OPT 223 Midterm 2 part 2 (macula 1 and 2)
1/195
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
196 Terms
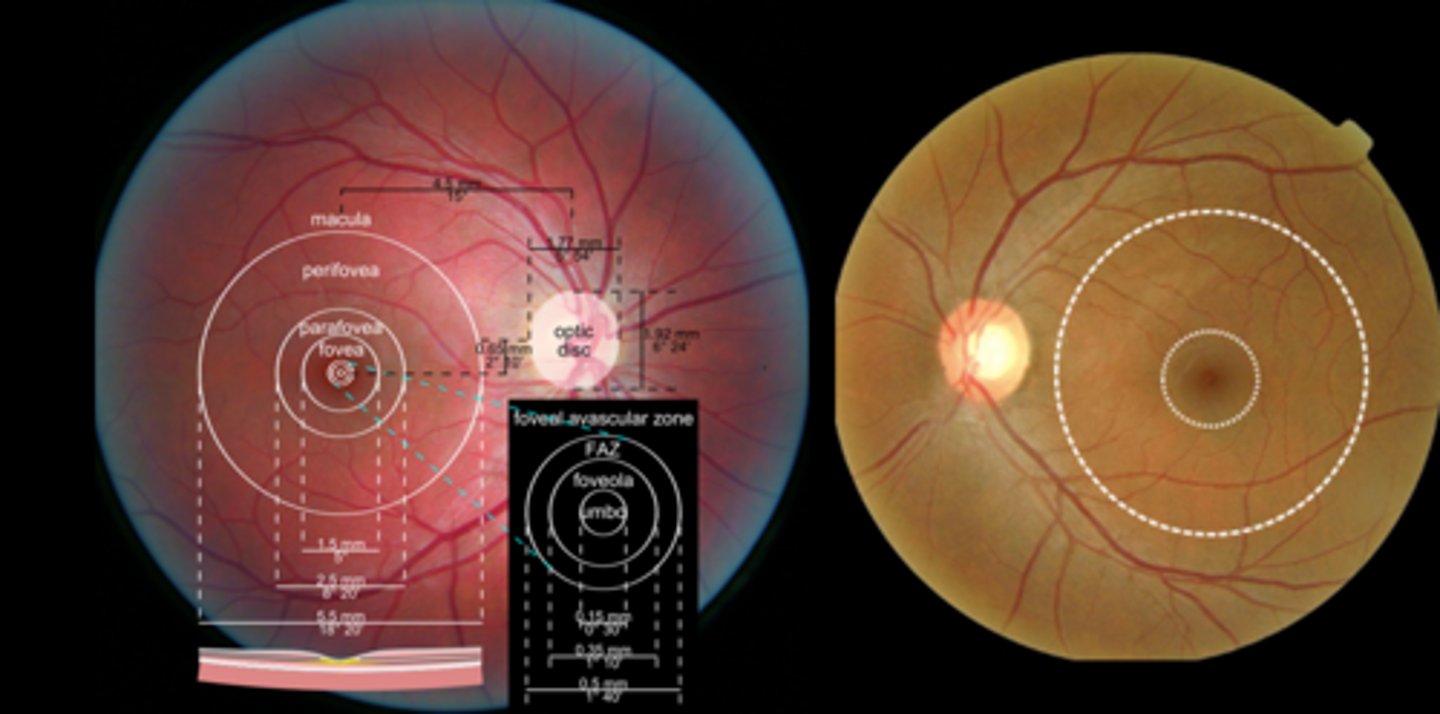
What is the size of the fovea?
1.5mm (similar to ONH)
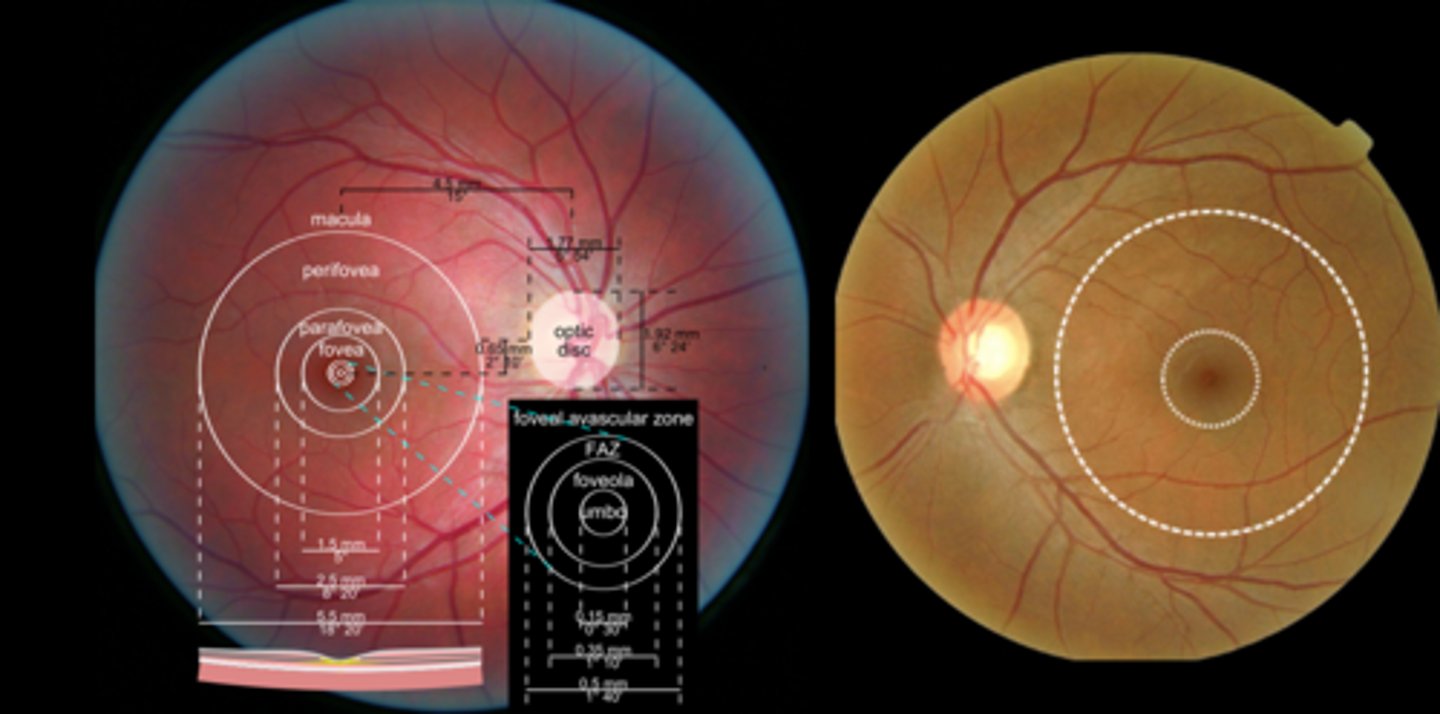
What is the size of the macula?
5.5mm
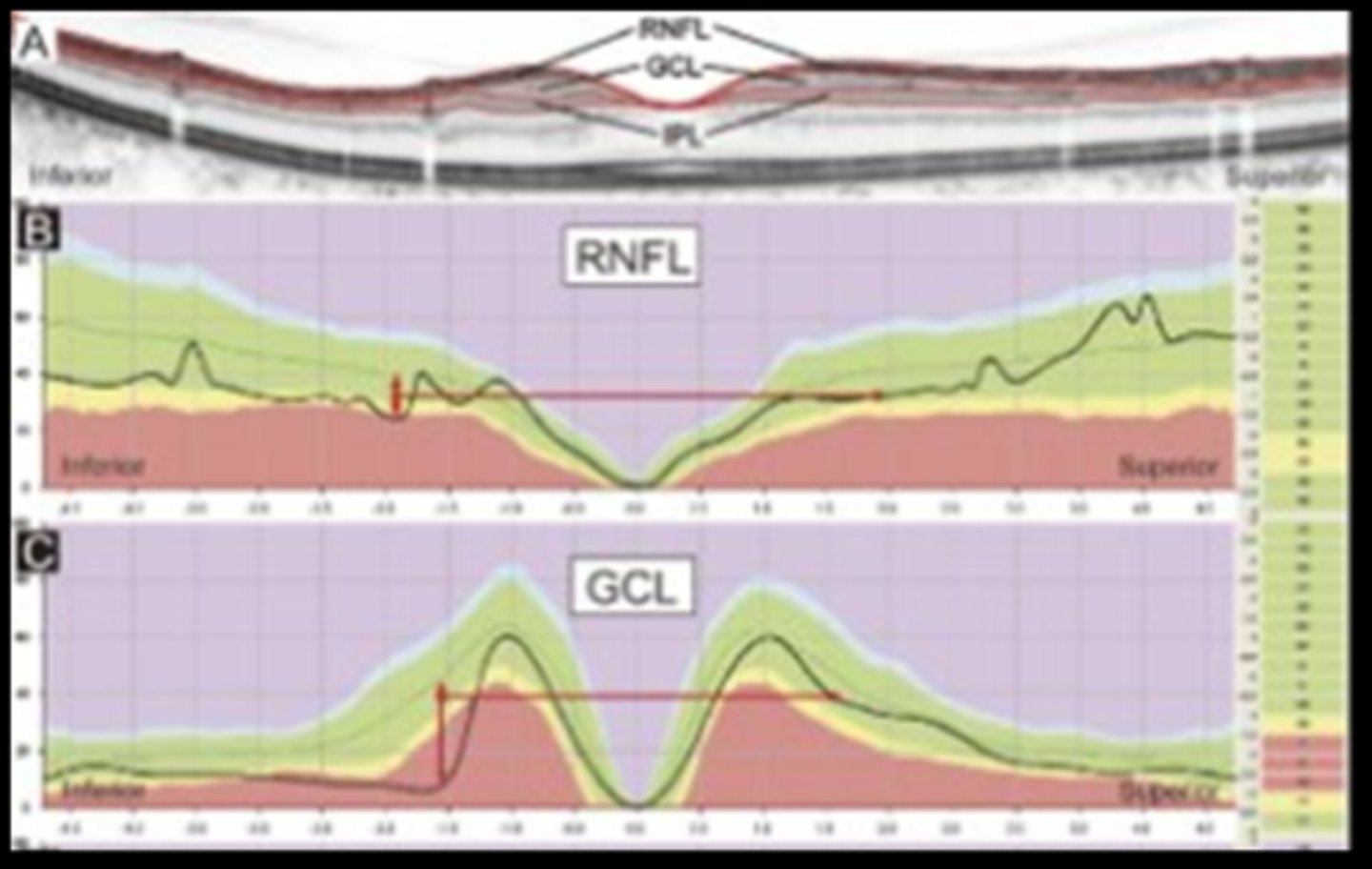
Recall: where is the rNFL thickest?
ONH rim
next is circumpapillary
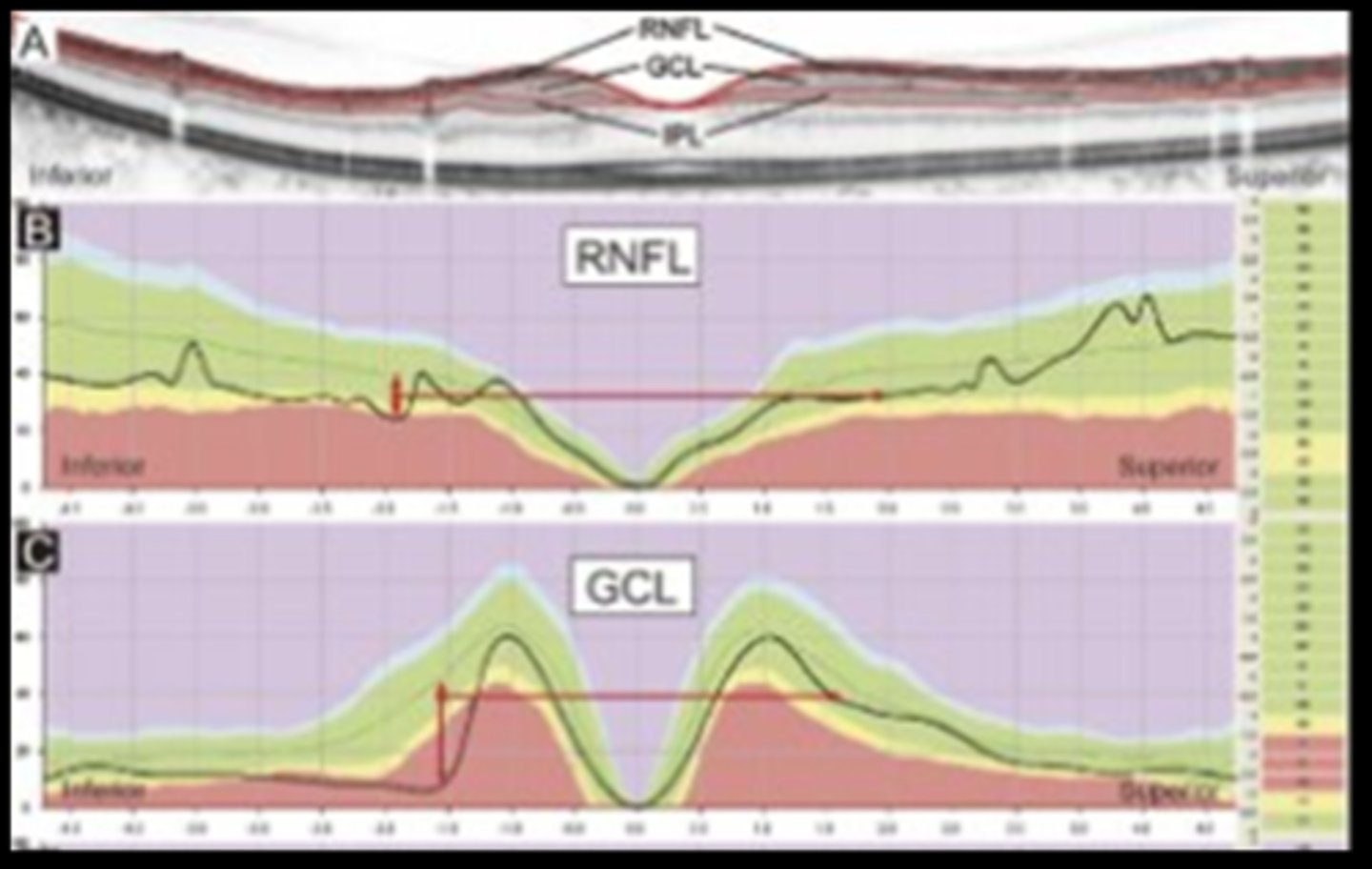
Recall: where is the GCL thickest?
parafoveally
What chair skills test is important in macular conditions?
Amsler
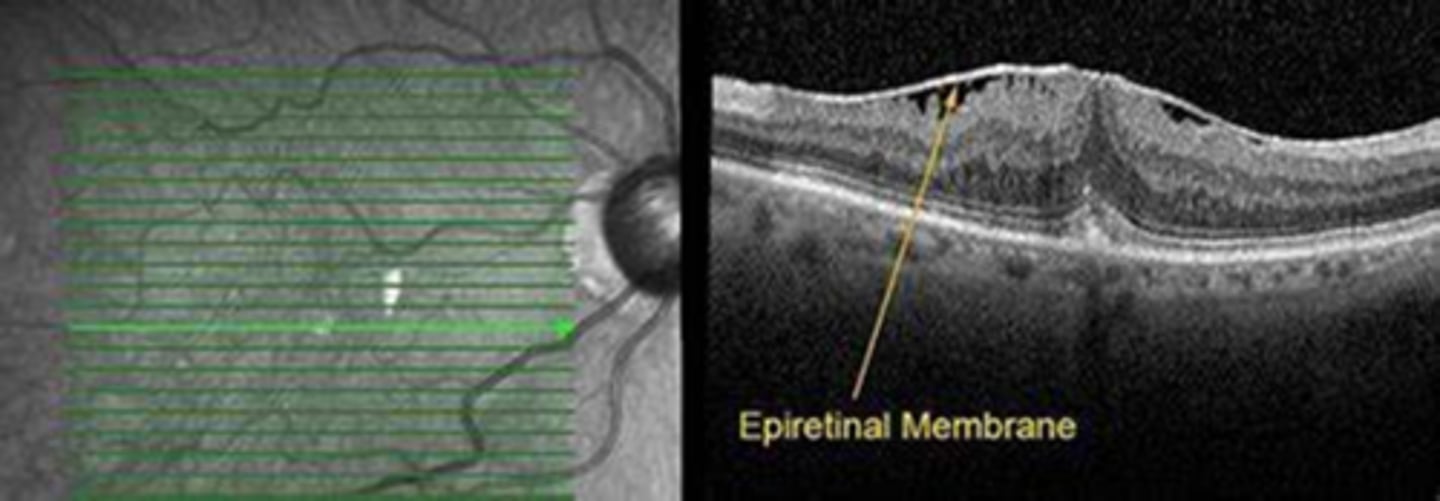
What is an epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
unilateral or bilateral proliferation and fibrosis of glial cells within/on the ILM
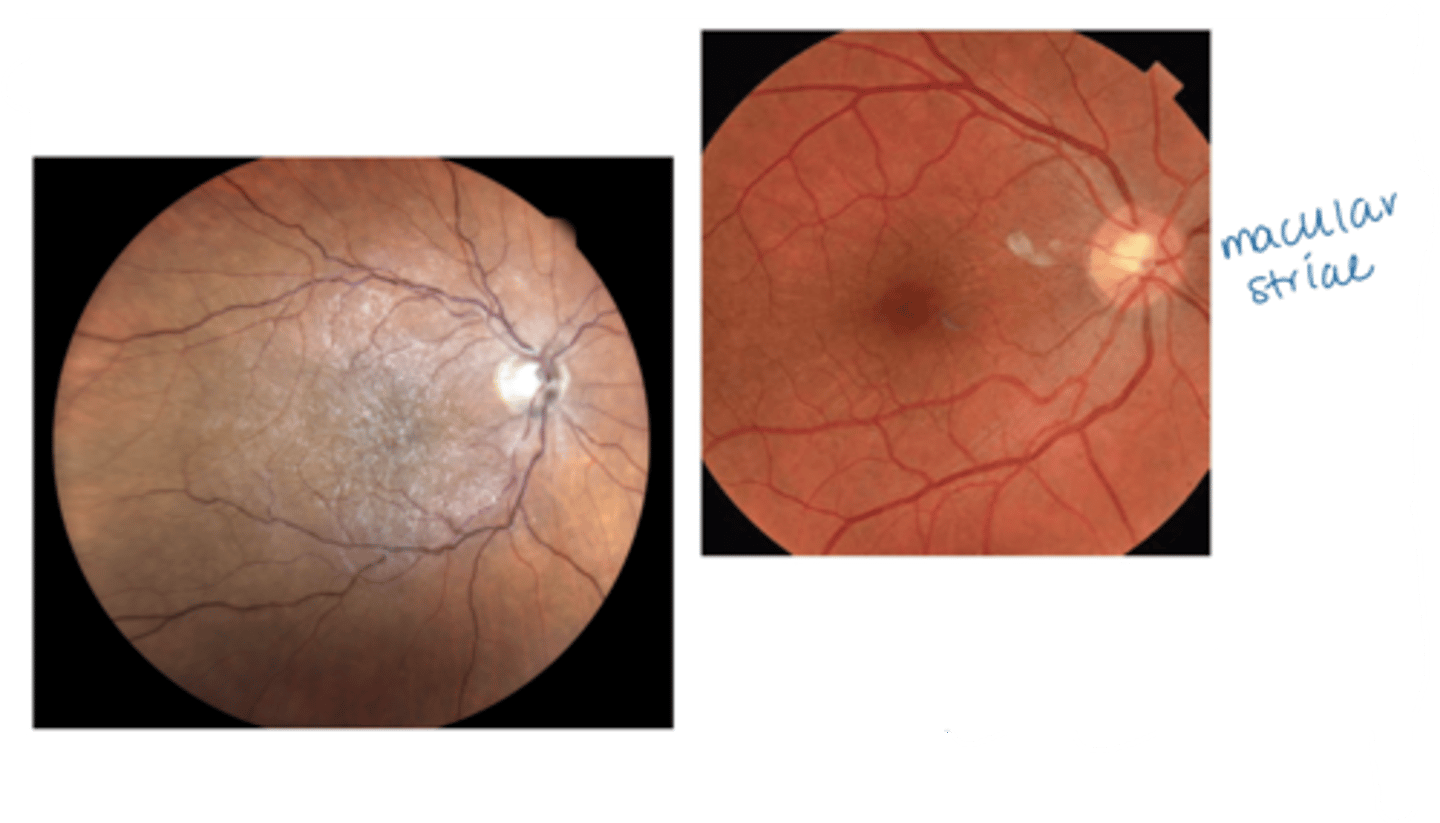
What is an epimacular membrane form of epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
specifically on macula
NOTE: this is the most common location!
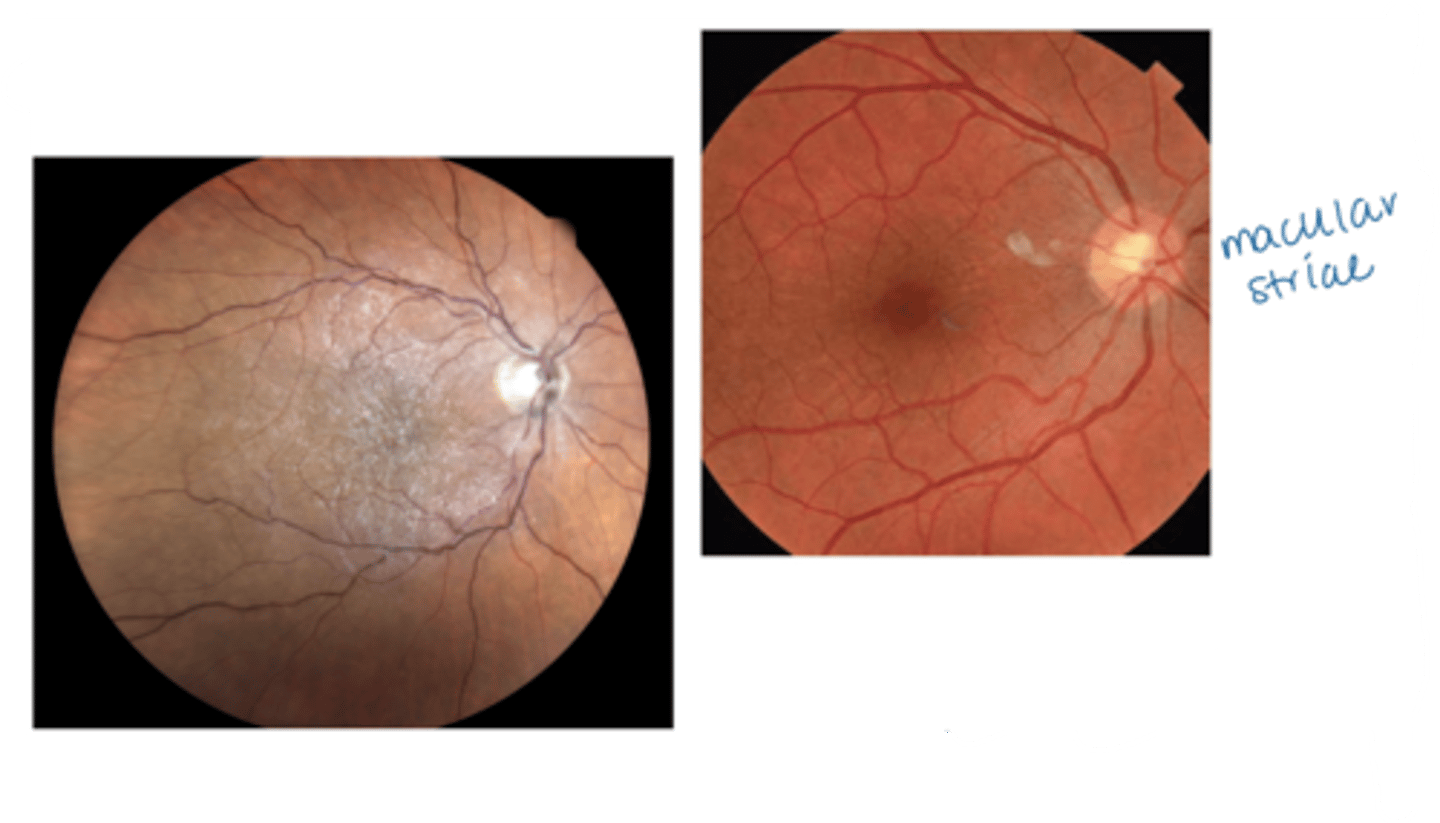
What is the cellophane maculopathy form of epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
asymptomatic, no change to macular contour
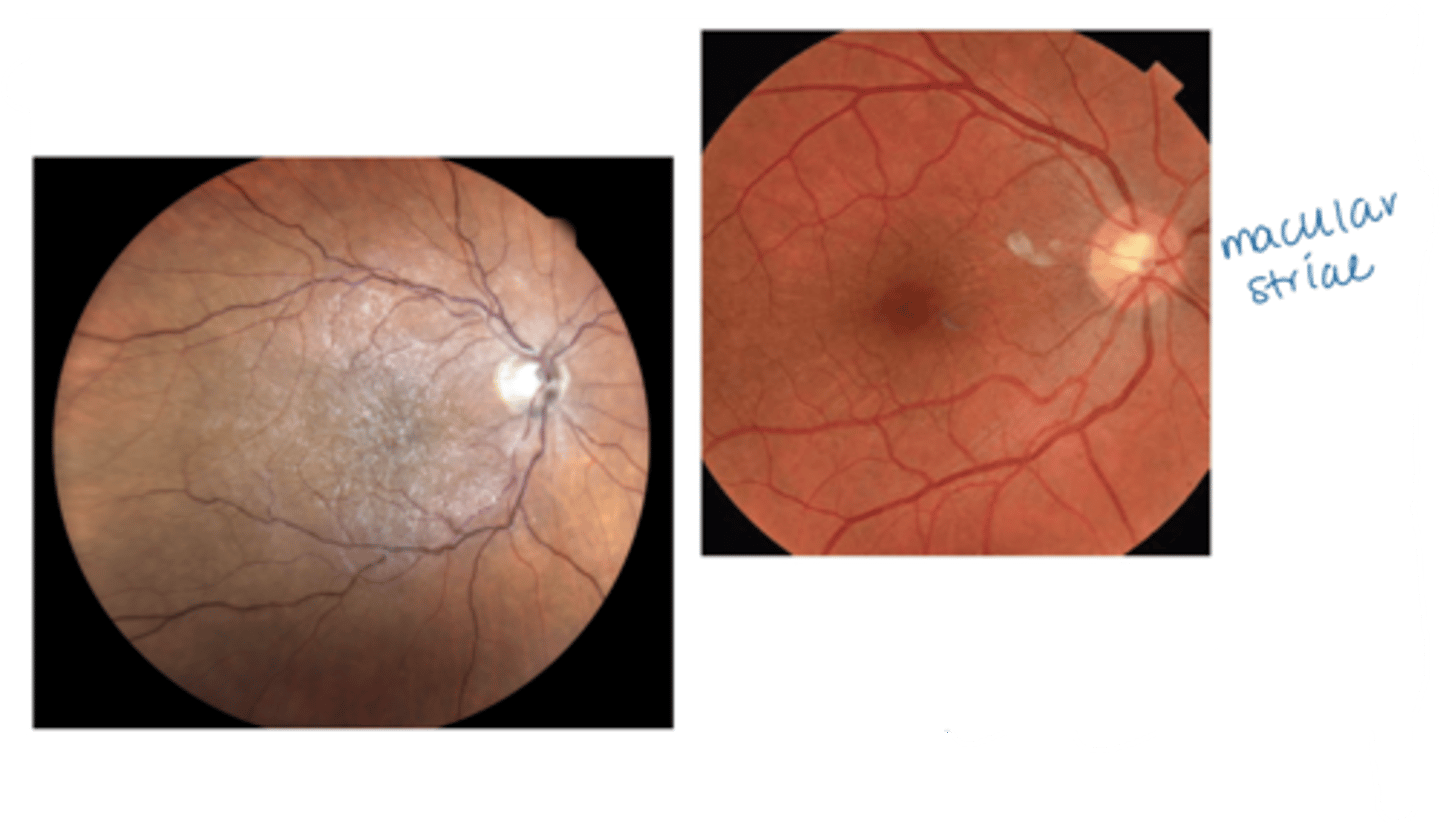
What is the macular pucker form of epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
change to macular contour, typically symptomatic
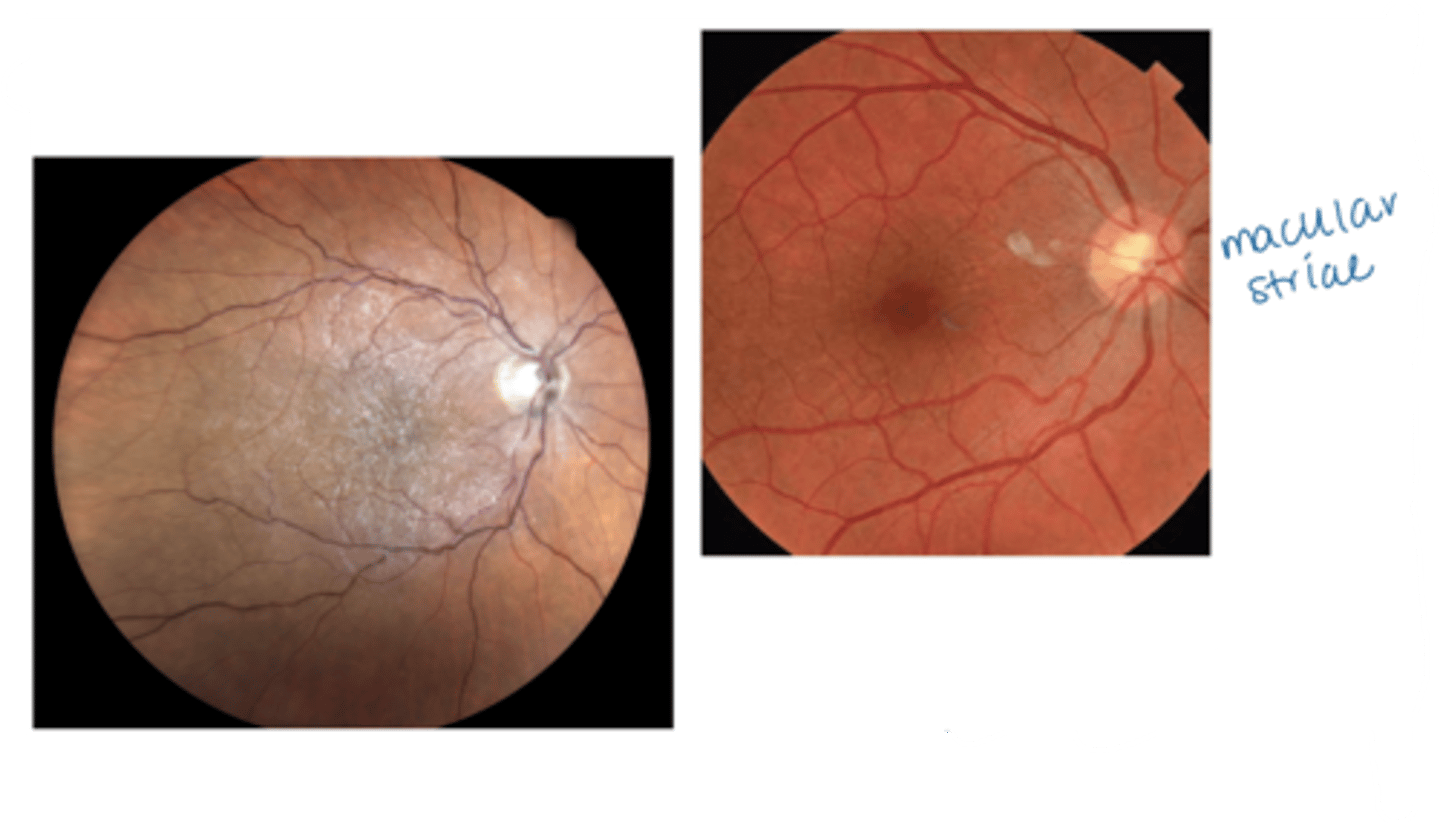
What are the signs of an epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
glistening sheen, abnormal reflectivity (focal or diffuse)
appears opaque when severe
+/- retinal wrinkling, striae
+/- pseudohole
+/- cystoid macular edema
+/- serous detachment
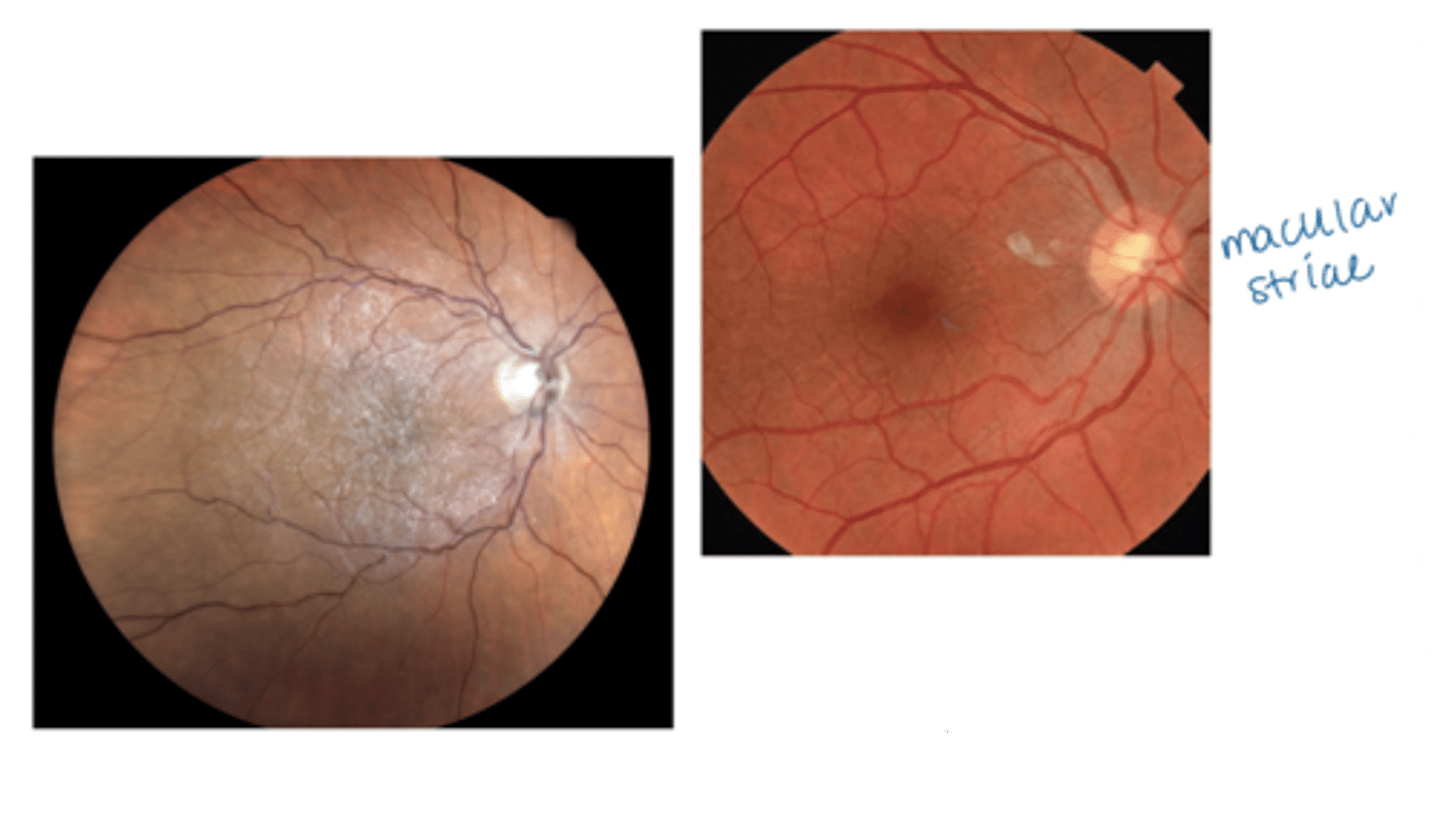
What are the symptoms of an epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
asymptomatic
reduced VA
metamorphopsia
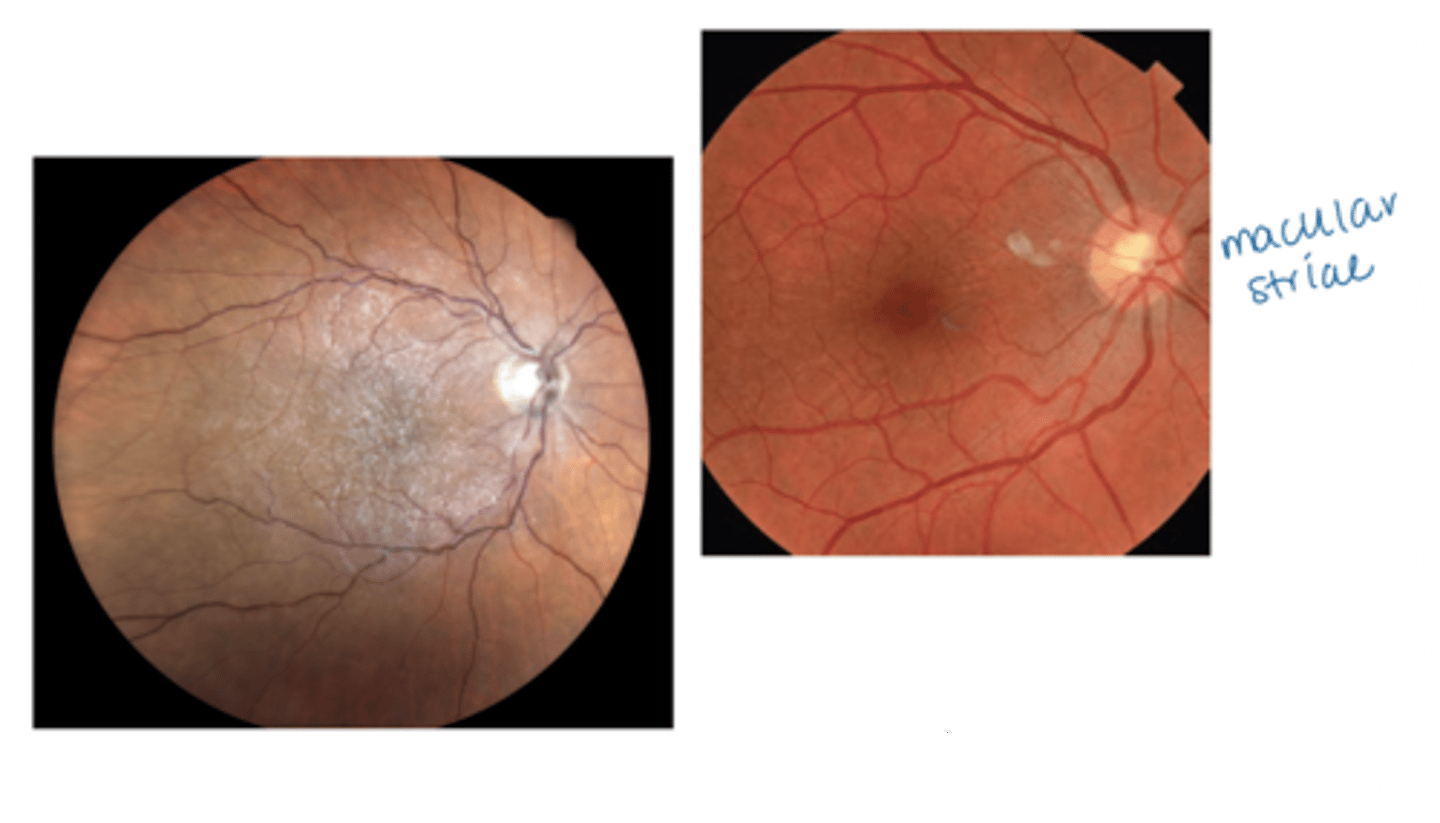
What is the etiology of an epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
