Larynx Anatomy
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
57 Terms
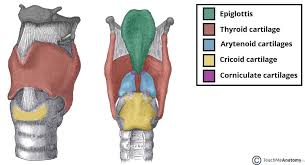
Epiglottis
protective cartilage flap that prevents food and water from getting into the respiratory tract
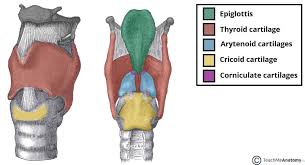
Thyroid
largest primary cartilage support structure that protects the vocal cords, rocks back and forth at cricothyroid joint, articulates with hyoid bone
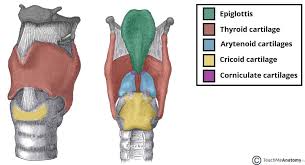
cricoid
last cartilage ring that anchors muscles and ligaments, also produces voice by controlling vocal cords
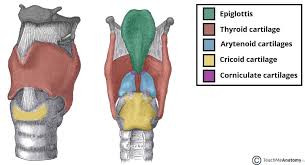
arytenoid
paired cartilage that produces sound and regulates airflow
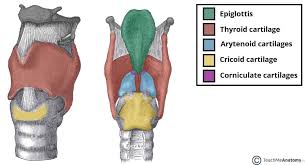
corniculate
paired cartilage on top of arytenoids that prop up and support the aryepiglottic folds, they also help assist arytenoid movement
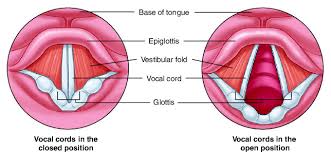
vocal folds
produces voice
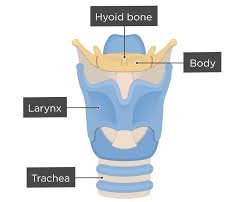
hyoid bone
provides support and movement for larynx, not directly connected to other bones (connected via ligaments and muscles) attached to tongue and 23 muscles
larynx functions
breathing, speaking, swallowing
cuneiform cartilage
located within the aryepiglottic folds to strengthen and support them
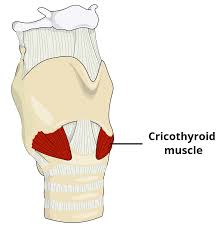
cricothyroid muscle
controls pitch by lengthening and shortening vocal folds
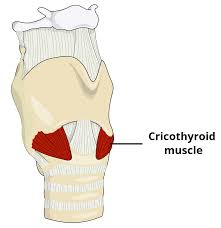
lengthening and shortening of vocal cords
the cricothyroid muscle contracts and lengthens the vocal cords to produce high pitch sounds and it shortens and relaxes to produce low pitch sounds
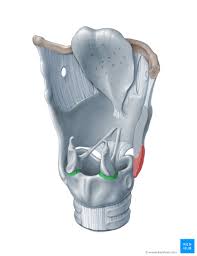
cricothyroid joint
synovial joint: rocking, gliding, rotation; creates changes in pitch
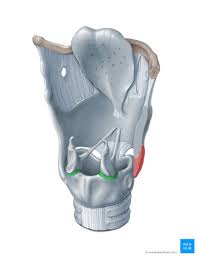
cricoarytenoid joint
synovial joint: rocking, gliding, rotation. Adduction of vocal folds, changes in vocal cord length
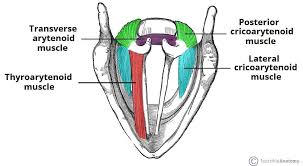
Adductor muscles
Lateral cricoarytenoid, transverse arytenoid, oblique arytenoid
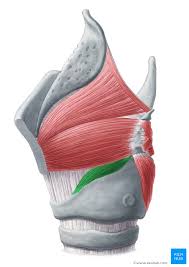
lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
adductor, pulls arytenoid cartilages together (vocal folds come together)
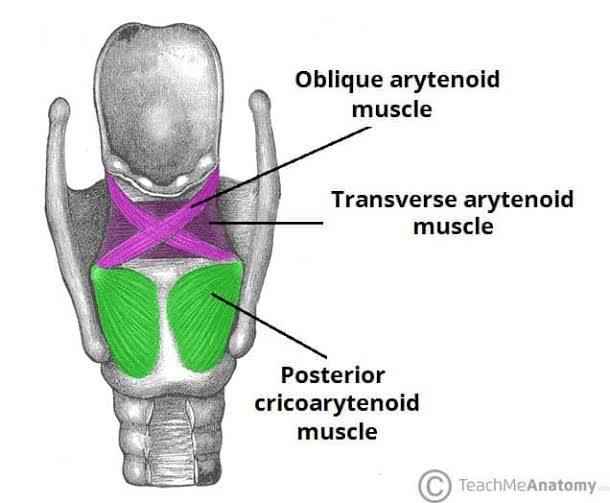
transverse arytenoid
adductor, pulls arytenoid cartilages together (vocal folds come together)
oblique arytenoid
adductor, pulls arytenoid cartilages together (vocal folds come together)
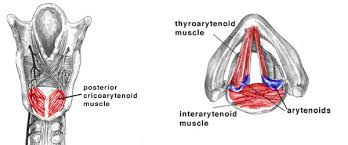
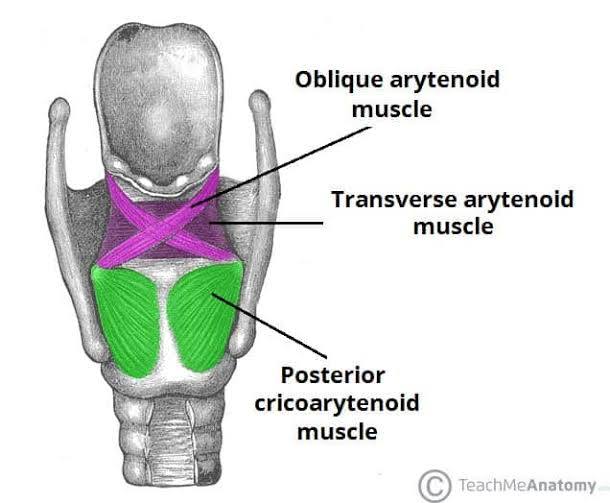
posterior cricoarytenoid muscles
abductor, opens airway for breathing, coughing
glottal tensors
cricothyroid muscles, pars recta, pars oblique, thyrovocalis (medial thyroarytenoid) muscles
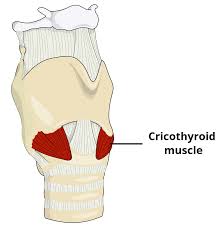
