Chapter 25: Seedless Plants
1/74
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BSC2011C Fall '25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
75 Terms
Why do aquatic plants have it “easy”?
No desiccation, no structural support needed, protection from UV rays, gametes are transported through water and gametes/zygotes aren’t threatened with desiccation.
What are some advantages to terrestrial living?
Abundant sunlight, abundant CO2, no competition, no predators.
What are some disadvantages to terrestrial living?
Threat of desiccation, UV ray harm, need of structural support, reproduction is water dependent and zygote is water dependent.
What were the first terrestrial plant strategies?
Lived near water/humidity, tolerance of desiccation, remained small, developed mechanism against UV rays, and used natural selection.
What does sporopollenin do?
Protects spores/pollen from desiccation.
What is the alternation of generations life cycle?
Describes the life cycle of organisms that have multicellular diploid and haploid life stages;
sporophyte stage → makes spores
gametophyte stage → makes gametes
What does the apical meristem in roots and shoots do?
Allows vertical growth
What does the waxy cuticle on leaves and stem do?
Prevents desiccation
What does lignin in vascular tissues do?
Provides structural support
What are spores’ cell walls made of?
Sporopollenin
In humans, what kind of cellular body are our diploid and haploid stages?
Diploid Stage — Multicellular
Haploid stage — Unicellular
In plants, what kind of cellular body are our diploid and haploid stages?
Both are multicellular
In seedless plants, what does the haploid gametophyte stage produce?
Haploid gametes through mitosis
In seedless plants, what does the diploid sporophyte stage produce?
Haploid spores through meiosis
For seedless plants, what is the diploid stage?
Sporophyte
For nonvascular seedless plants, what stage is dependent on another stage?
Sporophyte stage is dependent on the gametophyte (n) stage
What does the sporophyte produce?
Sporangia
What is the sporangium structure made up of?
Sporocyte cells

Name the top and bottom structures
Sporophyte; Gametophyte
What do spores germinate into?
New haploid gametophyte plants
What are homosporous sporophytes?
Sporophytes that only make one type of spore
What do the spores from homosporous sporophytes germinate into?
Monoecious gametophyte
Are seedless plants mostly homosporous or heterosporous?
Mostly homosporous
What are heterosporous sporophytes?
Make two different types of spores
What are microspores?
Male spores
What are megaspores?
Female spores
What do microspores develop into?
Male gametophytes which only make male gametes
What do megaspores develop into?
Female gametophytes which only make female gametes
Are all seed plants heterosporous or homosporous?
Heterosporous
For seedless plants, what is the haploid stage?
Gametophyte
What does the gametophyte stage in seedless plants produce?
Gametangia through mitosis.
What is gametangia?
Structures that make haploid gametes through mitosis.
What are male gametangium called?
Antheridium
What do antheridium produce?
Sperm
How are sperm able to swim in water?
Flagella
What is the female gametangium called?
Archegonium
What do archegonium produce?
Eggs
After the fusing of the sperm and egg, where does the diploid sporophyte develop?
Inside the archegonium
What is meristem tissue made up of?
Undifferentiated cells
What special characteristic do apical meristems have?
They can develop into any type of cell
Where are apical meristems located?
Shoot tip and root tip of plants
How do apical meristems help the plant?
Allow for vertical upward growth and vertical downward growth
How does upward growth of the shoot help the plant?
Gives plants access to the sun
How does vertical downward growth of the root help the plant?
Gives plants access to water and minerals
How does wax in the epidermal tissue help the plant?
Prevents water loss and covers the surface of leaves and stem.
What are nonvascular seedless plants called?
Bryophytes
What type of plants are the most similar to the earliest terrestrial plants?
Bryophytes
What are nonvascular plants?
Contain no conductive tissue to transport water and products of photosynthesis
How do water and glucose move in nonvascular plants?
Diffusion
What is the dominant stage in bryophytes?
Gametophyte haploid stage
In bryophytes, what is the dependent stage?
Sporophyte diploid stage
What are the three types of bryophytes?
Liverworts, hornworts, mosses
What is the bryophyte structure?
Nonvascular, thallus and rhizoids, very small, water-dependent fertilization, dominant gametophyte stage
What do sporophytes do to gametophytes in bryophytes?
Remain attached to and nutritionally dependent on the gametophyte
Where do gametangia grow from (in bryophytes)?
Thallus
How do archegonia/antheridia produce eggs/sperm?
Mitosis
What does fertilization in a bryophyte result in?
Diploid zygote
Where do diploid zygotes grow in bryophytes?
Archegonia (sporophyte stage)
What do sporangia produce?
Sporangia produce haploid spores via meiosis
What is the dominant stage in vascular seedless plants?
Sporophyte diploid stage
In vascular seedless plants, what stage is dependent?
Gametophyte stage is dependent on sporophyte stage
How do conductive vascular tissue help the plant?
Allows the plant to transport water, food, minerals and nutrients, and allows plants to grow tall
What does lignin in the xylem do for the plant?
Provides strength and structural support
How do roots in vascular seedless plants help the plant?
Anchors the plant and allows it to absorb water and nutrients from soil
How do leaves help vascular seedless plants?
Increased surface area for photosynthesis
What are microphylls?
Spine-shaped leaf with one unbranched vascular vein

What are megaphylls?
Large leaf with unbranched vascular system
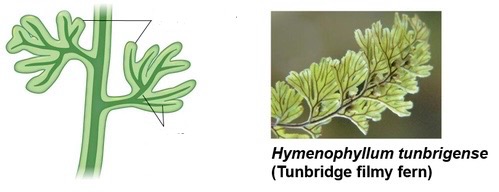
What are sporophylls?
Modified leaves with sporangia
What do sporangia contain?
Sori and strobili
What are sori?
Clusters underneath the leaf of a fern sporophyll
What are strobili?
Cone-like structures formed from sporophylls
What are examples of vascular seedless plants?
Lycopodiophyte and Monilophytes
In vascular seedless plants, how do male gametes move?
They swim, fertilization is water-dependent
Zygotes in vascular seedless plants are…
independent and dominant
Spores in VSPs germinate to what?
Haploid gametophytes