General and Special Senses
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Eye
The organ of sight that detects light and sends visual signals to the brain.
Pupil
The opening in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
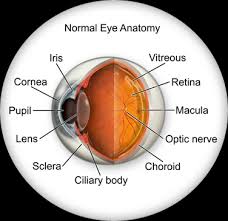
Medial and lateral canthus
The inner (medial) and outer (lateral) corners where the upper and lower eyelids meet.
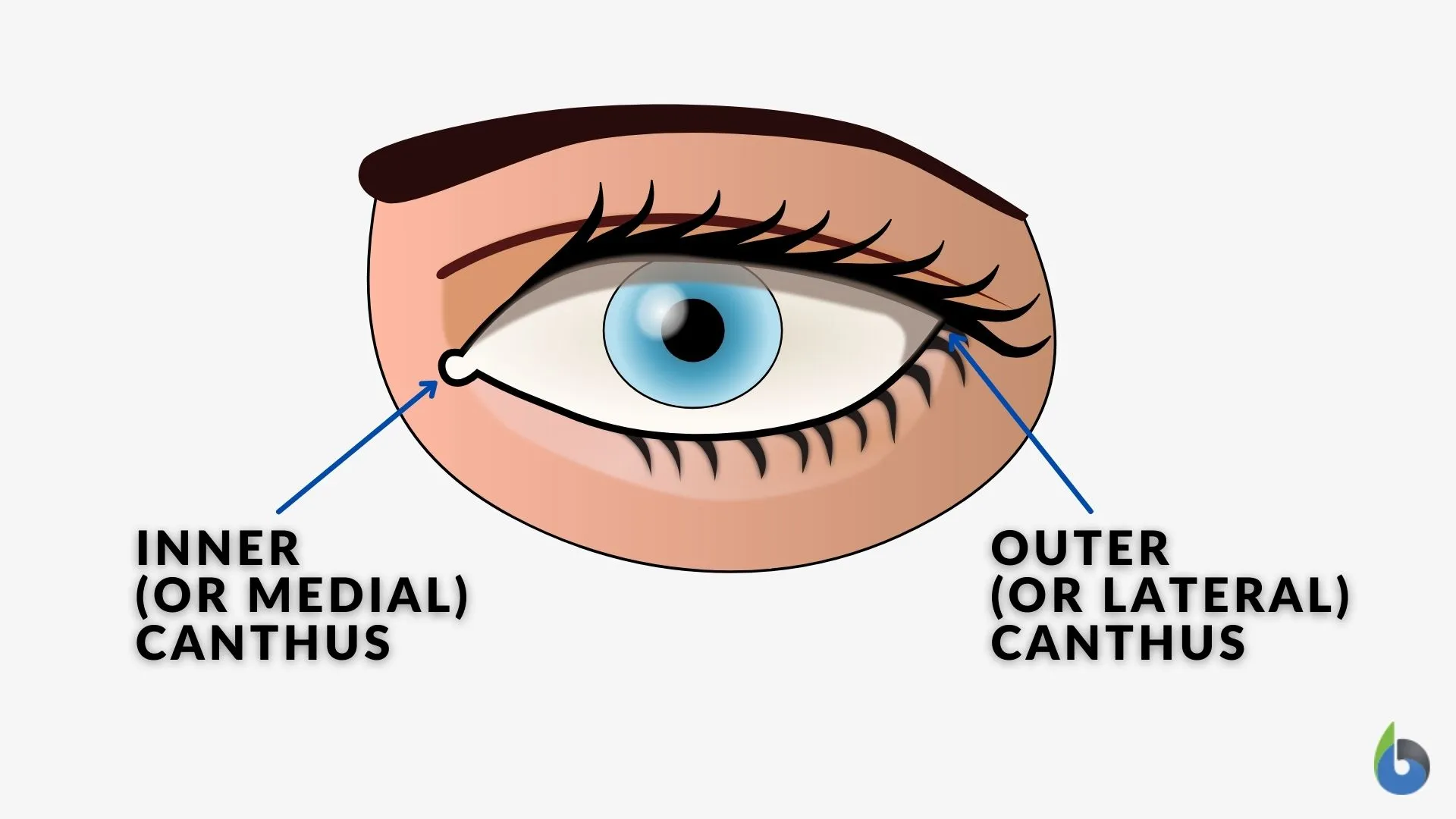
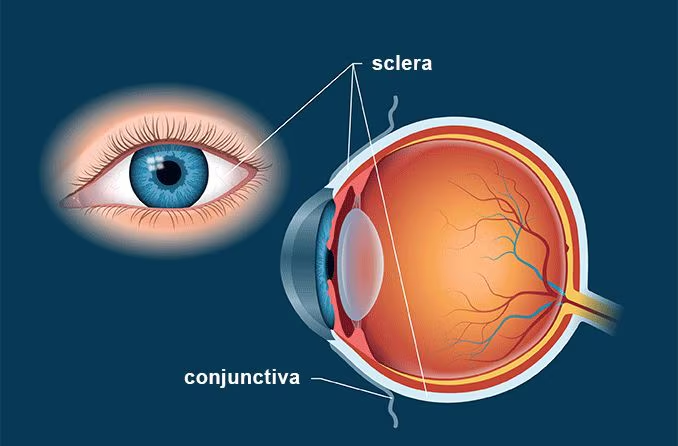
Conjunctiva
A thin, transparent membrane that covers the white of the eye (sclera) and lines the inside of the eyelids.