idiopathic > 50 years old
intraocular surgery
RD
vascular disease
chronic inflam
trauma
PVD
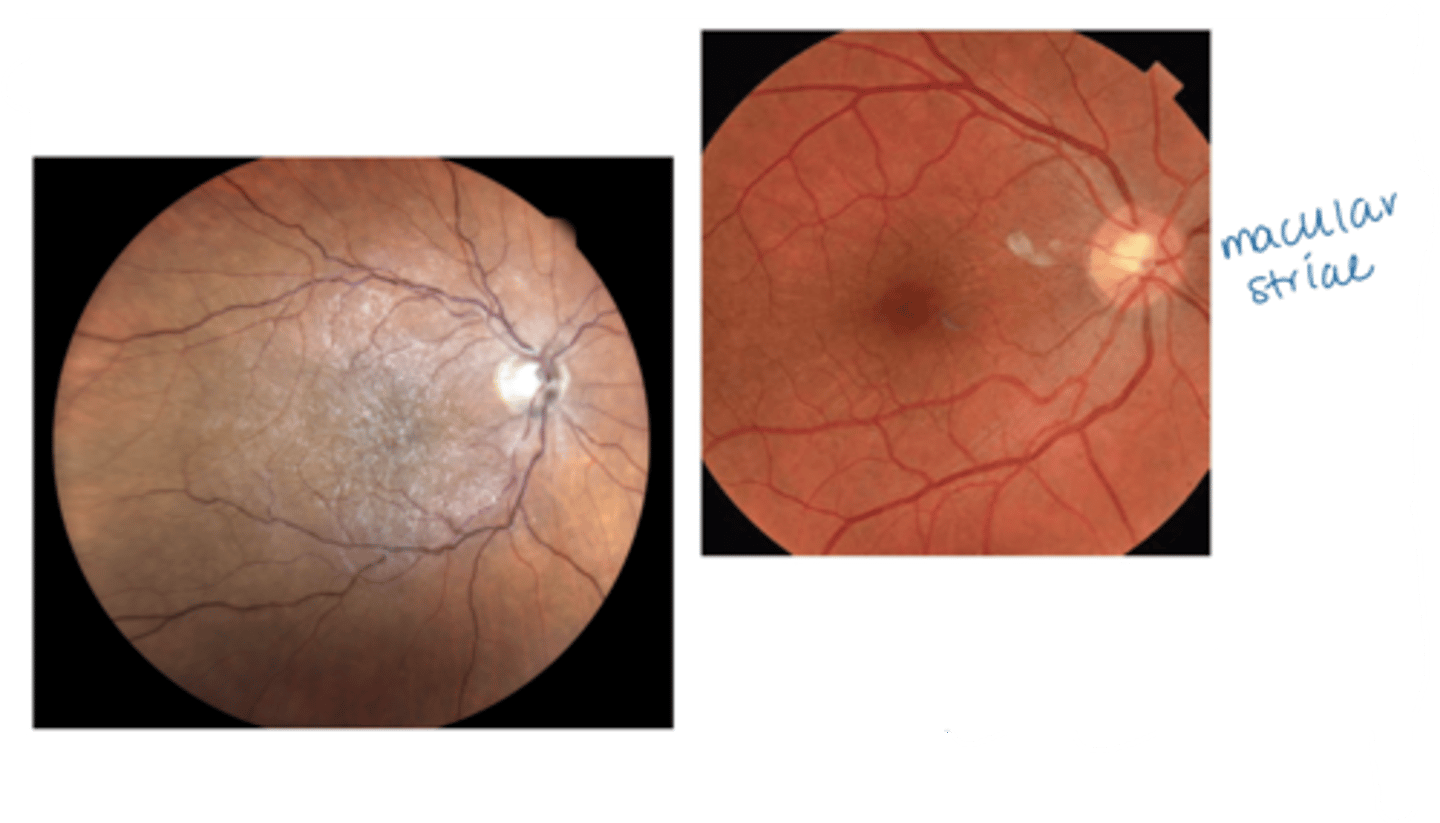
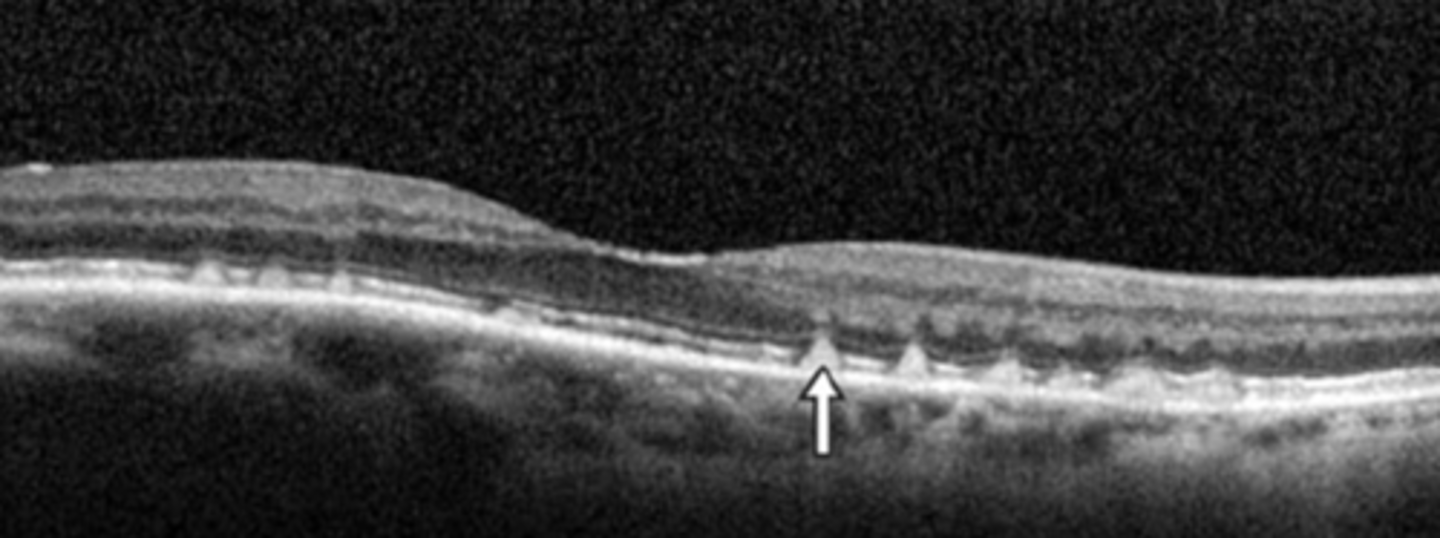
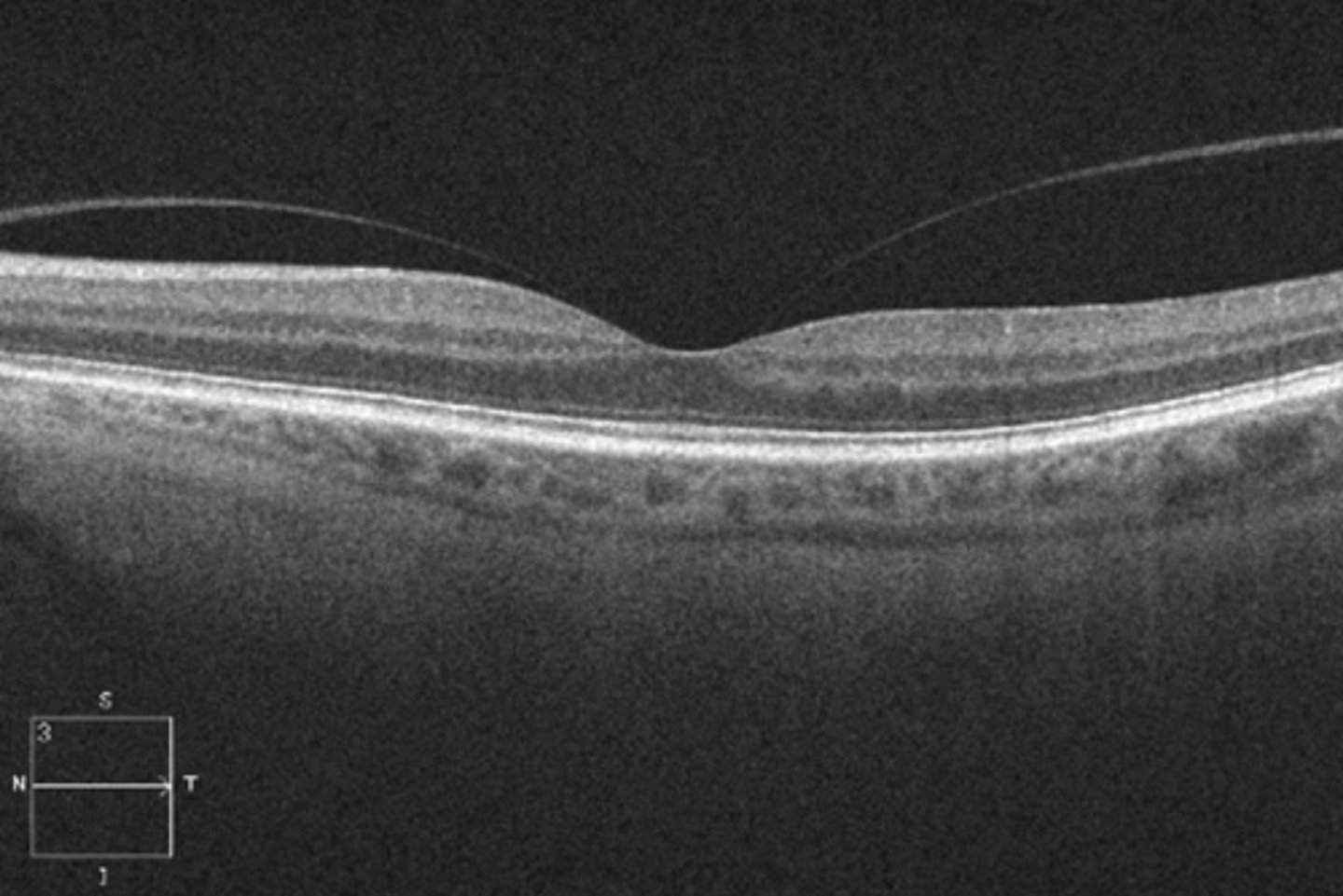
What does an epiretinal membrane (ERM) look like on OCT?
hyperreflective membrane within ILM (between RNFL and posterior hyaloid of vitreous) = more hyperR than vitreous face but same reflectivity as rNFL
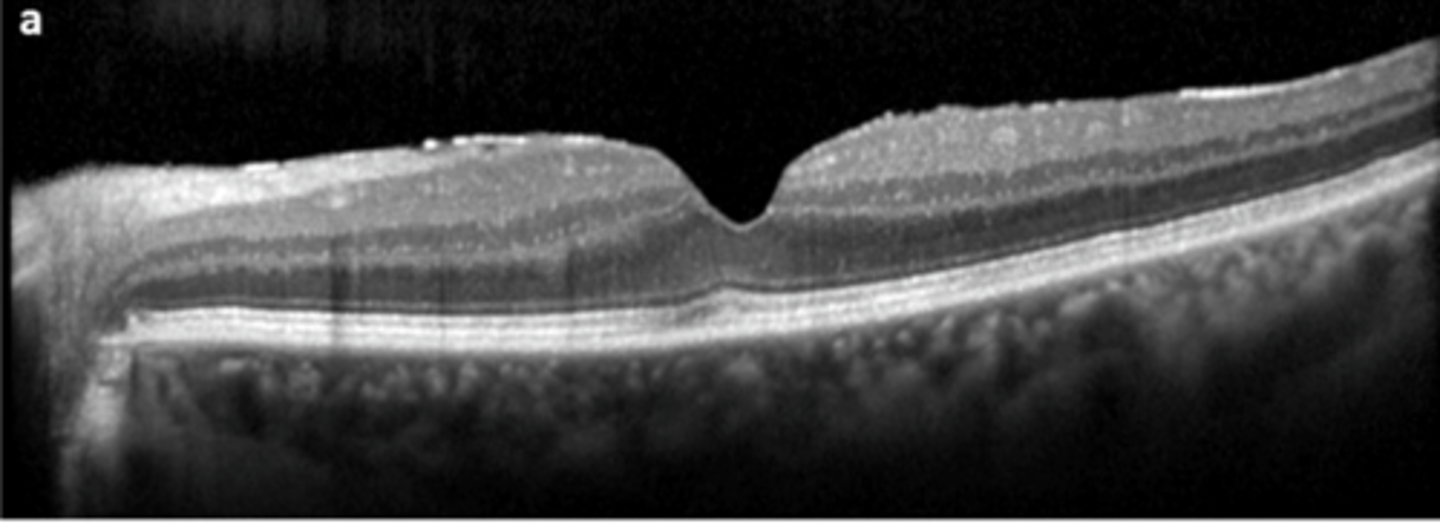
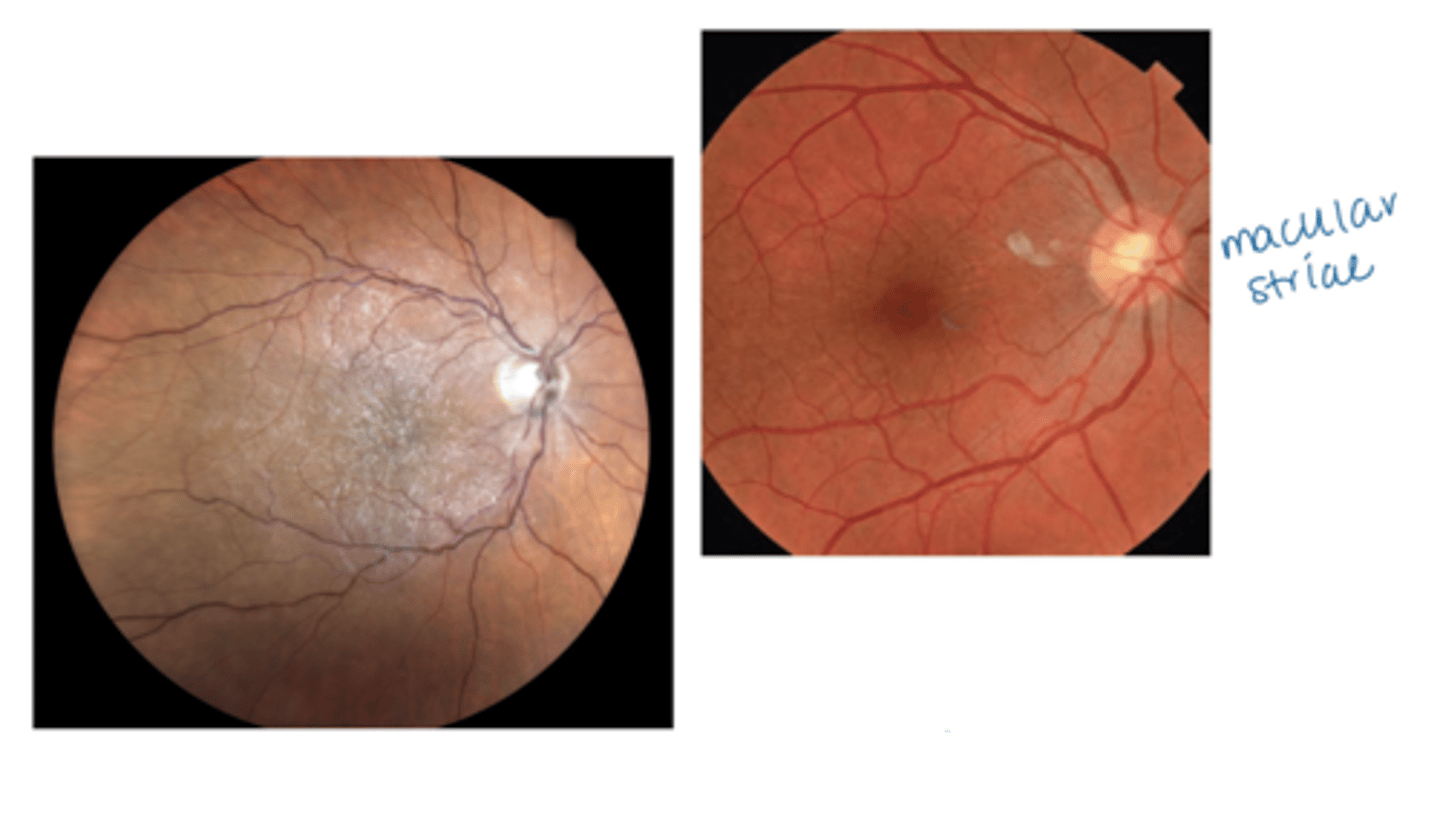
What sign of epiretinal membrane (ERM) is shown here?
macular pucker = distorted retina = blur, distortion
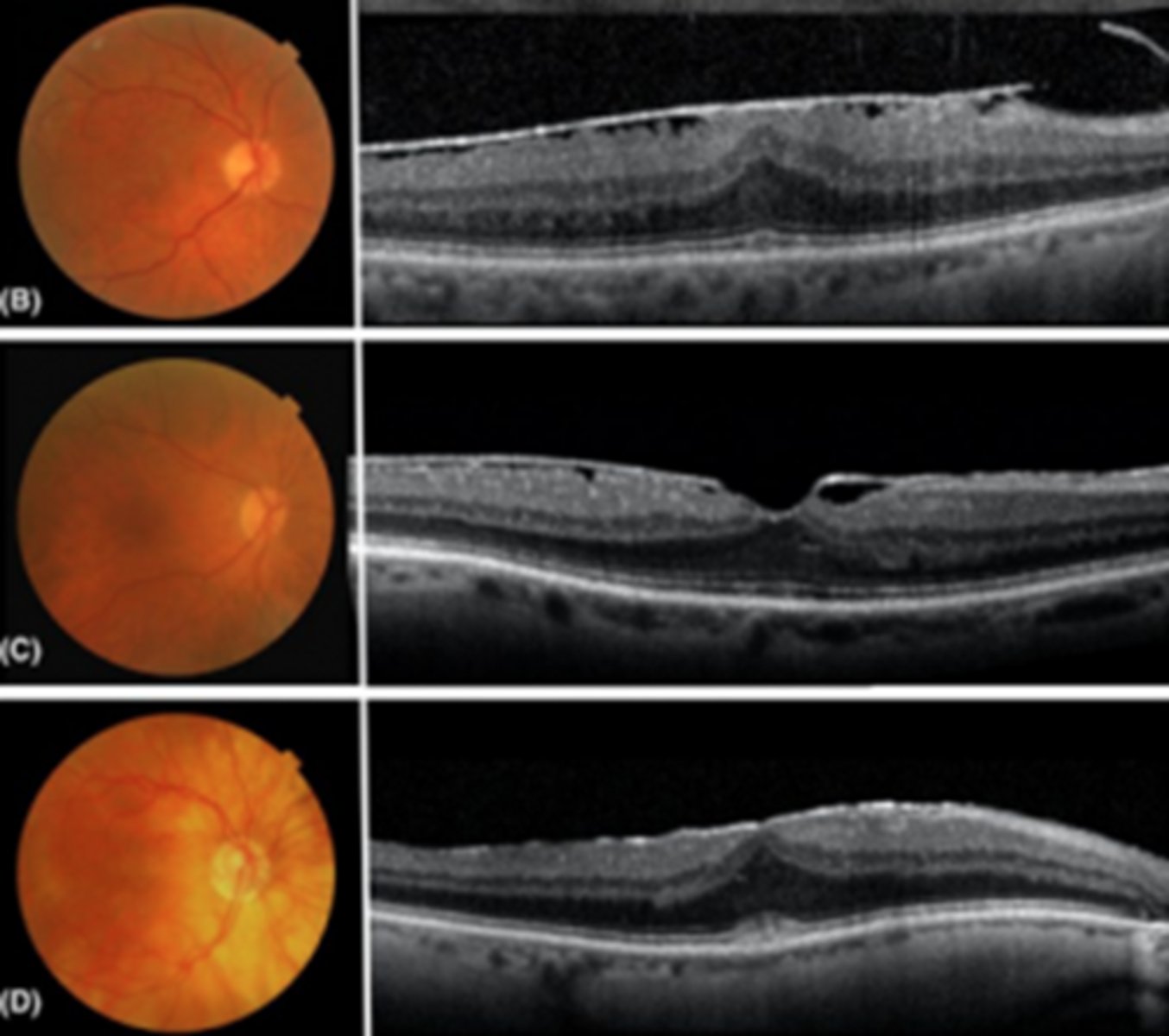
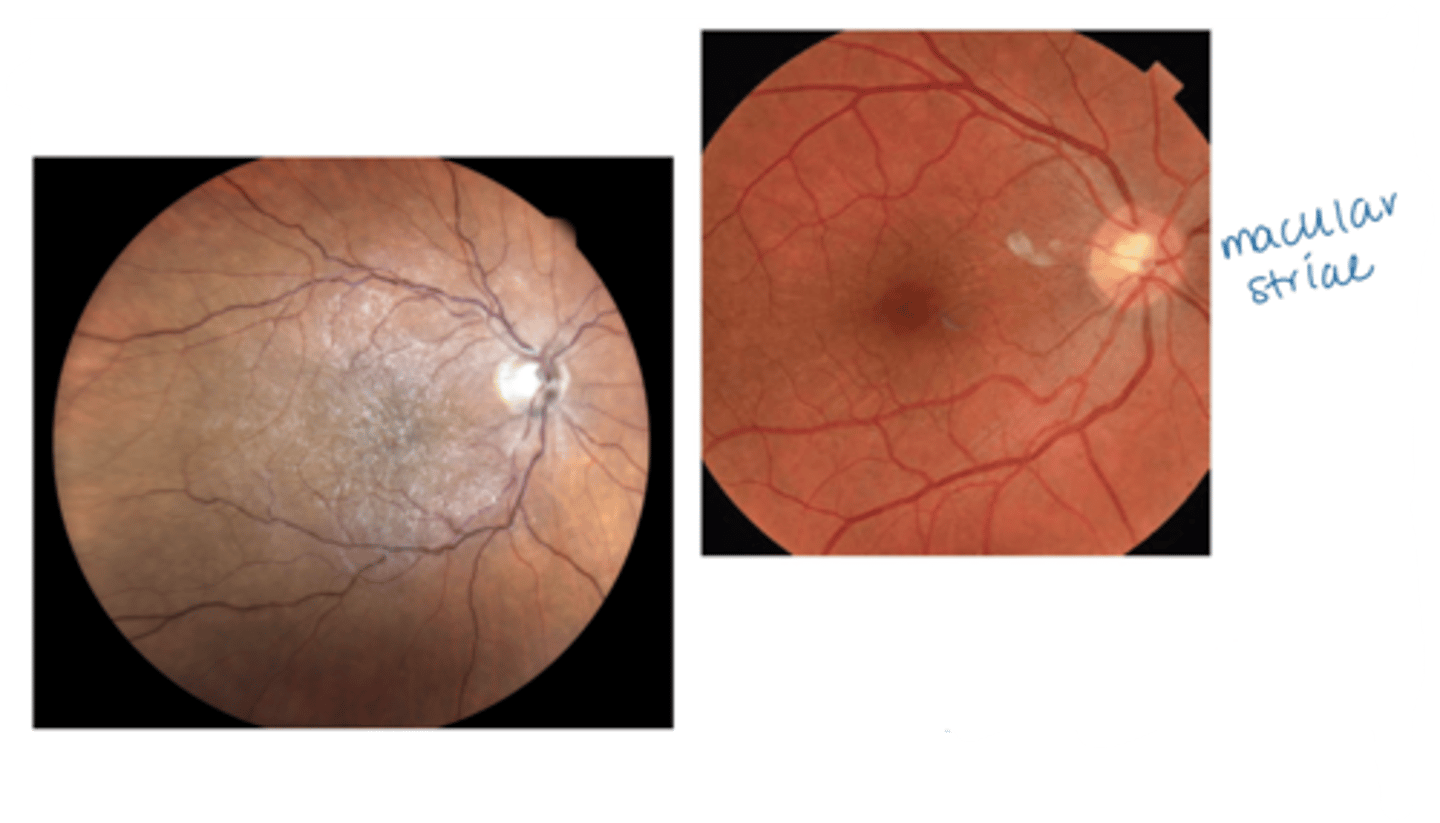
What sign of epiretinal membrane (ERM) is shown here?
macular pucker with retinal striae
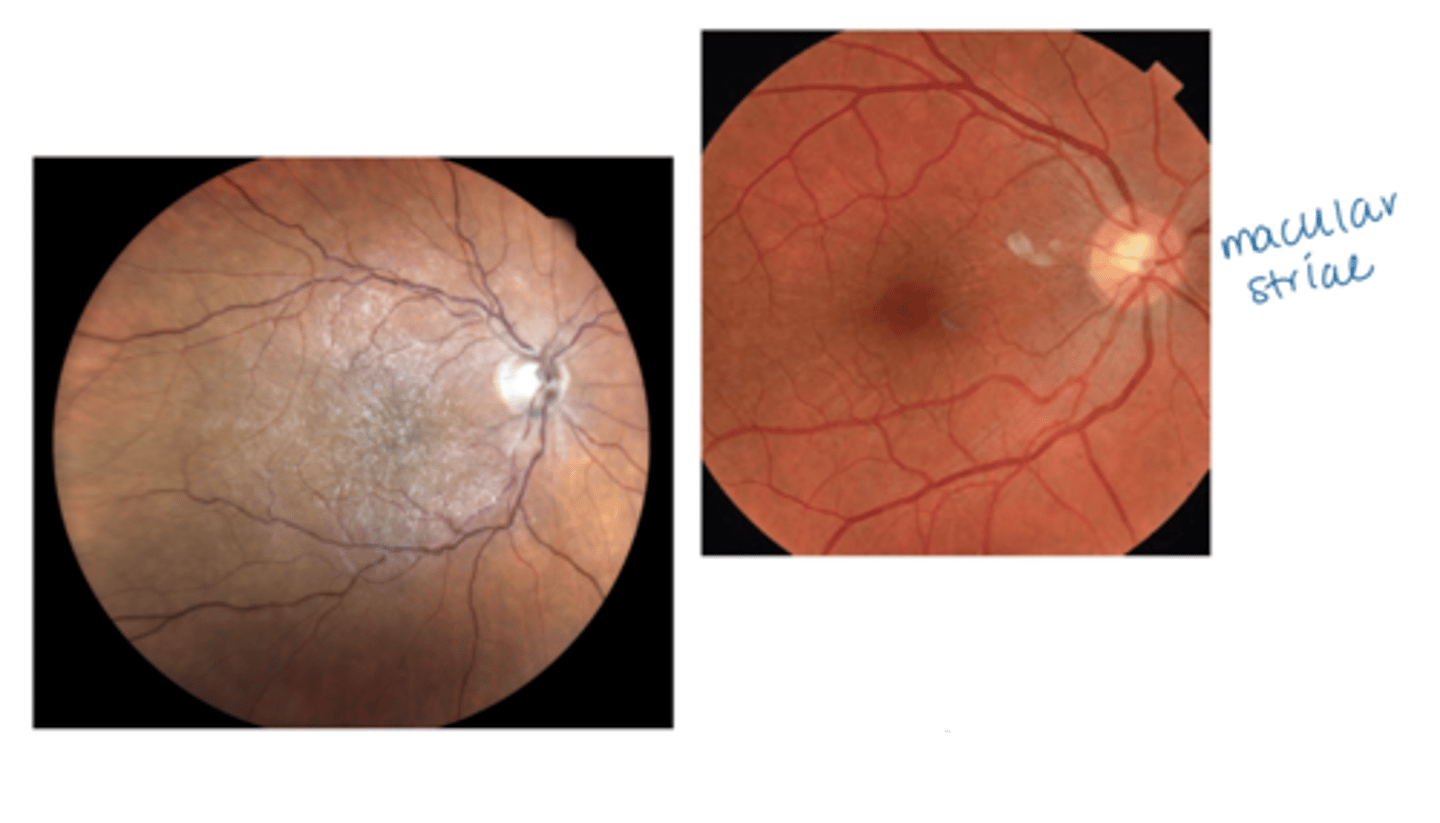
What sign of epiretinal membrane (ERM) is shown here?
macular pucker = pulling causes macular edema/cystic spaces
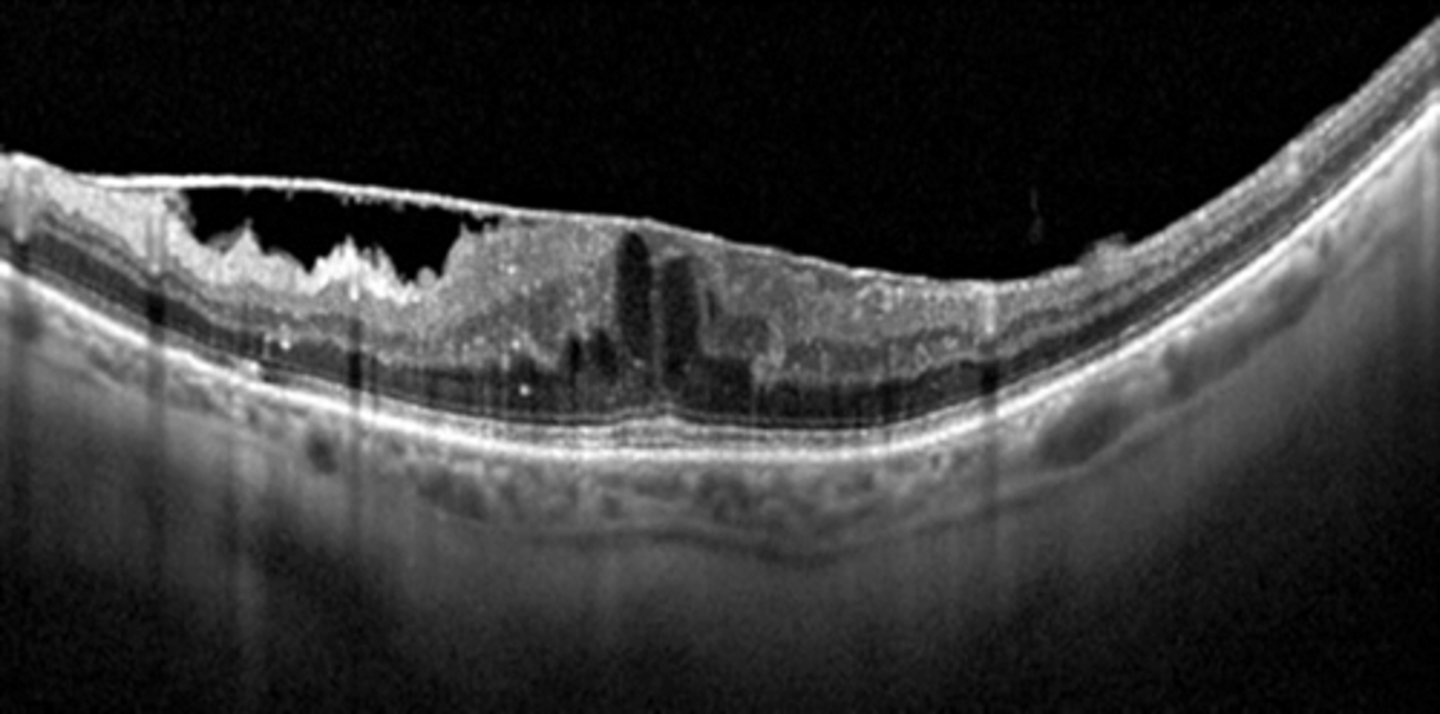
What is a pseudohole that can result from an epiretinal membrane (ERM)?
appears like a lamellar hole due to atypical foveal contour but there is no atrophy of layers
What is the management for an epiretinal membrane (ERM) with BCVA/QOL unaffected?
monitor q12 mos
What is the management for an epiretinal membrane (ERM) with BCVA/QOL affected?
monitor q6 mos
refer to retina = pars plana vitrectomy with ILM/ERM peel, VA may or may not improve
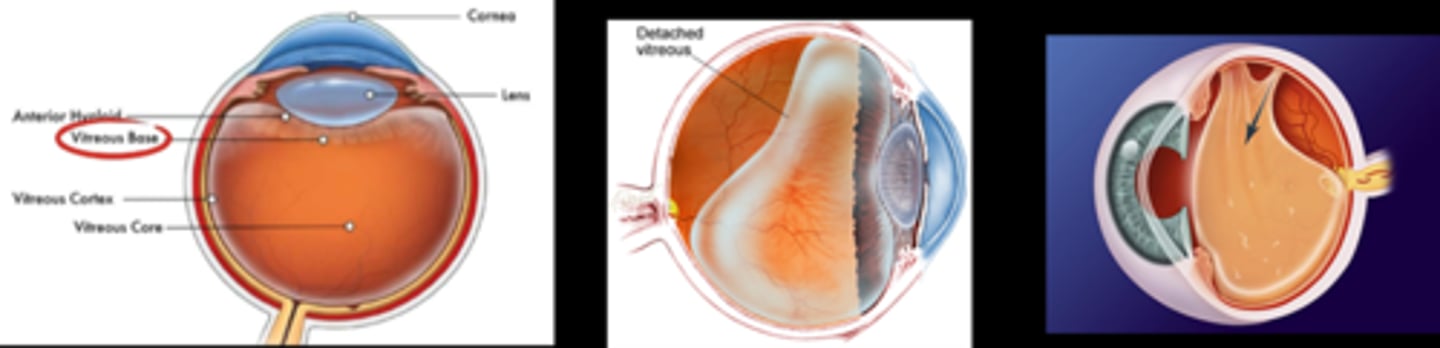
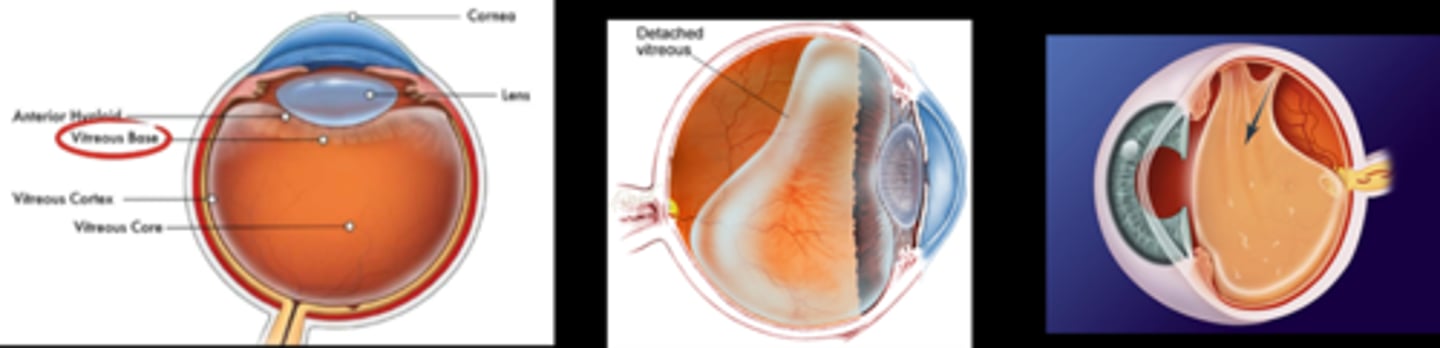
VMA, VMT, and PVD are all considered what types of conditions?
normal aging degenerations
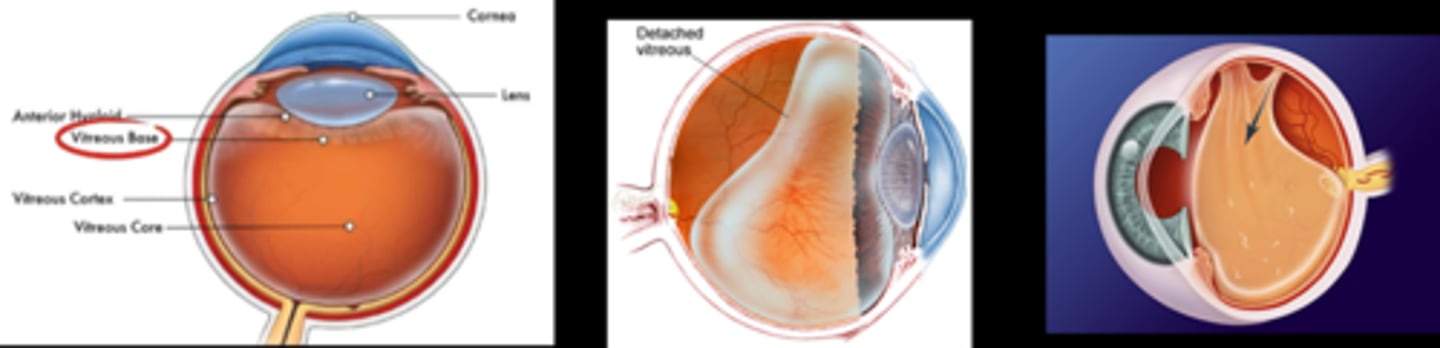
What is vitreomacular adhesion (VMA)?
early vitreous degeneration = vitreous cortex separates from ILM but still adhered elsewhere = posterior hyaloid becomes visible
What is the order of vitreous detachment likeliness?
