices
knowledge
traditions/beliefs
Best Practice for Effective Communication
Check perception by asking
questions, summarizing or paraphrasing the information that the individual has provided
obtain feedback to determine one has a correct understanding of what is being communicated
Communication is broken down as follow
Words – 7% of the content
Vocal tone constitutes 38% of the message
Body Language constitutes 55% of the message