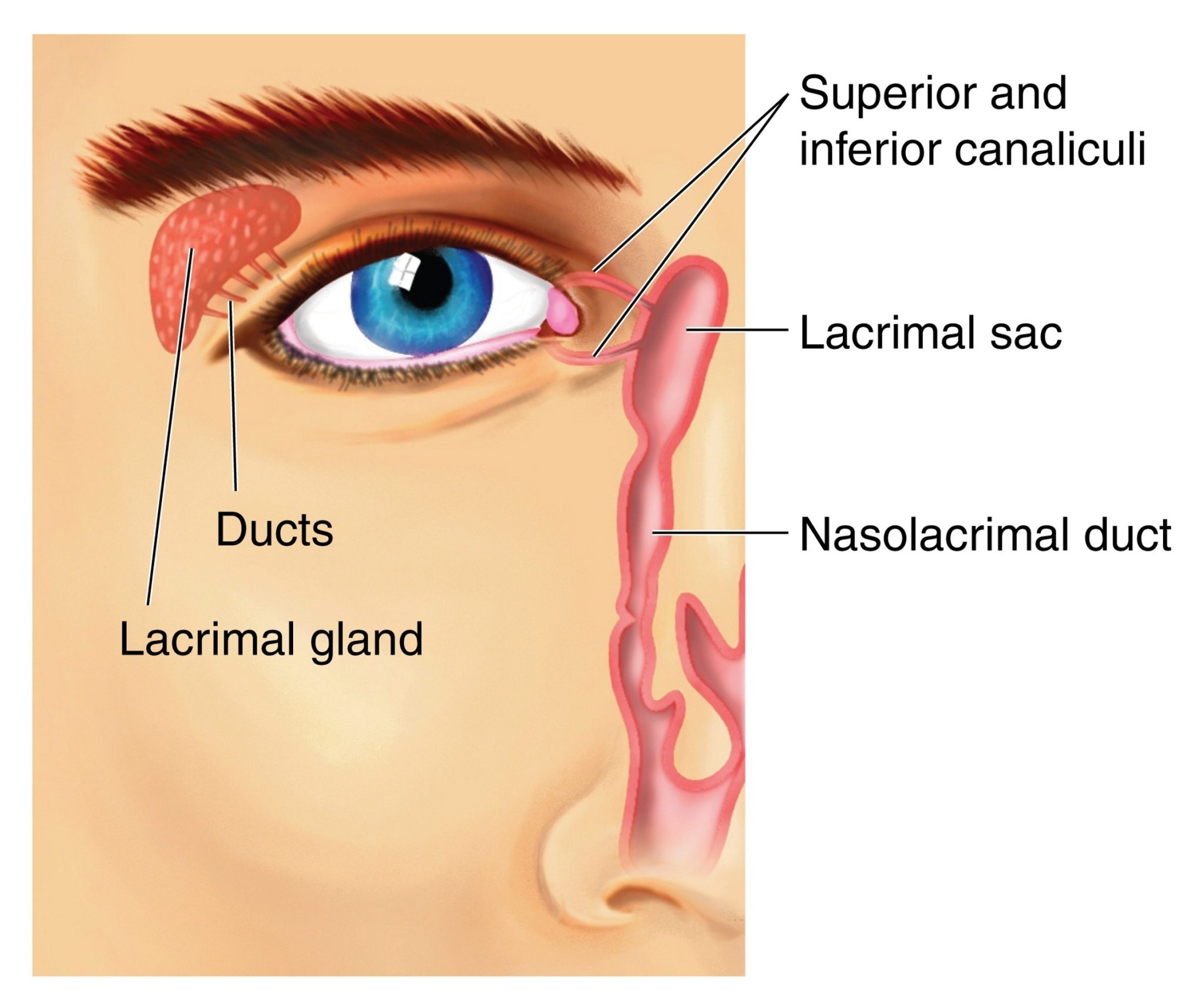
Lacrimal gland
Produces tears that lubricate and protect the surface of the eye.
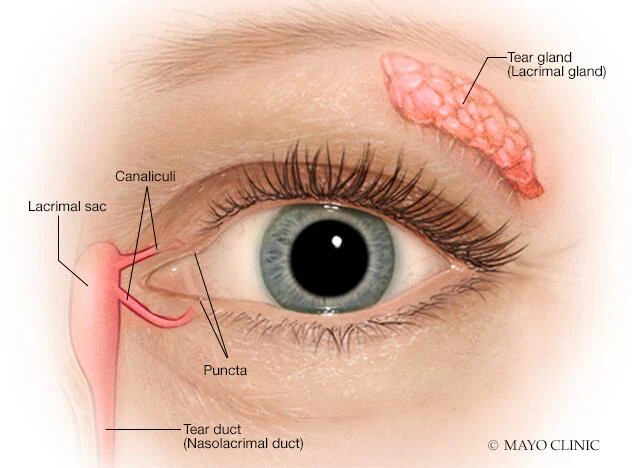
Nasolacrimal duct
Drains tears from the lacrimal sac into the nasal cavity.