cricothyroid muscles
glottal tensor, rocks thyroid cartilage forward to tense and lengthen vocal cords to change pitch
thyromuscularis (thyroid muscle)
relaxers
Auxillary musculature
thyroarytenoid, superior thyroarytenoid, aryepiglotticus, thyroepiglotticus
hyoid and laryngeal elevators
muscles that lift the hyoid bone and larynx and thyrohyoid muscle (swallowing)
hyoid and laryngeal depressors
muscles that pull the hyoid bone and larynx down (breathing and swallowing)
vocal folds
bands of mucous membranes, connective tissue, thyrovocalis muscle
The epiglottis is highly connected
to the thyroid, hyoid bone, and tongue

cartilage at front of vocal folds
thyroid cartilage

cartilage at back of vocal folds
arytenoid cartilage
quiet breathing glottis size
8 mm
forced respiration glottis size
16mm
larygeneal muscle group needed for inhalation
adductors, respiratory muscles
coughing
caused by irritation on respiratory tract tissue
cough is triggered by
vagus nerve
muscles used for coughing
abductors, adductors, tensors, elevators
when our cores tighten our vocal folds
adduct
valsalva maneuver
popping ears
swallowing process
larynx elevates, epiglottis folds down and covers larynx, aryepiglottic folds tense and adduct the vocal folds
vibration
movement possible by elasticity, stiffness, and inertia
elasticity
return to original state after being displaced
stiffness
strength of elasticity after being displaced
inertia
object in motion stays in motion
pitch
tone produced by vibration ex. guitar
Bernoulli effect
at a point of constriction with an increase in velocity there is a decrease in pressure which creates a suction, this cycle repeats
Bernoulli effect in relation to vocal folds
As air from the lungs travels through the narrow glottis, its speed increases, creating a drop in pressure. This low-pressure area pulls the vocal folds together, this cycle repeats, opens from posterior to anterior
frequency Hz
how many repetitive cycles of vibration per second
intensity dB
loudness and amplitude of the waveform
sustained phonation
holding the vocal folds in the air stream for vibration
simultaneous vocal attack
breath and vocal fold vibration stops at the same time
breathy vocal attack
airflow comes before closing the vocal folds
glottal attack
adduction of folds comes before respiration ex. uh oh
vocal register
a mode of vocal fold vibration
modal voice (register)
pattern of phonation used in daily conversation
glottal fry
pulse register, low in pitch, rough sounding
falsetto
highest register of phonation
whispering
non phonatory, no vibration despite tension
what effects pitch?
vocal fold mass, length, tension, elastic qualities
muscles associated with pitch
cricothyroid: stretch and thins vocal folds, thyrovocalis