MOST LIKELY
BV
fovea
ONH
LEAST LIKELY
Which area of the retina does the vitreous never detach?
ora serrata = base of vitreous
What is the process of vitreous aging?
liquefies = syneresis = fluid pockets cast shadows (floaters) = pockets collapse = vitreous contracts/pulls away from retina = flashes/photopsia, RD
How is the macula affected in vitreomacular adhesion (VMA)?
all retinal layers intact = no distortion = asymptomatic
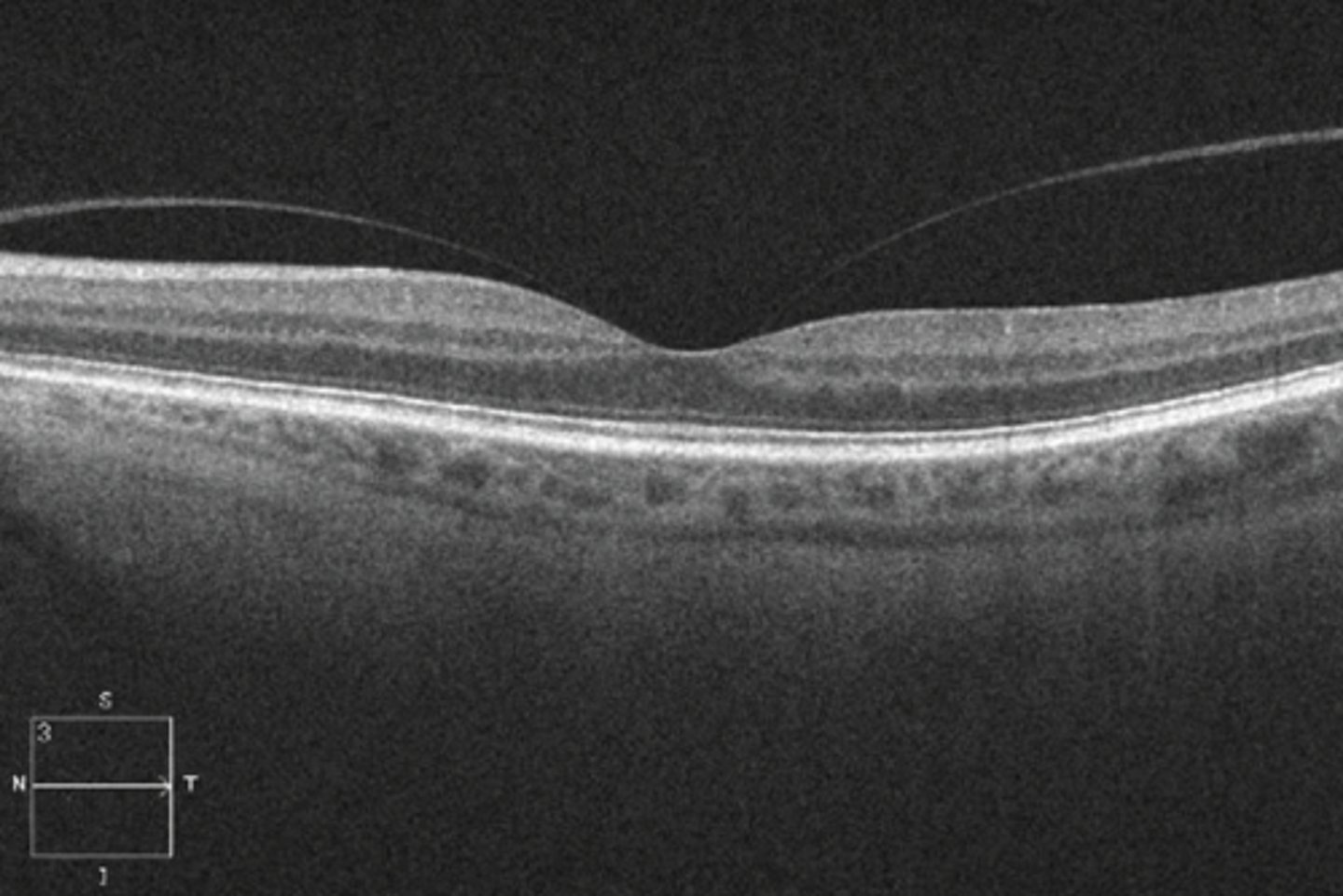
What are the signs of vitreomacular adhesion (VMA)?
none = may see some vitreous opacities, posterior hyaloid face seen on OCT (but OCT not necessary)
What is the management for vitreomacular adhesion (VMA)?
pt education on vitreous degeneration and S/S of RD
What are the 4 classifications of VMA/VMT?
focal = adhesion points =< 1500 microns apart
broad = adhesion points > 1500 microns apart
isolated = no macular disease
concurrent = w/ other macular disease
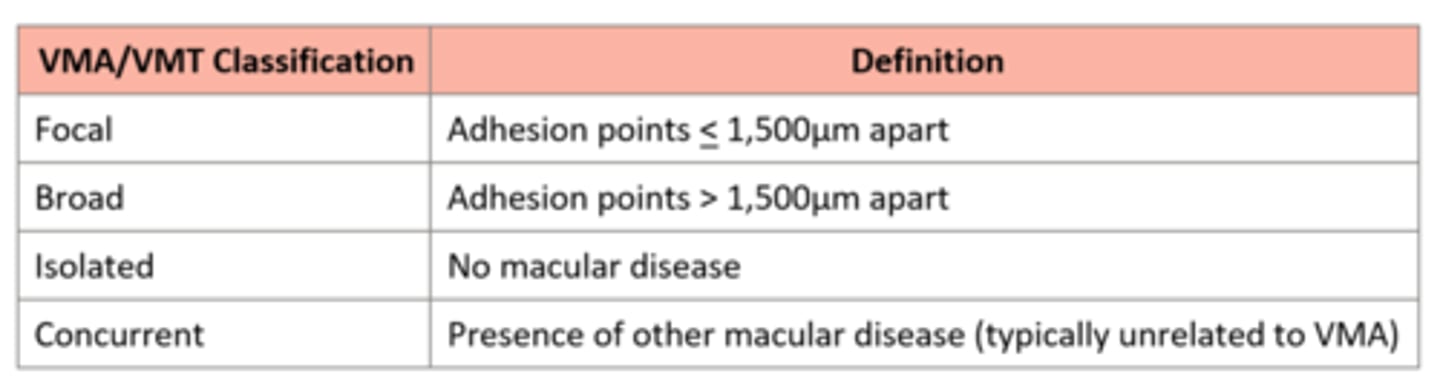
What is a vitreomacular traction (VMT)?
traction of retina by posterior hyaloid right before vitreous fully detaches from fovea = distortion of retinal layers, cystic spaces = tear/hole
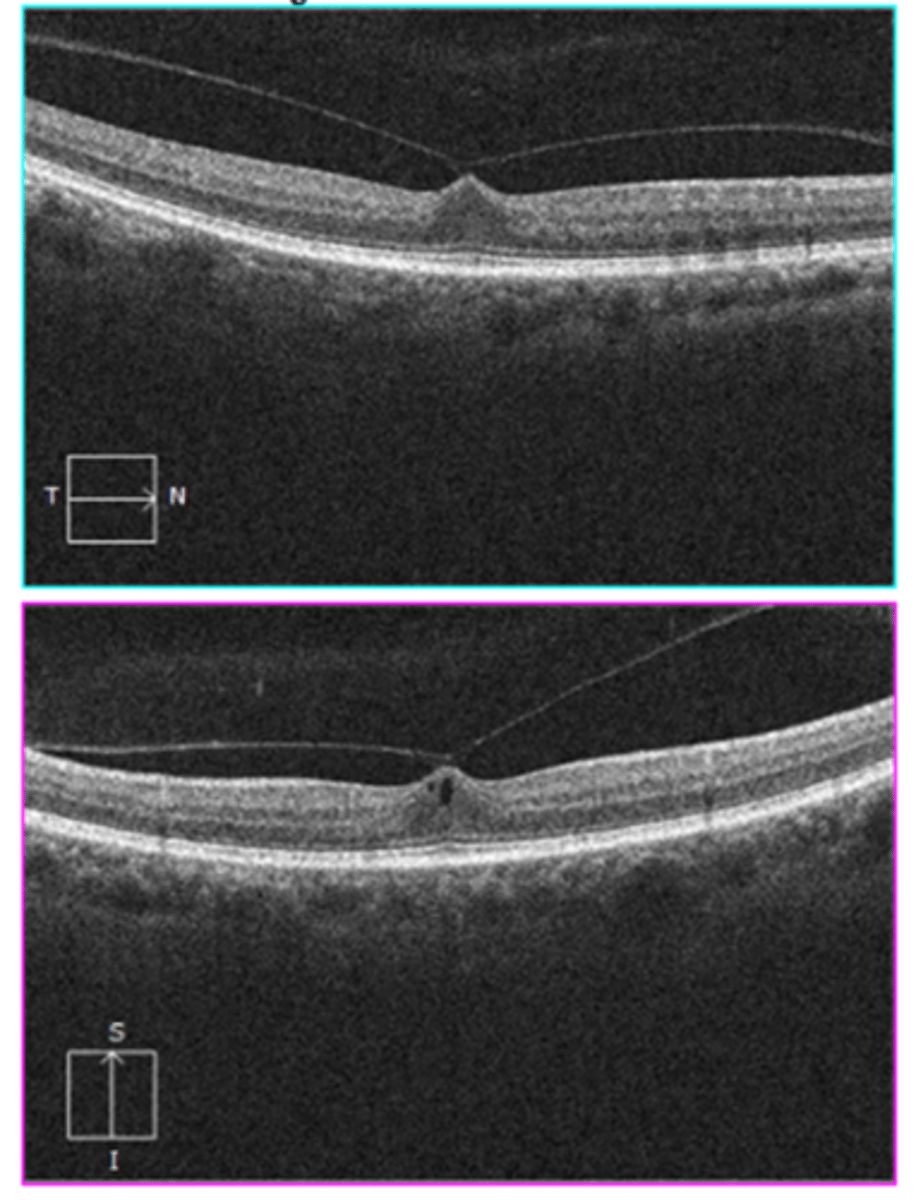
What are some S/S of a vitreomacular traction (VMT)?
blur
metamorphopsia
distorted/blunted foveal colouration
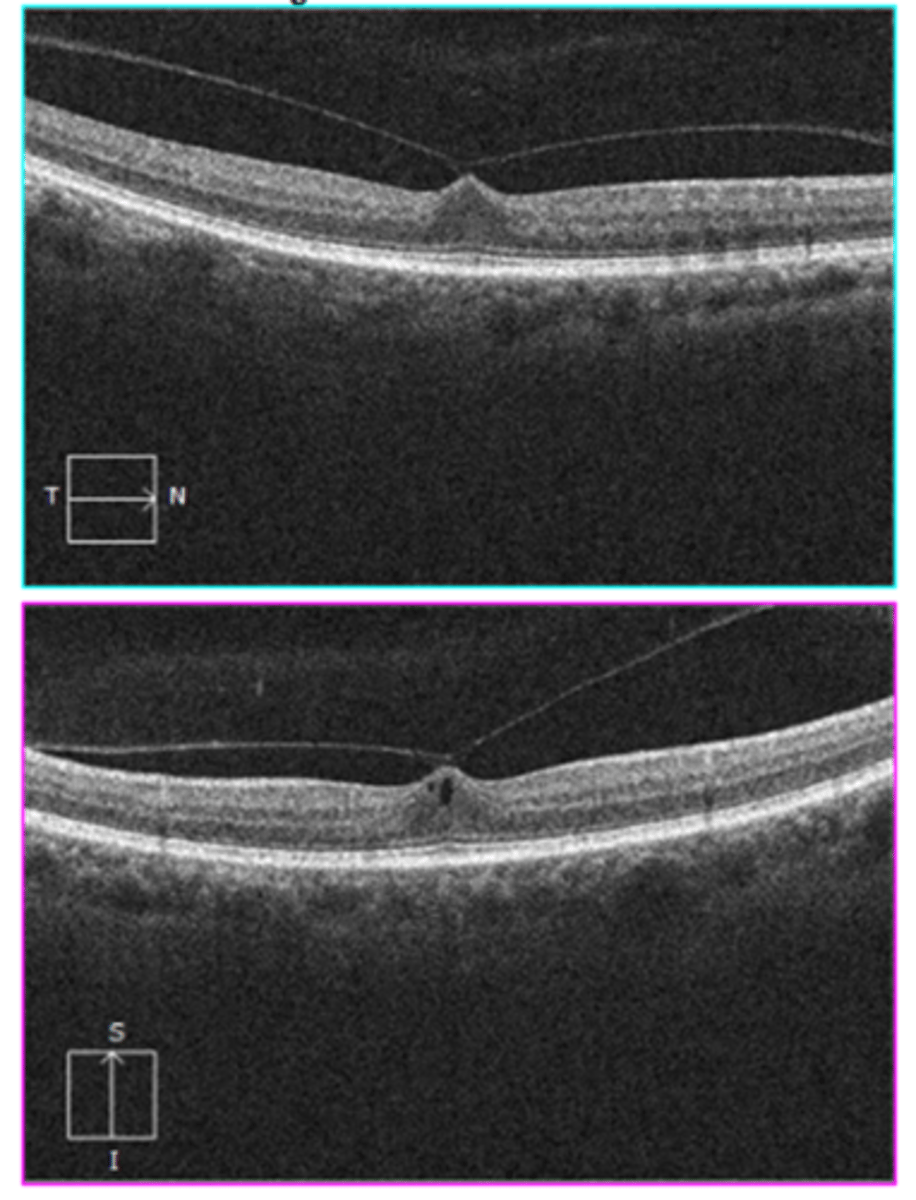
How does a vitreomacular traction (VMT) appear on OCT?
traction at area of vitreal adhesion causing distortion of foveal layers
may include foveal cyst, CME, or foveal detachment
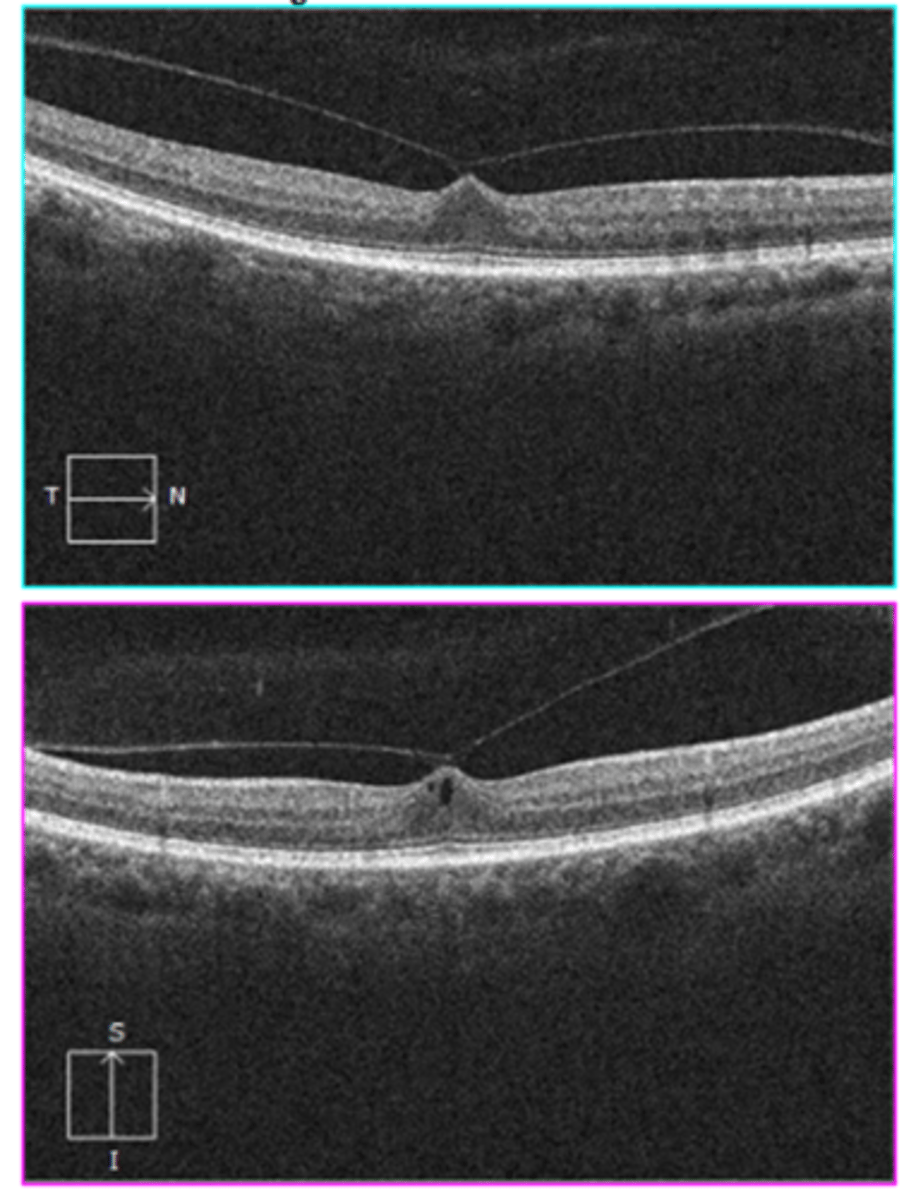
What is the management for an asymptomatic vitreomacular traction (VMT)?
educate on prognosis (cystic spaces may resolve over time after full PVD)
educate on S/S of RD
monitor
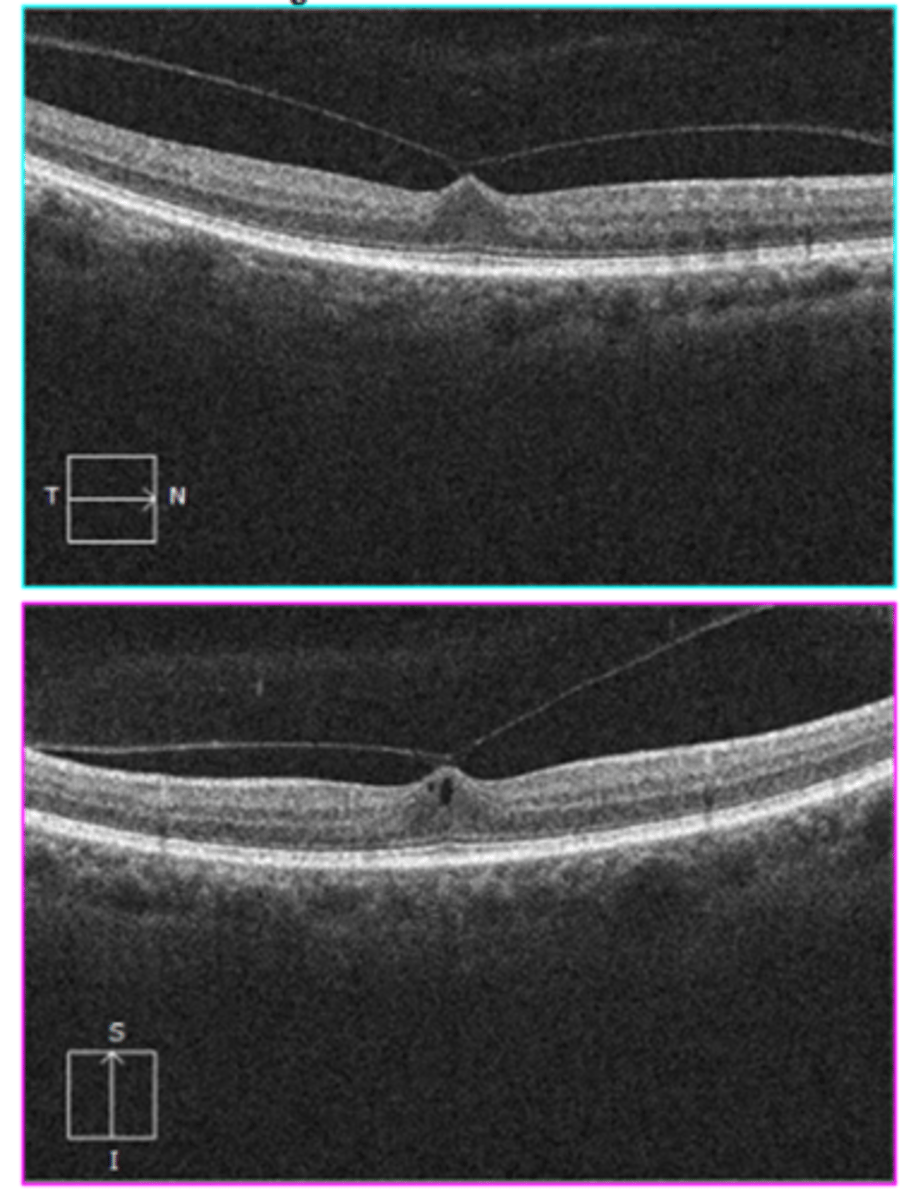
What is the management for a symptomatic vitreomacular traction (VMT)?
refer to retina for pars plana vitrectomy followed by ILM peel
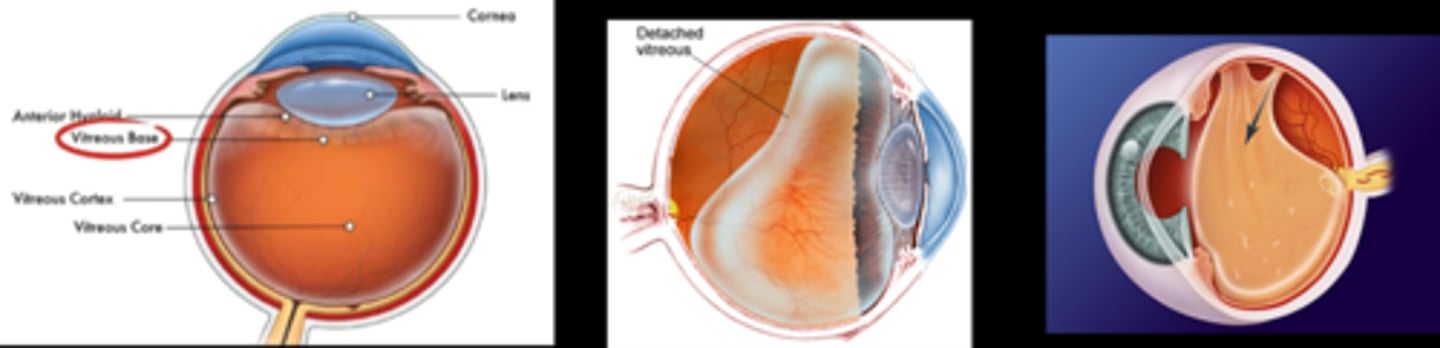
What are some risk factors for an earlier posterior vitreous detachment (PVD) (earlier than age 50+)?
longer axial length
trauma
surgery
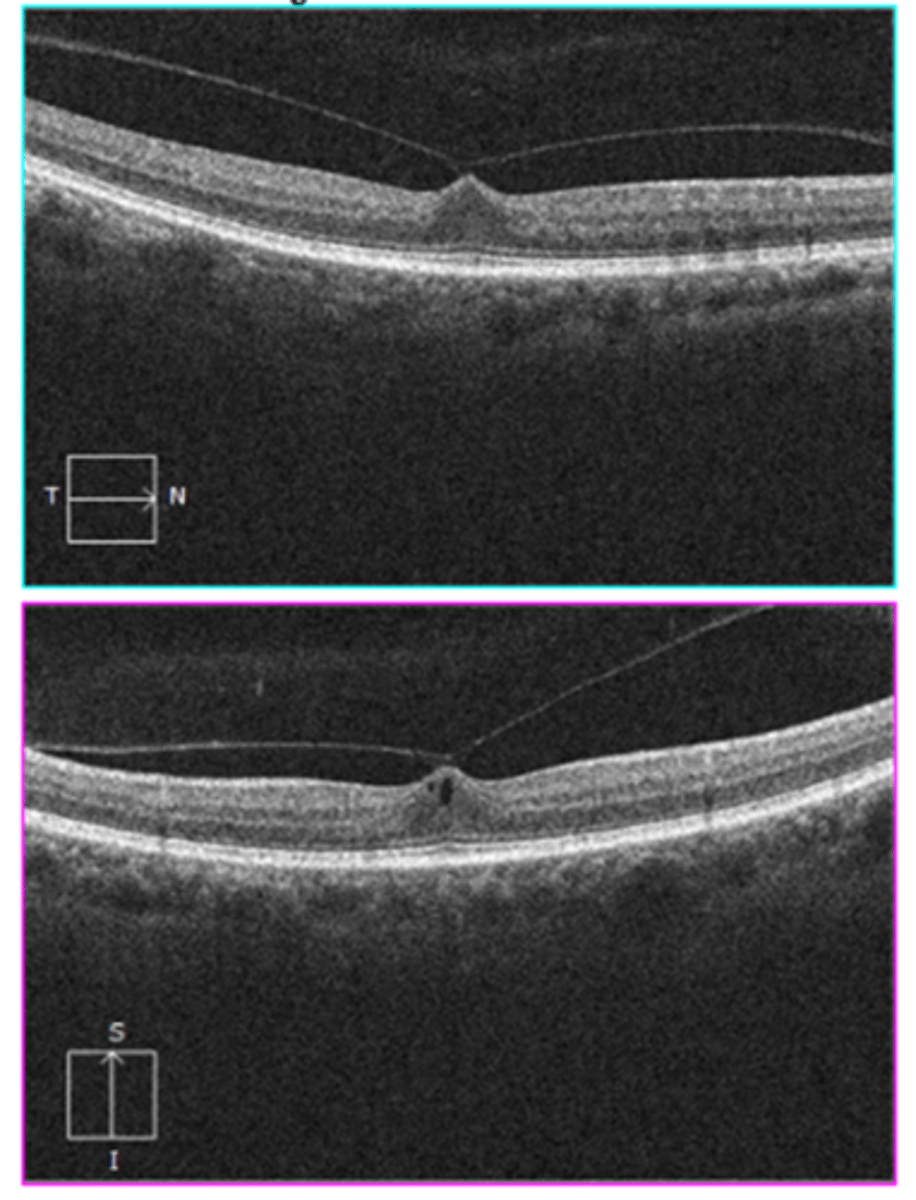
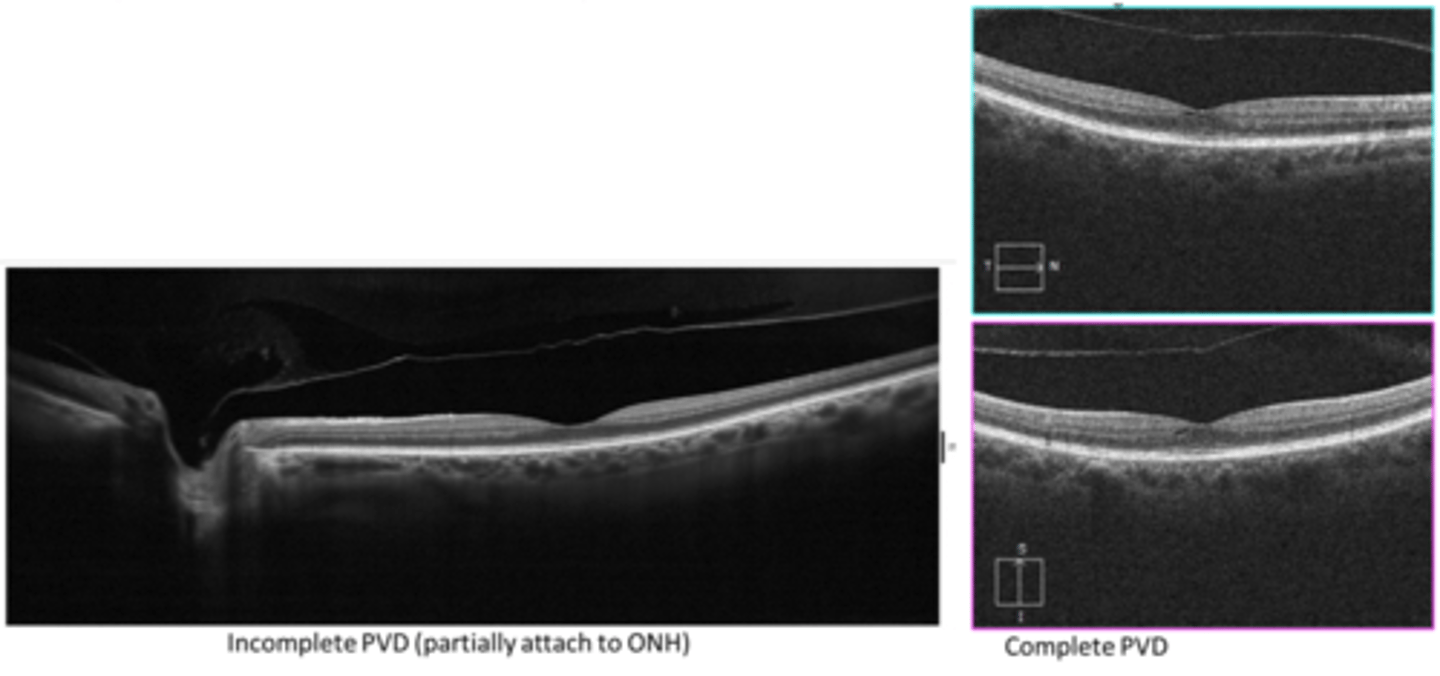
What is a partial PVD?
posterior hyaloid still attached at either ONH or fovea (often ONH)
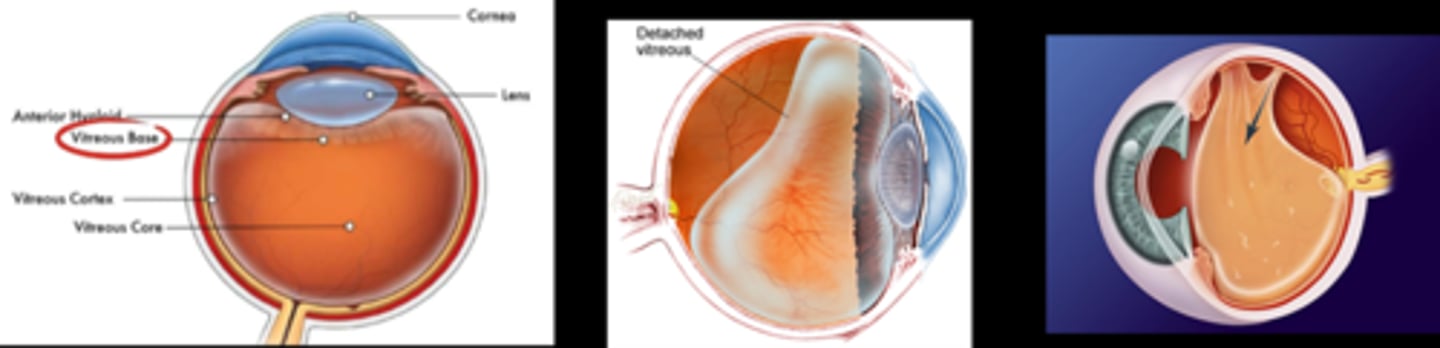
What is a complete PVD?
complete separation of posterior vitreous from posterior retina (esp ONH)
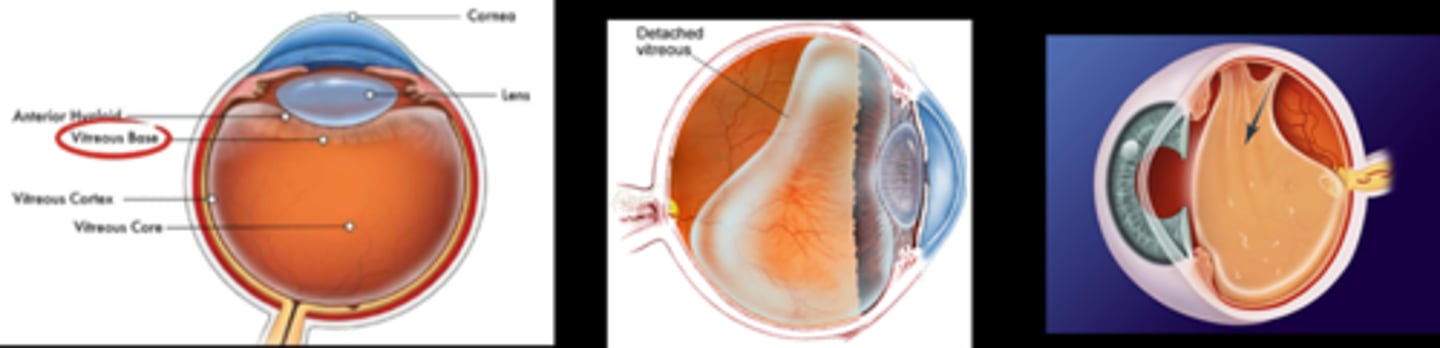
What are some symptoms of a PVD?
new floaters
cobweb floater
+/- preceded by flashes of light
What is this sign of a PVD shown here?
