Exercise Nutrition
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
146 Terms
What is the Effect of Creatine in a Sprint exercise
increases peak power during repeated 10 seconds efforts.
Why does Creatine improve Performance?
more PCr = more ATP available = able to exercise at higher intensity for longer. it is due to an increase in muscle phosphocreatine stores. it also dilutes cellular proteins causing protein synthesis.
Chronic Creatine intake and training
regular creatine intake and training enhances muscle growth relative to training alone.
Super- Training Effect
can train harder due to the anabolic effect of creatine. the extra cellular water promotes protein synthesis.
Creatine Side Effects
increases muscle size and body mass (1-2 kg over first few days due to an increase in intracellular water). Creatine draws more water into the cell causing u to gain 2-4 pounds. this is an issue is sports like running where being lighter is an advantage. it makes u bigger (good for football, bad for runners)
What stimulates Glucose uptake into the muscle
Skeletal Muscle Contraction and insulin release
Post-activity Carb ingestion
After a CHO depleting activity, you should consume carbs within 30-60 minutes after. this is because your body is looking to replenish its stores. High carb diet enhances performance
When to use fats vs. Carbs during exercise
carbs allow you to work harder and longer. Athletes need carbs. Higher intensity = need carbs. when u consume more fat, you will burn more fat. if you allow your body to adapt to the high fat diet, your performance is not hindered cuz the high fat diet can be used for low to moderate intensities
Carb Loading Process
6 days before competition, do about 90 minutes of PA, then decrease this everyday leading up to the comp, then doing none the day before the competition. you must also increase your carb intake leading up the comp day. 6 days out, have about 50% of your diet be carbs, this increases on day 4 to 70%. This stays until comp day. This allows the muscle to increase its glycogen stores and hold onto more glycogen in prep for race day.
what does CHO during exercise do?
helps maintain blood sugar and enhance performance
sports drinks during exercise
a glucose polymer sports drink is easier to digest than regular carbs and hits the bloodstream faster. the drink provides glucose just like regular carbs. you need it to replenish your glucose stores fast. It also has electrolytes that will help to replenish fluid loss. At low blood sugar, the liver runs out of glucose to supply the muscle and brain so we need to have a sports drink to replenish that to allow us to keep going harder for longer
gender differences in metabolism
women often under eat relative to energy expenditure leading to health issues and performances issues. Women have a better ability to down regulate their metabolism compared to men. Women basically slow their metabolism so they can go longer without food. intense training is seen by the female body as starvation so it down regulates metabolism so u can live.
RED-S
the ability of women to down regulate their metabolism causes RED-S (relative energy deficiency syndrome) it stops ur period
Roles of Nutrients
provide energy
provide the energy u need to survive
breakdown body tissue to survive
micronutrients are important b/c they facilitate the processes that allow us to use energy from macros by making ATP regeneration more efficient
promote growth and development
need amino acids to make protein and therefore build muscle mass
stimulating the muscle while taking protein will stimulate muscle building
regulate metabolism
What are the components of Screening for Athletes
medical check up
MSK screening
physiological testing
exercise testing for strength, power, endurance and VO2
psychological testing
performance levels could be low cuz of lack of confidence
nutritional screening
most informative when compared with:
dietary evaluation
biochemical testing of blood or urine
body comp analysis
clinical assessment of appearance or well-being
How is Diet Assessed?
Retrospective Techniques - not recommended
dietary history or recall
interviewer asks athlete to describe their normal food intake.
