biology final exam
1/438
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
439 Terms
in a certain species of salmon, some adult males are extremely large whereas other adult males are very small, compared to the females. there are no intermediate sized-adult males in the population this is probably due to
disruptive selection
which of the following is not an assumption for hardy-weinberg equilibrium
small population size
in a hardy-weinberg population, the frequency of the a allele is 0.4. what is the frequency of individuals with Aa genotype
0.48
must be present in a population before natural selection can act upon the population
genetic variation
the sum of all alleles in all loci in a population
gene pool
a group of organisms in an area that have the potential to interbreed
population
changes in allele frequency in a population over generations
microevolution
a trait that is either present or absent
discrete character
a trait that varies along a gradient, such as height
quantitative character
a farmer uses triazine herbicide to control pigweed in his field. for the first few years, the triazine works well and almost all the pigweed dies; but after several years, the farmer sees more and more pigweed. which of these statements explains why the pigweed reappeared?
triazine-resistant weeds were more likely to surive and reproduce
natural selection operates at what level of biological organization
the population
in general, each species of fruit fly found in the hawaiian archipelago is restricted to a single island. one hypothesis to explain this pattern is that new species formed after a small number of flies colonized each new island. this mechanism is called
the founder effect
evidence that supports the theory of evolution is found in the studies of:
artificial selection
biochemistry
embryos
all of these
fossils
all of these
__________ is a very strong oxidizing agent
H2O is split by enzymes, and the electrons are transferred from the hydrogen atoms to P680+, thus reducing it to P680.
_________ is released as a by-product of this reaction
P680+, O2
this is the reaction of photosynthesis:
6 CO2 + 12 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2 + 6 H2O
hydrogen atoms are transferred from water to carbon dioxide, what kind of reaction is that (redox or oxidation)
redox
in what stage of photosynthesis are water molecules split, atp and nadph formed, and oxygen is released?
stage name and where it takes place in the cell
light reactions, thylakoid membrane
________ catalyzed by the enzyme _______ is the one of the most abundant _________. the __________ function is used here
ribulose, rubisco, protein, carboxylase
the light reactions also generate _________ using chemiosmosis to power the addition of a phosphate group to ADP, a process called __________
atp, photophosphorylation
_____________, the most common photosynthetic pigment absorbes _________________ light and reflects ________ light
chlorophyll a, violet-blue and red, green
true or false: at the end of the citric acid cycle we get 6 nadh, 2 fadh2, and the equivalent of 2 atp
false
after glycolysis, pyruvate is sent to the ______ in eukaryotes
mitochondria
after glycosis, pyruvate stays in ________ of prokaryotes
cytoplasm
true or false: darwin’s theory of evolution means of natural selection relies solely on chance
false
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: sugar gliders and flying squirrels live in forests on opposite ends of the world
convergent evolution
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: basilosaurus, a transitional cetacean
fossil evidence
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: whales’ fins, bat’s wings, and cat’s paws all have the same bones
homology
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: islands have many endemic species that are similar to species found on the nearest large landmass
biogeography
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: the nucelotide sequence of genes are more similar in organisms sharing a more recent ancester
dna
match the line of evidence for evolution with the example from the lecture: mrsa strains are becoming more abundant
direct observation
which of the following was not one of darwin’s observations
random chance molds organisms to their environment
which of the following is not one of darwin’s inference
favorable traits will arise spontaneously by mutation
watson and crick (and franklin and wilkins) showed all of the following about dna except:
helicase unwinds dna in replication
match the enzymes listed with their function in dna replication: unzips the dna molecule
helicase
match the enzymes listed with their function in dna replication: adds dna nucleotides
dna polymerase iii
match the enzymes listed with their function in dna replication: removes rna primers and replaces with dna nucleotides
dna polymerase i
match the enzymes listed with their function in dna replication: finishes removing primers by repairing the sugar phosphate backbone
ligase
match the enzymes listed with their function in dna replication: adds rna nucleotides to form a 3’-OH group
primase
match the term with the descriptive phrase: contains okazaki fragments
lagging strand
match the term with the descriptive phrase: have CG-rich repeated sequences
telomeres
match the term with the descriptive phrase: are dna-histone complexes
nucleosomes
match the term with the descriptive phrase: an enzyme that prevents erosion of the ends of chromosomes
telomerase
which statement best describes the “particulate” nature of genes?
forms of genes are present or absent, though genes that are present may be masked
what mendel called “true breeding” we now call
homozygous
when medel crossed true breeding purple-flowered plants with true breeding white-flowered plants (P generation), what did he observe in the subsequent generation (F1)?
all purple-flowered plants
when mendel self-pollinated plants of the F1 generation from the previous question, what was his observation (in the F2 generation)?