Weiss ring = dense peripapillary glial tissue still attached to posterior vitreous but no longer attached to ONH = complete PVD
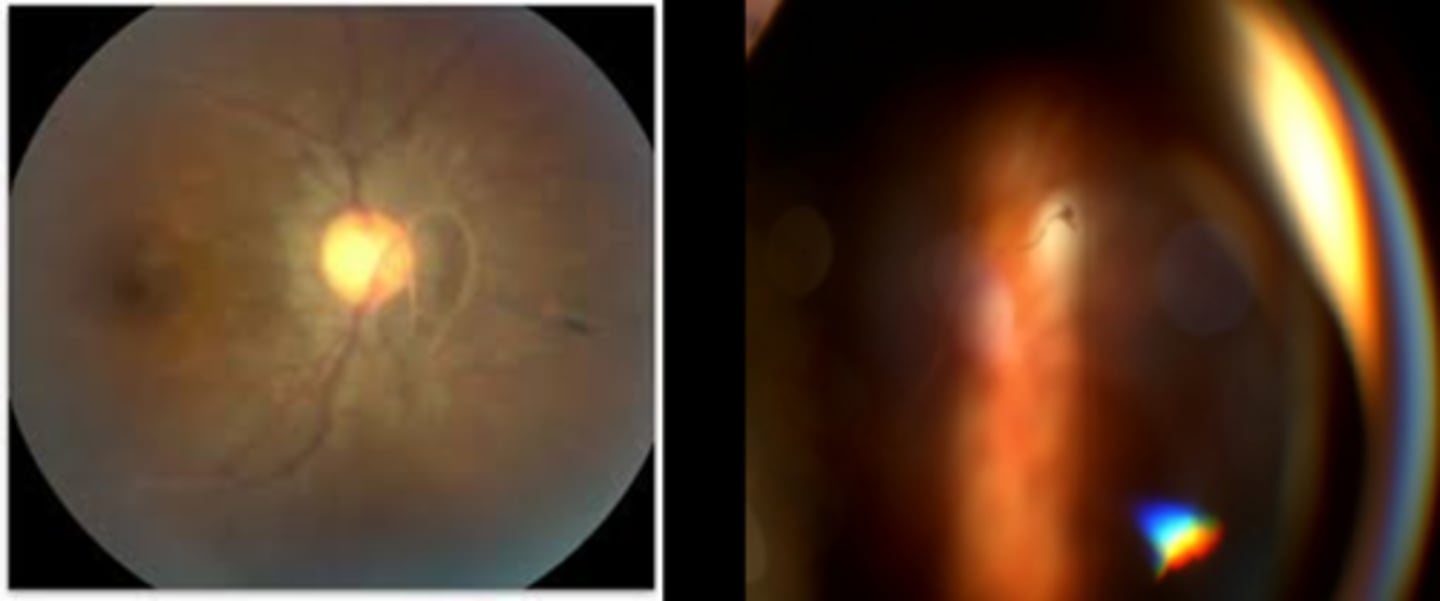
What is this sign of a PVD shown here?
posterior hyaloid face separate from retina = with optic section beam, go slightly off axis or off click-stop, and focus in front of the retina
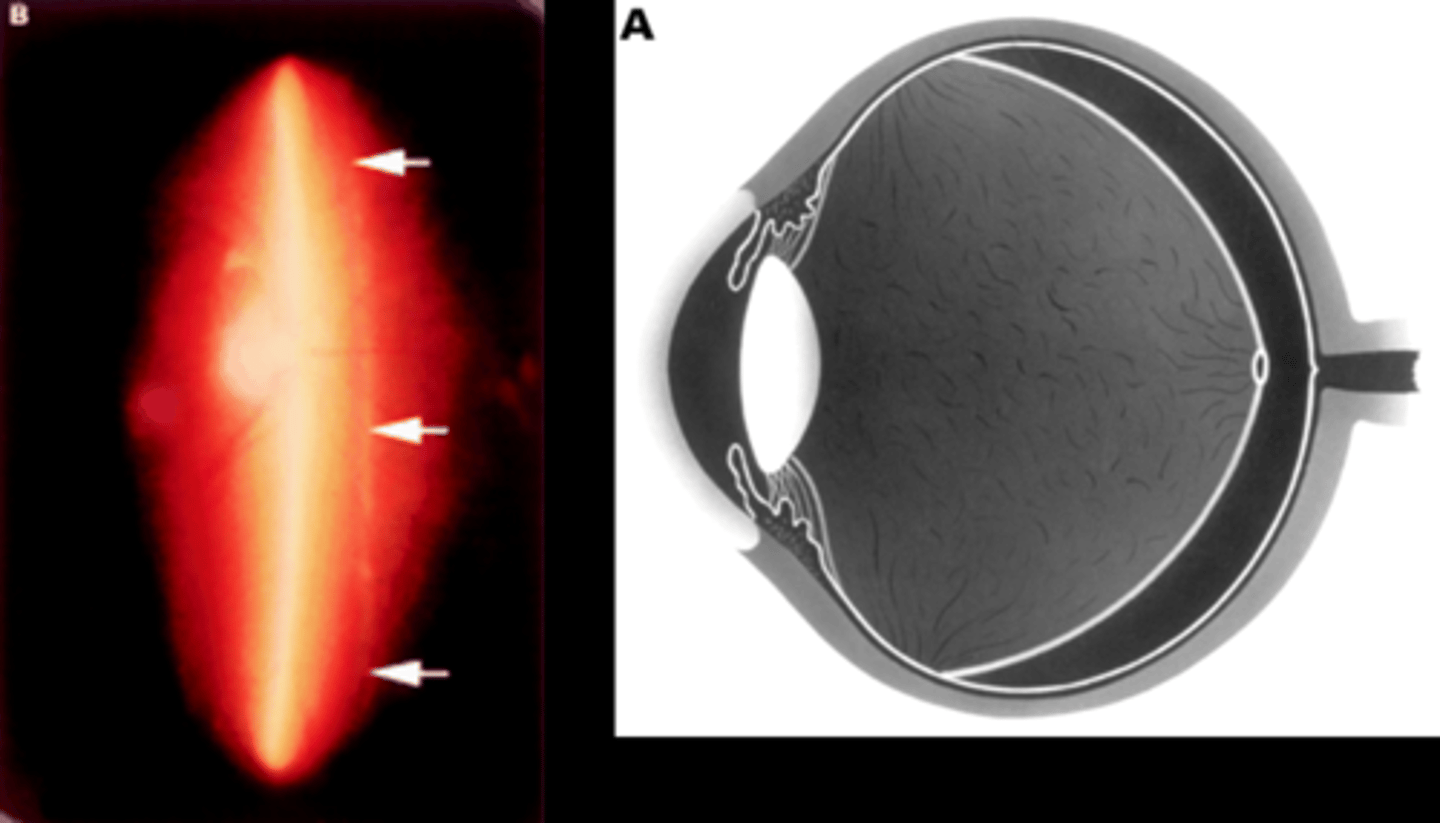
While we don't need an OCT to confirm a complete PVD when a Weiss ring is seen, what do we see on OCT?
posterior hyaloid partially or fully detached and floating above retina (may be too anterior to see if longstanding)
What is the management for a PVD?
pt education about brain adapting, will be more noticeable in bright light
f/u in 4-6 weeks from first onset of symptoms or after completion of PVD
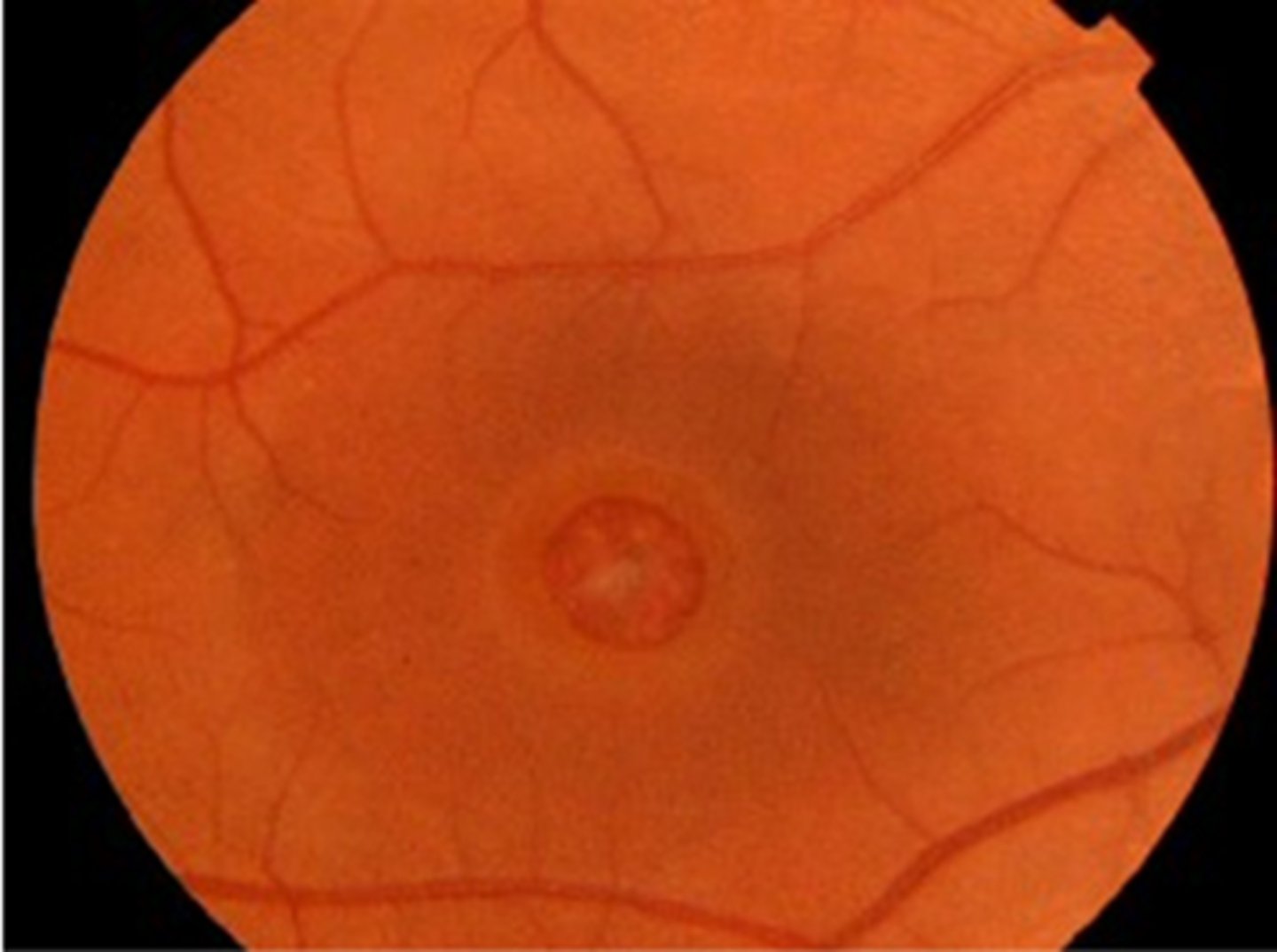
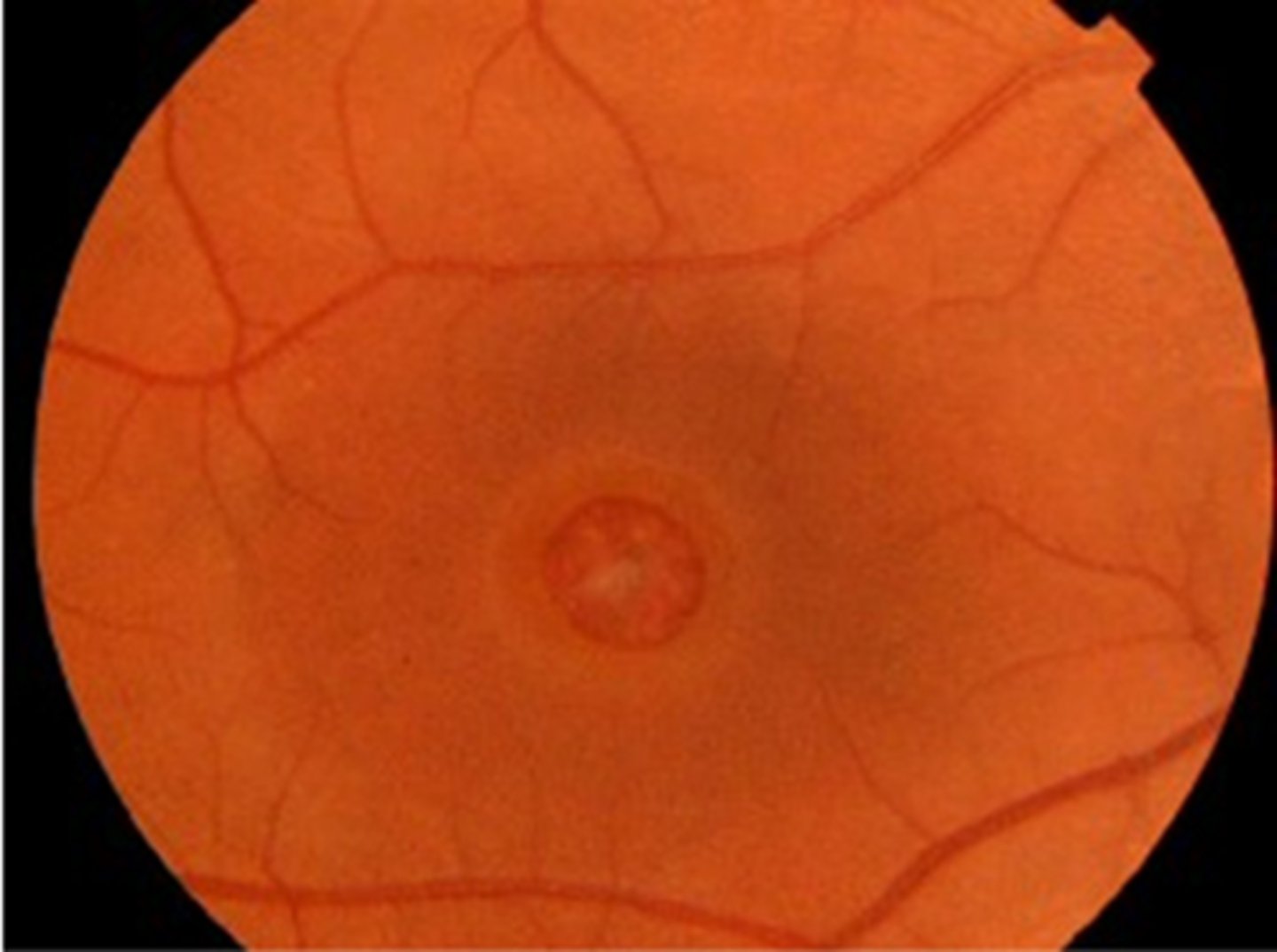
What are some possible complications of a PVD?
VMT
vitreous hemorrhage
lamellar macular hole
full-thickness macular hole
ERM
RD/tear
What is a full thickness macular hole?
absence of entire retina above the RPE at the fovea, giving appearance of an irregular foveal pit
What is the main cause/etiology of a full thickness macular hole?
PVD or trauma
What are some symptoms of a full thickness macular hole?
central VA loss (20/400 or worse)
central scotoma
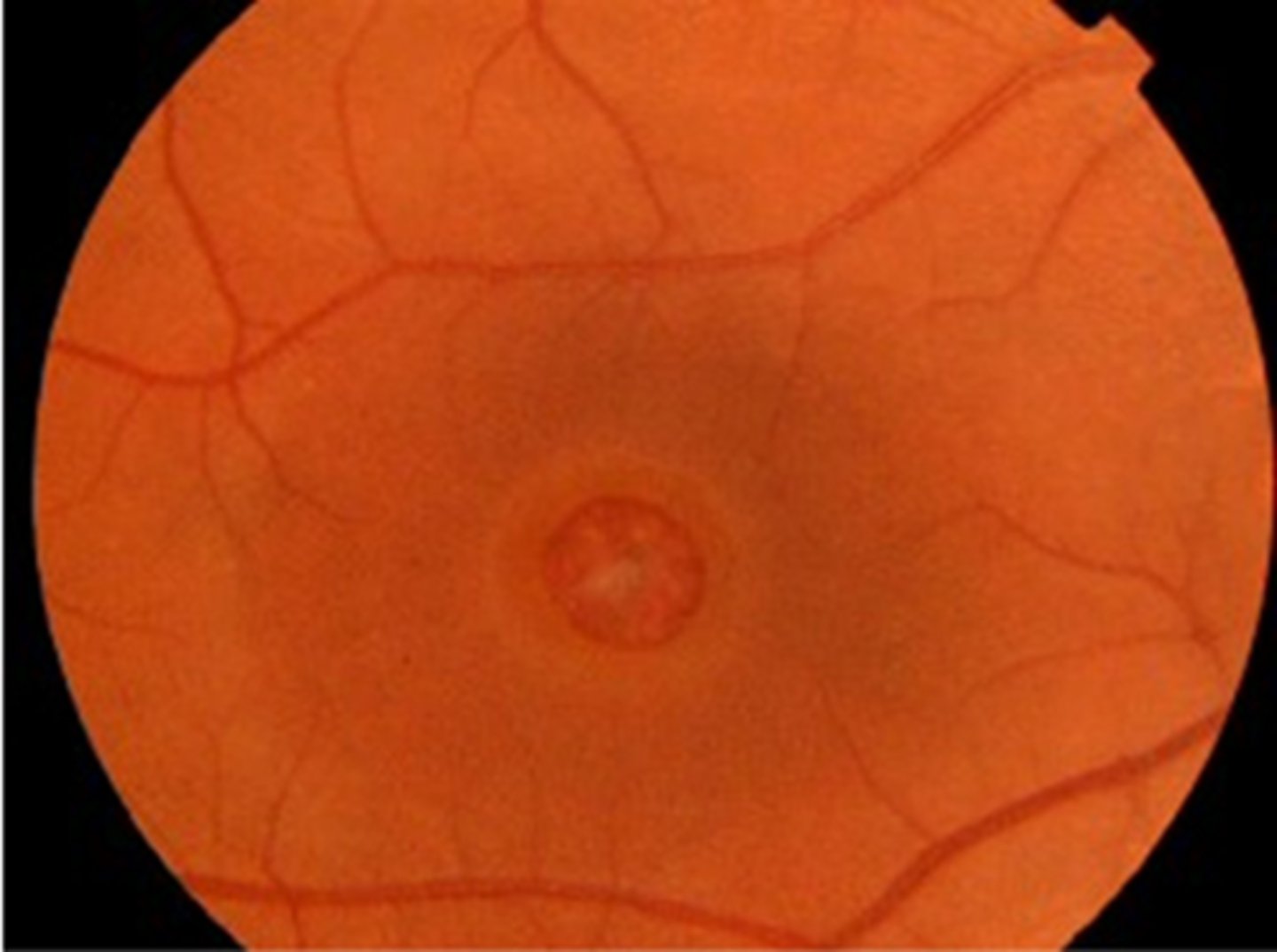
What are the signs of a full thickness macular hole?
red, round hole at fovea
+/- CME, cystic spaces parafoveally = lighter cuff around red hole
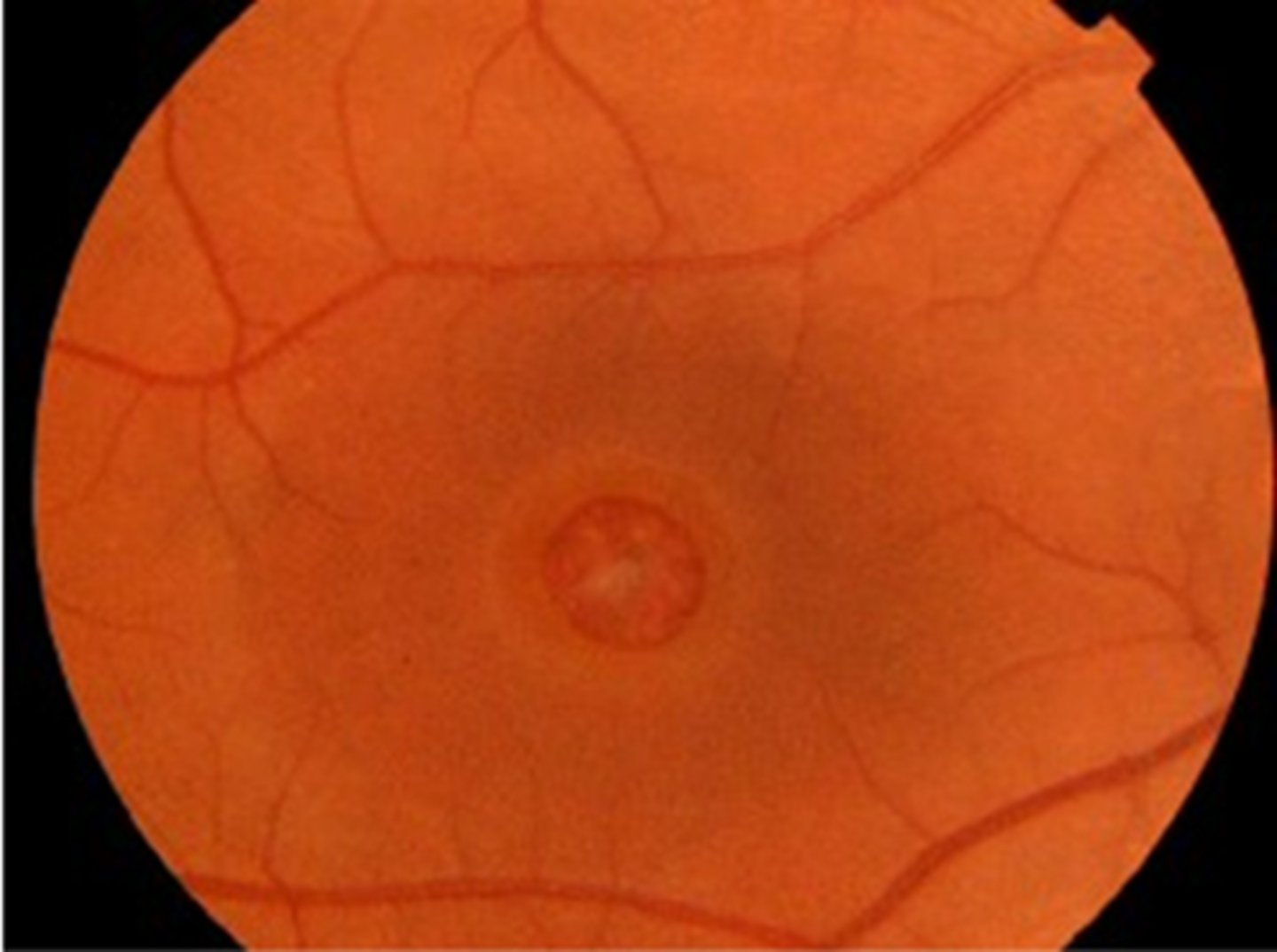
What is the Watzke-Allen sign of a full thickness macular hole?
place a vertical beam over fovea, pt should see a break in beam
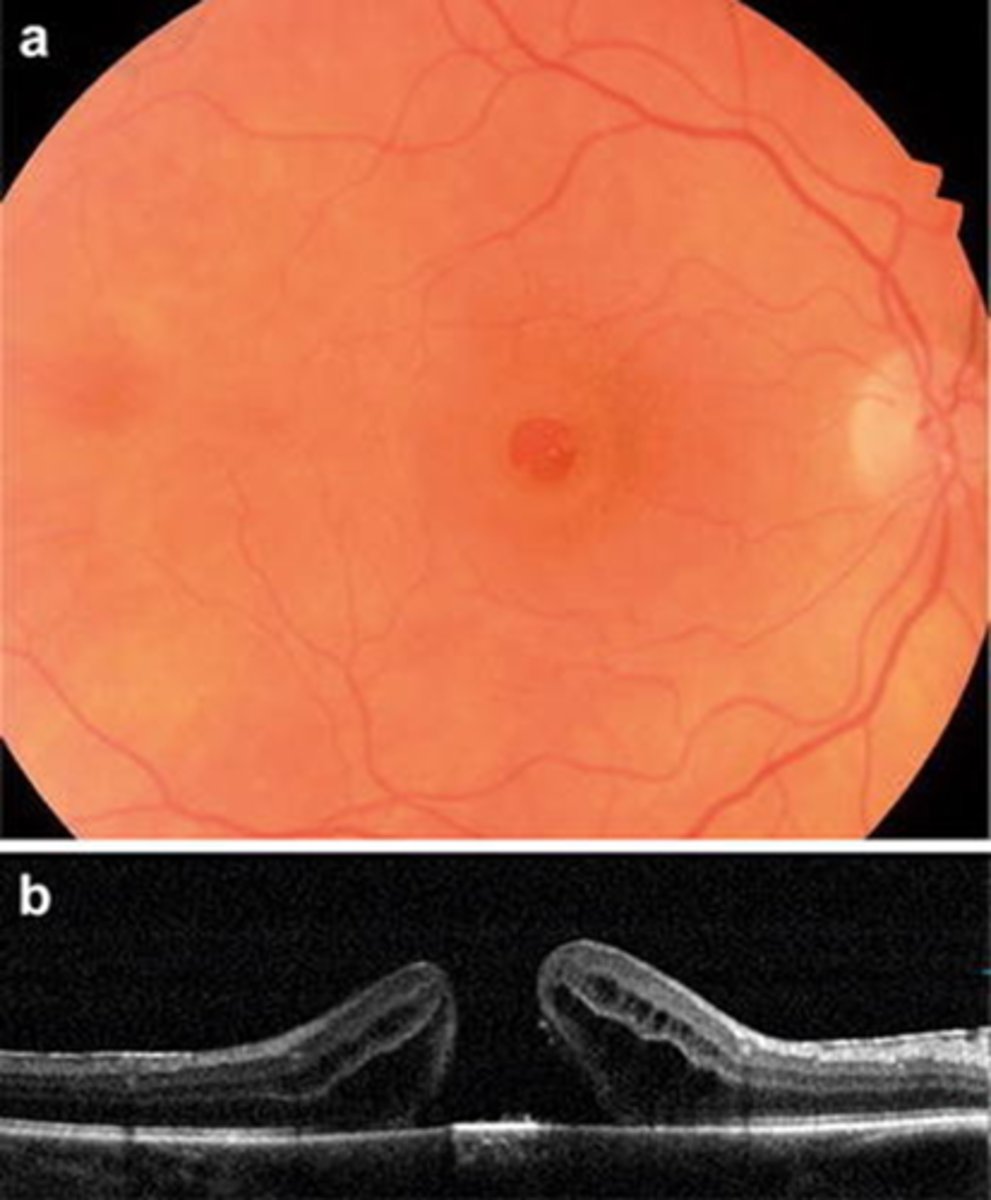
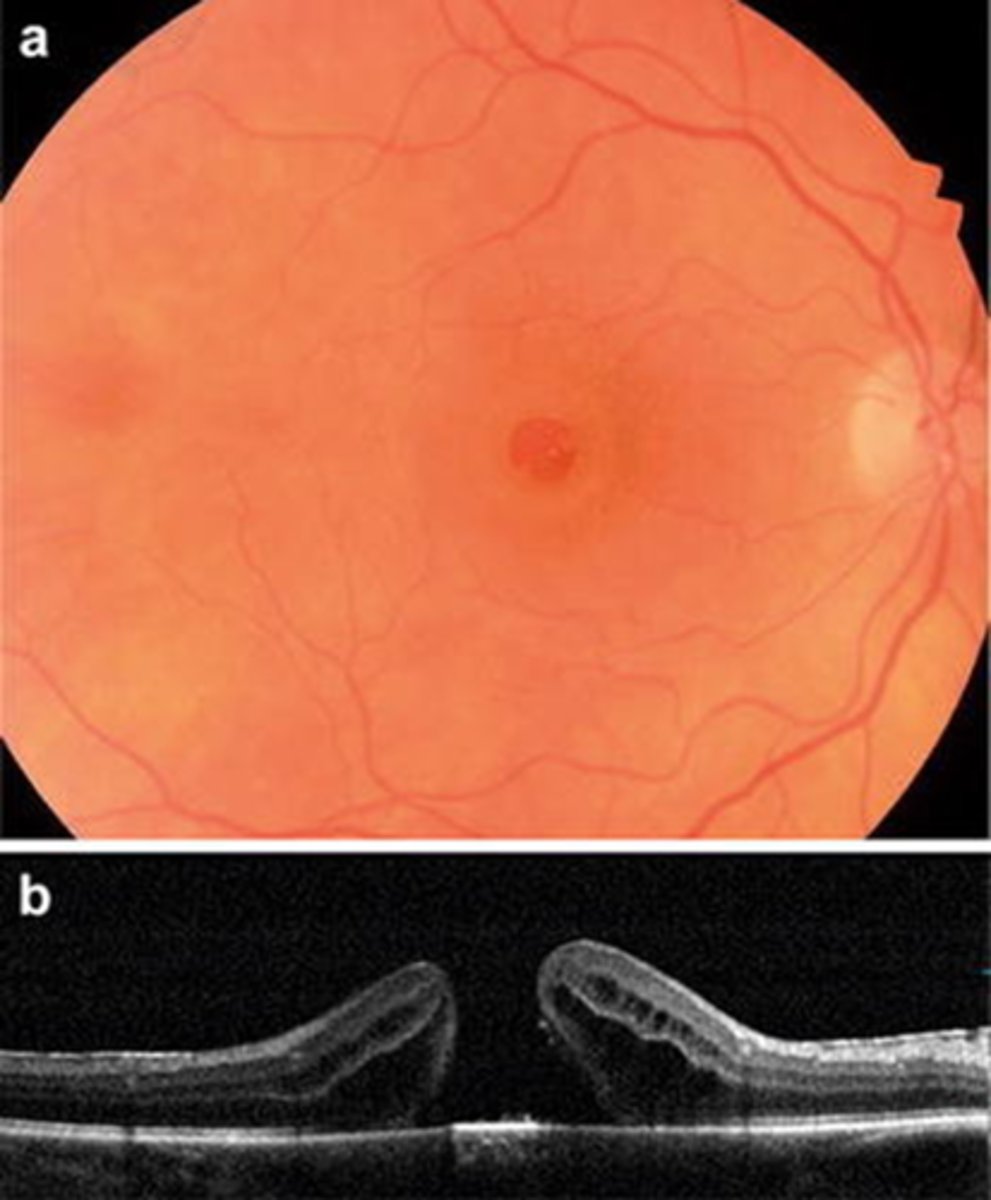
How does a full thickness macular hole appear on OCT, as shown here?
full hole at macula
parafoveal CME
ERM
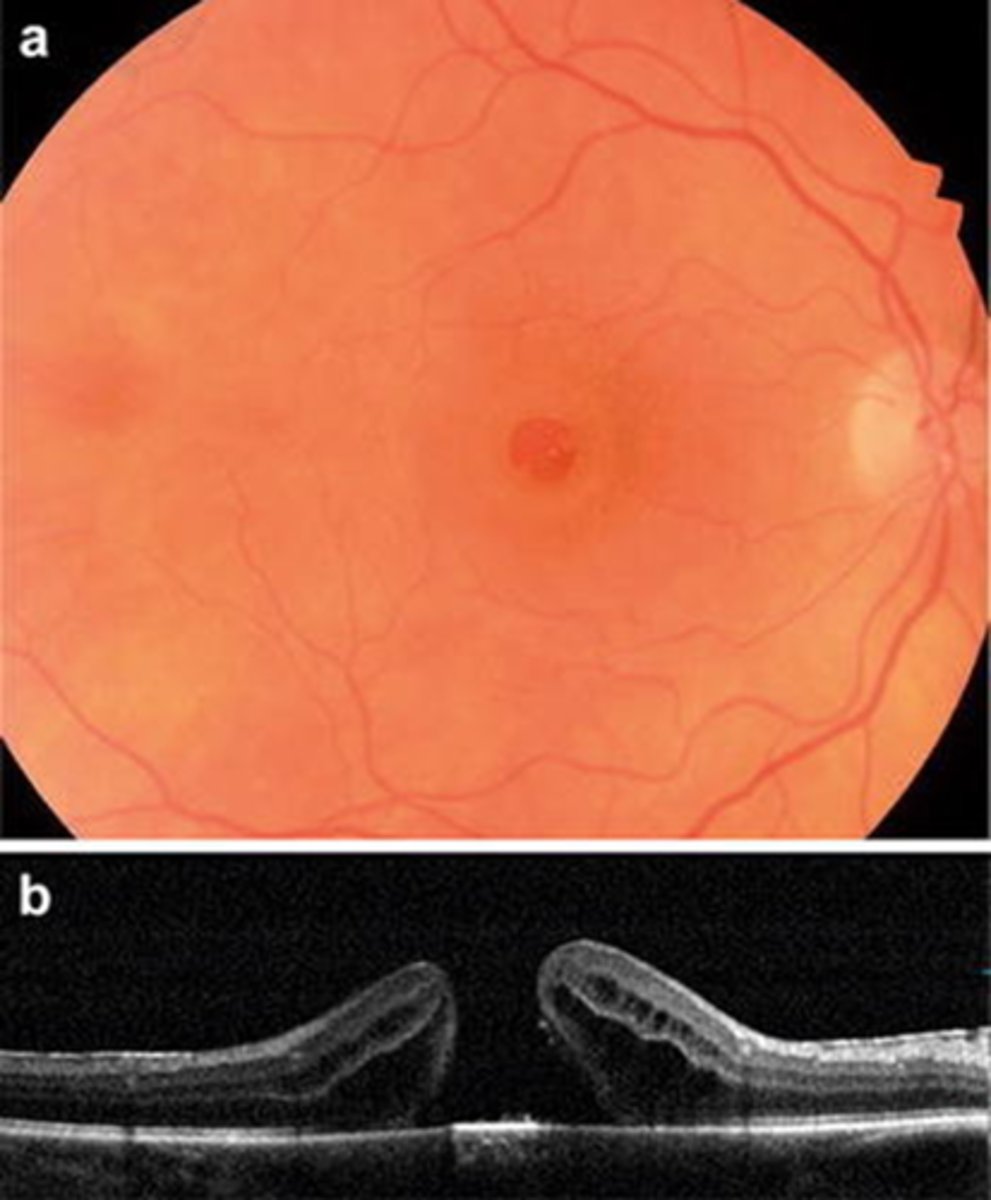
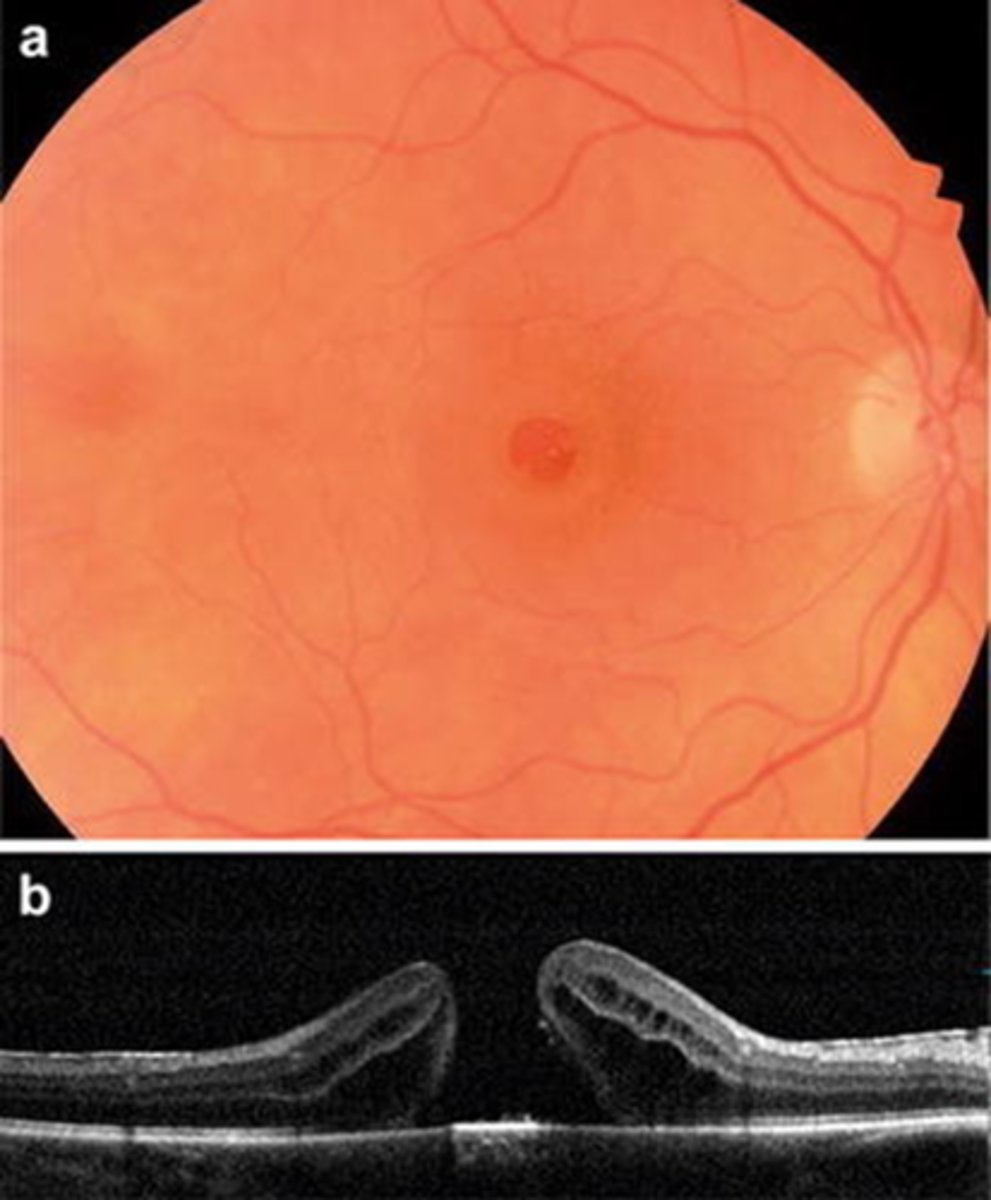
How does a full thickness macular hole appear on OCT, as shown here?
full hole at macula
parafoveal CME
foveal tissue attached to posterior hyaloid
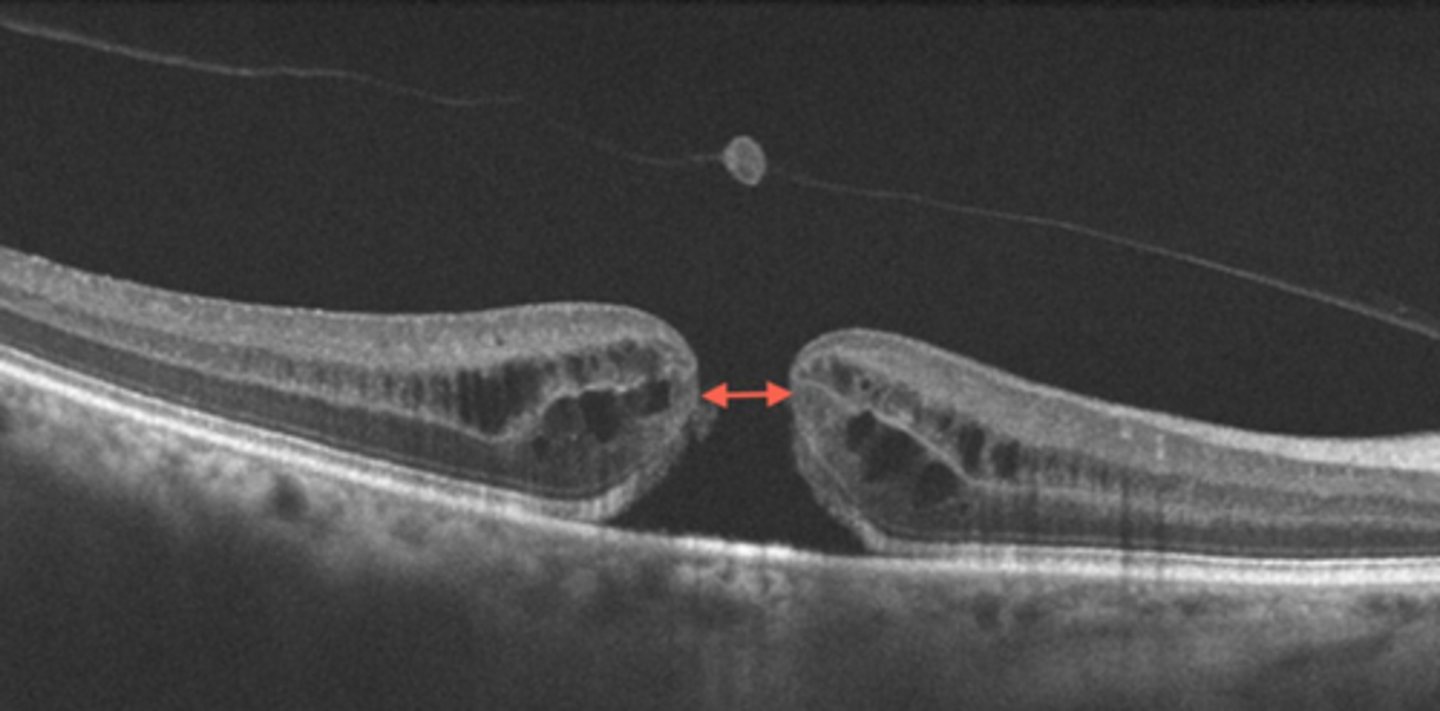
What are the 4 stages of the Gass macular hole classifications?
stage 1 = impending macular hole, loss of foveal depression
stage 2 = full thickness break < 400 microns
stage 3 = full thickness break > 400 microns, gray cuff of subretinal fluid, vitreous detached
stage 4 = stage 3 + complete PVD and Weiss ring
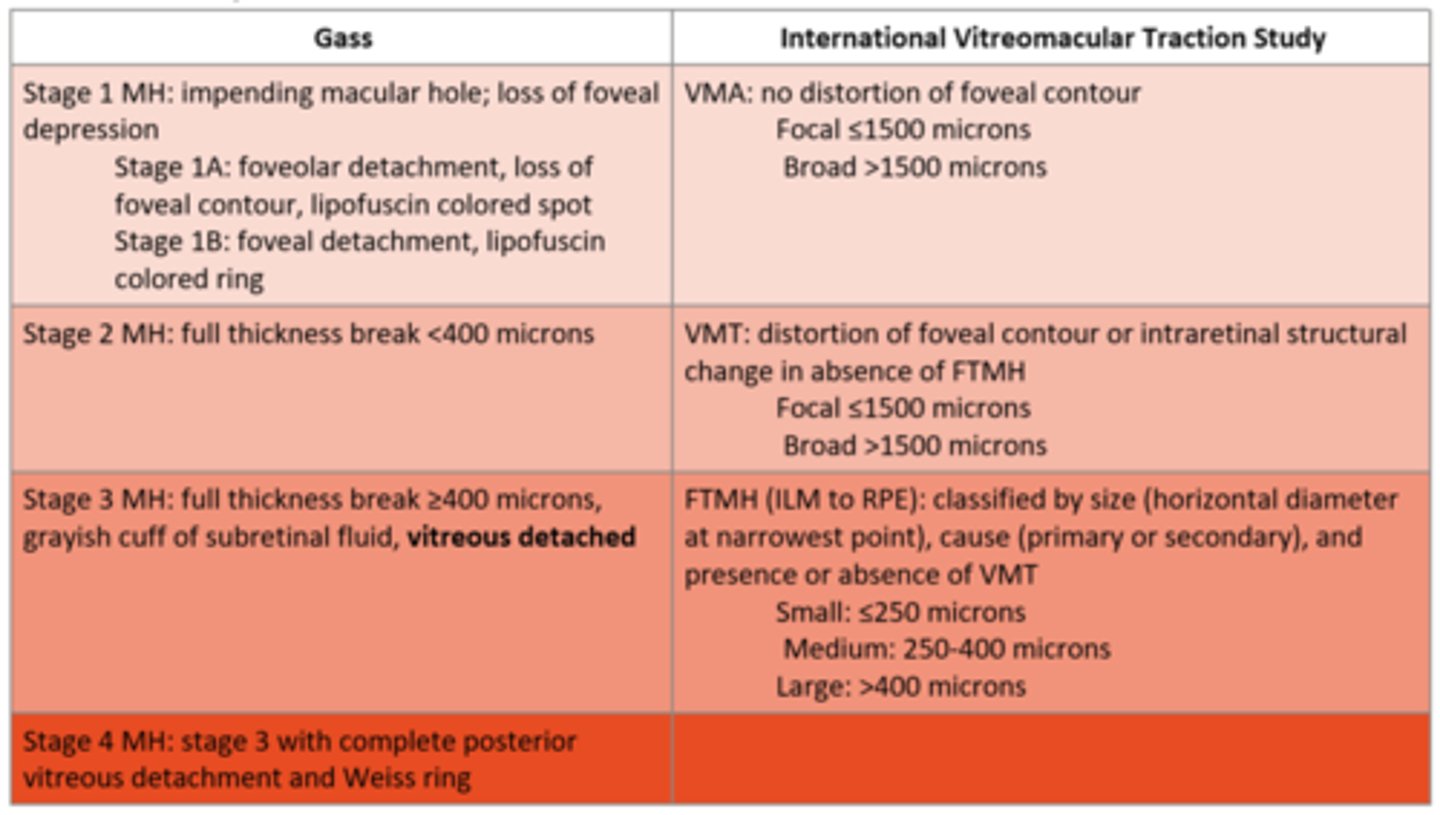
What are the 3 stages of the International VMT Study macular hole classifications?
