COMPSCI 1100 LECTURE (1st sem, 1st term)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/68
Earn XP
Last updated 10:52 AM on 3/16/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
1
New cards
UNIT 1: INFORMATION
TECHNOLOGY CONCEPTS AND MANAGEMENT
TECHNOLOGY CONCEPTS AND MANAGEMENT
123
2
New cards
Collects data, process data into information then converts information into knowledge for a specific purpose
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
3
New cards
TPS's predominant function is to record data collected at the boundaries of organizations, in other words, at the point where the organization transacts business with other parties. (ATM, POS, etc..)
Transaction Processing Systems
4
New cards
Information systems for planning, control, decision-making, and problem-solving.
Management Information Systems
5
New cards
Reports or the output part of MIS.
On-demand Output
6
New cards
It takes the optimal course of action, and gathers detailed data and information to help middle/senior
managers make decisions.
managers make decisions.
Group Decision Support Systems (GDSS/DSS)
7
New cards
To help high-ranking officers/executives direct an organization to focus on a long-range strategic plan.
Executive Information Systems/Executive Support System (EIS/ESS)
8
New cards
Incorporation of human expertise into a computer system that emulates our decision-making. - AI
Expert Systems
9
New cards
A database that contains data about part of a city, a country, a state, or even the entire world. (Google Maps, Waze, and other uses especially for agriculture)
Geographic Information System
10
New cards
In _____ information systems help focus on recording and reporting financial changes and
state, that the purpose of financial systems is to facilitate financial planning and business transactions.
state, that the purpose of financial systems is to facilitate financial planning and business transactions.
Accounting
11
New cards
- information systems help organize budgets, manage cash flow,
analyze investments, and make decisions that could reduce interest payments and increase revenues from financial transactions.
analyze investments, and make decisions that could reduce interest payments and increase revenues from financial transactions.
Finance
12
New cards
- ______ purpose is to pinpoint the people what they’re most likely to purchase or what the organization sells and to promote the appropriate products and services to those people. Also, The system identifies trends in the demand for the company’s products and services
Marketing
13
New cards
- _____ management systems maintain such records, including employees’ pictures, employee status and tax information, and other data that other systems such as payroll may use.
Human Resources
14
New cards
- ______ purpose is to control the inventory in paying suppliers, process customer orders, production schedules, quality assurance, and shipping products.
Manufacturing
15
New cards
Computing paradigms, which are the core of the architecture
It is the process of developing methodical information technology specifications, models, and guidelines using a variety of Information Technology notation processes.
It is the process of developing methodical information technology specifications, models, and guidelines using a variety of Information Technology notation processes.
INFORMATION ARCHITECTURE
16
New cards
Refer to those applications or services that are resident on a server that is
accessible using a Web browser. The only client-side software needed to
access and execute these applications is a Web browser environment.
accessible using a Web browser. The only client-side software needed to
access and execute these applications is a Web browser environment.
WEB-BASED IT ARCHITECTURES
17
New cards
UNIT 2.1: Computer History
1234
18
New cards
known to be the earliest device for computation
consists of three groves in the sand with a maximum of 10 pebbles in each groove
consists of three groves in the sand with a maximum of 10 pebbles in each groove
Sand Tables
19
New cards
derived from the Arabic word ‘abaq’ which means ‘dust’
consists of sliding beads arranged on a rack which has two parts: upper part and lower part
Abacus

20
New cards
a small instrument made of 10 rods on which multiplication table was engraved
enabled to perform multiplication and division
Napier Bones

21
New cards
jointly devised by Edmund Gunter & William Oughtred
based on the principle that actual distances from the starting point of the rule is directly proportional to the logarithm of numbers printed on the rule
Slide Ruler