last several week is more representative of real intake compared to last 24 hrs
food frequency questionnaire
checklist of food consumed
quick and easy
limitations
memory isn’t reliable. They also may change their answers to please the interviewers
prospective techniques - recommended
analysis of duplicate meals
most accurate but very expensive - have to analyze their portions with exactly
food records
best practical option
3-7 days of tracking food
use computerized food analysis data base
over 3 days of tracking u typically get lazy
include 2 weekdays and 1 weekend
limitations
may change their eating habits to please the interviewer
inaccuracies can occur due to missing foods in database
typically these underestimate intake (by up to 20%)
RNI
recommended nutrient intake: amount of nutrient necessary to meet the needs of essentially all of the population (CANADA)
RDA
Recommended Dietary Allowance: amount of nutrients necessary to meet the needs of essentially all of the population. 2 standard deviations on either side
AI
Adequate Intake: estimates based on observation of healthy individuals
used when there isn’t enough data to give RDA
more of an estimate
UL
upper limit: intake above this will cause health issues
EAR
Estimated Average Requirement: amount of a nutrient that would meet the needs of 50% of the population
problematic b/c it only uses the mean and there may be ppl who need higher requirements that if they follow this will not be meeting their dietary needs
Ergogenic Aid
A procedure or treatment that enhances performance. includes shoes, training, drugs, and imagery
functional food
a food that has health benefits
Neutraceutical
a food component that has or may have pharmaceutical benefits (e.g., antioxidants)
Explain the Balance Technique
it is the classic method used to determine dietary recommendations. it measures the amount of nutrients that is ingested vs the amount that is excreted from all routes. positive balance (anabolic) = ingestion>excretion, used to grow. negative balance (catabolic) = excretion>ingestion, used to lose weight. if you are an athlete, u wanna be in positive balance. most anabolic phase in childhood, second is in puberty. but you can still be in anabolic as an adult when building muscle or gaining weight.
Essential Nutrient
Indispensable nutrients. cannot be made in the body and therefore need tone ingested or deficiency will occur.
Conditionally Essential
Nutrient that is sometimes essential depending on needs at current time. Histamine is an example that is only needed sometimes in periods of growth
Non essential Nutrients
Dispensable. Can be made in the body from other compounds.
What is exercise (sports) nutrition
relatively new area of study. it is exercise (non-competitive PA) vs Sport (competitive)
what are the two areas of interest for exercise nutrition
nutrient requirements
how does regular exercise affect food requirements?
Regular exercise usually increase food requirements
performance Effects
can supplementation with food or food components enhance performance
more creatine than u eat normally will enhance performance, as well as carbs and amino acids
important questions to ask when evaluating a claim?
is there any underlying rationale for how the supplement works?
good data?
is the person selling it using it gain money?
is it too good to be true?
Epidemiological Research
determines whether a relationship exists between two variables but DOES NOT determine causation - only shows correlation
2 types of epidemiological research
retrospective
study past behaviour to see if it affects someone’s current life
Prospective
study things that happen now and see if it affects their future
look at what they are eating now and follow them for a year and see if they get heart disease now or in the next decade
Experimental Research
involves an intervention. necessary for developing a cause-effect relationship. potential cause is manipulated (individual variable). smaller sample sizes and more labour intensive. often times you can’t compare age groups tho
considerations when evaluating experimental research
is there a good rationale for the proposed effect?
were the methods appropriate?
bias?
control of other factors affecting results
number and type of subjects
sufficient dosage
harmful side effects
validity of tests used
data analysis
have the results been replicated by others?
contradictory results?
confirm or deny your own findings
New revisions in Canada’s New food guide
no more rainbow (sad)
serving sizes gone because they don’t apply to everyone
increase fibre
lower meat intake and lower sat fat
made simple statements as advice to ppl
plenty of fruits and vegs
eat plant protein foods
healthy fat, not sat fat
limit processed foods
make water ur drink of choice
choose whole grain foods
it decreased the CHO recommendations b/c Canadians have too many carbs
dairy is no longer its own food group, it is now within protein
What is the food exchange system
originally for diabetes
6 food groups - similar in group energy and macro content
diff in macro and energy content of different exchanges (i.e., veg = 25 cal, milk = 120 cal)
also, different fat content (varies in milk and meat fat %)
fat has over double as many cals as carbs and protein
low fat diet is the way to lose body fat - less carbs (less cals)
ppl tend to eat on a time-restricted energy diet - intermittent fasting
body adapts to new diet over first few days
example of food exchange system
125 ml of OJ, 17 small grapes, and 1 medium apple are all 60 cals,15 CHO and trace amounts of protein and fat
what are the 8 key nutrients
protein, vitamin A, thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin C, iron, calcium
What is nutrient density?