VMA = no distortion of foveal contour
VMT = distortion of foveal contour or intraretinal structural change in absence of FTMH
FTMH = hole from ILM to RPE, classified by size, cause, +/-VMT
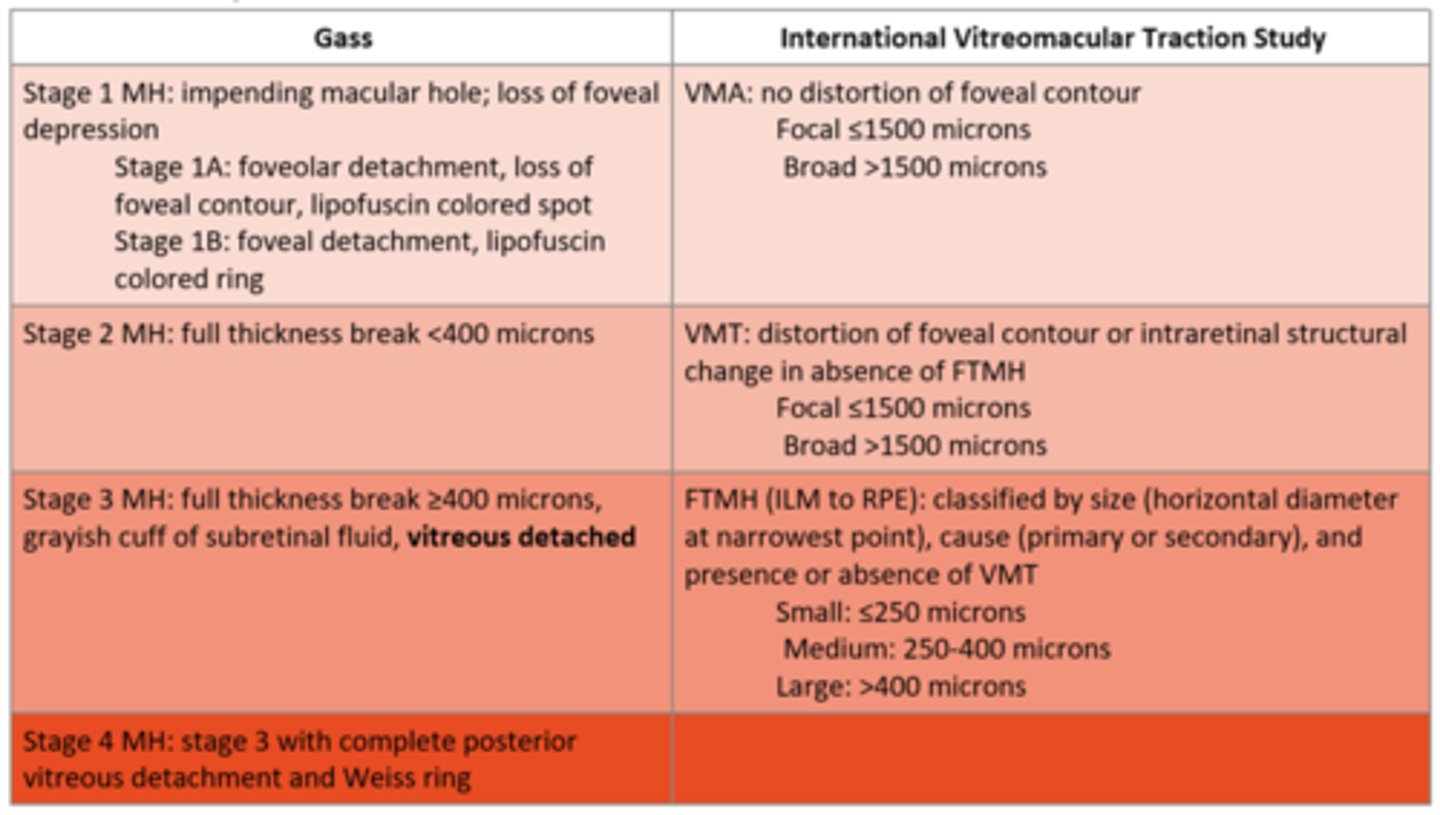
What is the management for a stage 1 macular hole (based on Gass)?
monitor, 50% spontaneous closure
refer to retina?
What is the management for a FTMH or symptomatic macular hole?
refer to retina for...
1. intravitreal injection of gas = expansile gas bubble requires face down position, <2500ft elevation for short period
2. pars plana vitrectomy w/ gas tamponade +/- ILM peel
What is the prognosis for a full thickness macular hole?
post-surgical improvement depends on preoperative characteristics, duration, etc.
if no surgery, unlikely to change vision
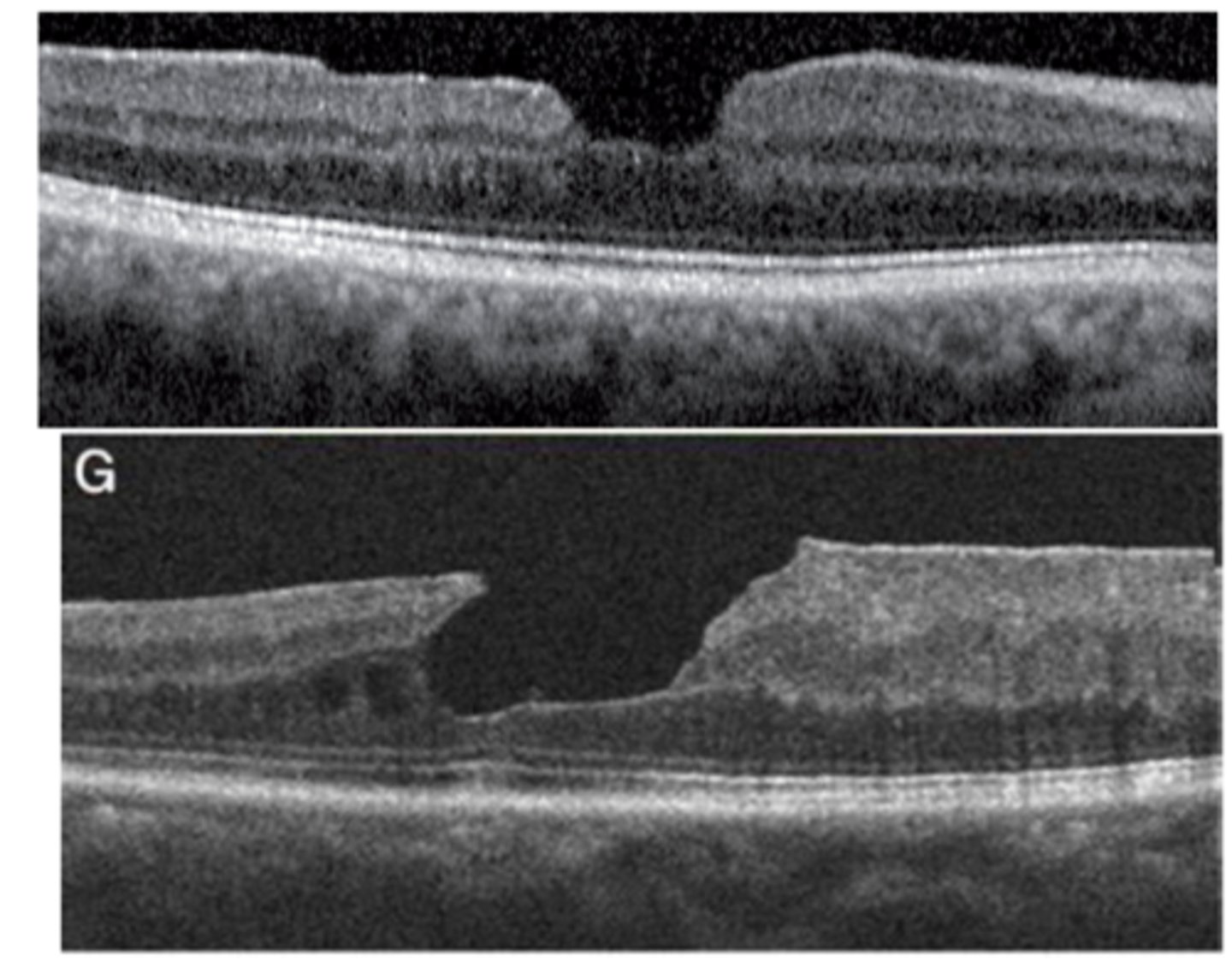
What is a lamellar macular hole?
irregular foveal contour and atrophy of inner retinal layers, with intact outer retinal layers (like PR's)
What are some symptoms of a lamellar macular hole?
blur
metamorphopsia
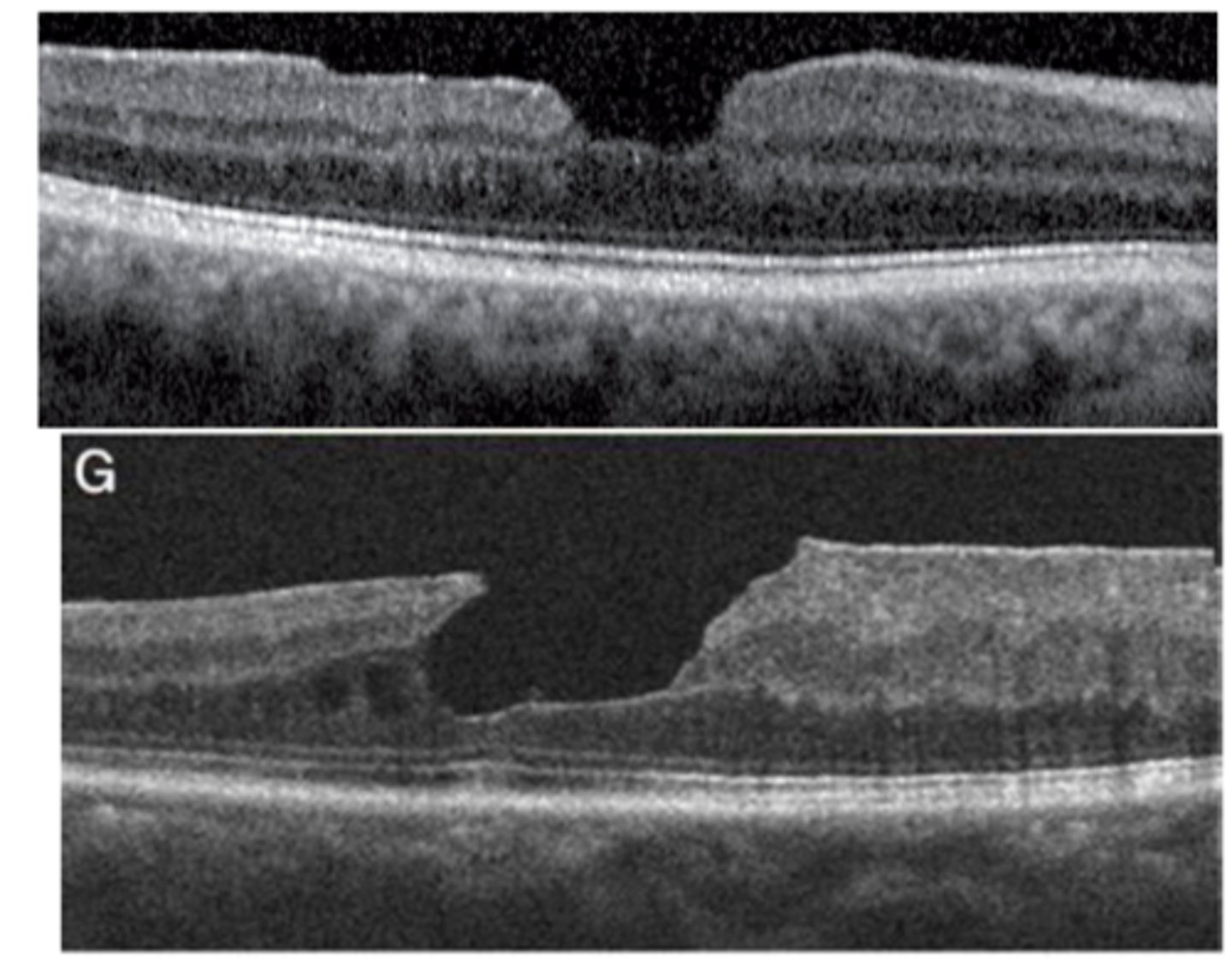
What are some signs of a lamellar macular hole?
blunted foveal reflex
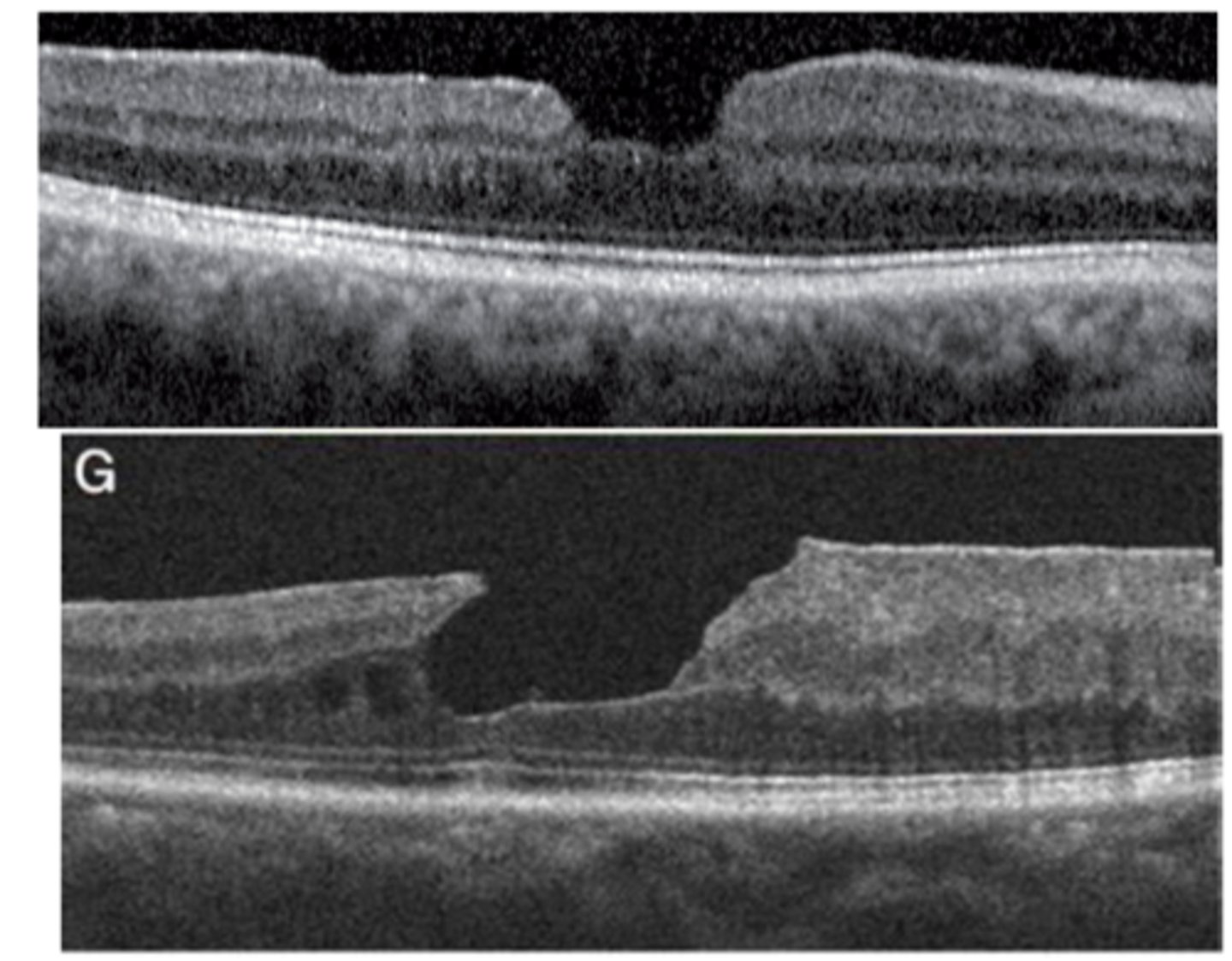
What is the management of a lamellar macular hole?
monitor
refer to retina for surgery (PPV, ILM/ERM peel, tamponade)
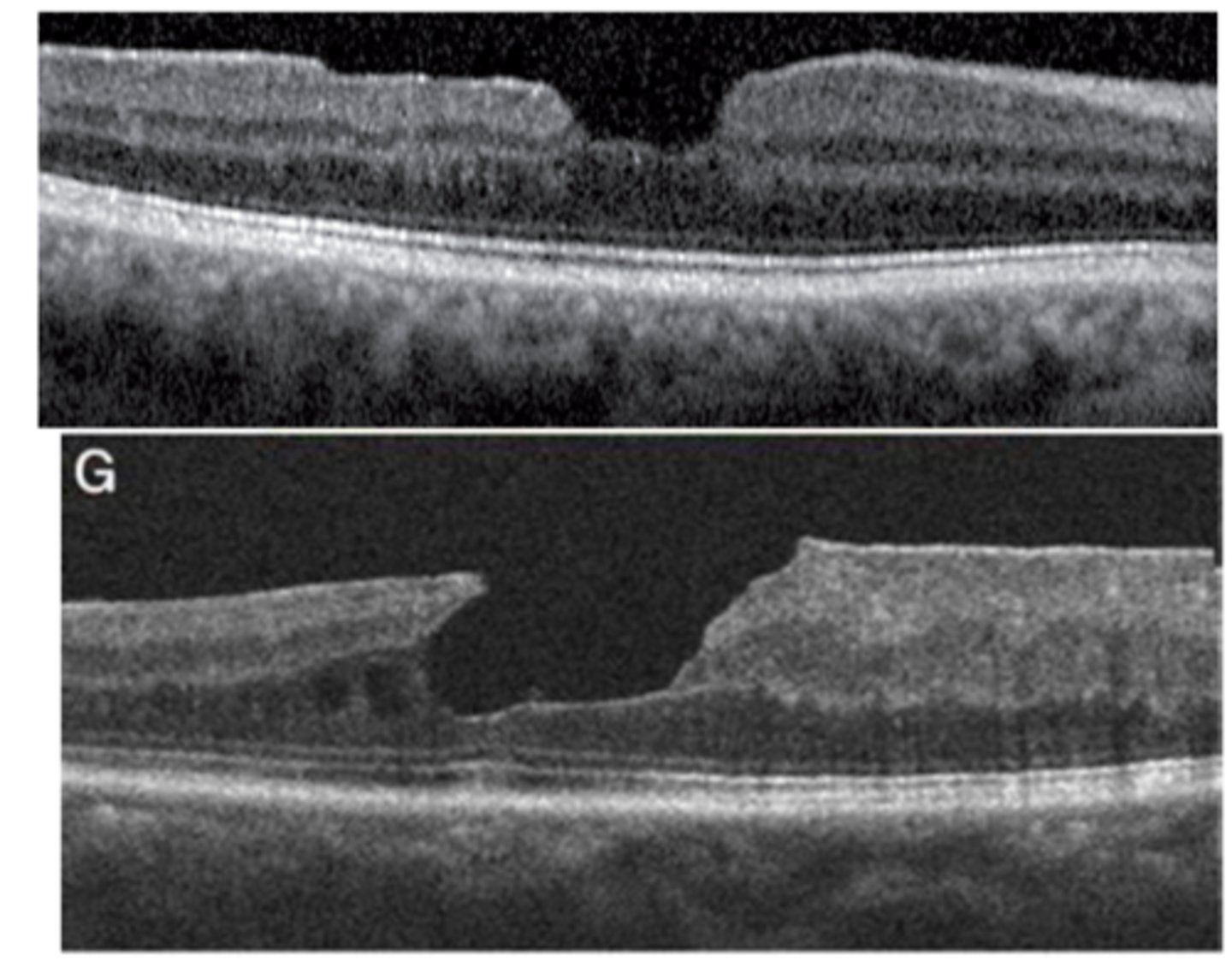
What is the prognosis of a lamellar macular hole?
typically stable vision (rarely progresses)
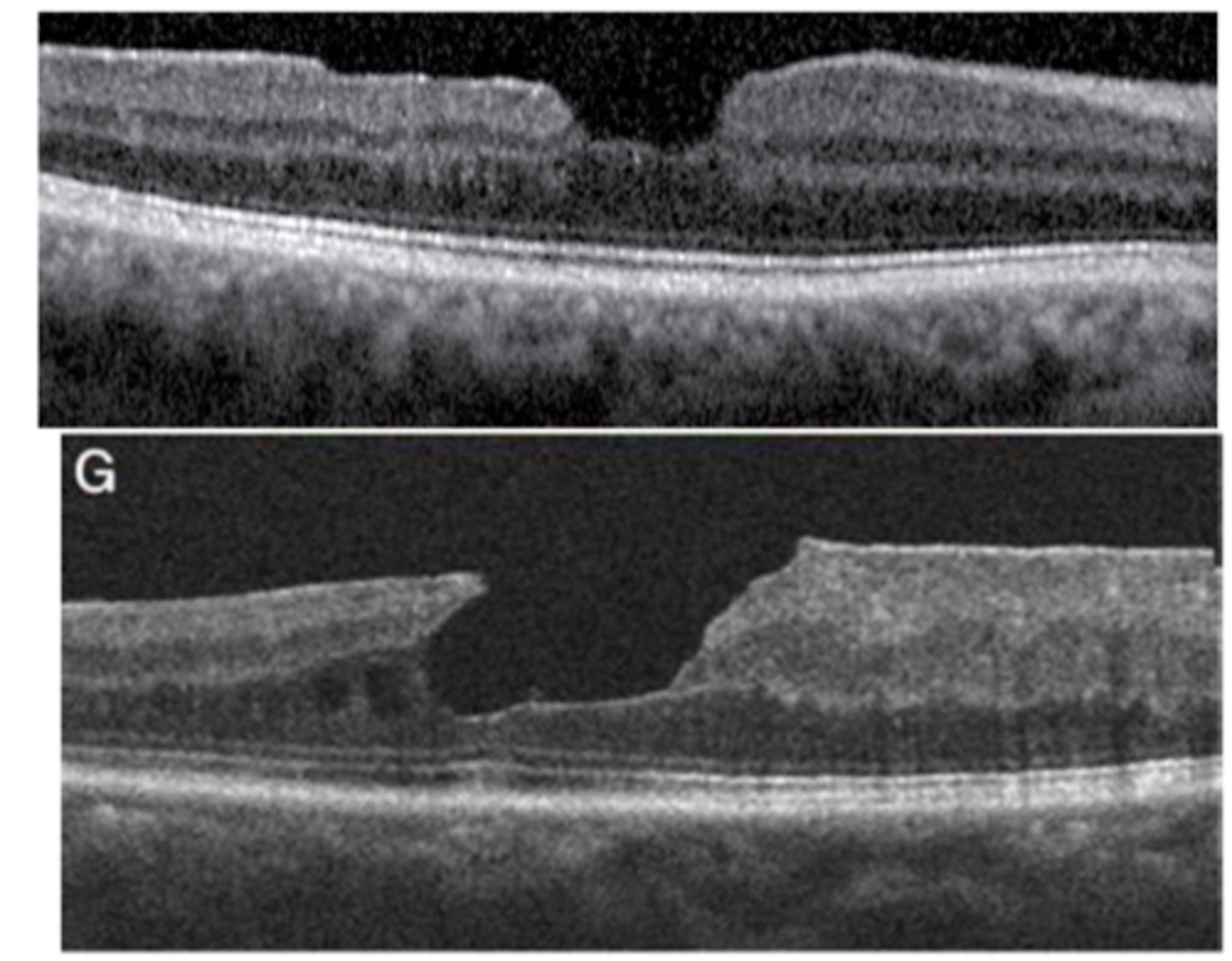
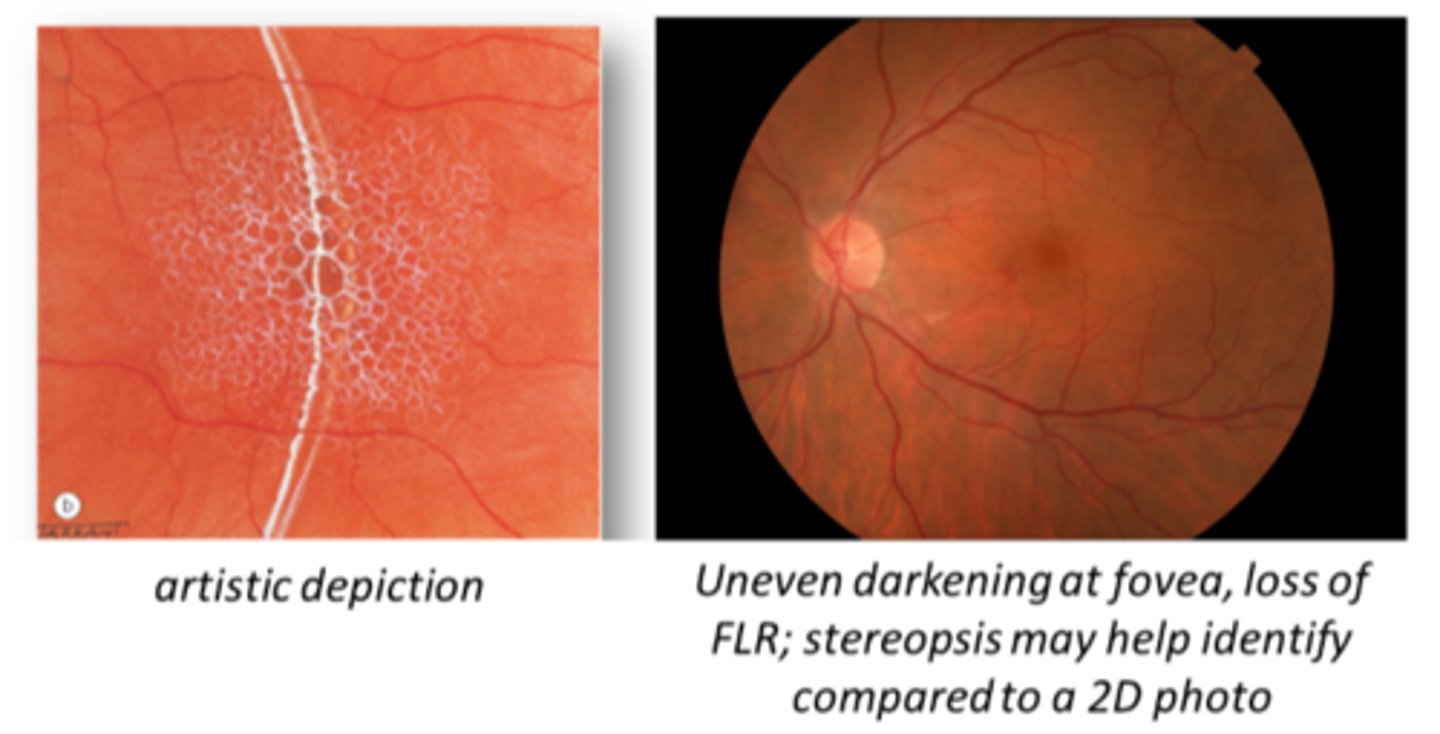
What is cystoid macular edema (CME)?
petaloid pattern of fluid-filled intraretinal cysts = petaloid due to Henle's fiber orientation
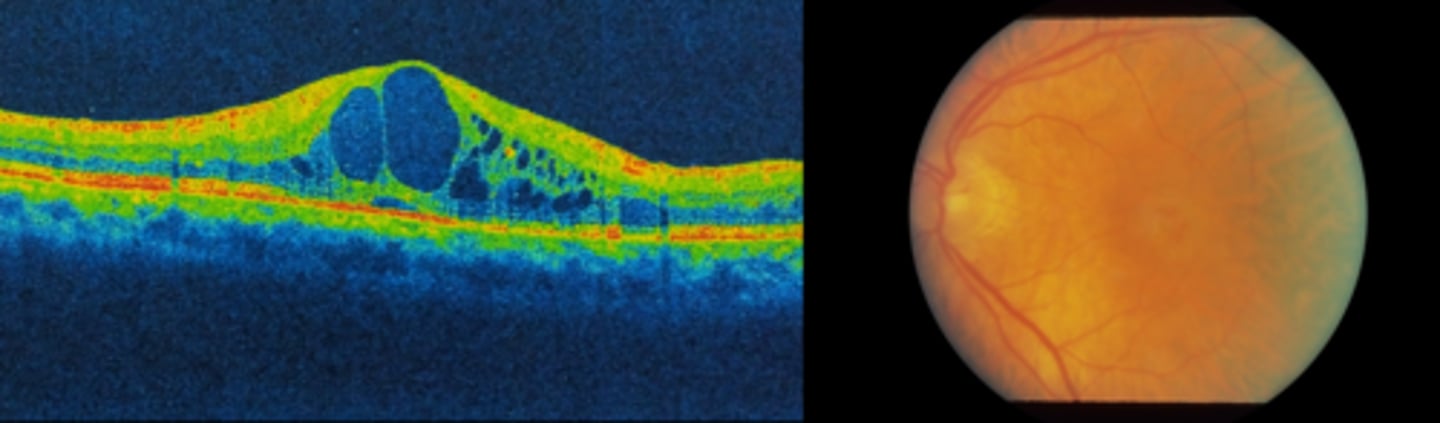
What layer do we typically see cystoid macular edema (CME) in?