22
New cards
He invented the first mechanical adding machine called Pascaline (1642
Blaise Pascal

23
New cards
He improved Pascal’s machine
Baron Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz
24
New cards
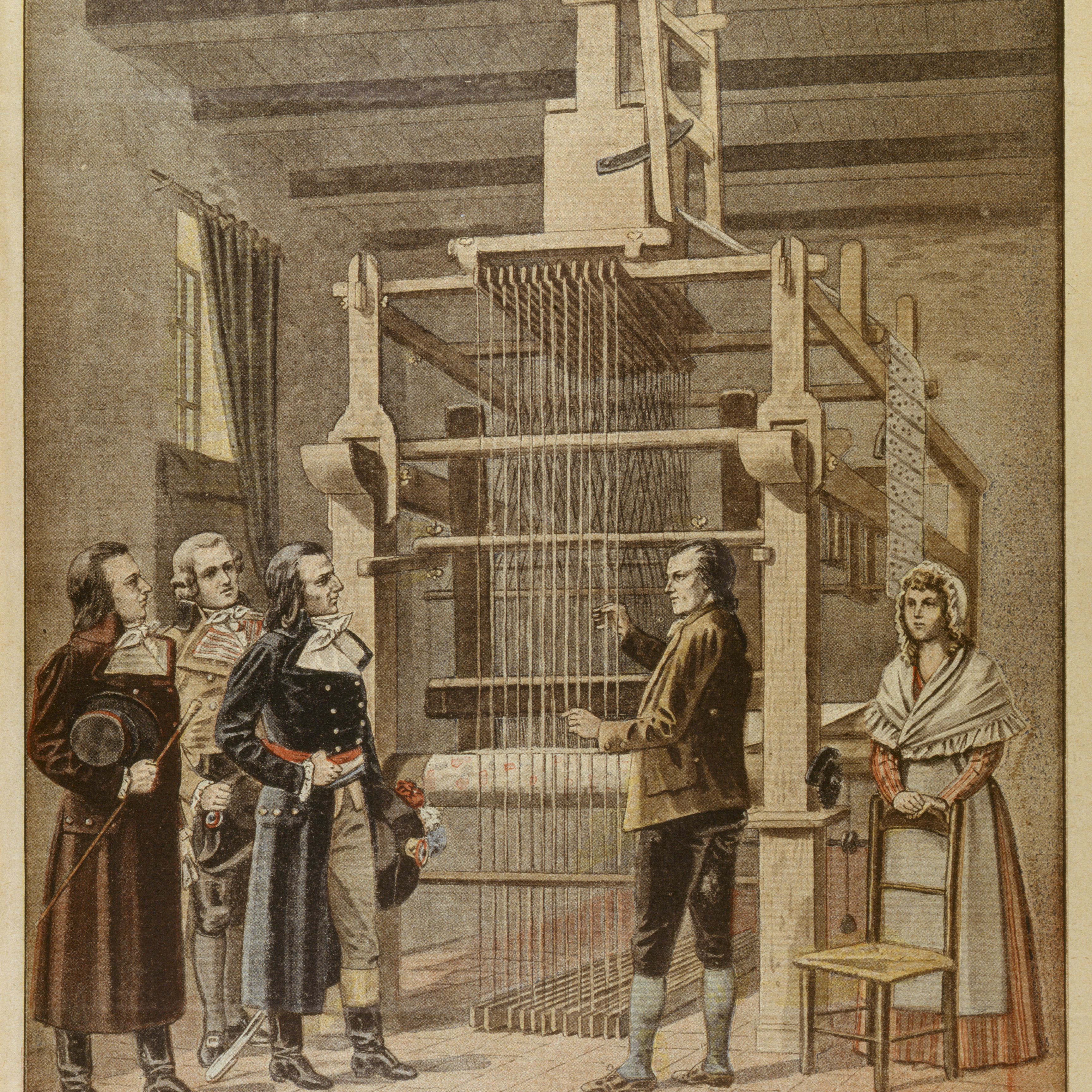
He invented a loom that used punch cards to control patterns into woven cloth (1801)
Joseph Marie Jacquard

25
New cards
Father of Modern Computer
Difference Engine: used to computer table of numbers using naval navigation and can only add & subtract
Analytical Engine: general purpose machine
Charles Babbage
26
New cards
Invented one of the first commercial machines which used a punch card to tabulate and process the data collected
Herman Hollerith