Muscles that control eye movement
Extraocular muscles that move the eye in various directions.
Sclera
The white, tough outer layer of the eyeball that provides structure and protection.
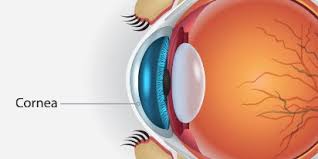
Cornea
The transparent front part of the eye that allows light to enter and helps focus it.
Iris
The colored part of the eye that controls the size of the pupil.
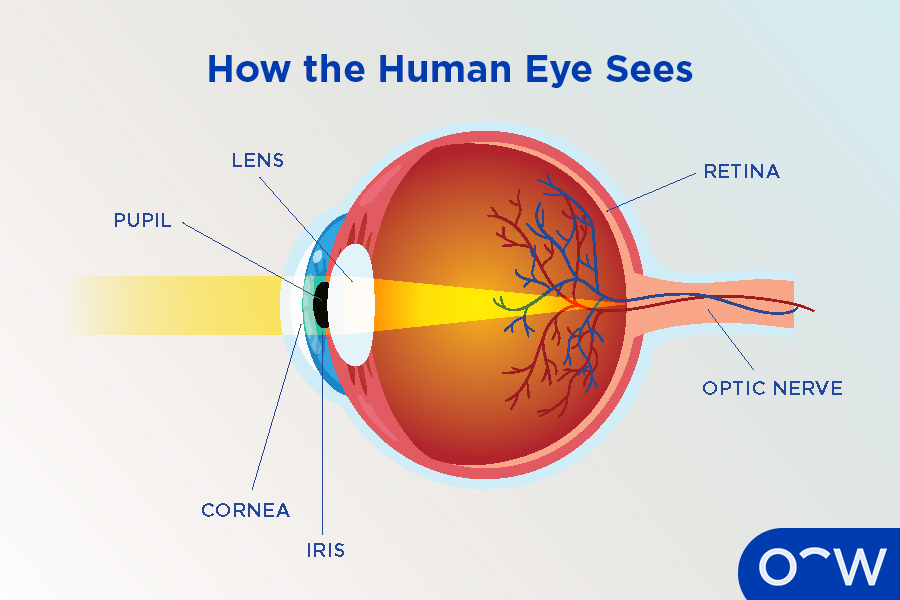
Lens
A transparent, flexible structure behind the pupil that focuses light onto the retina.
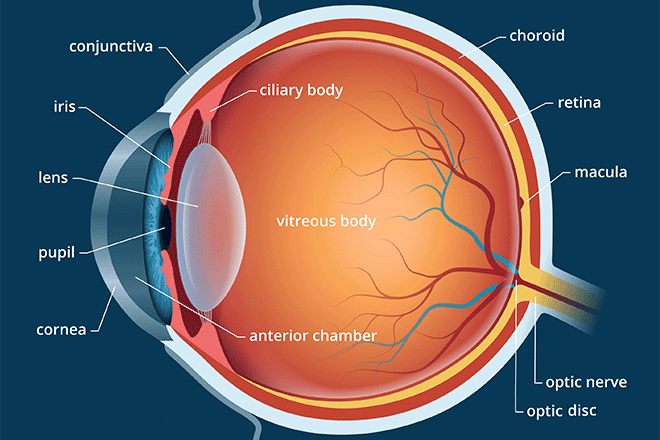
Retina
The light-sensitive layer of tissue at the back of the eye where visual images are formed.
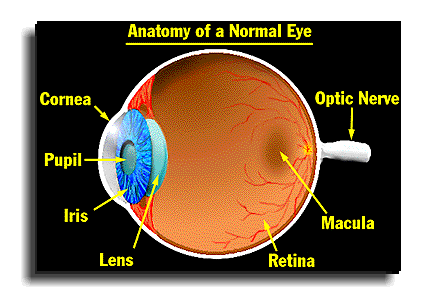
Optic disc
The 'blind spot' where the optic nerve exits the eye; lacks photoreceptors.
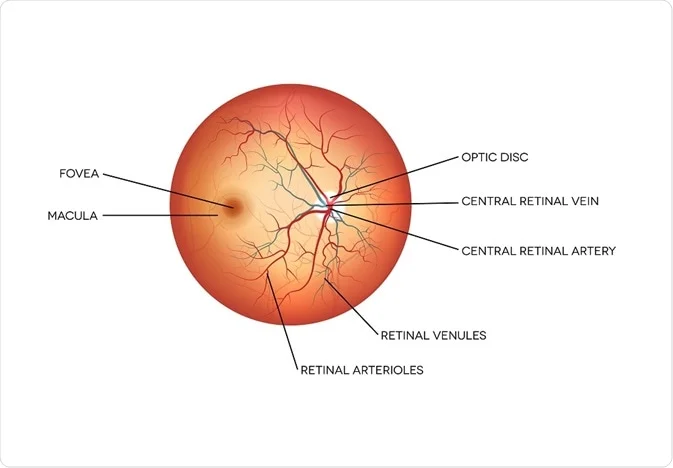
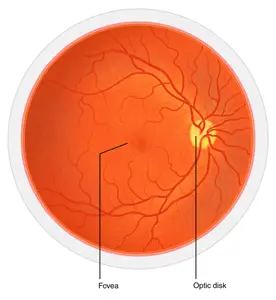
Fovea centralis
A small central pit in the retina packed with cones for sharp central vision.