OPL/INL bc perifoveal region is prone to fluid collection from the dual blood supply (but can extend to other layers)
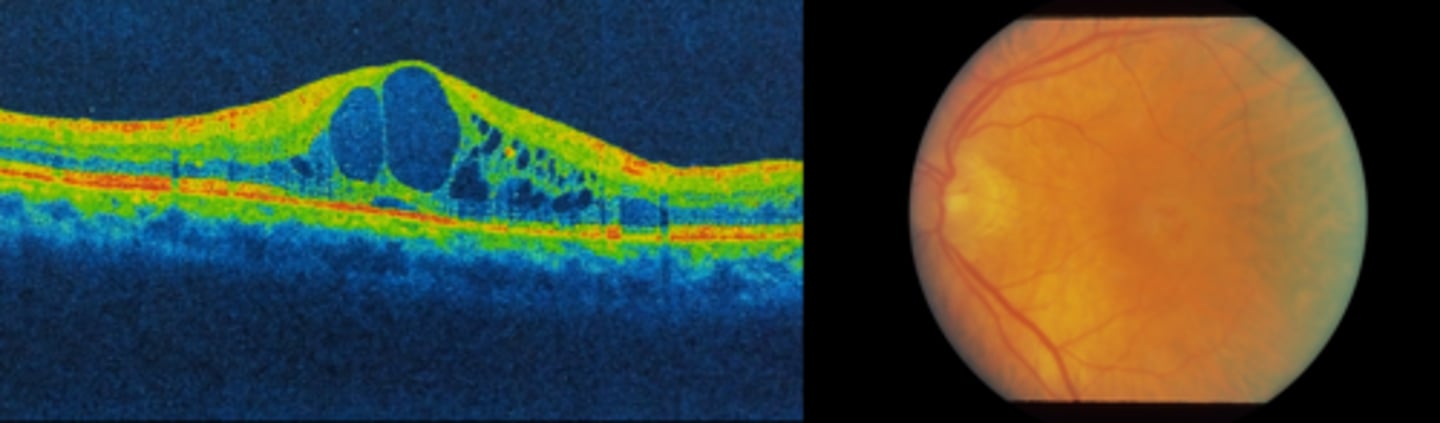
What are some symptoms of cystoid macular edema (CME)?
asymptomatic
VA reduction
+/- hyperopic shift
metamorphopsia
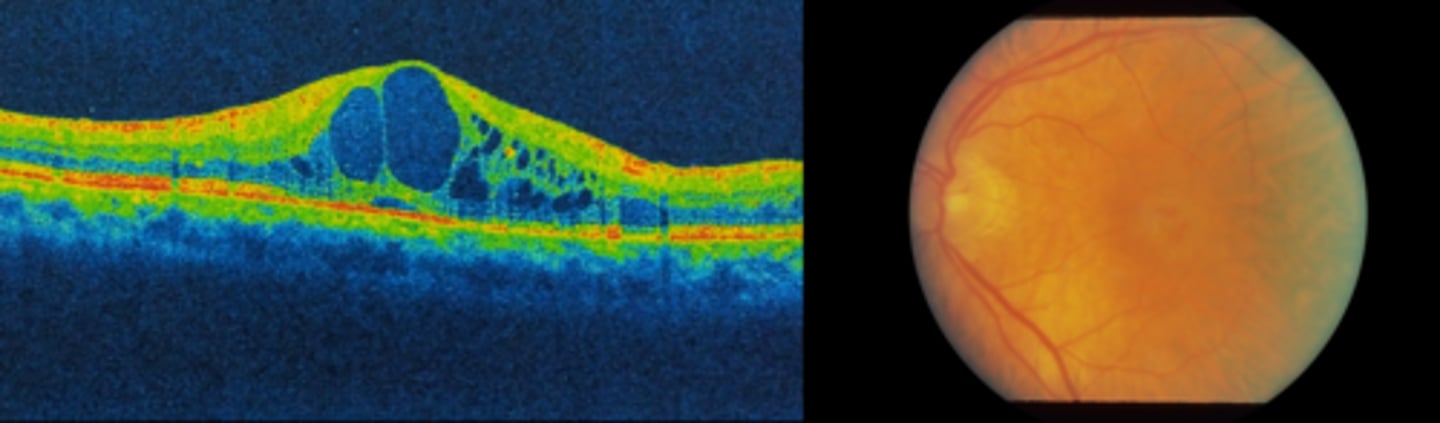
What are some signs of cystoid macular edema (CME)?
loss of FLR
loss of foveal depression = may see elevation, shading, shadowing, lighter areas
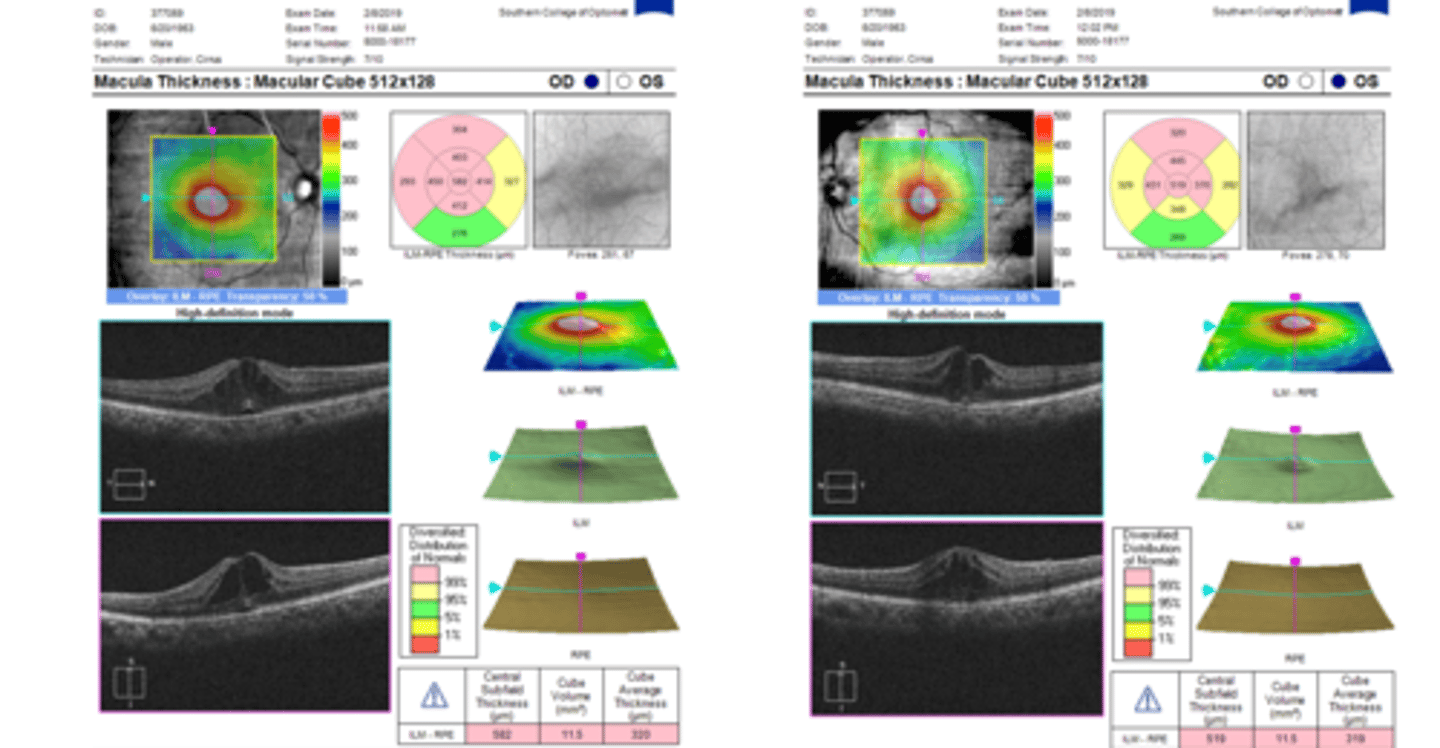
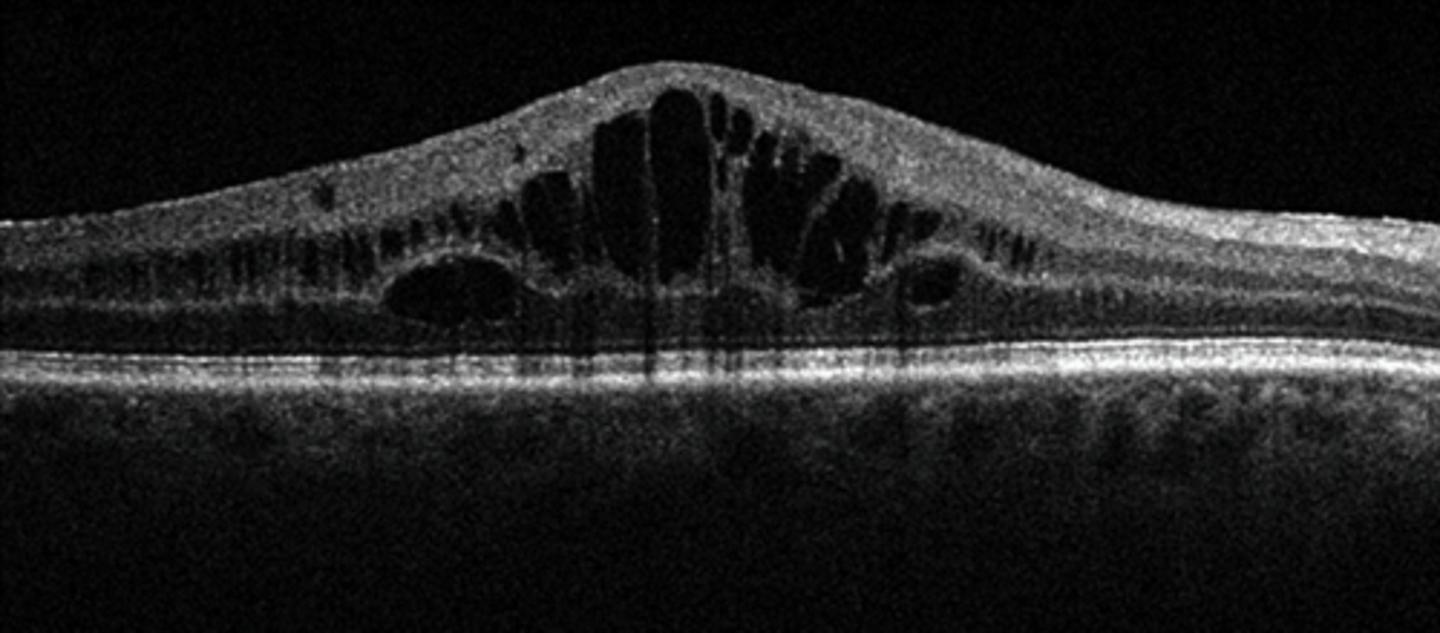
What is the appearance of cystoid macular edema (CME) seen on OCT?
optically empty hyporeflective cysts, mostly in OPL and INL
How does cystoid macular edema (CME) appear on FAF?
hyperAF due to disrupted RPE health
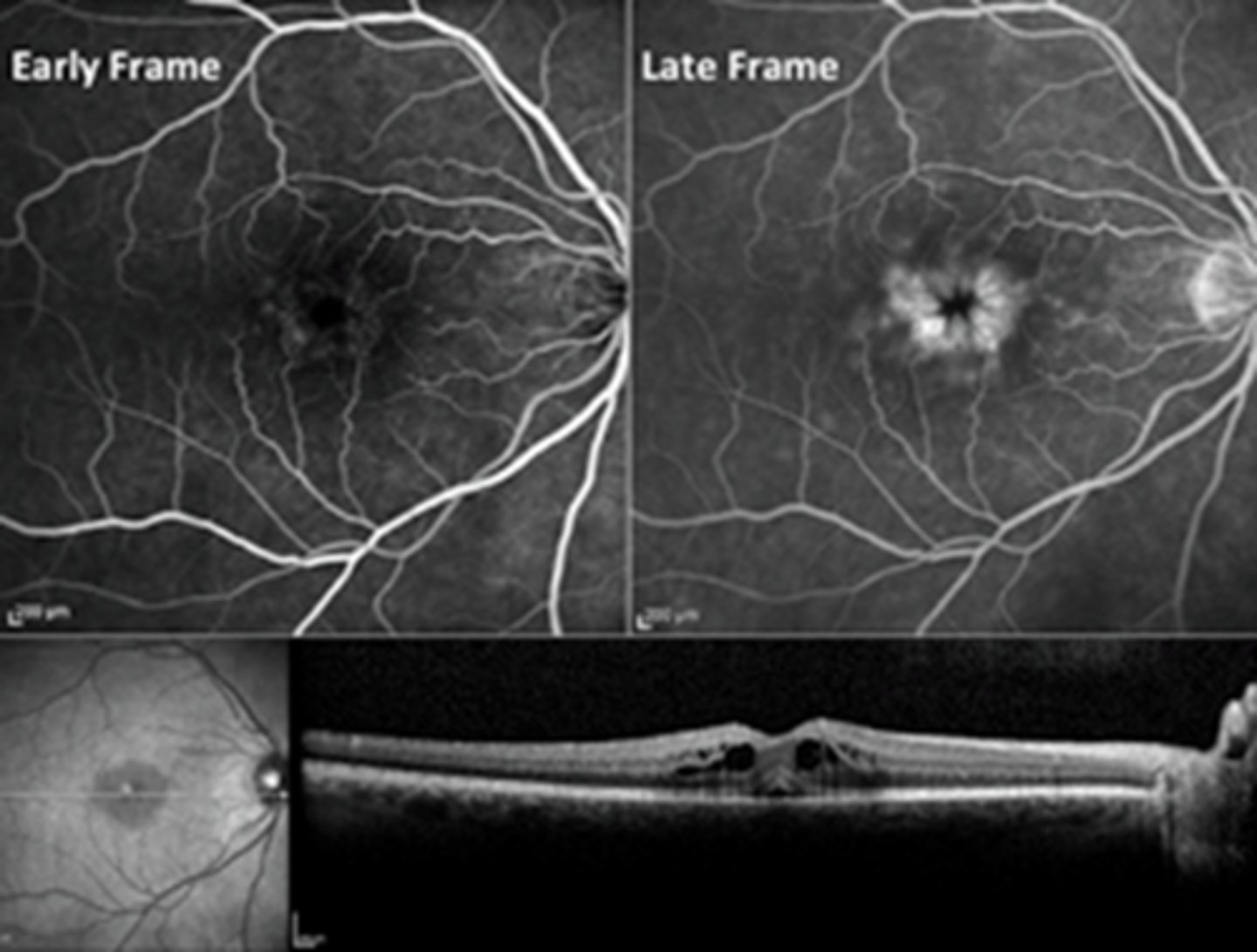
How does cystoid macular edema (CME) appear on IVFA?
in late phase, pooling hyperF fills into fluid cysts
NOTE: IVFA not typically ordered to diagnose/manage CME
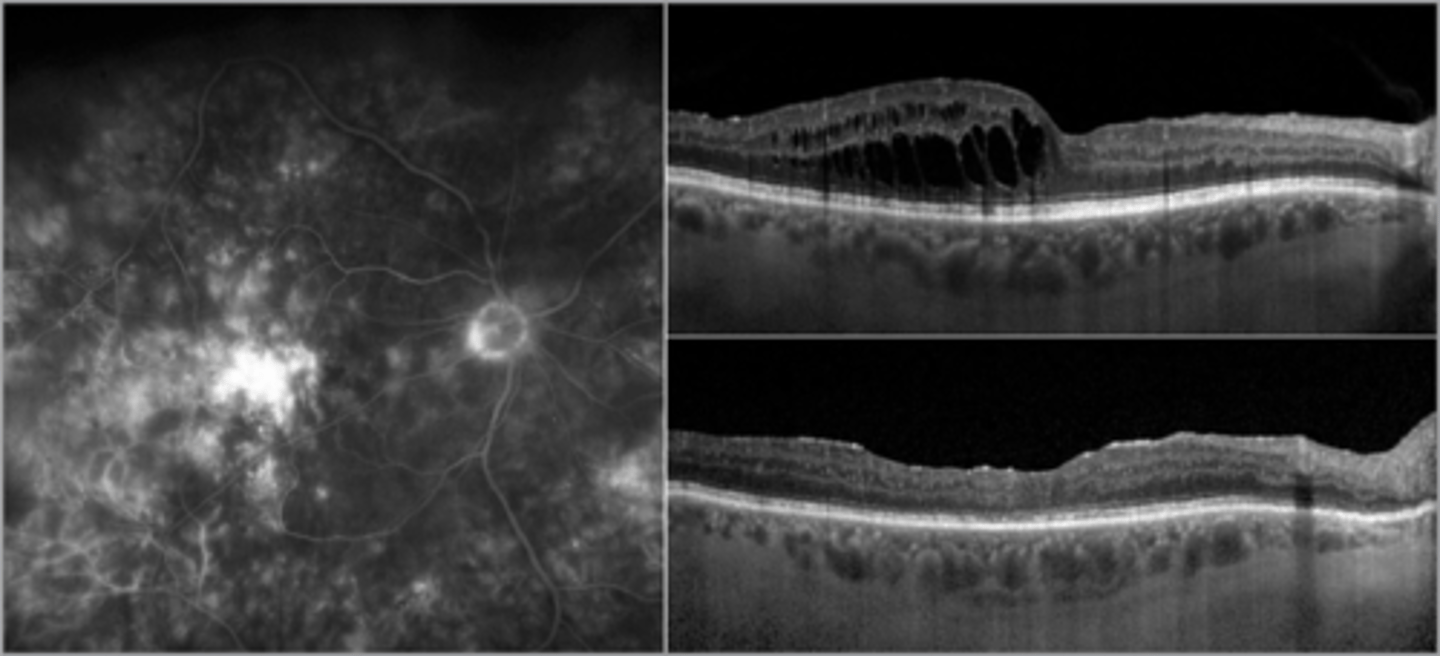
What is the prognosis for cystoid macular edema (CME)?
most cases are self-limiting (<3-4 mos) = vision improves
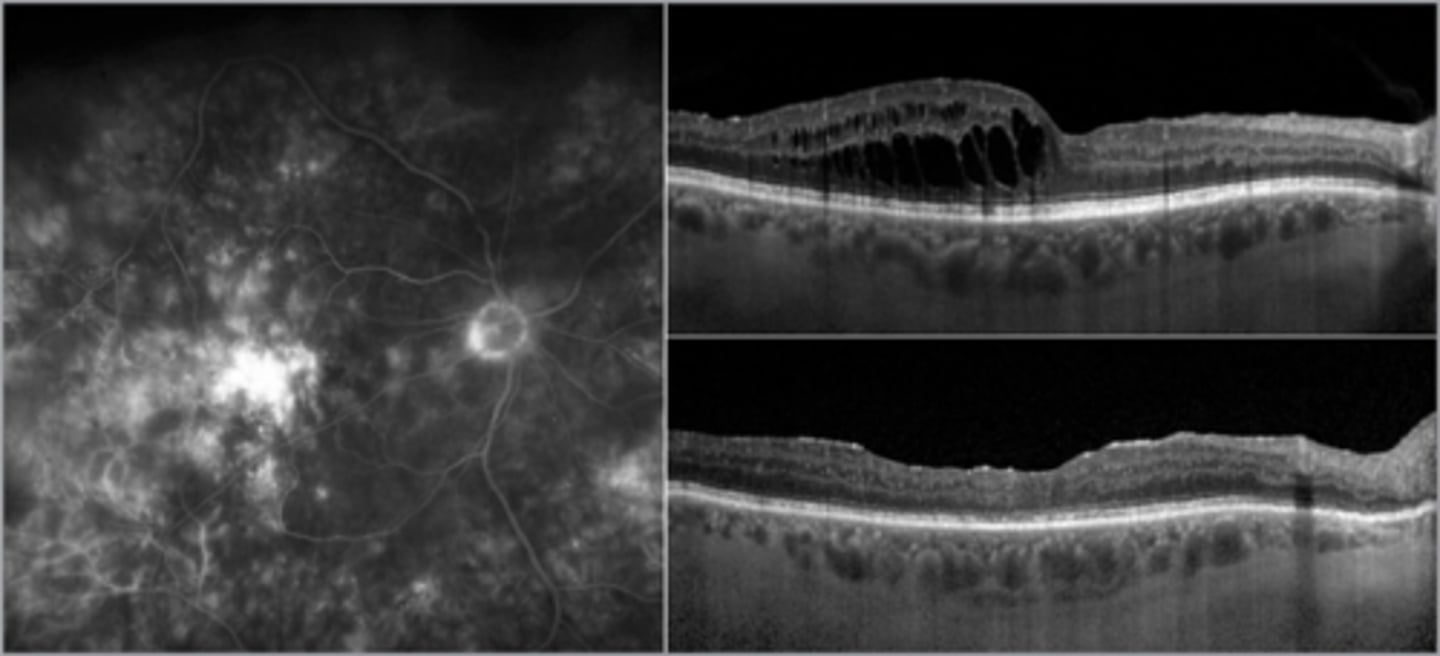
What is a possible complication of cystoid macular edema (CME)?
chronic CME (>6-9 mos) = retinal thinning/ischemia = vision loss
What are some possible etiologies of cystoid macular edema (CME)?
intraocular surgery like phacoemulsification (Irvin Gass syndrome)
chronic inflam
retinal vascular disease like BRVO, CRVO, DR
degenerative disease like ERM, VMT
retinal dystrophies
serous detachment
CNV
medications like PG analogs
What is the management of cystoid macular edema (CME)? List the 5 main tx based on different etiologies.
if Irvin gass syndrome = topical or oral NSAIDs
if inflam etiology = corticosteroids
if RP = oral CAIs
if BRVO or CNV = anti-VEGF
if tractional = PPV
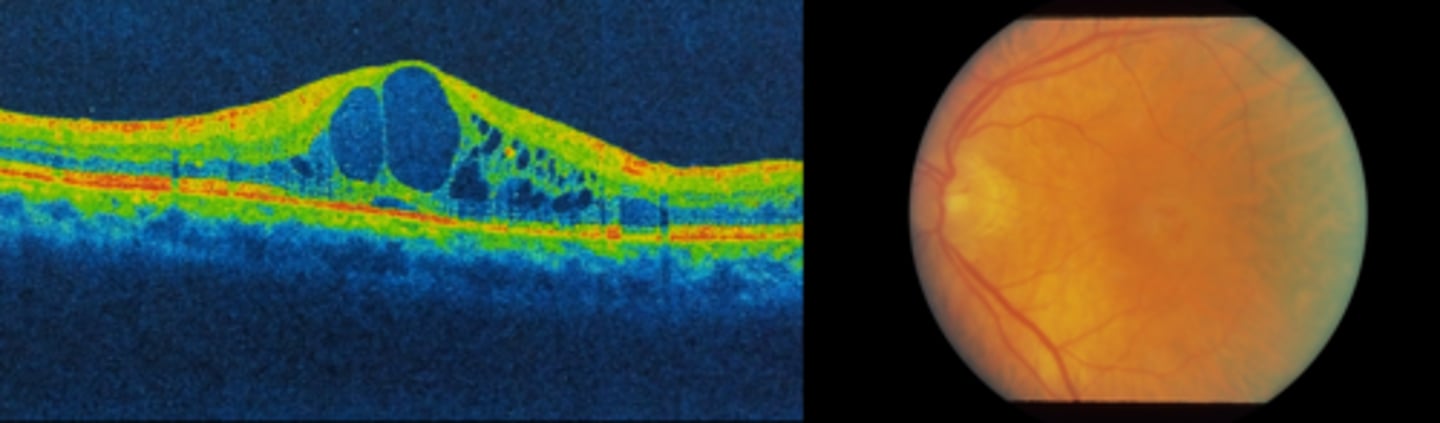
What is central serous retinopathy (CSR)?
localized serous detachment of sensory retina from RPE at the macula or posterior pole
NOT rhegmatogenous = no break in retina
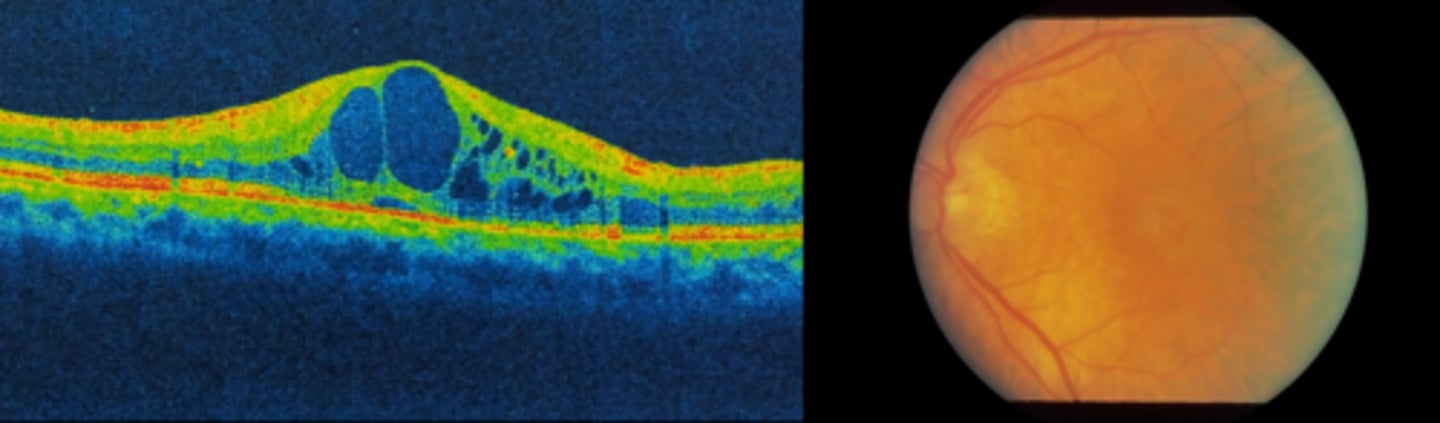
What is the pathophysiology behind CSR?
increased blood cortisol = increased choroidal BV permeability, RPE dysfunction = decreased BRB = fluid from choroid seeps into subretinal space
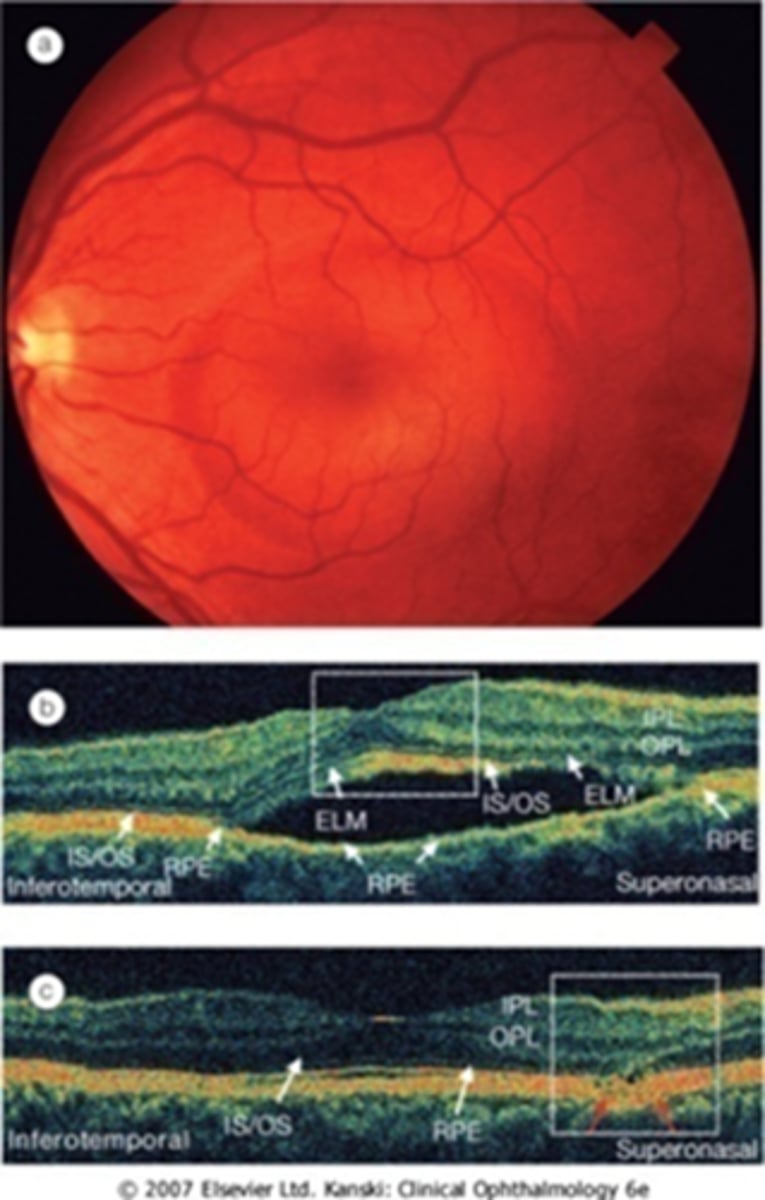
What are some possible underlying etiologies of CSR?
exogenous steroids
type A personality/stress
anxiety/depression meds
high BP
pachychoroid = thicker choroid
autoimmune disease
H pylori ulcer
MDMA
sildenafil
What is the main demographic affected by CSR?
males >>>>>> females
age 20-50
What are some symptoms of CSR?
unilateral blur
metamorphopsia
decreased contrast
reduced colour vision
mag changes
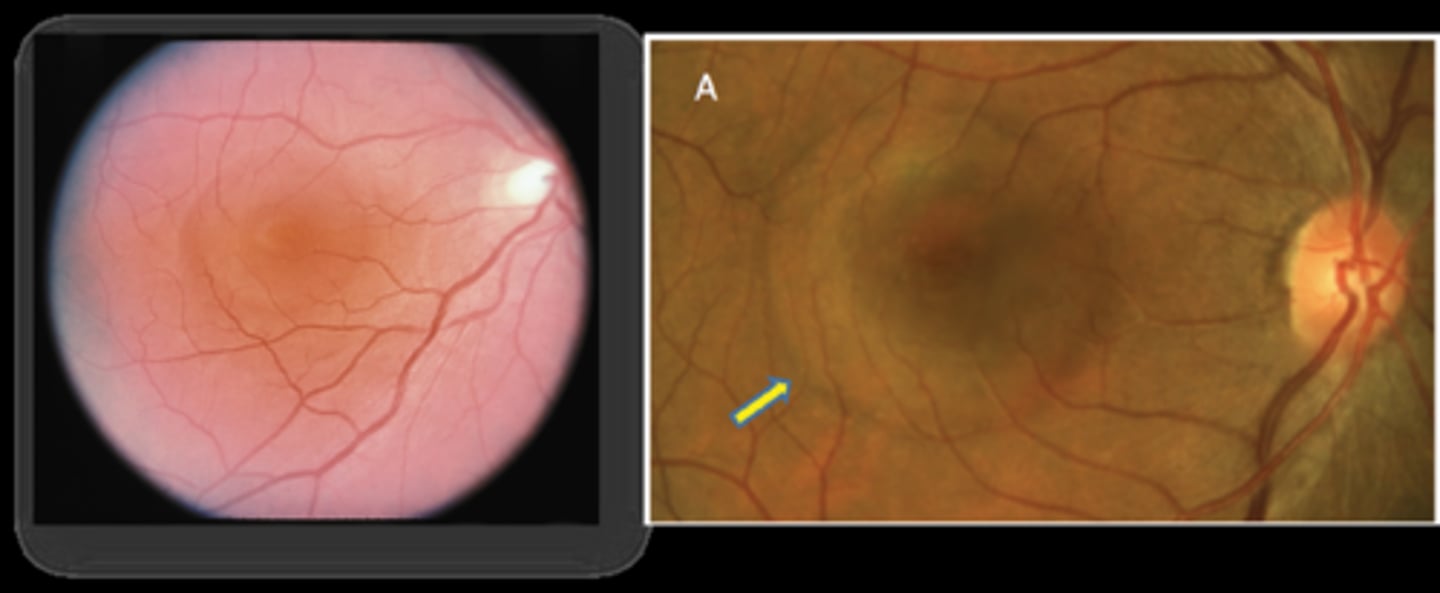
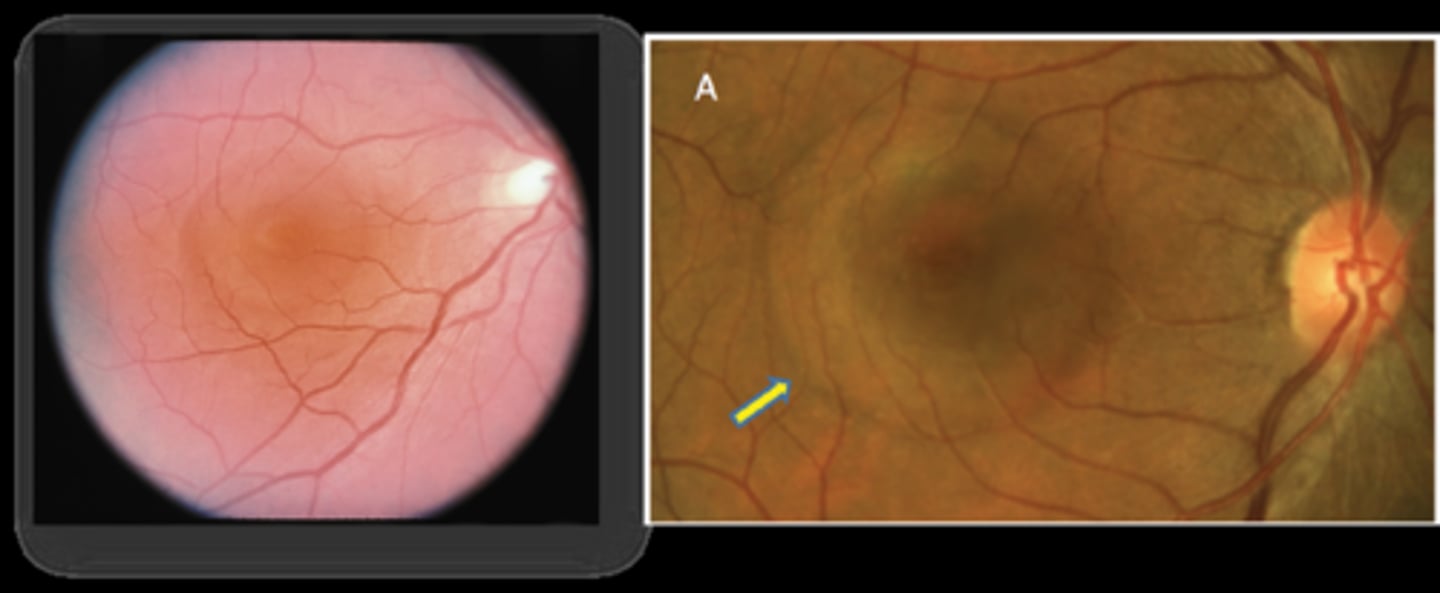
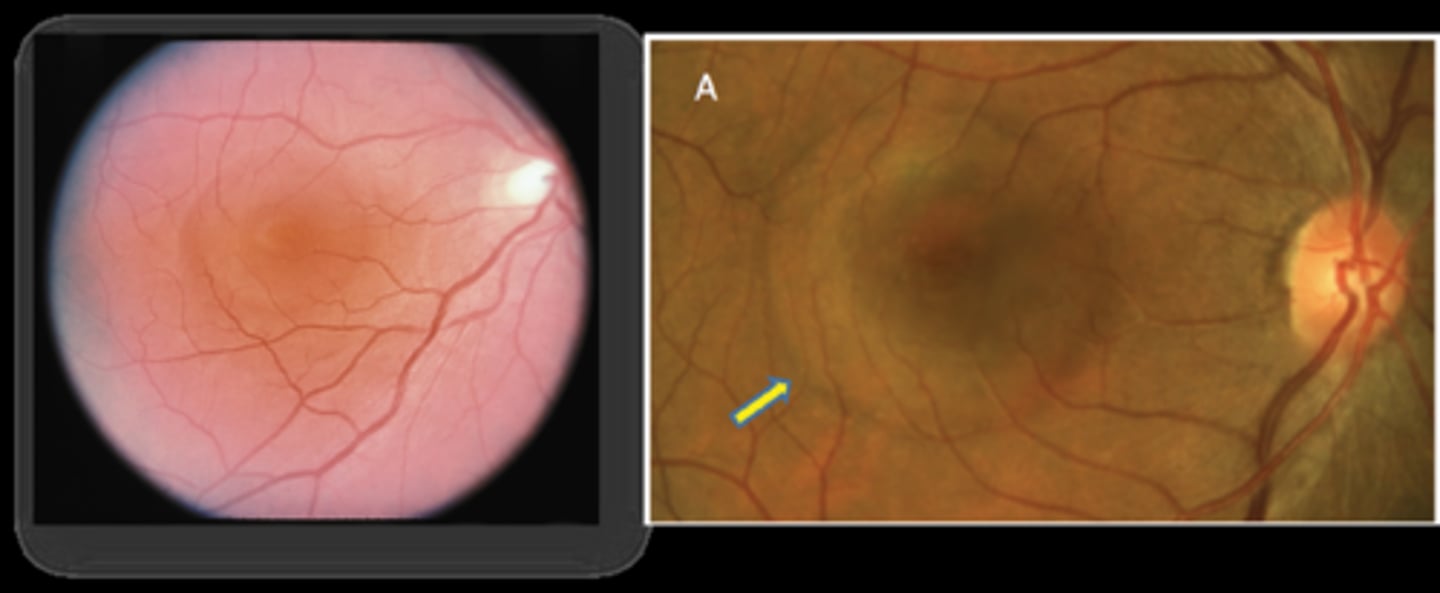
What are 2 signs of CSR?
round elevation of clear fluid at macula
hyperopic shift when PR's/retina moves forward
What are 3 signs of chronic CSR (3 mos or so)?