27
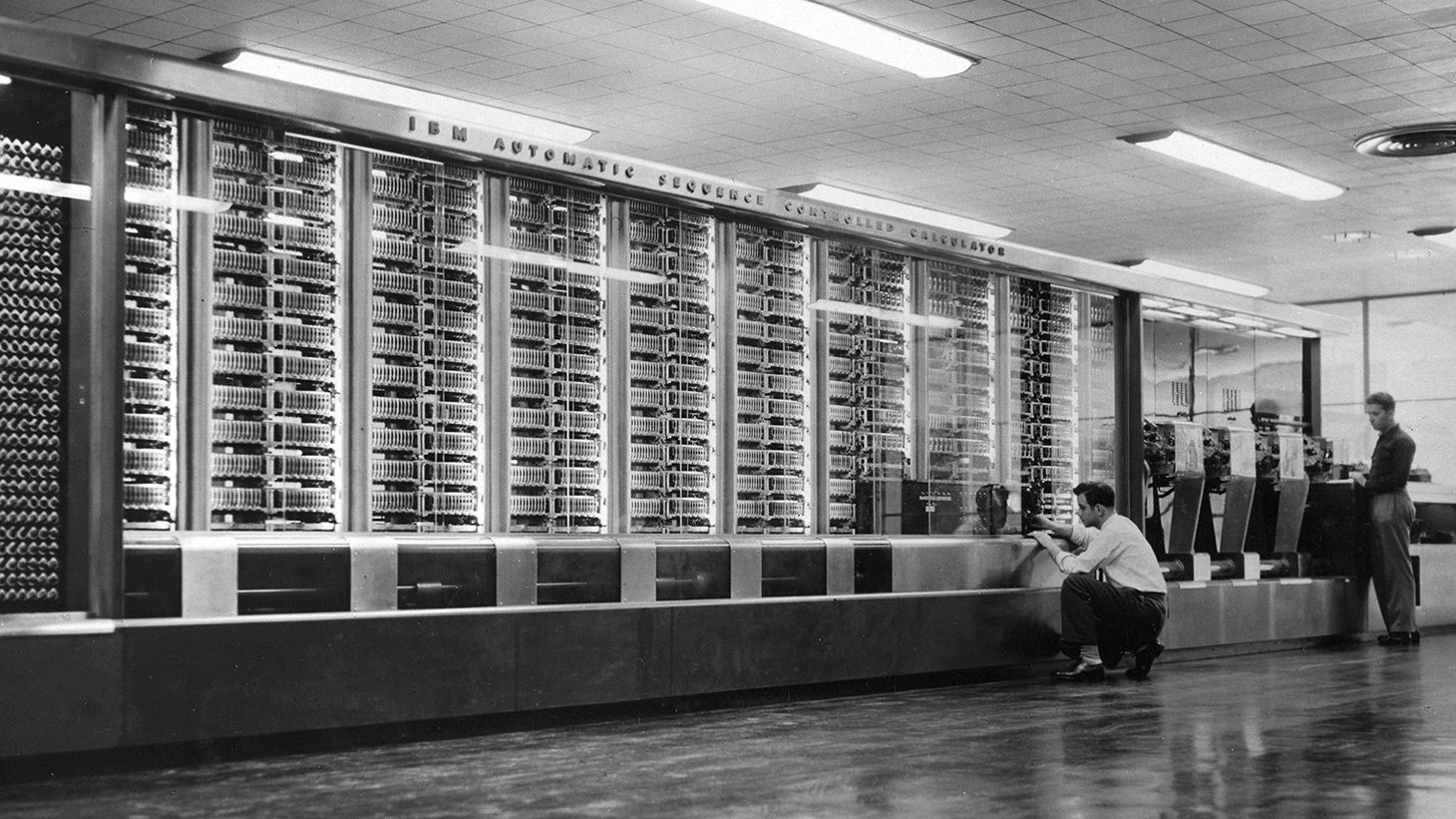
New cards
He led the designing of MARK I (1937); improved Babbage’s machine; His machine was considered the first electronic
machine using thousands of relays.
Howard Aiken