Auricle
The outer part of the ear that collects and directs sound waves into the auditory canal.
Auditory canal (External acoustic meatus)
The canal that channels sound waves from the auricle to the eardrum.
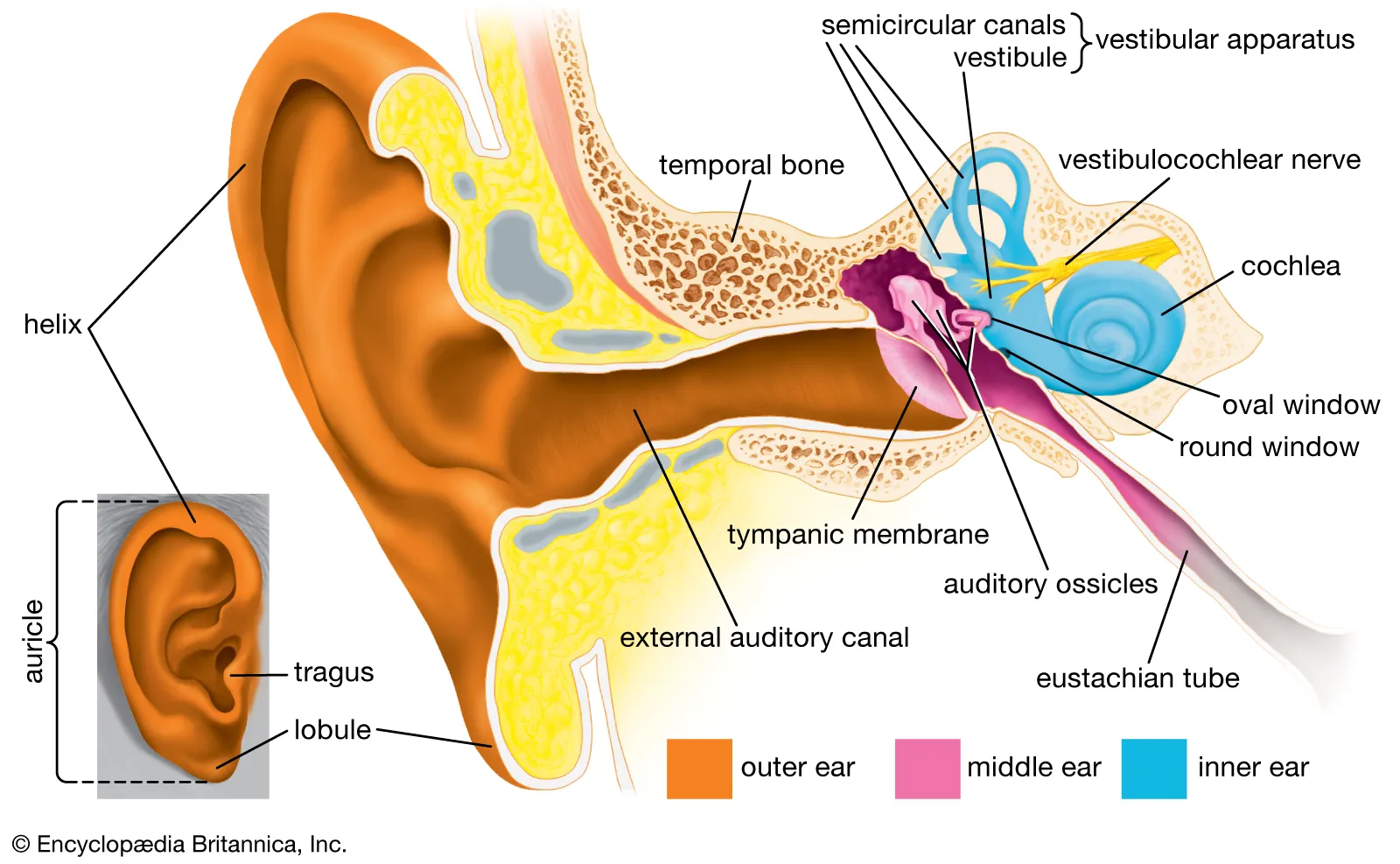
Tympanic membrane
Also known as the eardrum; it vibrates in response to sound waves.
