Fill in the blank
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
C
is the subunit of the ATP synthase that binds H+ from the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and then rotates the g subunit and releases H+ on the matrix side of the membrane.
lactate
HIF-1 causes in increase in the production of
thermogenin
transports H+ across the mitochondrial inner membrane to the matrix without making ATP, resulting in the production of heat in brown fat mitochondria.
linear with respect to blood glucose concentration
The Kt for glucose transport by GLUT 2 is 17 mM. The physiological range of blood glucose is 4 to 8 mM. As a result, for physiological blood glucose concentrations, the rate of transport of glucose by GLUT 2 is
S5 + S6 main chain carbonyls bind the Na+ at the optimum configuration
Describe selectivity filter for the voltage-gated Na+ channel
S4 segments has lysines and arginines that are positively charged
Describe voltage gate for the voltage-gated Na+ channel
a loop of the channel that blocks the channel shortly after opening to ensure depolarization goes the right way
Describe inactivation gate for the voltage-gated Na+ channel
cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase
What is the off switch for cAMP
GTPase
What is the off switch for Gs and Ras
phosphorylation of tyrosine near C terminal
What is the off switch for Src
phosphatase
What is the off switch for IRS-1
hexokinase
The enzyme _________________________________________ converts glucose to glucose 6-phosphate.
phosphoenol pyruvate
+ ADP → pyruvate + ATP
lactate
is a non-carbohydrate precursor that can be used by gluconeogenesis to make glucose.
HIF-1
is a transcription factor that causes increased synthesis of GLUT1 and GLUT3 under conditions of low oxygen.
pentose phosphate
In the _______________ pathway, 3 C5 intermediates are converted to 2 C6 and C3.
biotin
is the prosthetic group of pyruvate carboxylase.
protein kinase A
phosphorylates hormone-sensitive lipase in epinephrine-stimulated triacylglycerol mobilization.
Adipose triacylglycerol lipase
is the enzyme directly activated by CGI-58.
Carnitine
is attached to fatty acids during transport into mitochondria
Strum albumin
is the protein that carries fatty acids in blood.
oxaloacetate
Due to the removal of ___________________ from the citric acid cycle for use in gluconeogenesis, ketone bodies are overproduced during starvation.
arginine; ornithine
_________________ + H2O → urea + __________________
S-adenosyl methionine
is a one-carbon donor in most methylation reactions.
coenzyme B12
is the cofactor in the free radical reaction in the pathway of methionine catabolism.
Aspartate; glutamine
____________ + a-ketoglutarate → oxaloacetate + ______________
arginine; fumarte
argininosuccinate → _______________ + _________________
β (beta)
is the subunit of the ATP synthase that binds ADP and phosphate to make ATP.
H+
Thermogenin transports ____________ across the mitochondrial inner membrane, resulting in the production of heat in brown fat mitochondria.
ADP; Pi
In SERCA, Ca2+ is pumped by hydrolyzing ATP to _______ and ___________
H+
In E. coli, lactose is transported in symport with ________________
Leucine
The acetylcholine receptor channel is likely blocked by the amino acid ___________ in the middle of the M2 segment of each of its 5 subunits in the closed state
IRS-1; Grb2; Ras
insulin → insulin receptor → ___________________ → _______________________ → Sos→ ______________
JAK; STAT
leptin → leptin receptor → ______________________ → ______________________, which activates transcription in the nucleus
1,3- bisphosphoglycerate
glyceraldehyde 3-Pi + NAD+ + Pi → _____________________________________________ + NADH + H+
Lactate
pyruvate + NADH + H+ → _____________________________________ + NAD+ (anaerobic metabolism)
tumors
18F-labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose is used to detect _____________________________ in PET scans
2 NADPH; ribose 5-phosphate
_________________________________ and _____________________________________ are the products of the oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway.
hormone sensitive lipase; perilipin
______________________________________________ and _______________________________ are proteins phosphorylated by protein kinase A in epinephrine-stimulated TAG mobilization.
triacyl glycerols
ATGL hydrolyzes _________________________________
acetone
__________________________________ is one example of a ketone body.
ATP; AMP; PPi
fatty acyl-CoA synthetase reaction:
fatty acid + CoASH + ___________________ → fatty acyl-CoA + ____________________ + __________________
biotin
____________________________________ is a one-carbon donor in most carboxylation reactions such as for pyruvate carboxylase.