we want more nutrient dense foods. ex. 250 ml of pop has 25g of CHO and 100 cals. 250 ml of skim milk has 90 cals and 8 g of protein, 0g of fat, 12 g of CHO, and calcium, iron, vitamin A and Thiamin, riboflavin, niacin and vitamin c. Skim milk is much more nutrient dense
Different types of Vegetarianism
vegan (most restrictive)
no animal products
Ovovegetarian
eat eggs, no other animal products
lactovegetarian
eat milk products
ovolactovegetarian
eat milk and egg products
Pescovegetarian
eat fish
semivegetarian
eat chicken/fish but no red meat
Concerns with Plant-Based Diet: Vitamin B12, D
vitamin B12 is only found naturally in animal products, unless the food is fortified. Need to supplement Vitamin D all the time, especially in the winter!
Concerns with plant-based diet: Minerals
minerals are not absorbed as well from plant based foods because the plants create compounds that bind the minerals together (iron, zinc, calcium). could supplement iron
Concerns with Plant-based diet: proteins
unlikely to be deficient unless u get under 60g/day. complete protein = animal products. incomplete protein = plant-based.
What are complete vs. incomplete proteins
a complete protein is found in animal products and contain all the essential amino acids. An incomplete protein is found in plants. In an incomplete protein, one or more of the essential amino acids is not present.
what are complementary proteins
complementary proteins are those that you consume within the same day and NOT the same meal that together will allow you to get all the essential amino acids for that day. ex. beans and grains eaten in the same day, or veggies, milk, meat, fish, chicken, and eggs.
how many essential amino acids are there and what are they
9 of them. Methionine, Lysine, Phenylalanine, tryptophan, threonine, leucine, valine, histidine
What are the benefits of a plant-based diet
low total fat
low total saturated fat
high in fibre
low in calories (energy)
high antioxidant vitamins (C & E)
high in phytochemicals which may have positive health benefits
which foods do NOT require a food label
fresh fruits
fresh veggies
raw meat and poultry
raw seafood
those prepared/processed in store (bakery items, salads)
those with very few nutrients (tea, coffee)
alcoholic beverages
what does a Canadian food label contain
serving size
core list (CHO, fat, protein, and breakdown of each)
vitamin, minerals (% of daily intake)
ingredient list (descending order by mass)
health claims
What does Health Canada forbid the use of in foods as of 2018
Partially Hydrogenated Oils (PHO)
what does it mean if a food item is “Free” of something
“free” claims indicate the amount of a nutrient of energy is nutritionally insignificant
What does the nutrient content claim “light” mean
it is for substances that are low in fat, and low In calories, but NOT light in colour
what can u confidently make health claims about on food labels?
you can only make health claims that relate to a scientifically established relationship between diet and risk reduction. for example, sodium, potassium and high BP. OR, veggies and fruit reducing the risk of some types of cancer
food intolerance
an adverse rxn but not life threatening. ex. lactose intolerance
food allergy
allergic rxn to a food component that can result in swelling, rash, itching skin, tearing, and even breathing difficulties. anaphylactic shock and death (in minutes). allergies are usually to proteins in milk, eggs, fish, nuts, and wheat.