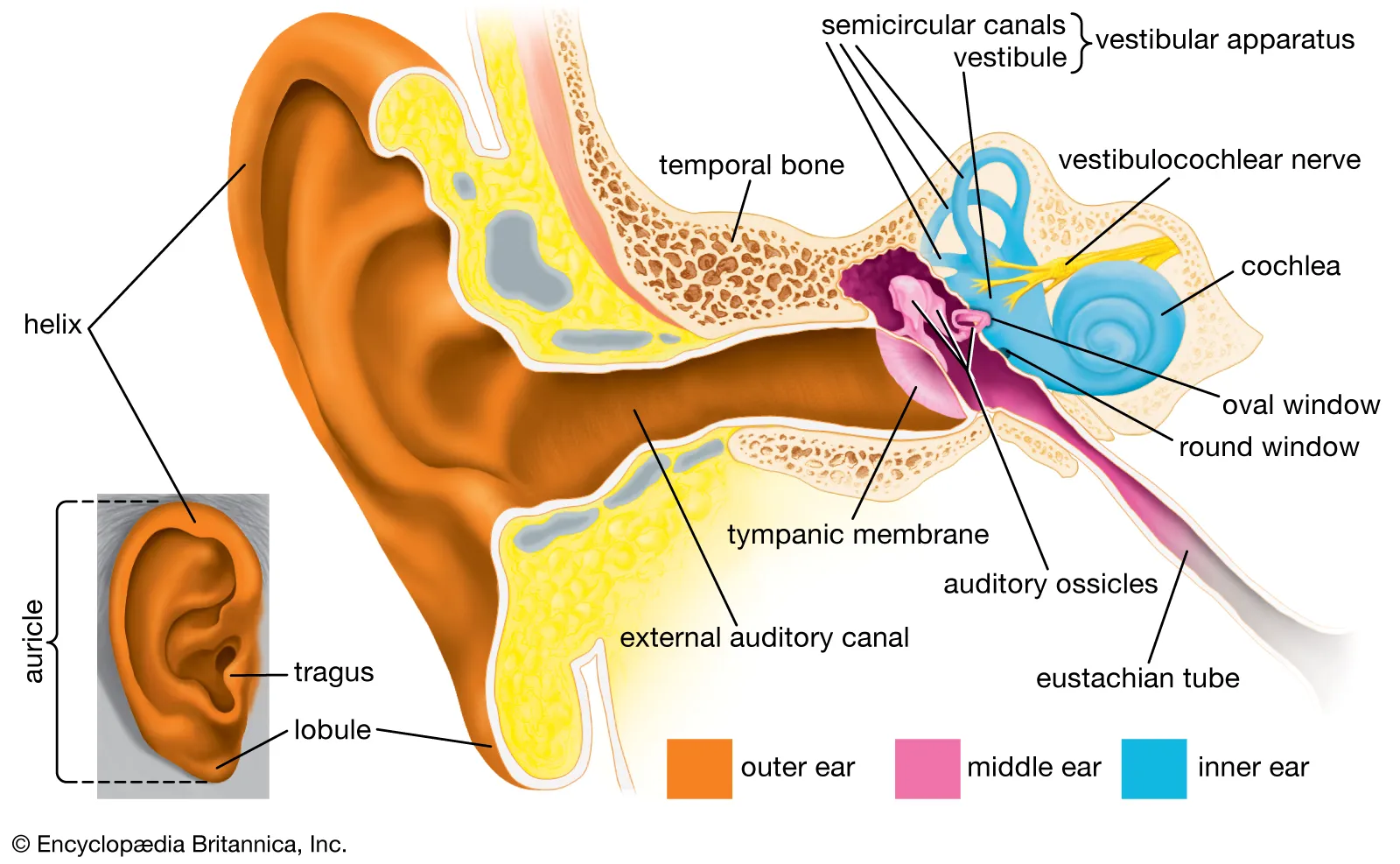
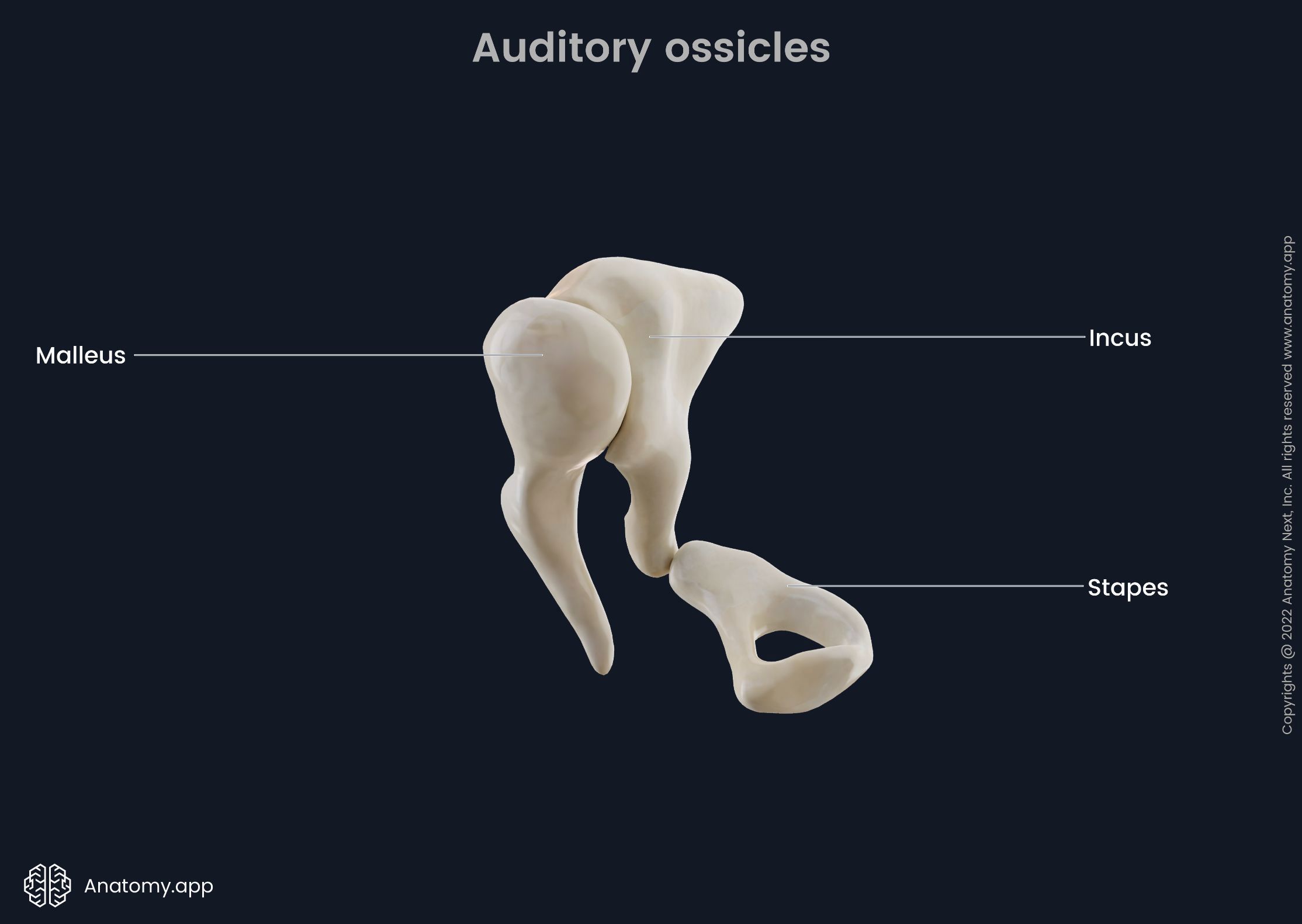
Auditory ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes)
The three small bones in the middle ear that transmit vibrations from the tympanic membrane to the inner ear.
Oval window
A membrane-covered opening that leads from the middle ear to the vestibule of the inner ear.