Valine
______________________________________________ is an amino acid that is degraded to propionyl CoA and then succinyl CoA in a coenzyme B12-dependent pathway.
aspartate
__________________________ is an amino acid that is degraded to oxaloacetate.
Alanine; glutamate
______________________________ + a-ketoglutarate → pyruvate + ____________________________
arginine
argininosuccinate → _____________________________________________ + fumarate
Glucagon→ glucagon receptor→ Gs→ adenylyl cyclase→ cAMP→ protein kinase A→ phosphorylase b kinase→ glycogen phosphorylase
Write out the pathway for glucagon-stimulated glycogen degradation in liver cells, beginning with glucagon and ending with glycogen phosphorylase
binds H+ from H+ half channel and rotates through membrane and releases H+ from other half channel
Describe the function of c subunit in ATP synthesis by the mitochondrial ATP synthase
C subunit rotates Ɣ subunit which causes a change in conformation of β subunit
Describe the function of Ɣ subunit in ATP synthesis by the mitochondrial ATP synthase
binds ADP + Pi and changes conformation to make and release ATP
Describe the function of β subunit in ATP synthesis by the mitochondrial ATP synthase
Thiamine pyrophosphate; Lipoamide; Flavin adenine dinucleotide
Name the 3 cofactors for the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex
phenylalanine hydroxylase
the enzyme deficient in phenylketonuria
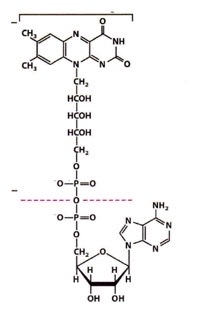
Flavin adenine dinucleotide
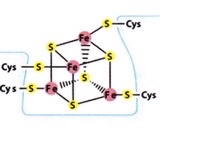
iron sulfur center
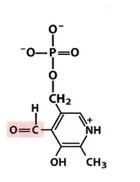
pyrodoxial phosphate
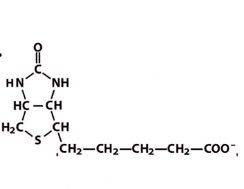
biotin
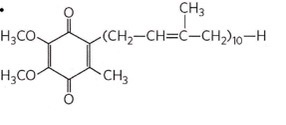
ubiquinone
NADH→ NADH dehydrogenase→ ubiquinone→ Cytochrome bc1→ Cytochrome C→ Cytochrome oxidase→ O2
Write out the pathway for mitochondrial electron transport from NADH to Oz. Write out the complete name of the complexes (not just the numbers).
succinate→ succinate dehydrogenase→ ubiquinone→ Cytochrome bc1→ cytochrome C→ cytochrome oxidase→ O2
Write out the pathway for mitochondrial electron transport from succinate to O2. Write out the complete name of the complexes (not just the numbers)
epinephrine→ β-adrenergic receptor→ Gs→ adenylyl cyclase→ cAMP→ protein kinase A→ phosphorylase B kinase→ glycogen phosphorylase
Write out the pathway for epinephrine-stimulated glycogen degradation in muscle cells, beginning with epinephrine and ending with glycogen phosphorylase.
1.) oxaloacetate + acetyl CoA→ citrate (citrate synthase)
2.) citrate→ isocitrate
3.) isocitrate→ ɑ-ketoglutarate (isocitrate dehydrogenase)(NAD+→ NADH, CO2)
4.) ɑ-ketoglutarate→ succinyl CoA (ɑ-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex)(NAD+, Co-ASH→ NADH, CO2
5.) succinyl CoA→ succinate (GDP, Pi→ GTP, Co-ASH)
6.) succinate→ fumarate (FAD+→ FADH2)
7.) fumarate → malate
8.) malate→ oxaloacetate (NAD+→ NADH)
What is the citric acid cycle pathway
1.) glucose→ glucose 6-Pi (hexokinase)(ATP→ ADP)
2.) glucose 6-Pi→ fructose 6-Pi
3.) fructose 6-Pi→ fructose 1,6 bis-Pi (phosphofructosekinase-1)(ATP→ADP)
4a.)fructose 1,6 bis-Pi→ dehydroxyacetone-Pi
4b.) fructose 1,6 bis-Pi→ glyceraldehyde 3-Pi
5.) dihydroxyacetone Pi→ glyceraldehyde 3-Pi (2)
6.) glyceraldehyde 3-Pi (2)→ 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (2) (NAD+, Pi (2)→ NADH (2))
7.) 1,3 bisphosphoglycerate (2)→ 3-phosphoglycerate (2) (2 ADP→ 2 ATP)
8.) 3-phosphoglycerate (2)→ 2-phosphoglycerate (2)
9.) 2-phosphoglycerate (2)→ phosphoenol pyruvate (2)
10.) phosphoenol pyruvate (2)→ pyruvate (2) (2 ADP→ 2 ATP)
What is the glycolysis pathway