Intermediate Accounting - Chapter 1
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Financial Accounting
provides relevant financial information to various external users.
capital markets
mechanisms to help an economy allocate resources efficiently.
corporation
dominant form of business organization that acquires capital from investors in exchange for ownership interest and from creditors by borrowing.
Rate of return
the gain or loss made on an investment relative to the amount invested, usually expressed as a percentage.
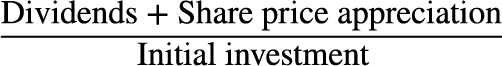
accural accounting
measures income according to the entity’s accomplishments and resource sacrifices during the period from transactions related to providing goods and services to customers, regardless of when cash is received or paid.
cash-basis accounting
measures income as the difference between cash receipts and cash disbursements during a reporting period from transactions related to providing goods and services to customers.
net operating cash flow
difference between cash receipts and cash disbursements fromtransactions related toproviding goods and servicesto customers during a reporting period.
Generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP)
set of both broad and specific guidelines that companies should follow when measuring and reporting the information in their financial statements and related notes.
Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC)
has the authority to set accounting standards for companies, but it relies on the private sector to do so
Committee on Accounting Procedure (CAP)
first private sector body that was delegated the task of setting accounting standards.
American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA)
national organization of professional public accountants.
Accounting principles board (APB)
the second private sector body delegated the task of setting accounting standards.
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
the private sector body responsible for establishing standards of financial accounting and reporting in the U.S.
Financial Accounting Foundation (FAF)
responsible for selecting the members of the FASB and its Advisory Council, ensuring adequate funding of FASB activities, and exercising general oversight of the FASB’s activities.
Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF)
responsible for providing timely responses to emerging financial reporting issueswithin the framework of existing GAAP.
conceptual framework
deals with theoretical and conceptual issues and provides an underlying structure for current and future accounting and reporting standards.
FASB Accounting Standards Codification
integrates and topically organizes all relevant accounting pronouncements comprising GAAP in a searchable, online database.
International Accounting Standards Committee (IASC)
umbrella organization formed to develop global accounting standards.
International Accounting Standards Board (IASB)
objectives are to develop a single set of high-quality, understandable global accounting standards, to promote the use of those standards, and to bring about the convergence of national accounting standards and International Accounting Standards.
International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS)
developed by the IASB and used by more than 120 jurisdictions
auditors
independent professionals who render an opinion about whether the financial statements fairly present the company’s financial position, performance, and cash flows in compliance with GAAP.
Certified Public Accountant (CPA)
licensed individuals who can represent that the financial statements have been audited in accordance with generally accepted auditing standards.
Objectives-oriented/principles-based accounting standards
approach to standard setting stresses professional judgment, as opposed to following a list of rules.
Rules-based accounting standards
standards that specify appropriate accounting treatments using precise thresholds or definitions and requiring little professional judgment for interpretation.
Institute of Management Accountants (IMA)
primary national organization of accountants working in industry and government.
Institute of Internal Auditors
national organization of accountants providing internal auditing services for their own organizations.
Conceptual framework
deals with theoretical and conceptual issues and provides an underlying structure for current and future accounting and reporting standards.
predictive value
confirmation of investor expectations about future cash-generating ability.
material
has qualitative or quantitative characteristics that make it matter for decision making.
faithful representation
exists when there is agreement between a measure or description and the phenomenon it purports to represent.
convervatism
practice followed in an attempt to ensure that uncertainties and risks inherent in business situations are adequately considered.
qualitative characteristics
identifies four enhancing qualitative characteristics: comparability (including consistency), verifiability, timeliness, and understandability.
cost effective
the perceived benefit of increased decision usefulness exceeds the anticipated cost of providing that information.
The four assumptions underlying GAAP
the economic entity assumption,
the going concern assumption,
the periodicity assumption, and
The monetary unit assumption.
economic entity assumption
presumes that economic events can be identified specifically with an economic entity.
going concern assumption
in the absence of information to the contrary, it is anticipated that a business will operate indefinitely.
periodicity assumption
allows the life of a company to be divided into artificial time periods to provide timely information.
monetary unit assumption
states that financial statement elements should be measured in a particular monetary unit (in the United States, the U.S. dollar).
Recognition
process of admitting information into the basic financial statements.
measurement
process of associating numerical amounts with the elements.
disclosure
including pertinent information in the financial statements and accompanying notes.
historical cost
bases measurements on the amount given or received in the original exchange transaction
net receivable value (NRV)
estimated selling prices of inventory in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal, and transportation.
Depreciated (or amortized) cost
reduces historical cost to reflect depreciation (or amortization) recognized to date.
current cost
are the costs that would be incurred to purchase or reproduce an asset
present value
bases measurement on future cash flows discounted for the time value of money
fair value
bases measurements on the price that would be received to sell assets or transfer liabilities in an orderly market transaction.
fair value option
allows companies to report specified financial assets and liabilities at fair value.
full-disclosure principle
financial reports should include any information that could affect the decisions made by external users.
revenue/expenses approach
recognition and measurement of revenues and expenses are emphasized; with balance sheet accounts adjusted as necessary to reflect revenues and expenses.
Asset/liability approach
recognition and measurement of assets and liabilities drives revenue and expense recognition.