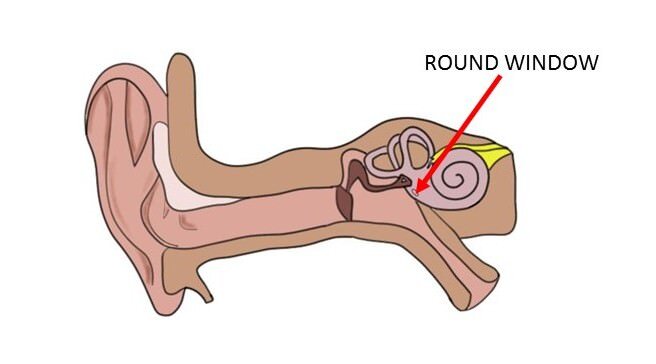
Round window
A membrane-covered opening that allows for movement of fluid within the cochlea.
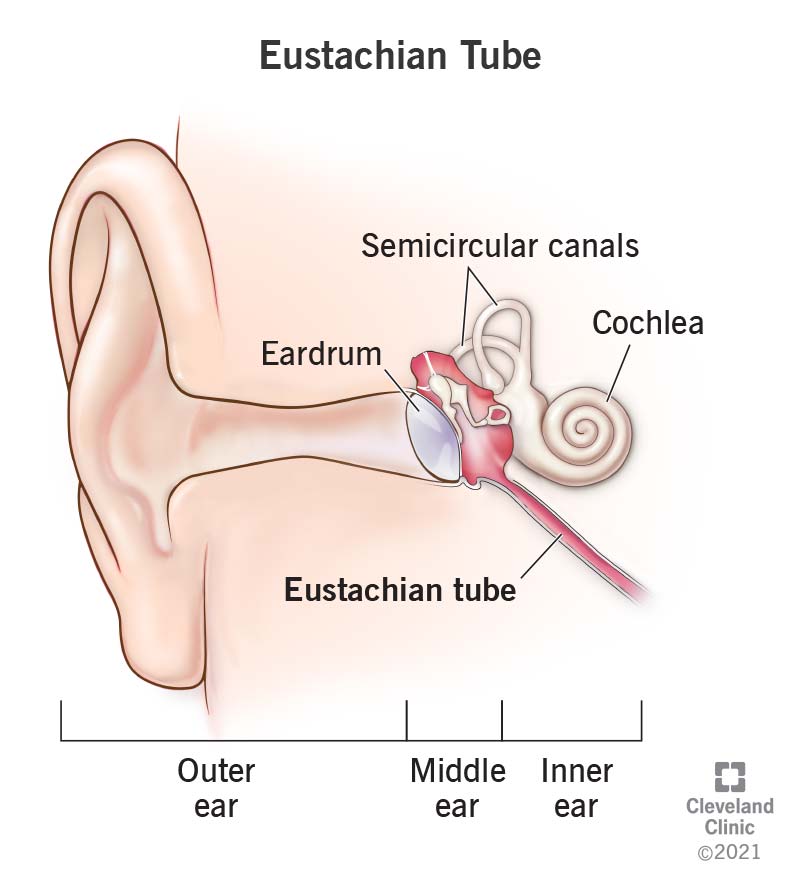
Auditory tube (Eustachian tube)
Connects the middle ear to the throat and helps equalize pressure.