Food poisoning
nausea, vomiting, diarrhea caused by bacteria in food (salmonella, e.coli, etc. much of this is due to poor food handling.
food additives
things that are added to food. they are generally safe but make sure they are approved
food processing
can reduce nutrient density or introduce bacteria
what are food supplements
they are poorly regulated. they are man-made, isolated from a food or are chemically made. they are used significantly to enhance performance. not all of them are safe tho. some of them that claim to do stuff don’t actually do that stuff. some supplements are banned by certain organizations.
explain the PCr fuel available to muscles
PCr is for immediate use. it has a small supply of about 3-5 seconds of intense exercise. PCr is formed oxidatively (using O2) from foods that have been eaten previously. It can provide energy anaerobically as well. if you take creatine in large amounts, you can phosphorylate it, then u can increase your power
Anaerobic Glycolysis
provides ATP quickly but also produces lactic acid which will lower the pH of the muscle cell causing discomfort and ultimately process shutdown. it uses only CHO in the form of glucose. without NAD+, anaerobic glycolysis will shut down.
Ox Phos
provides more ATP than the other systems but it does so at a much slower rate because it is limited by the ability to deliver and use O2. It is heavily affected but training, if you are trained, you can deliver more O2 to the muscle and therefore provide more ATP than you could before. you DO NOT form lactic acid
explain glycolysis briefly
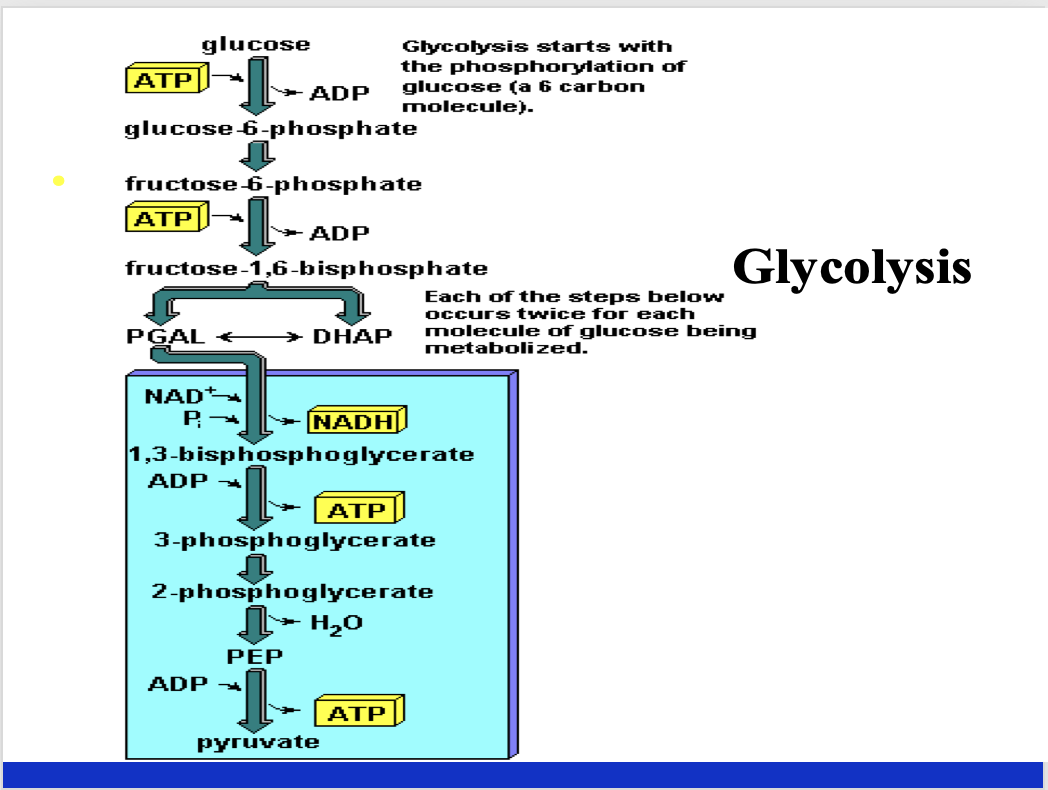
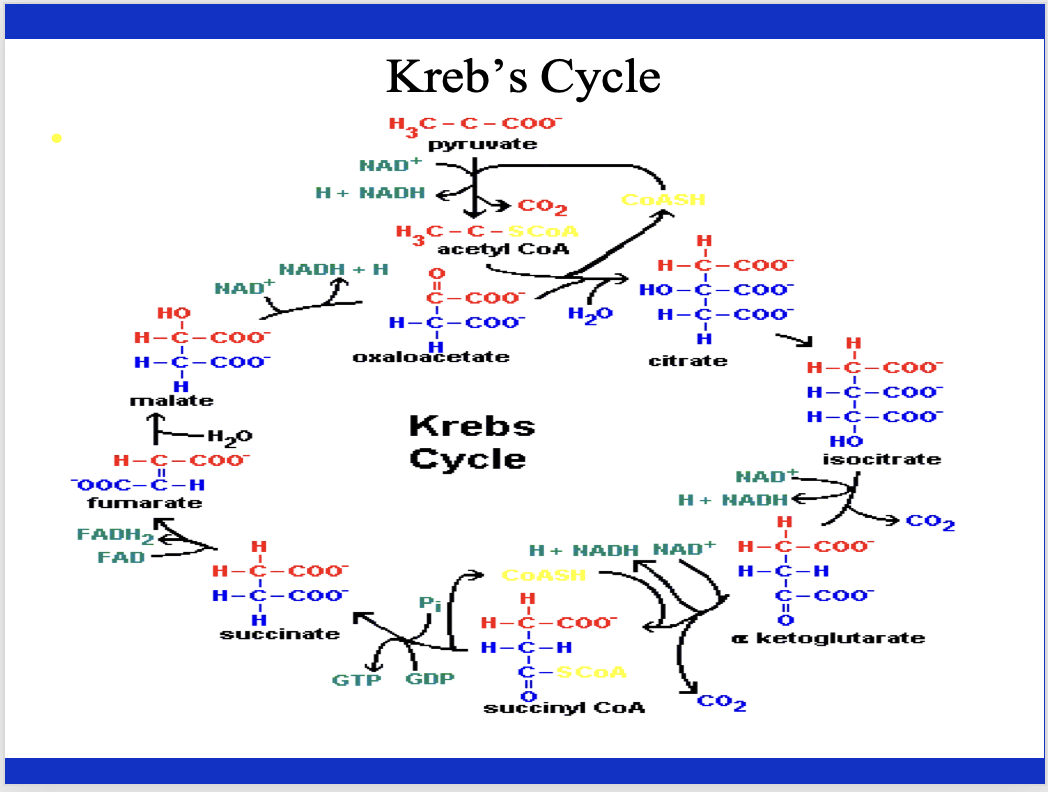
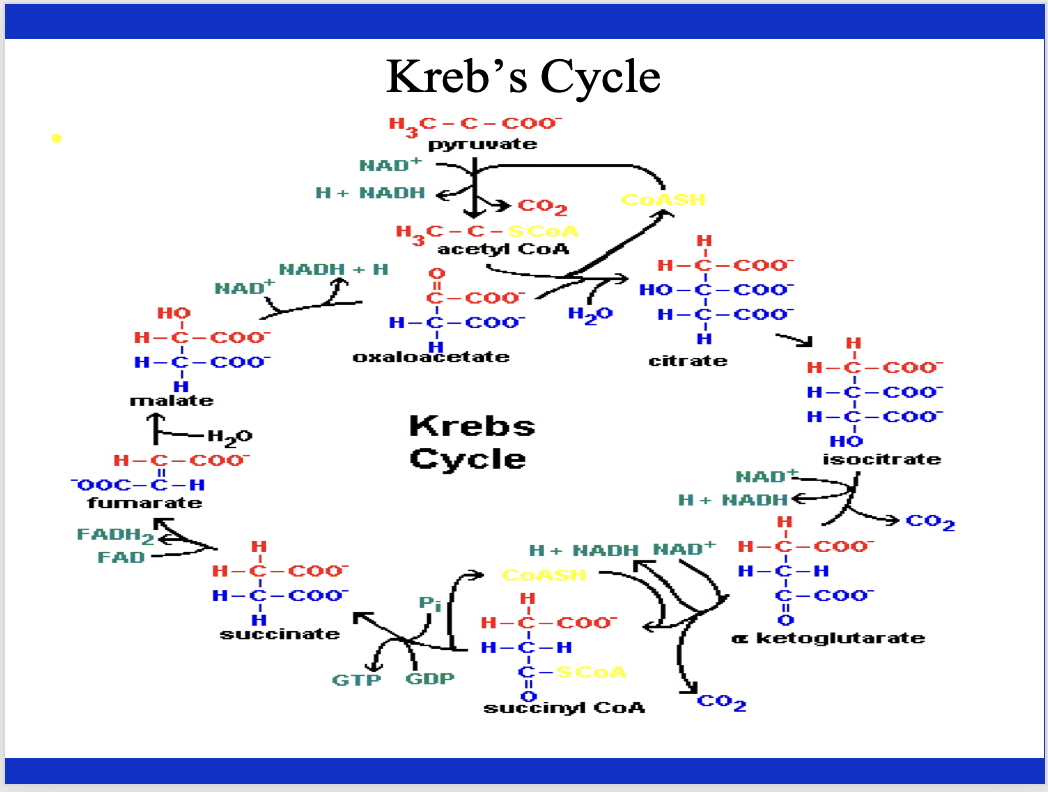