3:1 purple to white-flowered plants
different forms of the same gene we call
alleles
mendel found that different versions of the same gene separate when the parent produces gametes. this is the law of
segregation
match the terms below with their definitions: one allele masks the appearance of another allele
complete dominance
match the terms below with their definitions: two alleles of the gene are expressed simultaneously, such that the heterozygote has an intermediate phenotype
incomplete dominance
match the terms below with their definitions: multiple alleles can be expressed simultaneously
codominance
match the terms below with their definitions: one genotype can affect many aspects of phenotype
pleiotropy
match the terms below with their definitions: two or more genes can affect a single phenotype
epistasis
ecology is the scientific study of
abundance and distribution
the symbols +, -, and o are to be used to show the results of interactions between individuals and groups of individuals in the examples that follow. the symbol + denotes a positive interaction, - denotes a negative interaction, and o denotes where individuals are not affected by interacting. the first symbol refers to the first organism mentioned.
cattle egrets (cattle birds) live together with grazing cattle. when cattle move, insects are flushed out which let egrets see and eat them. while egrets do nothing for the cattle, which interactions exist between the cattle egret and grazing cattle?
+/o
two species of squirrels live on either side of the grand canyon. it is believed that a long time ago, before being separated by the canyon, they were the same species. this is an example of
allopatric speciation
coral reef communities have a special relationship between coral and algae. coral lives with unicellular algae by supplying some nutrients, in return, algae carries out photsynthesis to provide organic food for corals. what ecological relationship is being described?
mutualism
which of the following is an example of a commensalism?
cattle egrets eating insects stirred up by grazing bison
which of the following animals is typical in savanna ?
elephant
in the open sea, which of the following is the main primary producer?
phytoplankton
at what stage of meiosis does crossing over occur?
prophase i
when an animal zygote is formed, what type of cell division occurs next?
mitosis
consider an animal cell where n = 3. match the arrangement of chromosomes with the stage of cell division: six sets of chromosomes align at the metaphase plate
metaphase of mitosis
consider an animal cell where n = 3. match the arrangement of chromosomes with the stage of cell division: three pairs of homologous chromosomes align at the metaphase plane
metaphase of meiosis i
consider an animal cell where n = 3. match the arrangement of chromosomes with the stage of cell division: three pairs of sister chromatids line up at the metaphase plate
metaphase of meiosis ii
which of the following does not contribute to new combination of genes in offspring?
separation of sister chromatids in mitosis
true or false: sex chromosomes are not strictly homologous, (an x chromosome has different genes than a y chromosome), but they act as if they are homologous during meiosis
true
true or false: in meiosis, only one division results in two genetically identical daughter cells and in mitosis, two divison (reductive division) and results in up to four genetically distinct daughter cells.
false
dna replication produces two identical dna molecules called _____ which separate during mitosis
sister chromatids
which of the following process may contribute to cells becoming cancerous
external growth factors
loss of density dependent inhibition
production of growth factors by the cells themselves
loss of anchorage dependent inhibition
all of these
all of these
what is metastasis?