fluid becomes turbid
debris accumulates = "leopard spots"
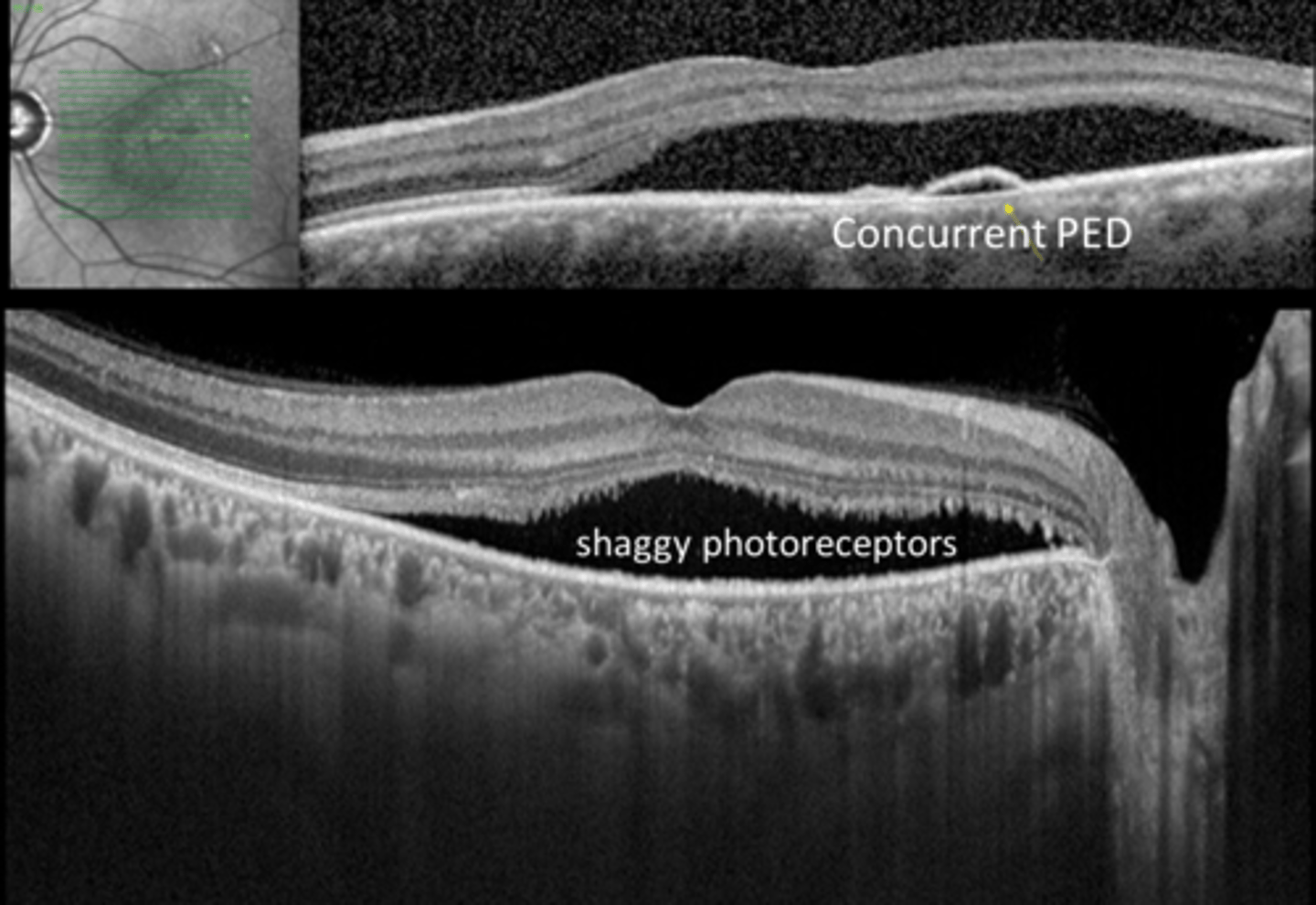
shaggy PR's seen on OCT
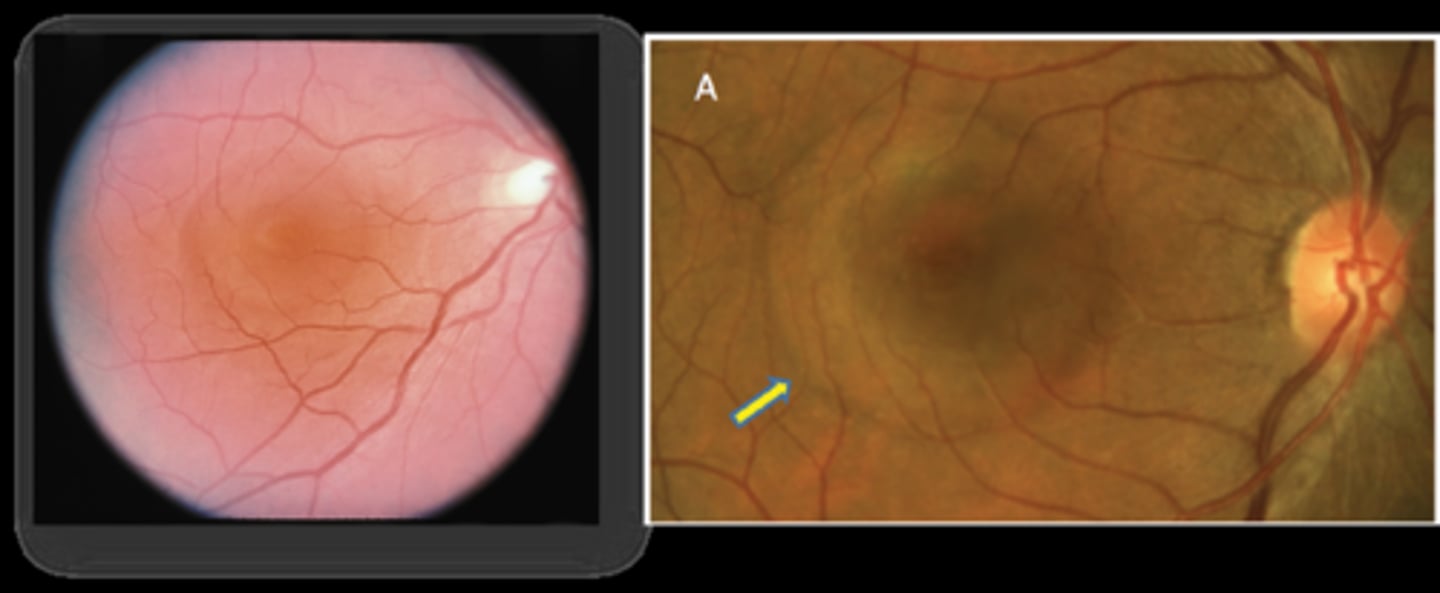
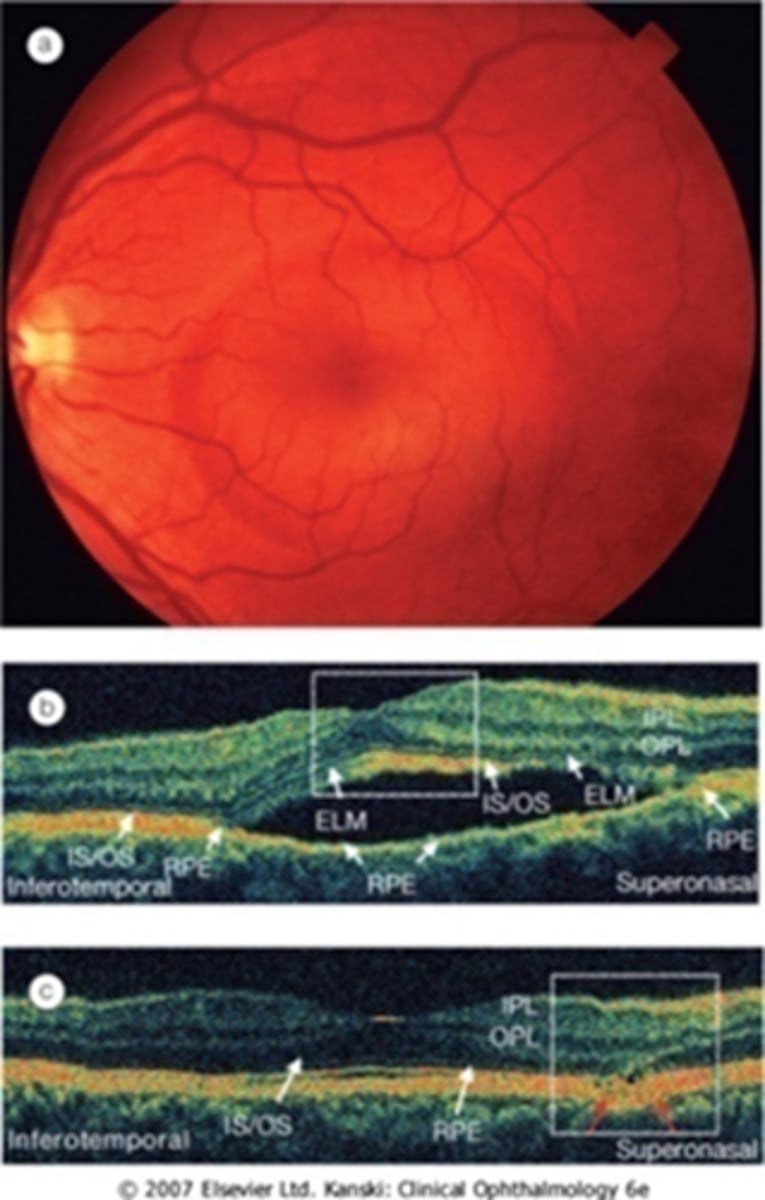
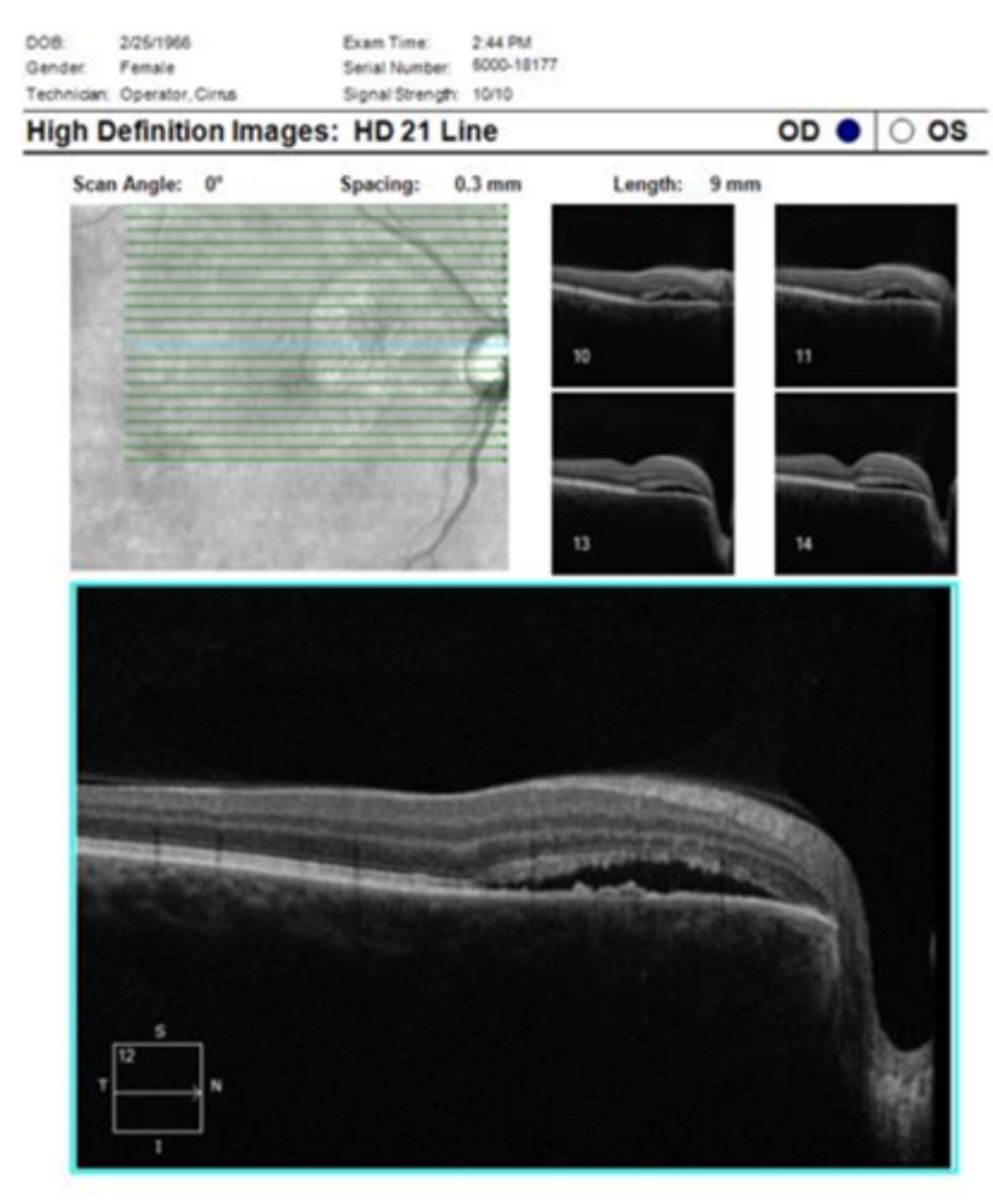
What do we see with CSR on OCT when diagnosing/tracking improvement over time?
neurosensory RD at central macula
+/- concurrent PED (RPE detachment)
+/- shaggy PR's
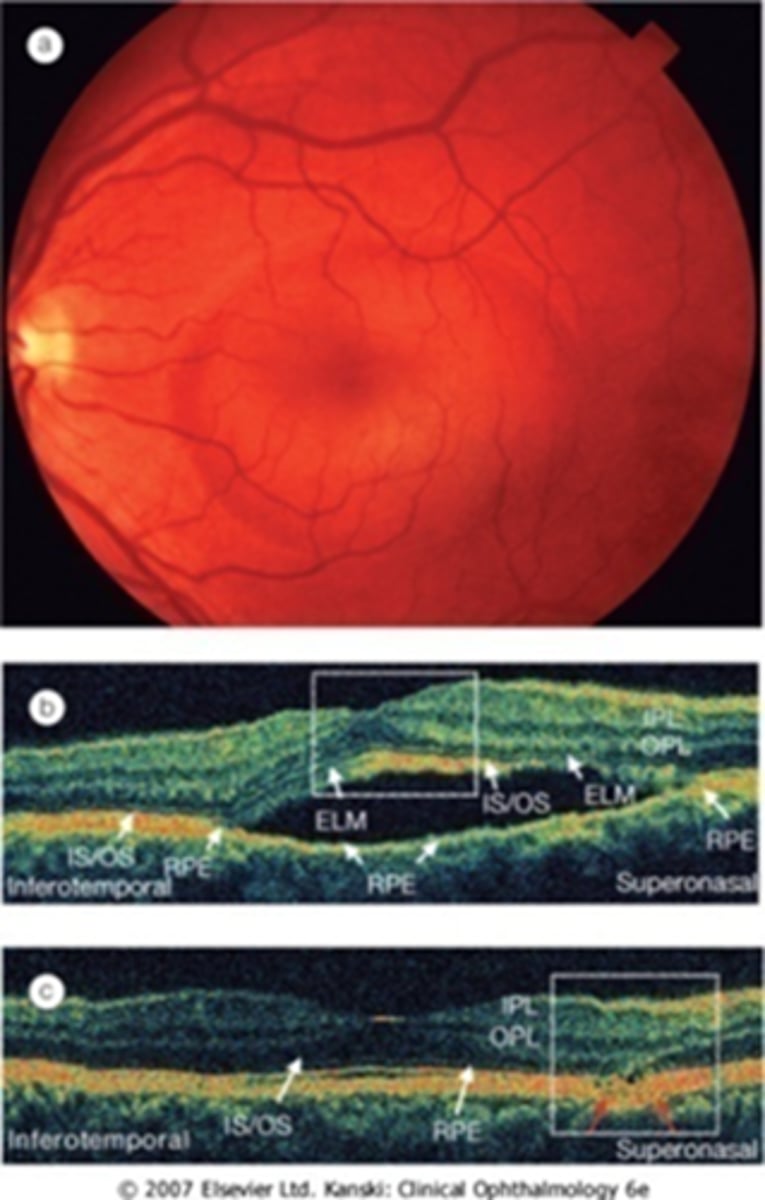
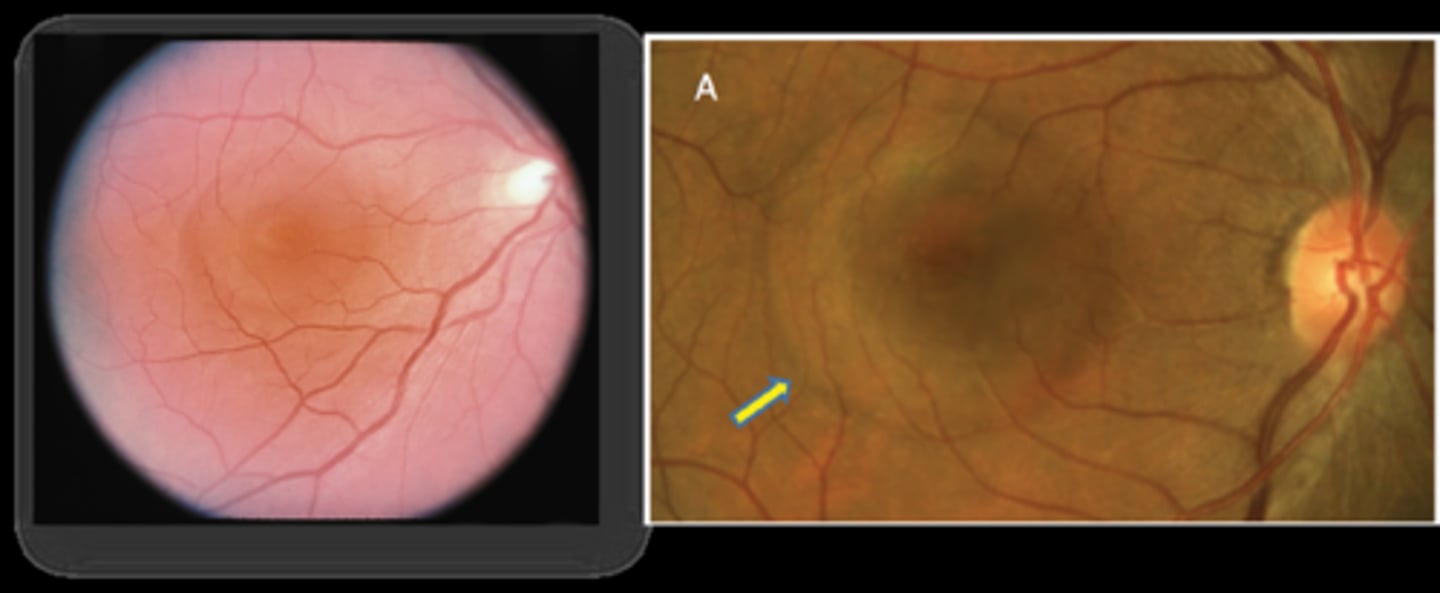
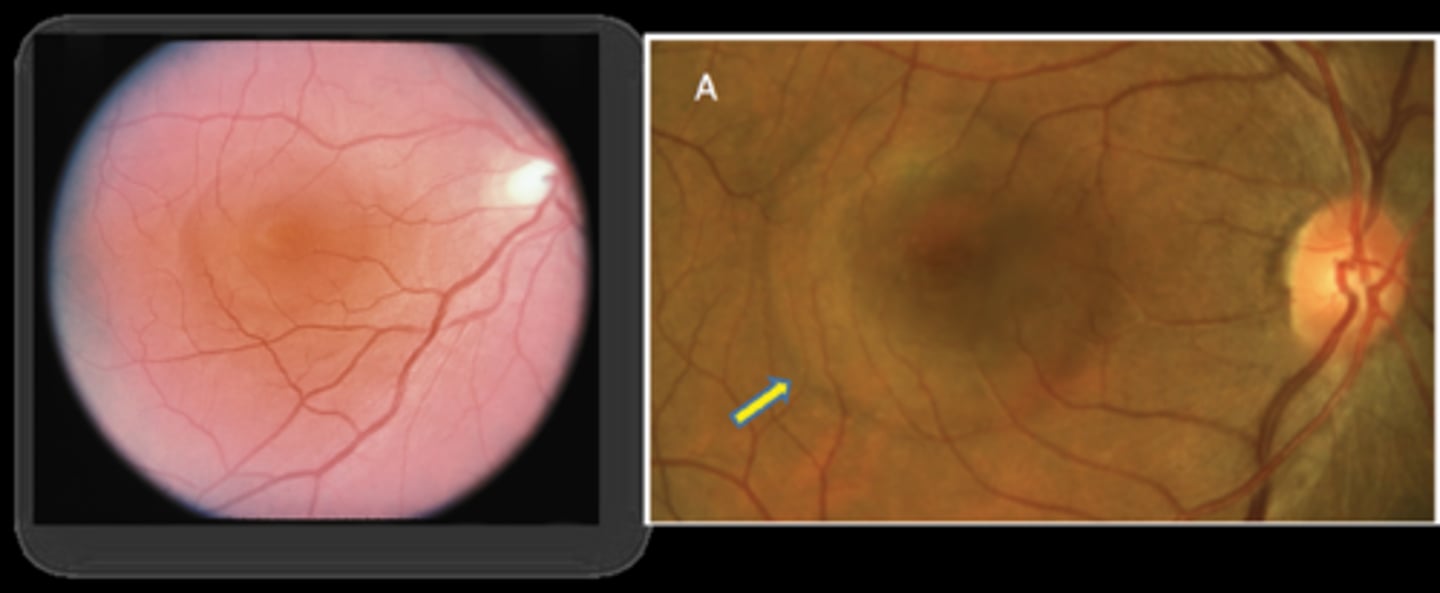
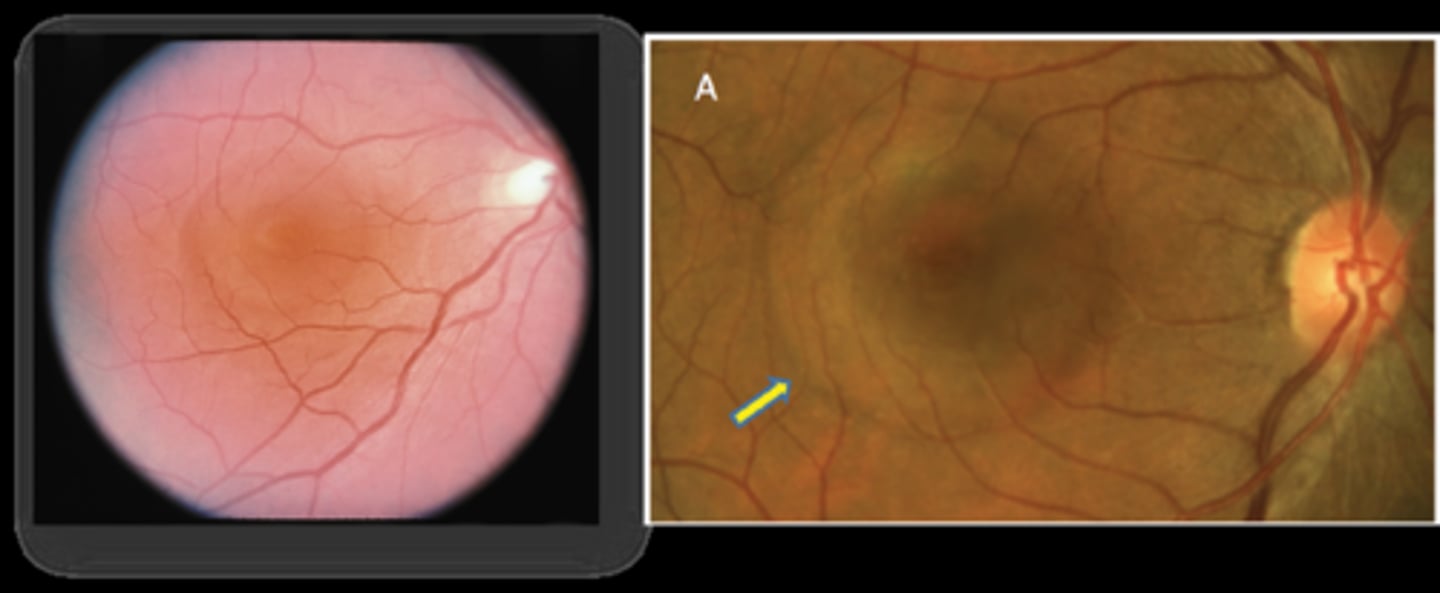
What is unique about this case of CSR?
more at outer macula, not directly involving fovea
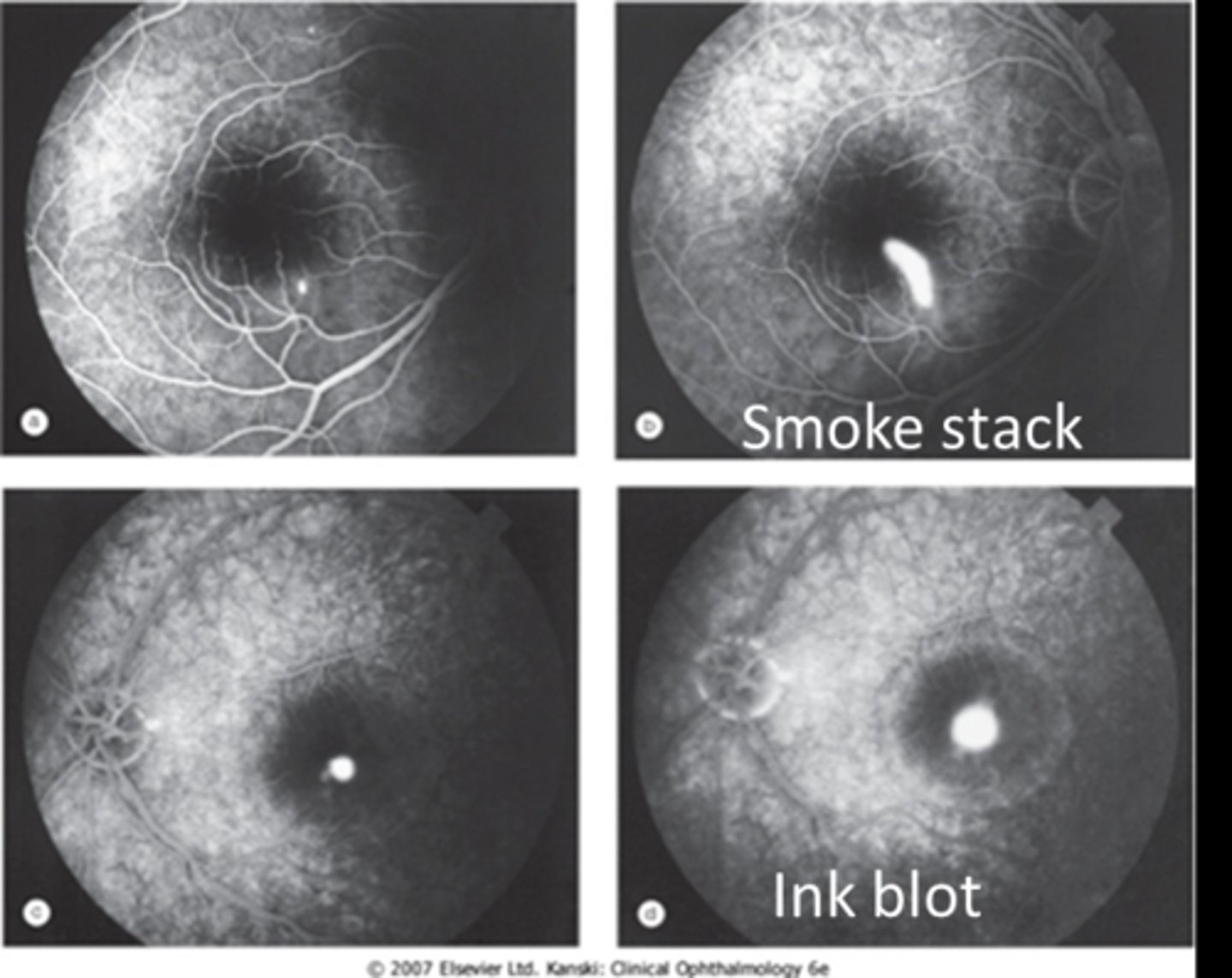
While not needed to diagnose CSR, what do we see in early and late phase IVFA?
early = hyperF spot at RPE defect
late = fluid enters through RPE and leaks/pools in either a smoke stack or ink blot pattern
What is the most common/likely prognosis of CSR?
acute CSR resolves on it's own in < 3 mos
How do we manage acute CSR (< 3 mos)?
manage cause/triggers
monitor with OCT
How do we manage chronic (> 6 mos) or recurrent CSR?
anti-corticosteroids = eplerenone, spironolactone (these may increase blood K+)
laser photocoagulation (last resort)
photodynamic therapy (last resort)
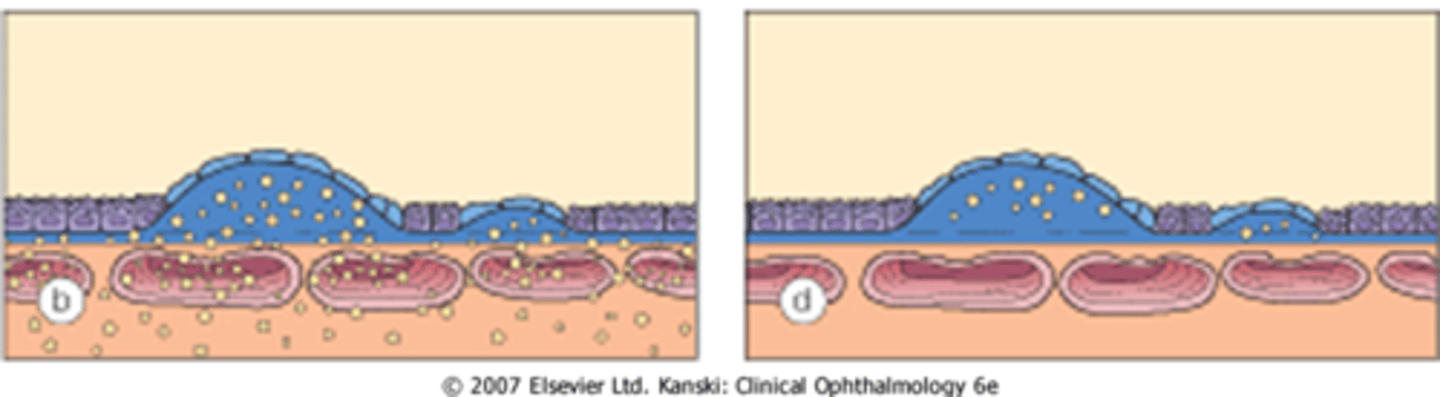
What is the pathology of drusen?
compromised RPE metabolism = lipofuscin waste product buildup = Bruch's thickens, RPE thins = atrophic changes in retina, choriocapillaris
What is a sign of drusen?
pale yellowish, small circular deposits that can remain stable, grow, or reabsorb
Where is drusen vs pseudodrusen located in the retinal layers?
drusen = subRPE = between RPE and Bruch's
pseudodrusen = subretinal = between retina and RPE
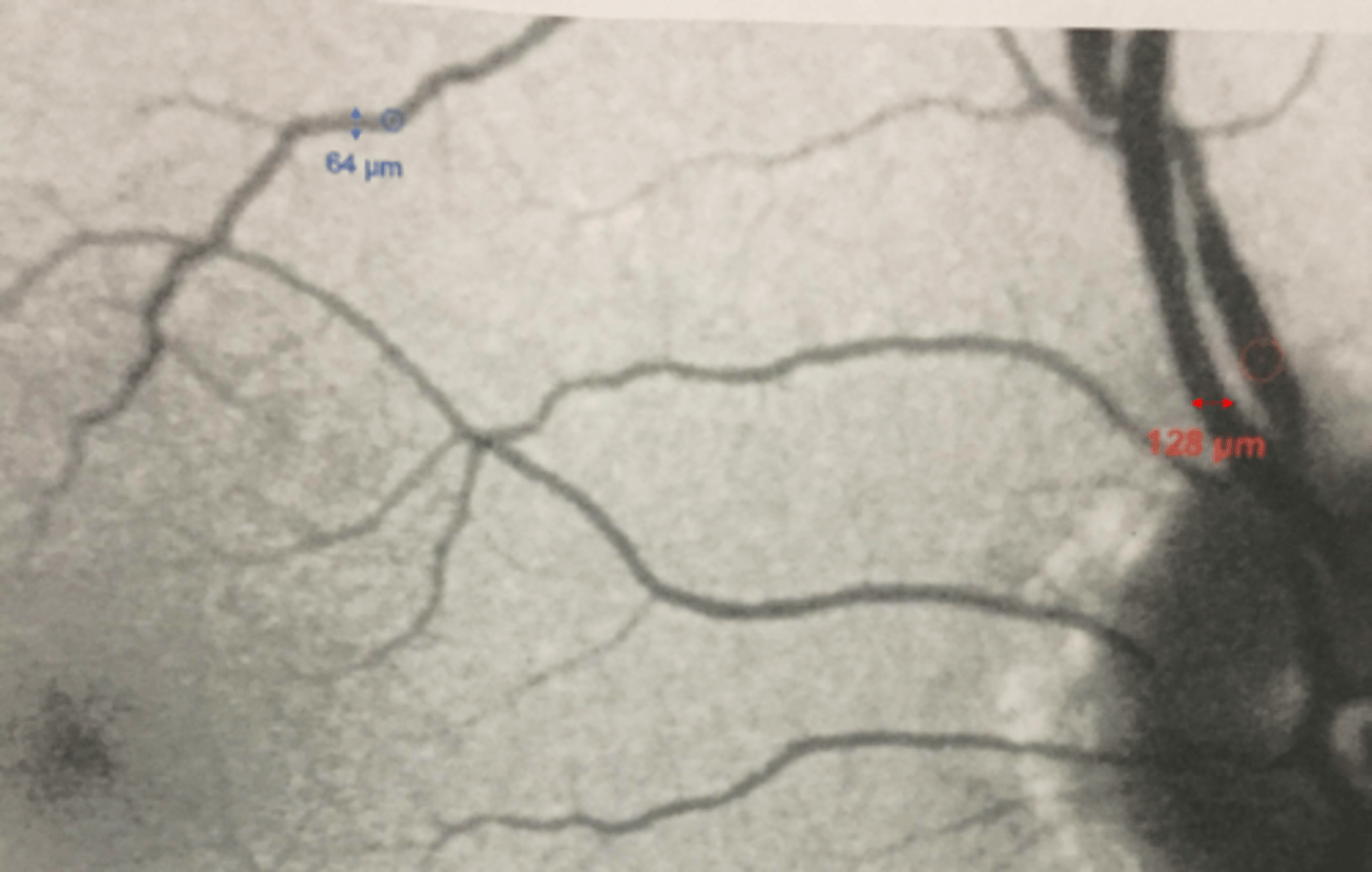
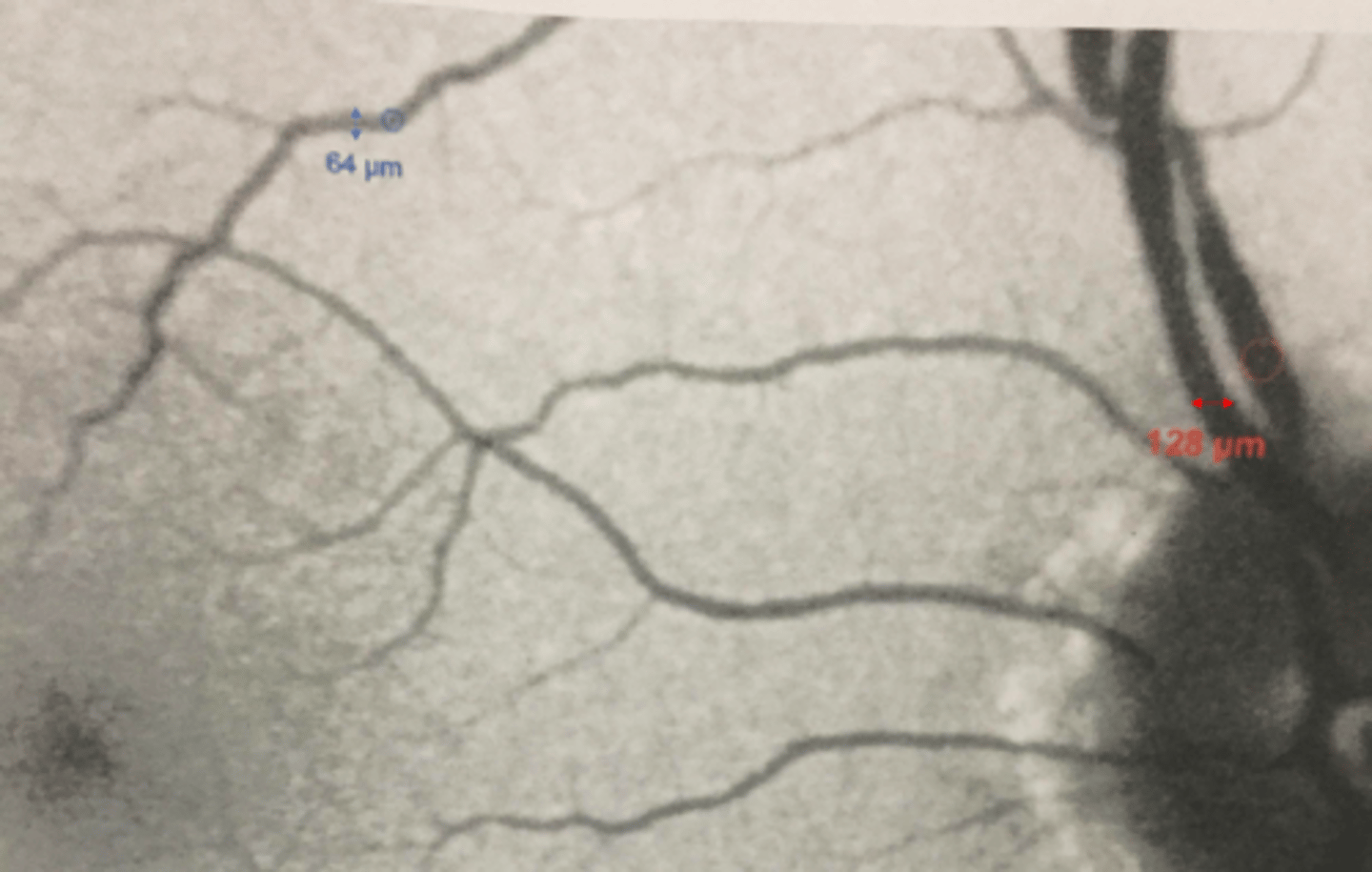
How do we distinguish between small vs intermediate vs large drusen size?