Explain the Krebs cycle briefly. What are some key things associated with the Krebs cycle.
you do not form lactate because O2 is not limited. Key thing: Krebs cycle is a CYCLE! it recreates itself. at several places there is the formation of NADH (3 places for each time around), a very similar compound of FADH2, both of which produce a lot of ATP.
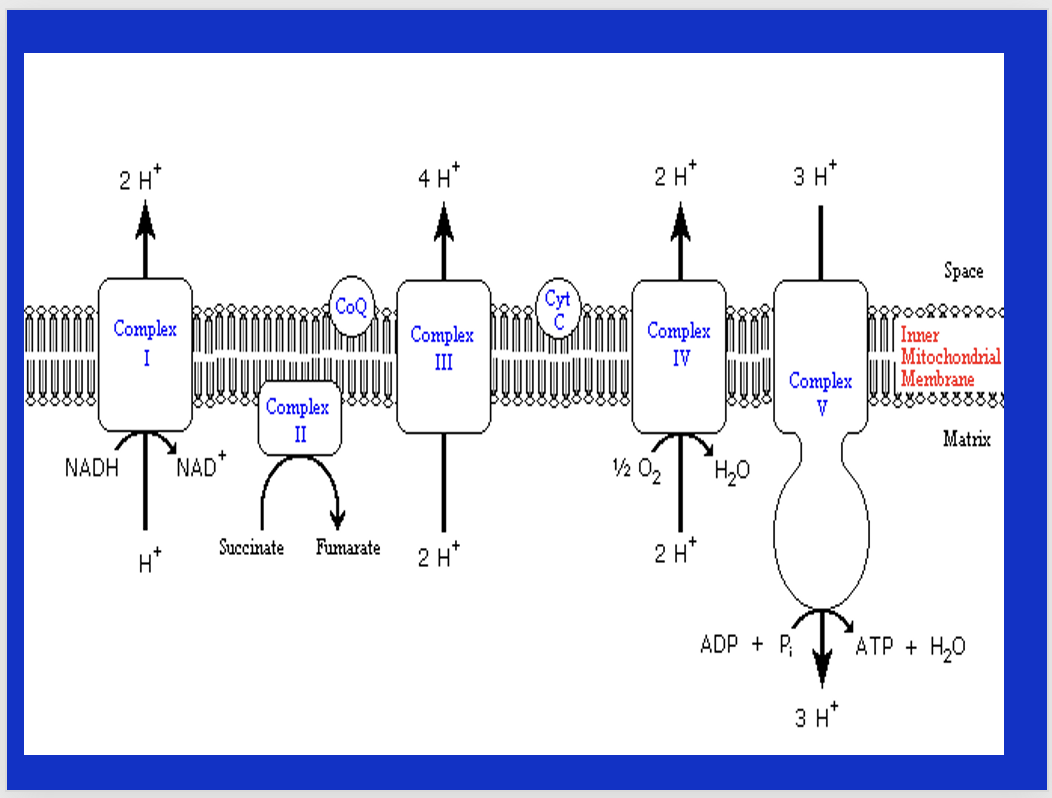
Explain the ETC
occurs in the matrix of the mito. it is a series of protein complexes. at complex 1, NADH gives up an H+ and electrons to become NAD+. H+ moves thru complexes until it reaches the ultimate acceptor of electron at O2. The product of the ETC is water! CO2 is produced (we exhale it). the proton gradient allows ATP synthase to spin and create ATP and water. the ETC can become more efficient with training but it 80% determined by genetics.
