USMLE Social Sciences | Quizlet
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
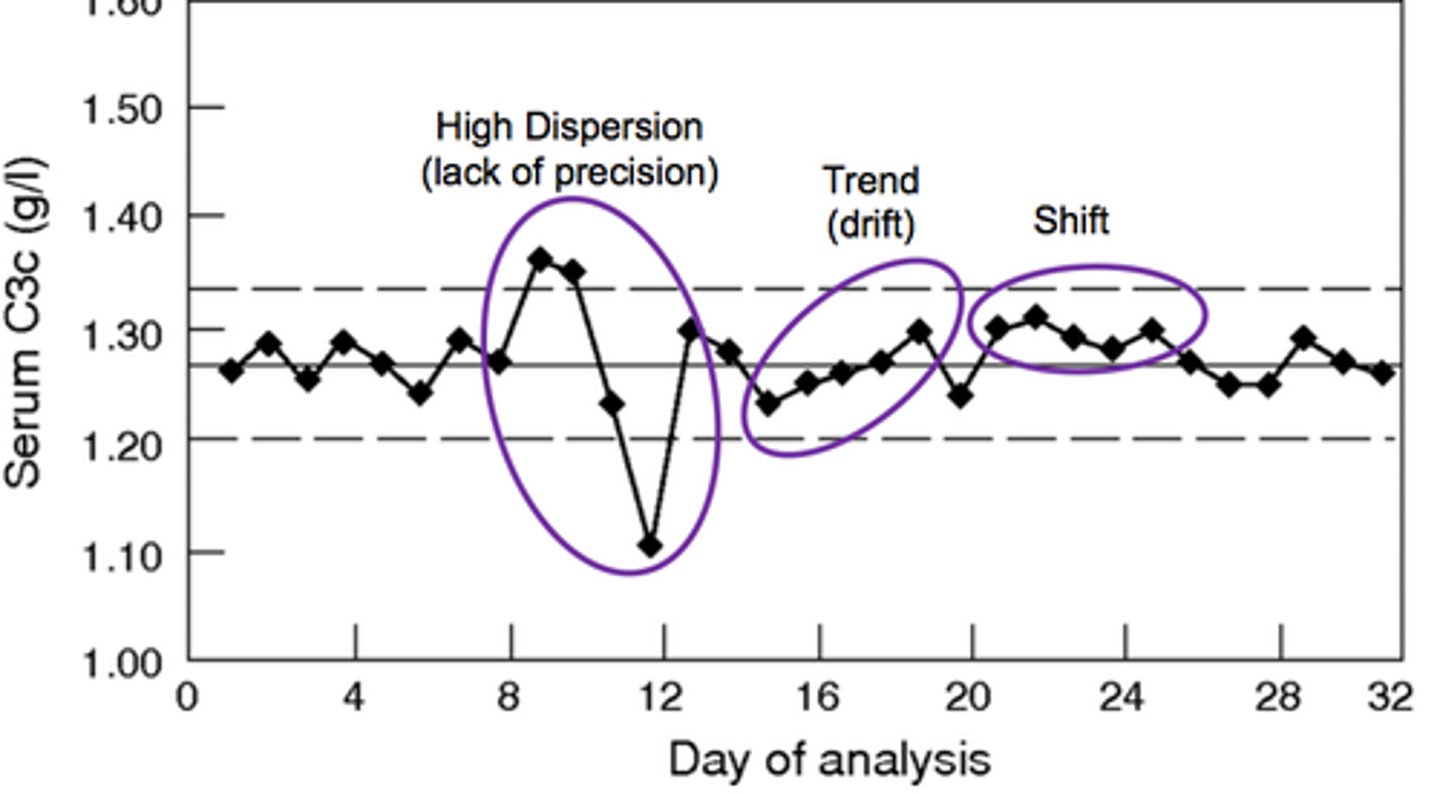
-A quality improvement tool that graphs a process performance outcome (eg, no-show rate) over time (eg, before and after a quality improvement intervention).