small = smaller than 64 micron diameter of a macular venule
intermediate = between 64-128 microns
large = larger than 128 micron diameter of a vein near ONH
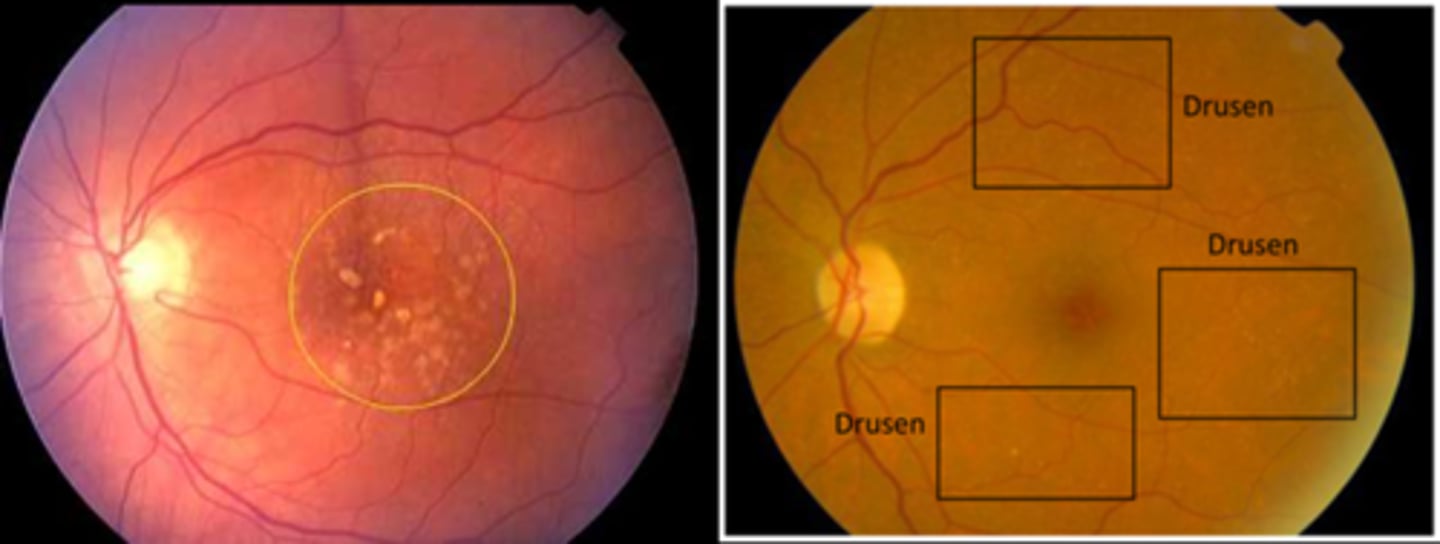
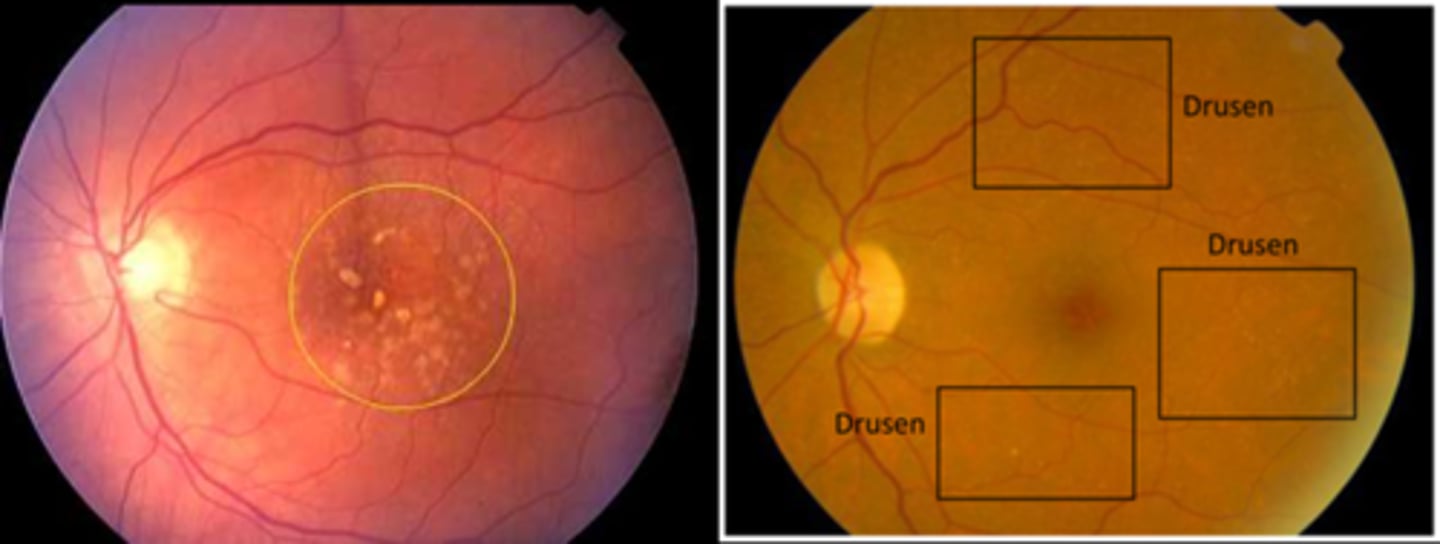
What is macular drusen?
one or a few small drusen in the macula = age-related drupelets or possible early AMD
What is ARMD drusen?
numerous small (hard) or intermediate (soft) or large drusen in the macula
NOTE: often seen with geographic atrophy, RPE hyperplasia pigment
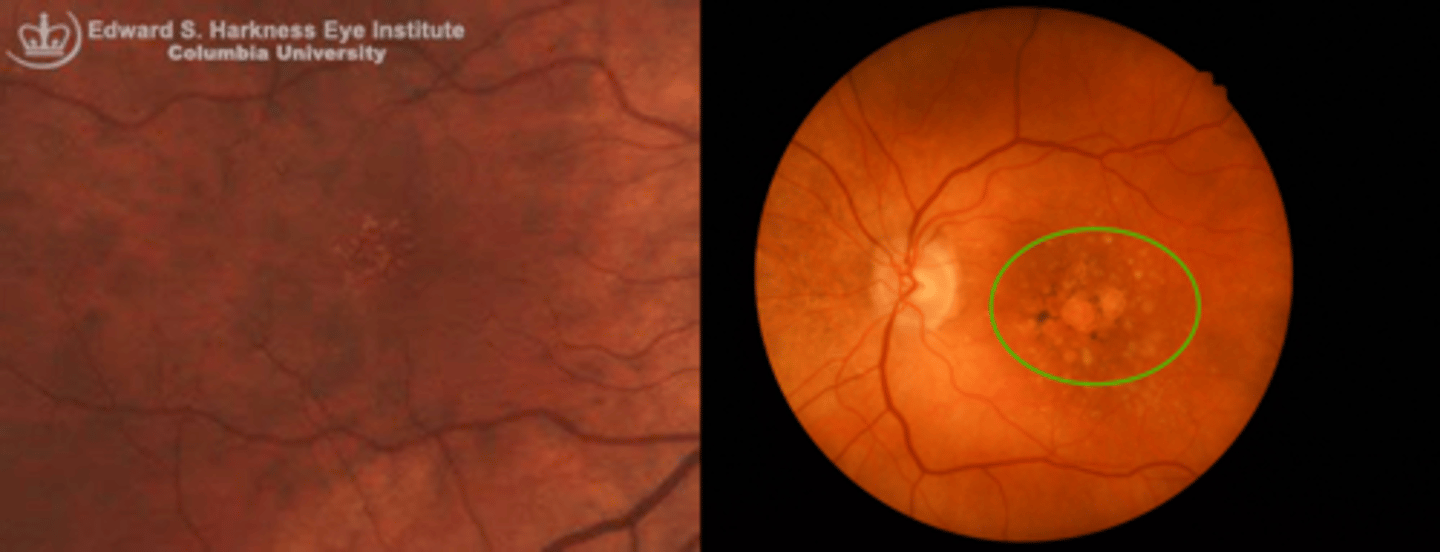
What is basal laminar drusen aka cuticular drusen?
patterned grouping of drusen in outer macular or midperiphery = part of AMD spectrum but NO increased risk of CNV/GA
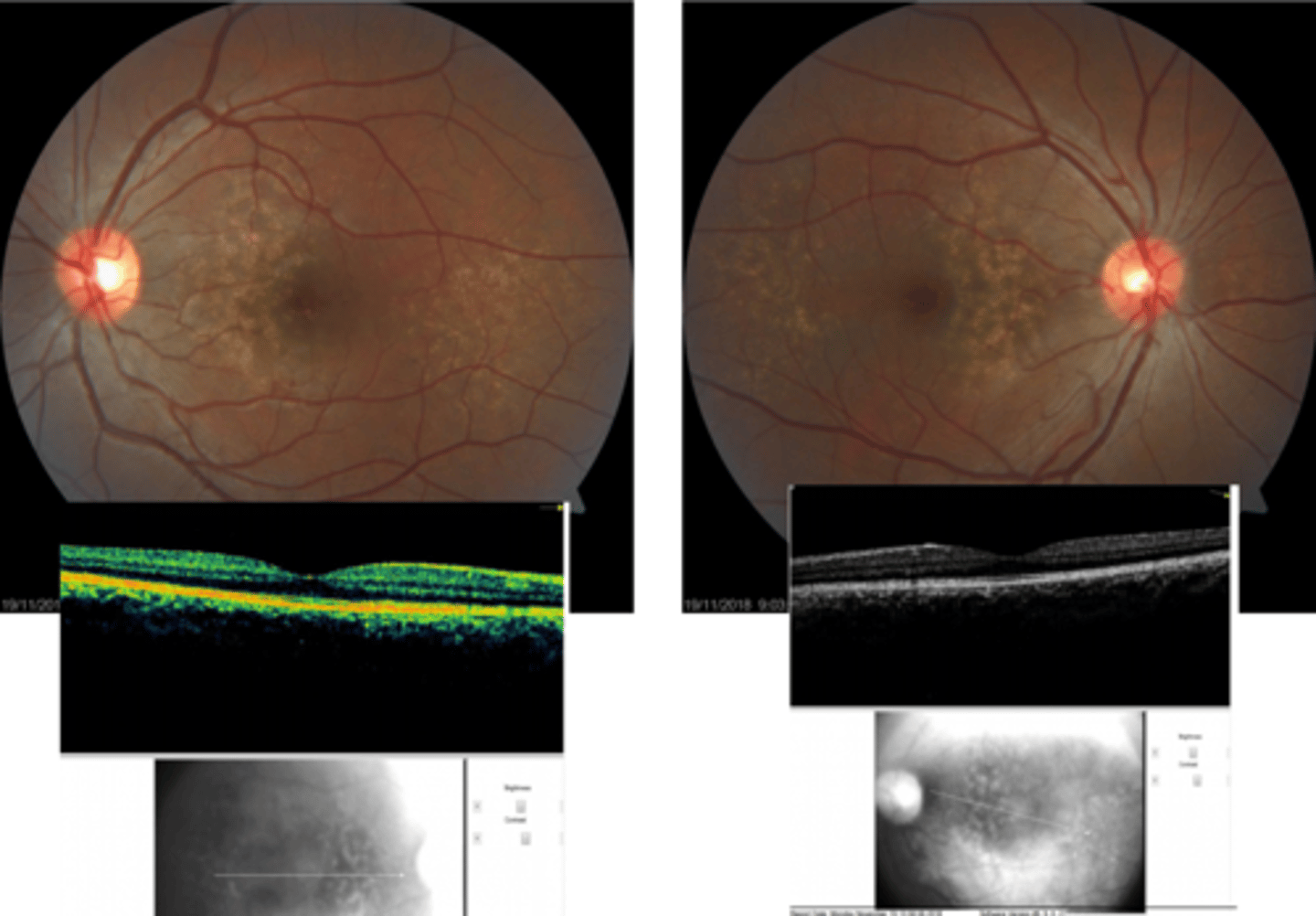
In what demographic do we see basal laminar drusen aka cuticular drusen?
younger females
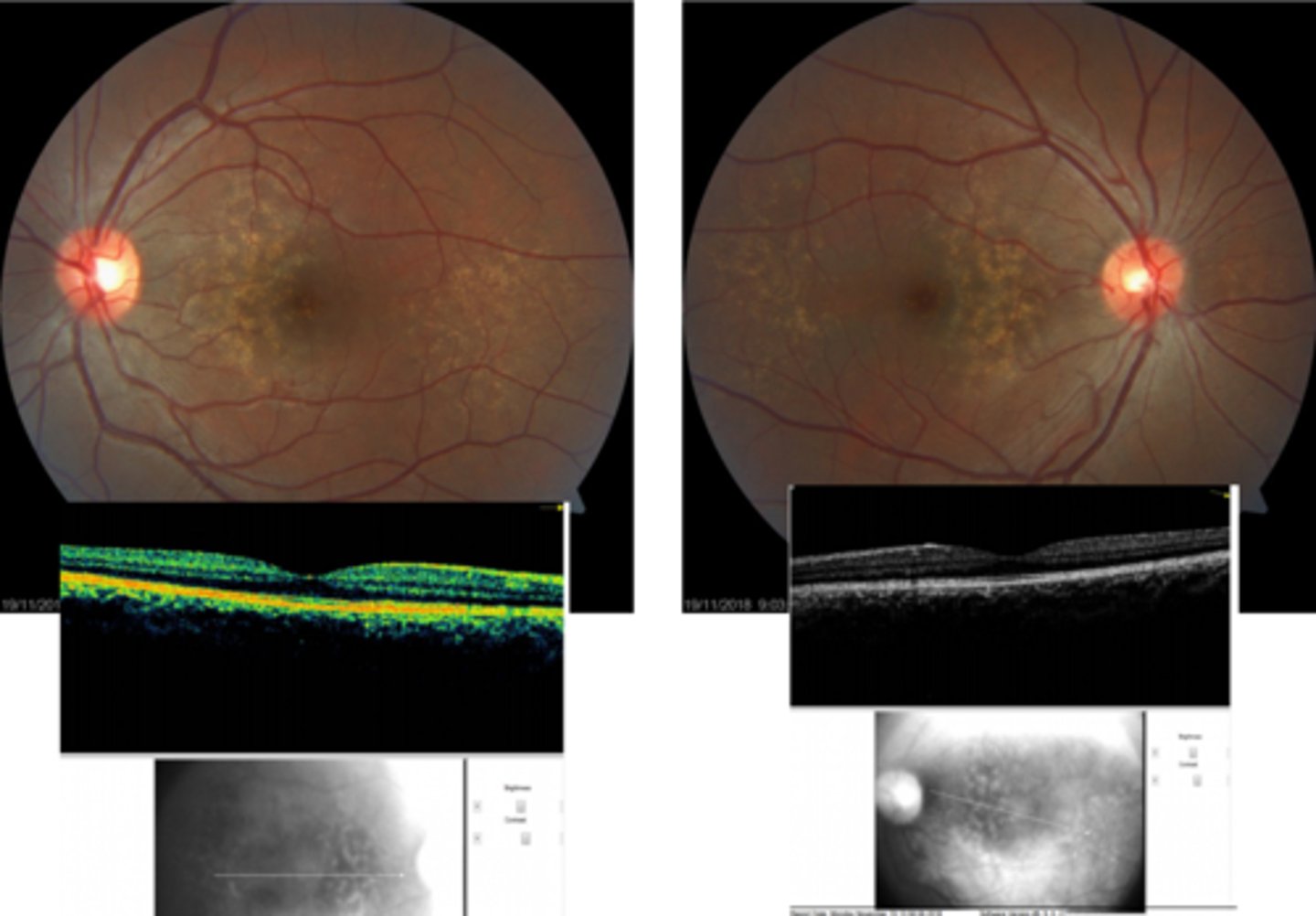
How does basal laminar drusen aka cuticular drusen appear on OCT?
very little RPE elevation, possibly optically empty beneath
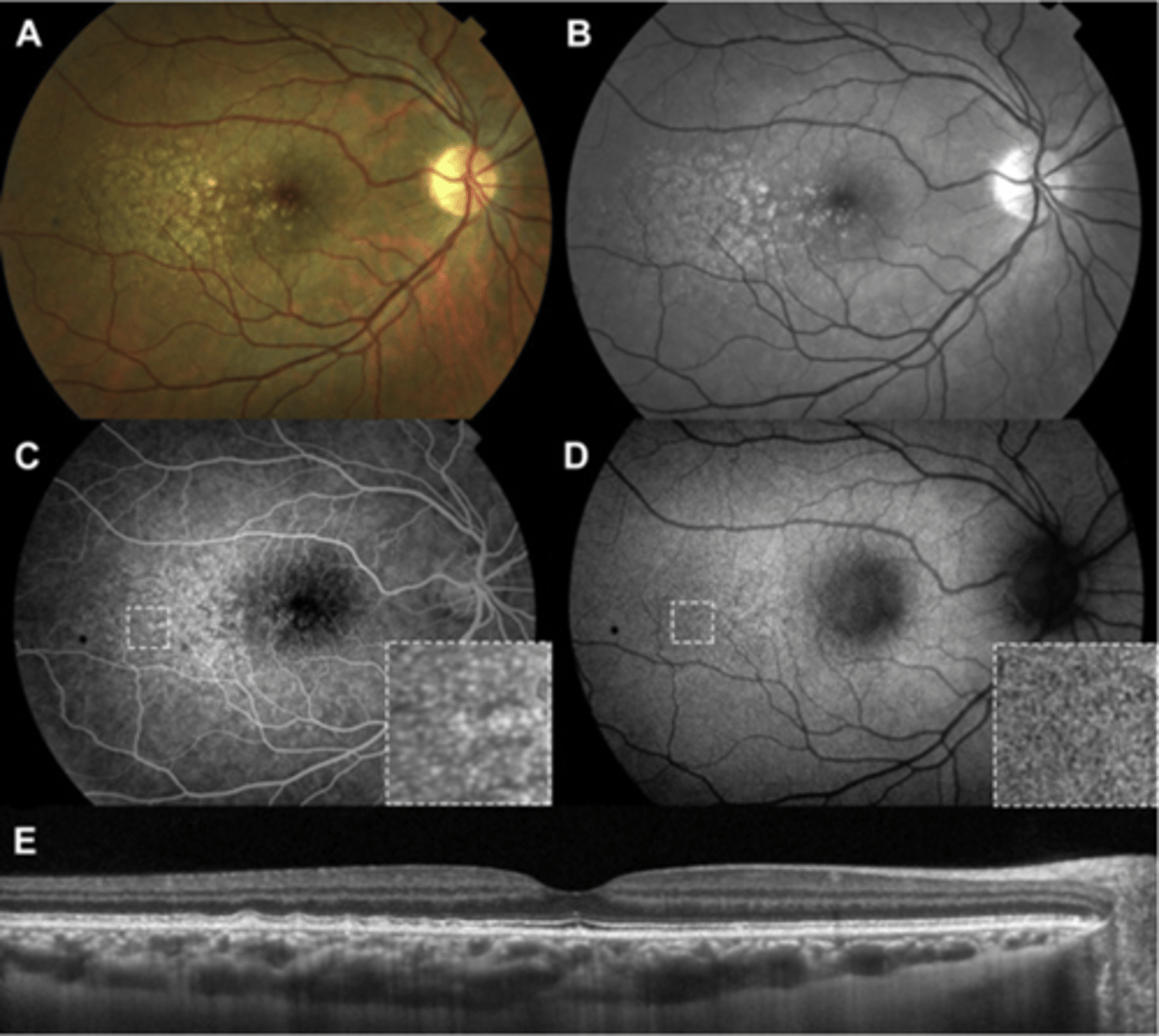
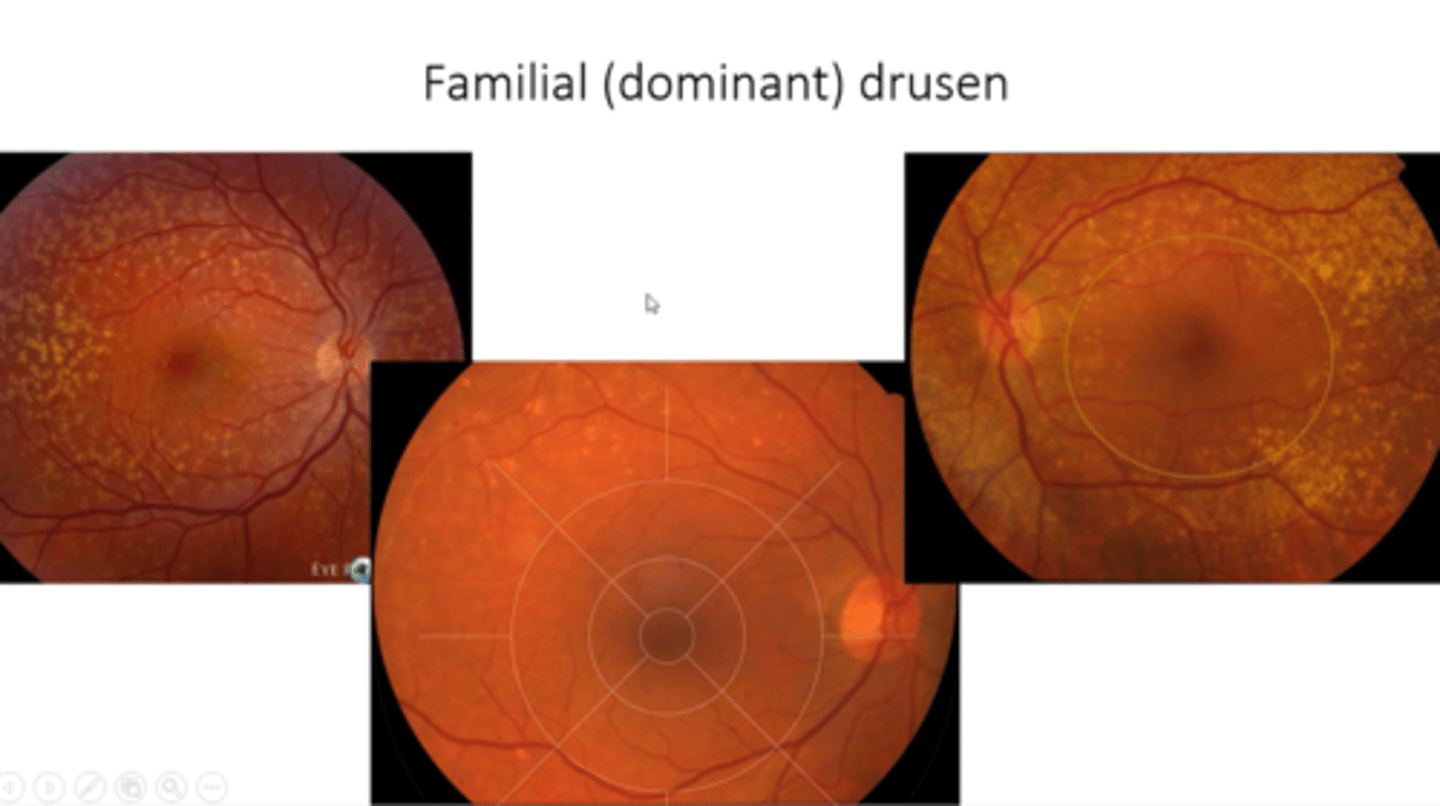
What is familial (dominant) drusen?
midperipheral drusen outside macula = dominant, young as 20
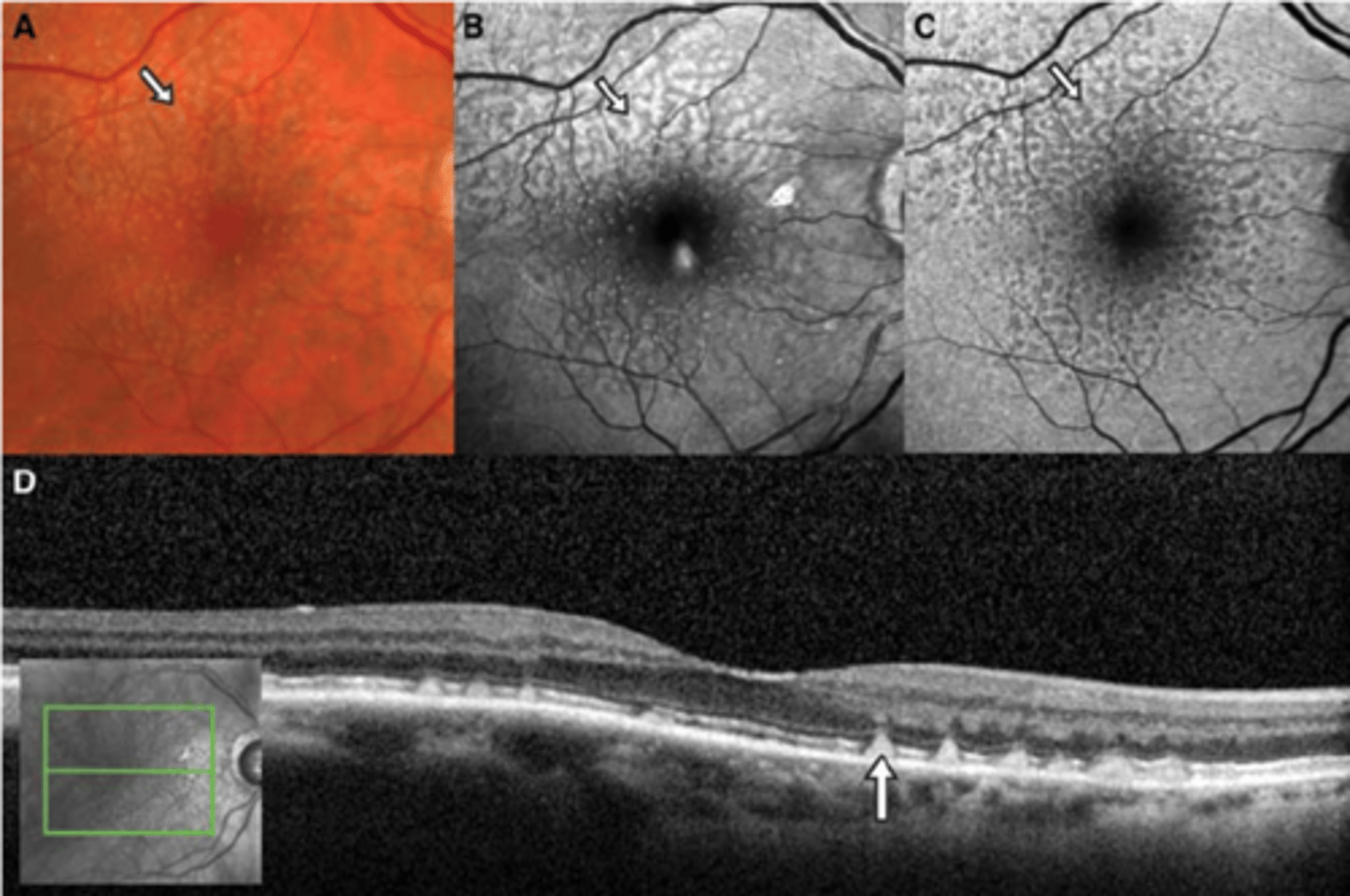
What is pseudodrusen aka reticular drusen?
subretinal reticular net-like pattern of drusen anywhere in posterior pole or periphery
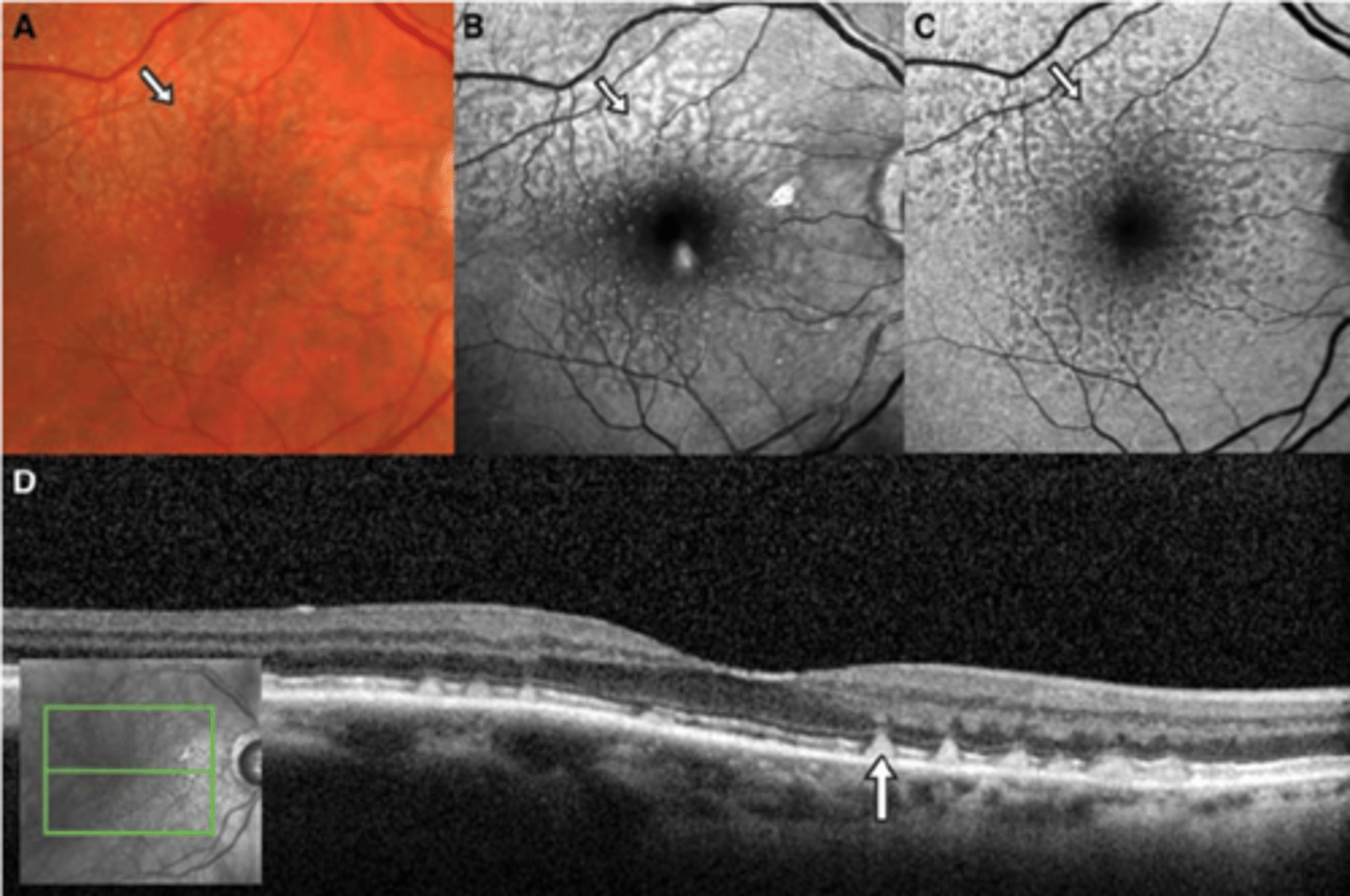
What can pseudodrusen aka reticular drusen increase the risk of?
increased risk of AMD progression
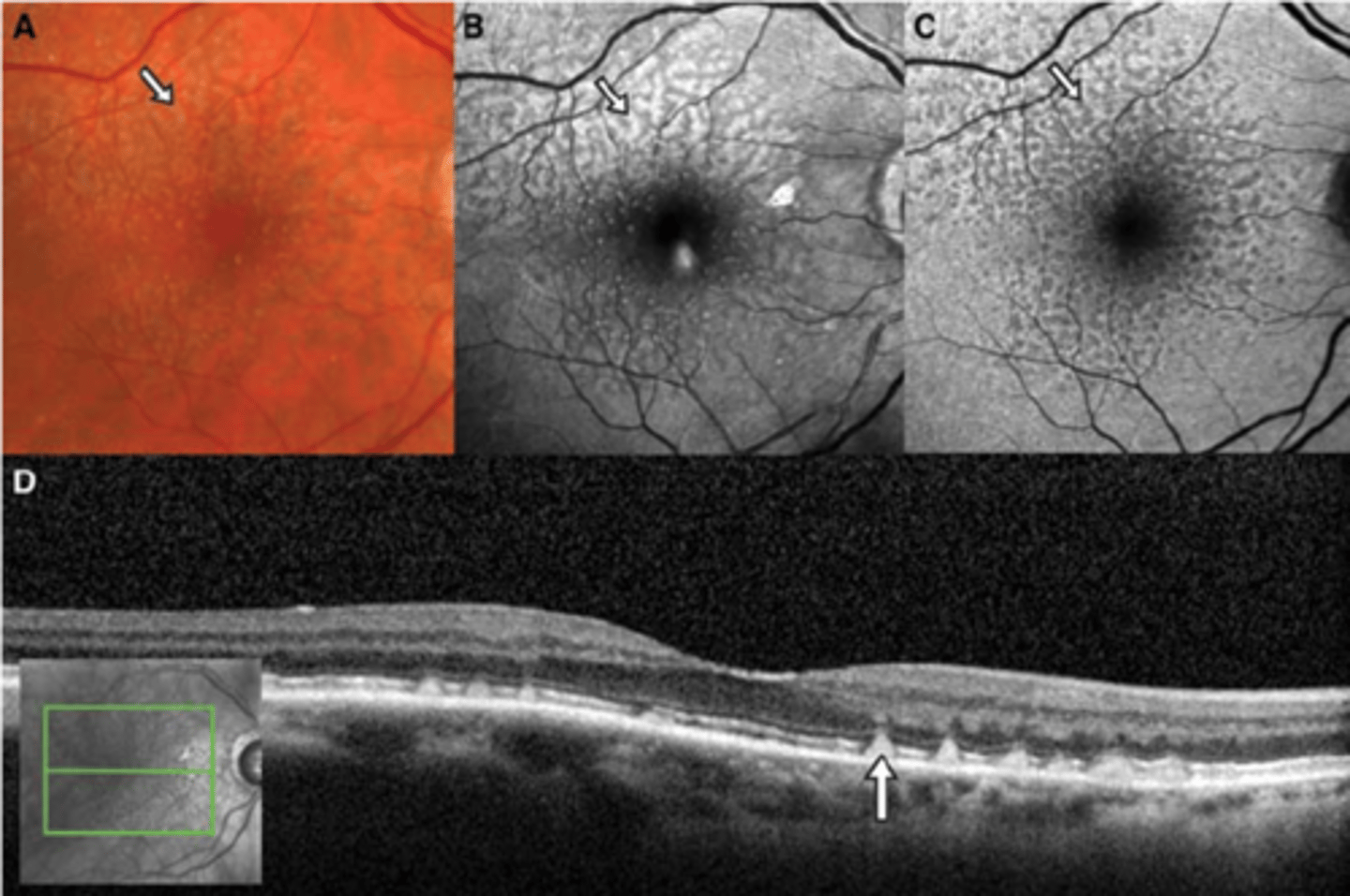
How does pseudodrusen aka reticular drusen appear on OCT?
bumps are above RPE = RPE still a thick, straight line
What is a complication of ONH drusen?
can calcify, migrate anteriorly as pt ages = compresses rNFL = glaucoma-like damage
While most drusen is due to RPE dysfunction, what choroidal condition can cause drusen?
nevus (neoplasm) = presence of drusen overlying a nevus indicates benign, longstanding nature = low risk of converting to choroidal melanoma
How does subRPE drusen appear on OCT?
localized RPE elevation (subRPE deposit)
large drusen RPE elevation called PED
Bruch's thin line can become visible now
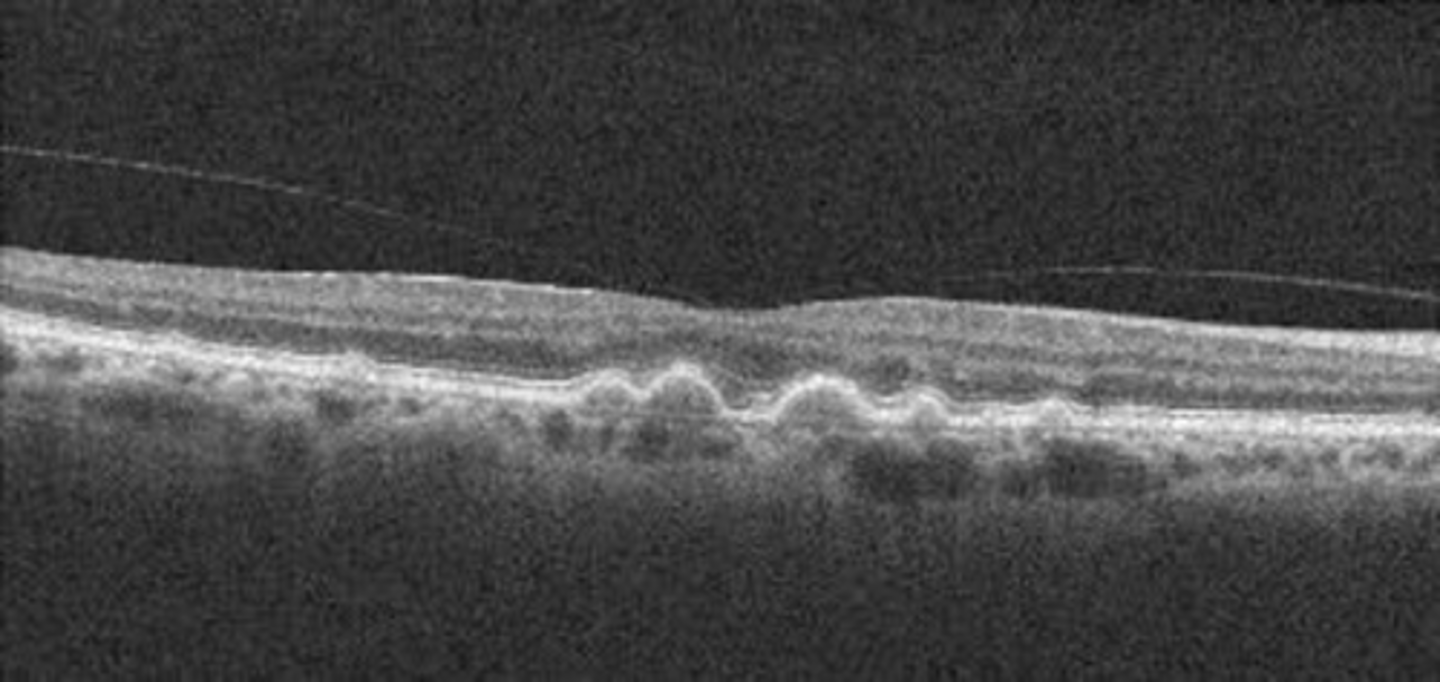
How does subretinal pseudodrusen appear on OCT?
PIL elevation with RPE flat beneath