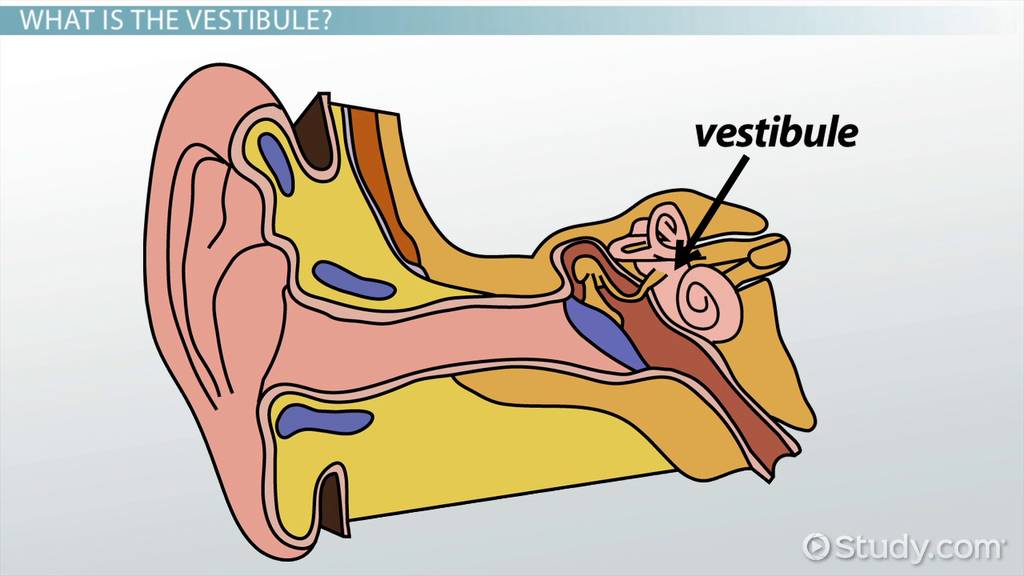
Vestibule
The central part of the bony labyrinth that helps with balance.
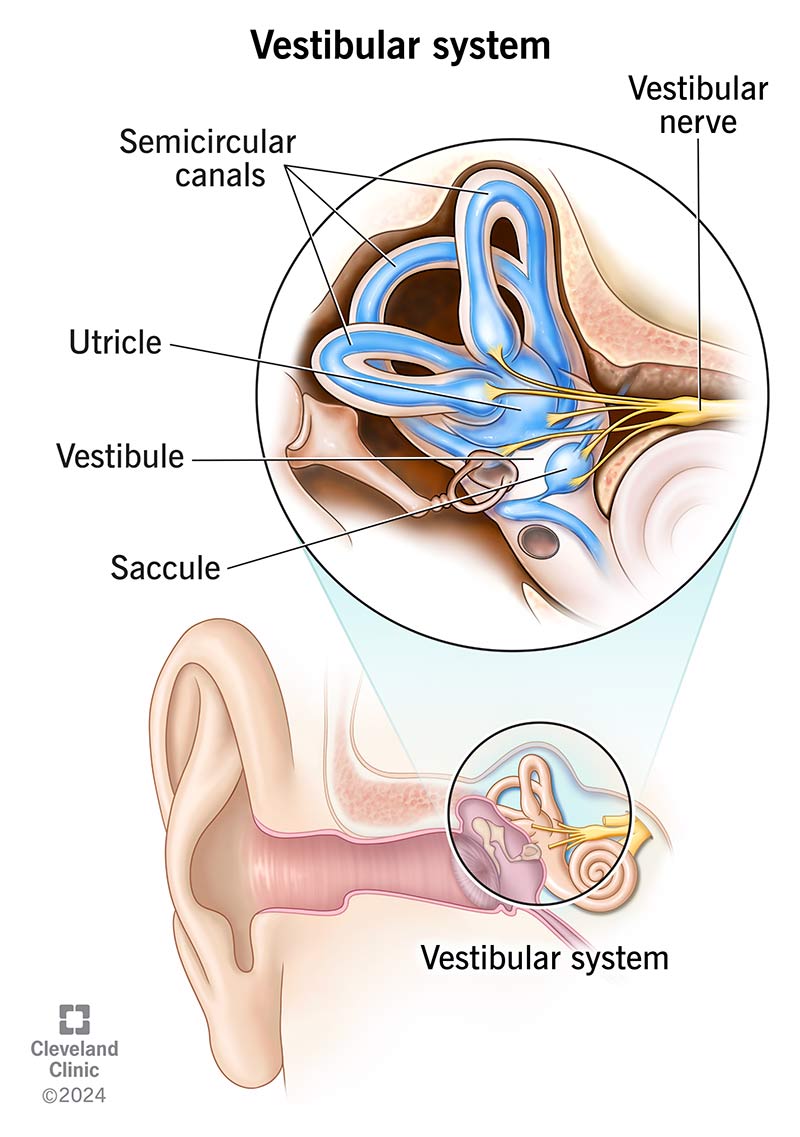
Semicircular canals
Three looped structures that help maintain balance and detect head rotation.