-Allow visualization of trends (≥5 consecutive points with consistent directional change) and systematically determines effectiveness of a quality improvement intervention.
Run chart
............... is used following a "close call," an event that could have resulted in patient harm but was prevented in time, such as when an incorrect medication dose is ordered for a patient, but the error is detected by the nurse before administration.
A near-miss analysis
............ is a prospective, systematic, team-based approach that consists of identifying steps in a process and finding solutions to any problems that may arise, with the goal of ensuring safe outcomes.
Failure mode and effects analysis
Initial steps of of failure mode and effects analysis:
1) Interdisciplinary team formation
2) Process definition
3) Process mapping (eg, flowchart)
4) Identification of major areas of risk (ie, failure modes)
Communication breakdown during signout (eg, omitted information during handoff between providers) is a leading cause of transfer-of-care errors and can be prevented with ................ and ................
-standardized signout processes (eg, checklists, mnemonics)
-redundancy (eg, separate documentation of cross-coverage events)
Checklists are an important tool to prevent undesired medical outcomes that result from physician communication failures during .................. process.
the patient handoff
Device automation, which substitutes human effort with computerized processes to reduce error-inducing variability, is best suited to ..................
constant, predictable processes (eg, continuous drug infusion via smart pump, routine vital signs monitoring).
............... bias, in which over-reliance on previous experiences (eg, a commonly seen case; a rarer but memorable, high-stakes case) influences diagnosis.
-Dyspnea diagnosed as influenza during peak influenza season
-Correct diagnosis is pulmonary embolism.
Availability
................ bias, in which previous documentation or patient context (eg, patient demographics, descriptions of patient or past diagnoses in the medical record) influences diagnosis.
-Abdominal pain diagnosed as opioid withdrawal in patient described as drug-seeking
-Correct diagnosis is bowel obstruction.
Framing
................. bias, in which patient symptoms are incorrectly interpreted to fit a presumed diagnosis (eg, discounting inconsistent aspects of presentation, over-emphasizing pertinent positives).
-Burning throat pain after eating spicy food diagnosed as acid reflux despite weight loss.
-Correct diagnosis is malignancy
Confirmation
Cognitive bias and associated diagnostic errors can be reduced by applying ...................
metacognition
(ie, understanding and reflecting on one's own thought patterns and biases)
................... occurs when the process of informed consent is influenced or biased by a provider's self-interest.
Conflict of interest
Decision-making capacity of a patient with psychotic illness
If a patient's psychotic symptoms do not interfere with understanding or ability to communicate a choice regarding medical treatment, the patient has the right to refuse treatment, even if it would be lifesaving.
Physicians should have a high suspicion for ............. in children with sudden changes in mood, behavior, or academic work, as well as in children with stressful family environments or parents with active drug/alcohol abuse.
abuse
When dealing with an angry patient, the most appropriate response is to remain nondefensive, acknowledge that the patient is upset, and begin the discussion with an ..................
open-ended question
What is the management of a hospitalized patient with borderline personality disorder who has polarized views of the admitting senior resident as "good" (eg, "You're a great doctor") and the first-year resident as "bad" (eg, "You're not good at your job")?
All providers to see the patient jointly as a team
A six-step protocol for delivering bad news
SPIKES:
1. creating an appropriate SETTING;
2. addressing the patient's PERCEPTION of his/her situation;
3. seeking the patient's INVITATION;
4. giving KNOWLEDGE to the patient regarding diagnosis and prognosis;
5. addressing the patient's EMOTIONS;
6. providing a management STRATEGY and SUMMARY of what had been discussed so far.
Oral advanced directives to a patient's attending physician can be honored if ..................
-a patient is diagnosed with a terminal or irreversible condition, and then
-the instructions are given to the attending physician in the presence of two witnesses.