Digestion
complex compounds (food) becomes simple compounds (nutrients). Anabolic Process
Absorption
nutrients → stored as complex compounds for later use (ex. simple sugars stored as glycogen). anabolic process
Catabolic processes in the body include:
Mobilizing stored energy (breaking down complex compounds to simple) to fuel muscle contraction. includes ATP, PCR stores, anaerobic glycolysis, and Ox Phos
metabolism
all physical and chemical transformations in the body. it includes anabolism and catabolism
anabolic
synthesis during growth or training (overload leads to increased skeletal muscle mass and strength with strength training)
catabolic
the formation of ATP from phosphogens, or breakdown of glycogen to glucose to lactic acid and ATP, or glycogen, fat, and/or protein to CO2, H2O and ATP
what is growth
anabolism > catabolism
metabolic rate
it is the measure of how rapidly the body is using its stored energy. when it is expressed for one day it is called the Total Daily Energy Expenditure (TDEE).
what is metabolism determined by
resting energy expenditure
food intake
physical activity
what is RMR or REE
RMR is resting metabolic rate. REE is resting energy expenditure. They are both the basal functioning and a small increment due to previous PA. Typically RMR is measure. RMR exceeds BMR by about 10%. RMR = 1kcal/kg/hr.
what is RMR effected by:
muscle mass
age
gender
fitness
weight loss
low energy diet
hormones
caffeine
smoking
environmental temperature
RMR for men vs. women
men have more muscle mass. women need more excess fat and energy to support pregnancy. men are also typically more fit. therefore mens RMR is typically slightly higher.
explain the thermic effect of exercise (TEE)
it varies significantly between ppl (can be 15-30% of TDEE but near 0 in sedentary and as high as 50% in ultra-endurance athletes). it is measured as litres of O2 (1L = 5kcals), METs (10-20x RMR with aerobic exercise), or estimated from HR, Ve, onset of blood lactate accumulation, and perceived exertion. TEE increases due to PA
fuel use and fatigue is determined by:
Exercise intensity and exercise duration
Low intensity exercise
can sustain for many hours. Fat is the primary fuel source due to lots of stores, fatigue comes from hypoglycemias (low blood sugar) and dehydration
moderate to heavy exercise
30-90 min continuous or 5-15 min intermittent. CHO is used for fuel. fatigue is due to glycogen depletion, hypoglycemia, and dehydration.
high intensity
sustain for a few min. exclusively carbs for fuel. fatigue occurs long before carb depletion due to low pH in the muscle
Max intensity exercise
can only last a few seconds. fatigue due to PCr depletion. you are only using ATP and PCr, no carbs.
what is a carb (CHO)
it is an organic compound that is made of carbons, hydrogen, and oxygen. there are simple sugars, and complex carbs, and glycogen
what are simple sugars
disaccharides and monosaccharides. disaccharides include maltose (glucose+glucose), Lactose (glucose + galactose), Sucrose (glucose + fructose). monosaccharides include Glucose, Fructose and Galactose.
what are complex carbs
these are starches and are 3 or more glucose molecules combined.
Oligosaccharide = 3-9 glucose molecules.