28
New cards
First electronic computing machine, which introduced the idea of binary arithmetic, regenerative memory and logic circuits
AB Computer (Atasoft Berry Computer)
29
New cards
World’s first electronic digital computer used to decode intercepted message
Colossus
30
New cards
Developed a concept of storing a program in memory.
John von Neumann machine
31
New cards
Developed for calculating artillery firing tables
ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer)
32
New cards
First electronic computer to use stored program concept
EDVAC (Electronic Discrete Variable Automatic Computer)
33
New cards
Machine to run the first successful program
EDSAC (Electronic Delay Storage Automatic Computer)
34
New cards
First commercially available computer
First general-purpose computer which was designed to handle both numeric and textual information
UNIVAC (Universal Automatic Computer)
35
New cards
Was invented at Bell Labs in 1947 but did not see widespread use in computers until the late 1950s
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic or assembly language which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words
One of the major developments in this generation includes the progress of machine language to assembly language.
Second-generation computers moved from cryptic binary machine language to symbolic or assembly language which allowed programmers to specify instructions in words
One of the major developments in this generation includes the progress of machine language to assembly language.
Transistor
36
New cards
Was the hallmark of the third generation of computers
The technology allowed dozens of transistors to be mounted on a single chip together with other electronic components.
This generation started using semiconductor memories, microprocessors, and multiprogramming.
Another development was the use of an operating system that allowed machines to run many different programs at once with a central program that monitors and coordinates the computer’s memory
The technology allowed dozens of transistors to be mounted on a single chip together with other electronic components.
This generation started using semiconductor memories, microprocessors, and multiprogramming.
Another development was the use of an operating system that allowed machines to run many different programs at once with a central program that monitors and coordinates the computer’s memory
Integrated Circuits
37
New cards
Family of computers and their peripherals which are mutually compatible and all worked together
IBM System/360 series
38
New cards
Developed by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC)
The first commercially successful minicomputer
PDP 8
39
New cards
Built onto a single piece of silicon, known as chip; about 0.5 cm long and not more than 0.05cm thick
Microprocessor
40
New cards
Built onto a single piece of silicon, known as chip; about 0.5 cm long and not more than 0.05cm thick
Microprocessor
41
New cards
Approximately 180 transistors
Large Scale Integration (LSI)
42
New cards
Approximately 275,000 transistors
Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI)
43
New cards
Developed by MITS (Mirco Instrumentation Telemetry Systems)
One of the first microcomputers
Altair 8800 (1975)
44
New cards
One of the first highly successful mass-produced microcomputer products
Designed by Steve Wozniak of Apple Computer
Apple II
45
New cards
A supercomputer designed, manufactured and marketed by Cray Research
CRAY I
46
New cards
‘Lisa’ stood for ‘Local Integrated Software Architecture
First commercial personal computer to use graphical user interface with 1MB RAM, 12-inch black monitor, 2 5 ¼ floppy disk driver, 5MB of profile hard drive and used Motorola 680000 microprocessor
Apple Lisa (1983)
47
New cards
Computers will use Super Large-Scale Integrated chips
Mega Chips
48
New cards
Computers will use multiple processors and perform parallel processing thereby accessing several instructions at one time and working at the same time
Parallel Processing
49
New cards
A series of related technologies that tries to simulate and reproduce human behavior including thinking, speaking, reasoning.
Artificial Intelligence (AI)
50
New cards
UNIT 2.2: Computer System and
its Components
its Components
2131
51
New cards
- defined as general purpose information processing machine
used to troubleshoot various problems related to data processing
allows users to input, manipulate and store data
a basic, complete and functional computer
used to troubleshoot various problems related to data processing
allows users to input, manipulate and store data
a basic, complete and functional computer
Computer System
52
New cards
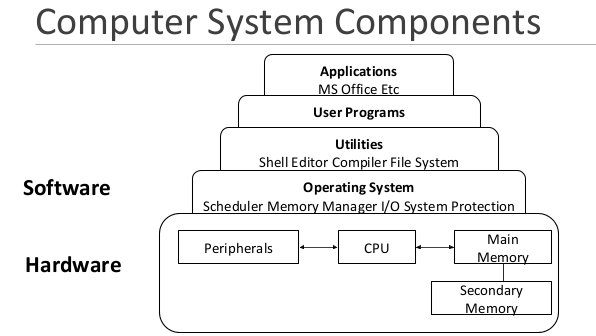
Computer System Components
Two main components:
Two main components:
Hardware - tangible parts
Software – intangible parts: data and programs
Software – intangible parts: data and programs
53
New cards
physical machine, consisting of mechanical parts and electronic circuit
Computer Hardware -
54
New cards
defined as the major component of a computer
also known as the ‘processor’ or the “electronic brain” of the computer
consist of the electronic circuits which are necessary to perform a variety of operations on the data
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
55
New cards
Several major units of a computer hardware
– Central Processing Unit (CPU)
– Main Memory (RAM)
– Secondary Memory (HDD/SSD)
– Peripherals (I/O devices)
– Main Memory (RAM)
– Secondary Memory (HDD/SSD)
– Peripherals (I/O devices)
56
New cards
Central Processing Unit (CPU)
Major components:
Major components:
Arithmetic Logic Unit
Control Unit
Registers
Control Unit
Registers
57
New cards
where data and numerous programs are currently being executed by the CPU are stored
Main Memory (RAM)
58
New cards
provides stable storage for both programs and data in a longer period of time
often referred to as the disk
often referred to as the disk
Secondary Memory
59
New cards
also known as mass storage devices because of their capacity to store relatively large amounts of data and many programs.
Disk drives
60
New cards
used in getting and displaying information
Input/Output Devices
61
New cards
EXAMPLE OF AN INPUT DEVICES
Keyboards
Pointing Devices
Sensors
Card Readers
Remote Control
Pointing Devices
Sensors
Card Readers
Remote Control
62
New cards
EXAMPLE OF AN OUTPUT DEVICES
Printings/Plotters
Monitors
Monitors
63
New cards
Basic Computer Hardware Operations
Input unit
Storage unit
Processing unit
Output unit
Storage unit
Processing unit
Output unit
64
New cards
inputs the data and programs for computer processing
Input unit
65
New cards
stores the input data and programs
Storage unit –
66
New cards
conducts calculations on the input data and controls input unit, storage unit, and output unit
Processing unit –
67
New cards
output the result of computer processing in a certain format
Output unit –
68
New cards
set of computer programs and algorithms that tells the
computer what to do and how to do it.
computer what to do and how to do it.
Computer Software –
69
New cards
Three categories of Computer Software:
System Software
Programming Software
Application Software
Programming Software
Application Software