Vestibular duct
The upper chamber of the cochlea filled with perilymph; part of the sound transmission path.
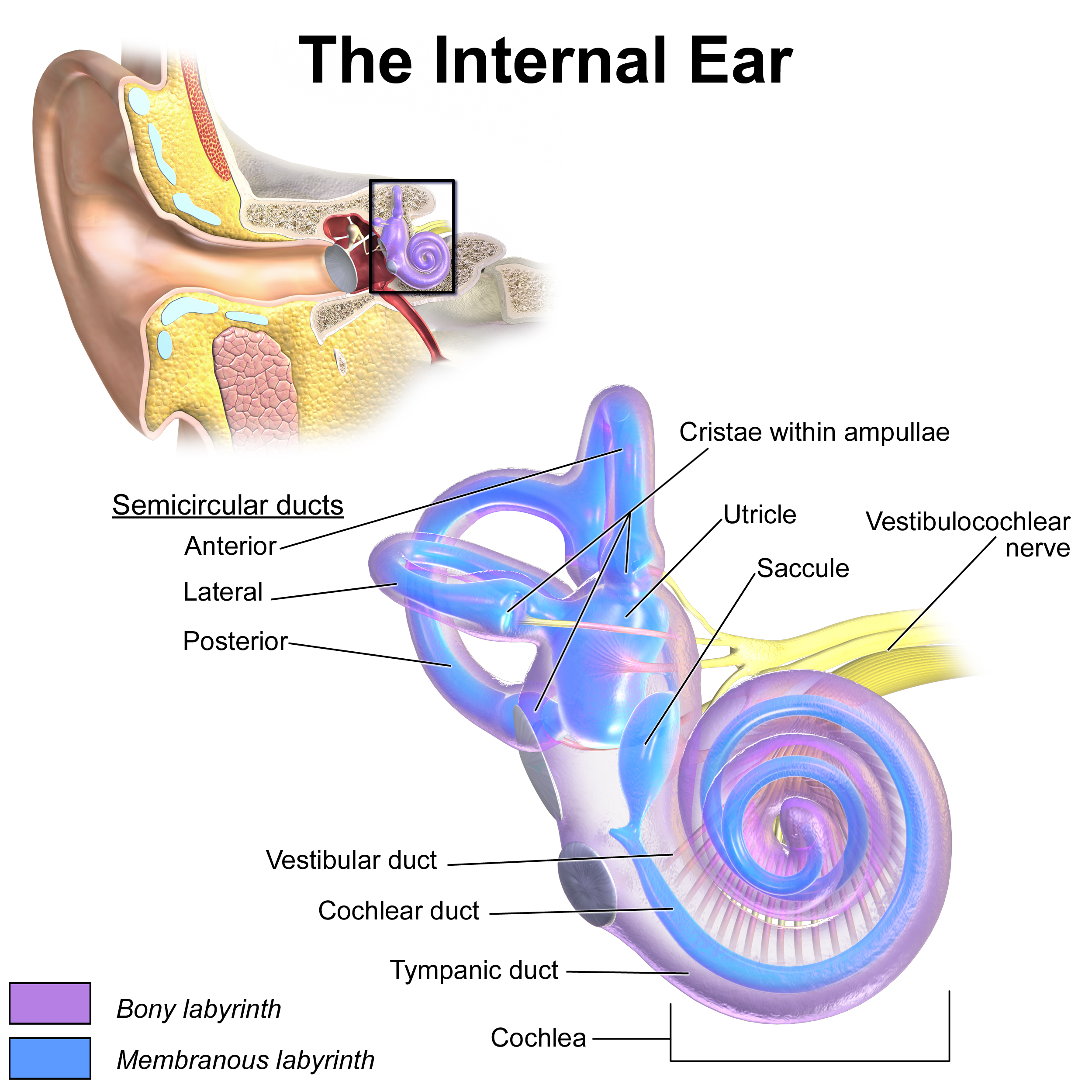
Tympanic duct
The lower chamber of the cochlea, also filled with perilymph.
Cochlear duct
The middle chamber of the cochlea filled with endolymph and contains the organ of Corti (the sensory organ of hearing).