the process where cancerous cells or growth factors spread throughout the body
true or false: bacteria divide by mitosis
false
match the stage of mitosis to the process described: telophase
nuclear envelopes reform
match the stage of mitosis to the process described: anaphase
sister chromatids separate
match the stage of mitosis to the process described: prophase
chromatin condenses into chromosomes
match the stage of mitosis to the process described: interphase
dna is replicated
match the stage of mitosis to the process described: cytokinesis
organelles are distributed to daughter cells
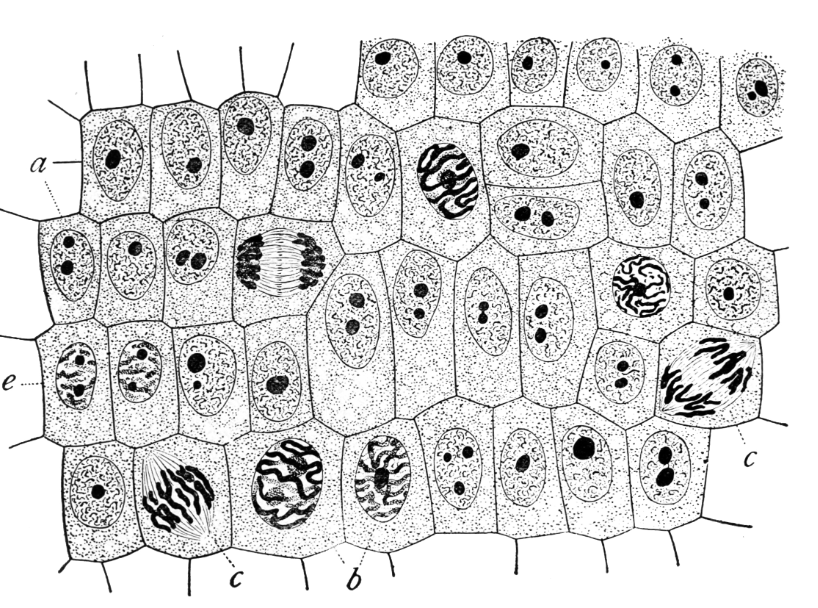
the cells labeled “b” are in which phase of mitosis?
prophase
what is the basic unit of structure and function in living organisms
a cell
to see the ultrastructure (organelles) of cells, electron microscopes are used. match the type of electron microscopy to its description: a two-dimensional (flat) view through a specimen
transmission
to see the ultrastructure (organelles) of cells, electron microscopes are used. match the type of electron microscopy to its description: a 3-dimensional view of the surfaces of cell structures
scanning
to separate a cell’s components by fractionation, each round of spinning is _______. (faster and slower are the rate of rotation (rpm) and longer and slower are the period of time for spinning).
faster and longer
which of the following is not found in prokaryotic cells
membrane bound organelles
which of the following is not eukaryotic
archaea
match the universal cell component to its definition: semi-fluid substance inside of cell
cytosol
match the universal cell component to its definition: dna molecule or molecules, contain genes
chromosomes
match the universal cell component to its definition: boundary of cellular contents, made of phospholipid bilayer and proteins
plasma membrane
match the universal cell component to its definition: organelle of protein synthesis
ribosomes
which of the following statements about eukaryotic cells is false?
they never have cell walls
true or false: a prokaryotic cell has no mitochondria or chloroplasts
true
true or false: a plant cell has no mitochondria, only chloroplasts
false
match the component of the nucleus to its description: compacted dna and proteins
chromosomes
match the component of the nucleus to its description: uncompacted dna and proteins
chromatin
match the component of the nucleus to its description: lining of the membrane of the nucleus
lamina
match the component of the nucleus to its description: the double layer of membranes surrouding the genetic material
envelope
match the component of the nucleus to its description: a complex of proteins that allow material to enter and leave the nucleus
pore
ribosomes assemble what type of polymer
polypeptides/proteins
which organelles were thought to have evolved from independent, prokaryotic organism engulfed by an early eukaryotic cell? (select all that apply and only those that apply)
mitochondria
golgi apparatus
ribosomes
chloroplasts
smooth er
rough er
mitochondria and chloroplasts
select all the parts of the endomembrane system. do not select any of the organelles that are not part of the endomembrane system.
lysosomes
plasma membrane
nuclear envelope
ribosomes
smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum
mitochondria
golgi apparatus
vacuoles
lysosomes, plasma membrane, nuclear envelope, smooth and rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus, and vacuoles
select all functions of the smooth er:
protein synthesis
synthesize lipids
carbohydrate metabolism
store Ca2+ ions
detoxify poisons
dna storage
synthesize lipids, carbohydrate metabolism, store Ca2+ ions, and detoxify poisons
match the organelle to the function it performs: storage of dna
nucleus