Polysaccharides are 10+ glucose molecules.
glucose polymers or maltodextrin are short (10-20 glucose).
but starches or fibre or glycogen are thousands of glucose molecules.
Starch is amylopectin and is digested and absorbed rapidly.
Amylose is another example, but it is digested and absorbed slowly.
last kind of complex carbs are dietary fibre. it is a polysaccharide that are resistant to digestive enzymes, they increase satiety and reduce CAD and colon cancer.
glycogen
complex chain of glucose
found in animals
12 layers of glycogen - each one has a protein in the center.
Glycemic Index (GI)
numerical system ranking foods based on the rise in circulating blood sugar (rate of entry into the blood) (do not use when trying to lose weight.)
it is better than simple vs. complex carbs.
ranking system
70 or more = high index
56-69 = mid
<55 = low index
it assess the rate at which glucose enters the blood after you eat a CHO
assumes 50g of CHO per serving
it does NOT consider how much CHO is in a serving of food
Glycemic Load (best classification)
assesses the actual impact of CHO consumption. it assesses glucose entry speed into blood and amount of CHO in a serving (GI x grams of CHO per serving)
20 or more = high
11-19 = mid
10 or less = low
popcorn and watermelon have low GL but high GI
limitation: both GI and GL are altered when consumed with other food
what is a normal blood glucose
80-100mg/ml of blood or 4.4-5.5 mM
what happens when insulin is secreted
when insulin is secreted from beta cells of pancreas which promotes glucose uptake by cells (including fat cells)
what happens when blood glucose drops
the liver will release more glucose to maintain blood glucose as long as it has enough stores to support that
where is CHO stored In the body
blood, liver, muscle, gluconeogenesis (formation of new glucose from glycogen stores)
functions of CHO
major energy source (Brain and CNS, exercising muscle especially at high intensities
combined with fat or protein to form cell membranes
form smaller CHO compounds which are critical for muscle growth
Carb Loading (Super-composition)
important because body CHO stores can be limited and depleted in one exercise bout
it is beneficial for continuous exercise at moderate to high intensity.
Carb loading procedure
6 days before competition, do about 90 minutes of exercise and gradually decrease this over the time period leading up to the comp. DO NO EXERCISE the day before.
6 days before competition, make sure ur diet consists of 50% carbs. on days 4, increase this to 70%.
this procedure allows your body to store excess glycogen for the race day
how much CHO is enough?
DO NOT EXPRESS IN % of total intake
CHO loading = at least 5g/kg closer to 8-10 g/kg if possible
mass will increase with CHO loading by about 1kg
females may be less able to carb load due to less reliance on CHO during exercise. immediate post exercise ingestion is more critical in women
more training = more sensitive to glucose
timing of CHO intake before exercise
1-4 hours prior to exercise
4-5g/kg
in many forms (fluid containing simple sugars or glucose polymers (maltodextrin) solutions or solid CHO
under 1 hour before
1-2g/kg
glucose polymers or low GI CHO - absorbed slower (must be low GI or there may be tummy issues
under 10 min to exercise
0.8-0.85g/kg of glucose polymer solution (40-50% solution)
timing of CHO during exercise
30-60g/hr (1g/min) of 6-8% solution. mixture of a drink that is glucose and fructose is better because they use different transporters and there is no backlog.
what is the CHO oxidation rate during exercise
initially, as u consume more carbs, there is a linear effect, but with complex carbs, it doesn’t go up as much (levels off at 1g/min)
max rate u can consume more carbs and oxidize CHO is 1g/min
can consume more CHO is consumed as glucose and fructose since they have different transporters. but always consume more glucose than fructose cuz too much fructose causes tummy issues.
timing of CHO intake after exercise
over 5-6g/kg within a critical window. the critical window is 30-120 min after exercise, especially for woman. liquid CHO before leaving. 1.2 g/kg/hr
more CHO is synthesized when u eat CHO within the first 30 min after exercise. you store more glycogen the closer after exercise you eat