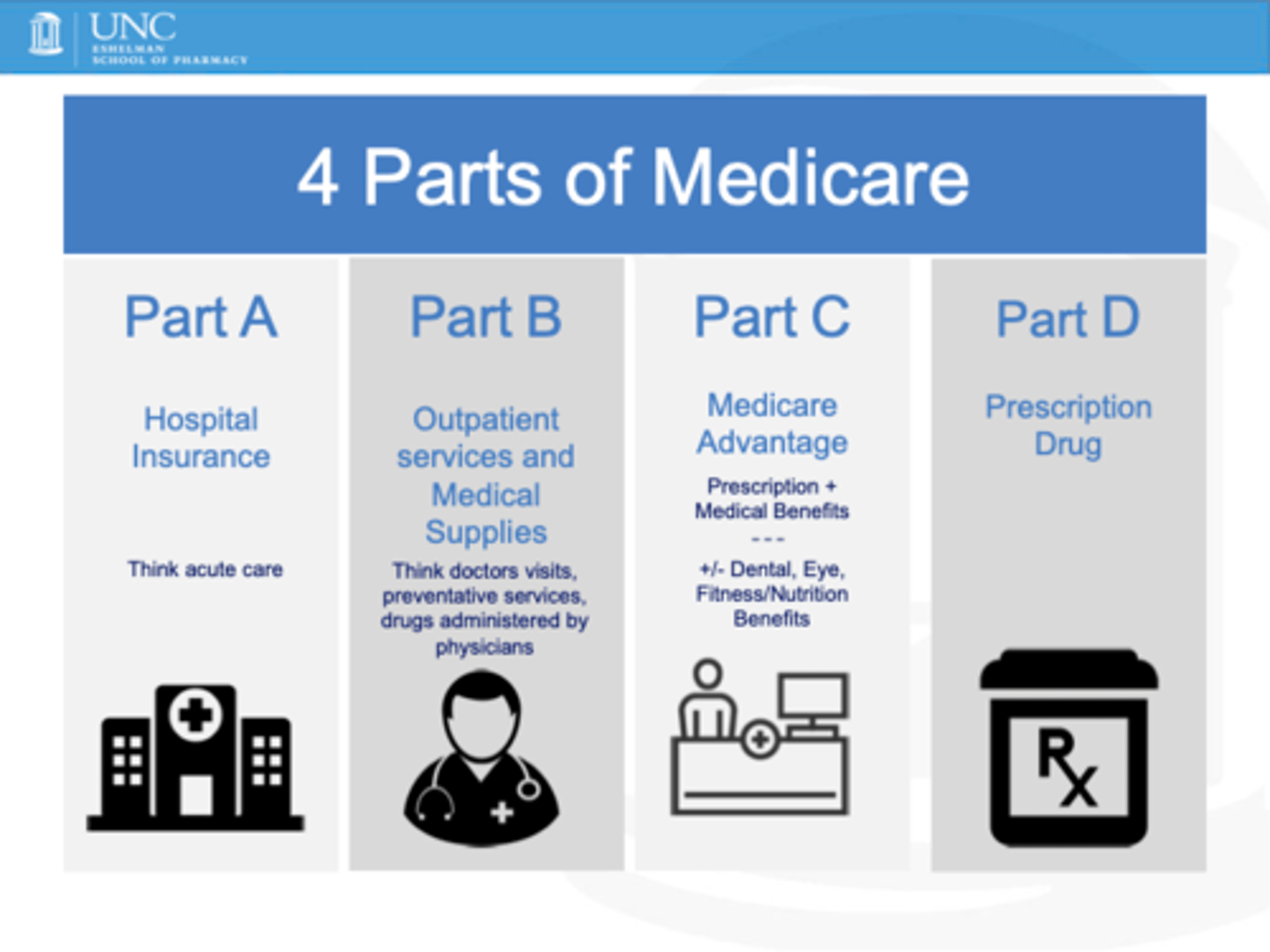
-Medicare part A covers primarily .............. services.
-Part B covers .............. services.
-Part C (Medicare Advantage) allows enrollment in private insurance plans.
-Part D covers .................
-inpatient
-outpatient
-prescription drugs
Root cause analysis - Steps?
1) Collect data
2) Create causal factor flow chart
3) Identify root causes
4) Generate recommendations & implement changes
5) Measure success of changes