Ch 10: axial skeleton - muscle and joint
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
Actions of the trapezius
All: scapular retraction. Upper/lower: upward rotation. Upper: elevation. Lower: depression
Actions of lats
GH adduction, extension, internal rotation, horizontal adduction
Actions of Rhomboids
scapular retraction, elevation, downward rotation
Actions of levator scapulae
scapular elevation
Actions of serratus anterior
scapular protraction, upward rotation
True or False: the erector spinae group is responsible for gross movements of the spine
true: the ES group crosses many segments of the spine
What movment does bilateral contraction of the erector spinae group produce?
trunk, neck, and head extension, anterior pelvic tilt
What movement does unilateral contraction of the erector spinae produce?
iliocostalis is most effective lateral flexor, longissimus and iliocostalis ipsilaterally rotates the head and neck
Which erector spinae muscle has the largest internal moment arm?
iliocostalis because it is furthest away from the spine
True or False: the transversospinal muscles are responsible for gross movements of the spine?
False: they do not cross as many segments, leading to more controlled movements and functional stabilization
What muscles are included in the transversospinal group?
semispinalis, multifidi, rotatores
What is the bilateral action of the transversospinal muscles?
extension
What is the unilateral actions of the transversospinal muscles
lateral flexion, contralateral rotation
What muscles are included in the short segmental group?
interspinalis and intertransversarius
Why is the short segmental group responsible for fine motor control of the axial skeleton?
highly segment, each individual muscle crosses one IV junction, high density of muscle spindles = better proprioception
What is the bilateral action of the short segmental group?
extension
What is the unilateral action of the intertransversarius?
lateral flexion
What are the muscles of the anterior lateral trunk?
rectus abdominis, external obliques, internal obliques, transversus abdominis
Which abdominal muscle has the smallest cross sectional area?
rectus abdominis
Which abdominal muscle has the largest cross sectional area?
internal obliques
What is the bilateral action of the rectus abdominis, external/internal oblique?
reduce the distance between xiphoid and pubis symphysis in order to produce trunk flexion or posterior pelvic tilt
What is the unilateral action of the rectus abdominis, external/internal oblique?
lateral flexion and rotation
If the trunk rotates to the right, which oblique is responsible for ipsilateral rotation?
internal oblique
Actions of the iliopsoas?
hip flexion and anterior pelvic tilt
Bilateral action of quadratus lumborum?
extension of lumbar spine
unilateral action of quadratus lumborum?
lateral flexion of lumbar spine
What are intrinsic core stabilizers?
short, deep, segmented muscles
What are extrinsic core stabilizers?
longer attachments outside of vertebral column
Examples of intrinsic trunk stabilizers?
transversospinal group, short segmental group
Examples of extrinsic trunk stabilizers?
erector spinae, quadratus lumborum, abdominals, psoas
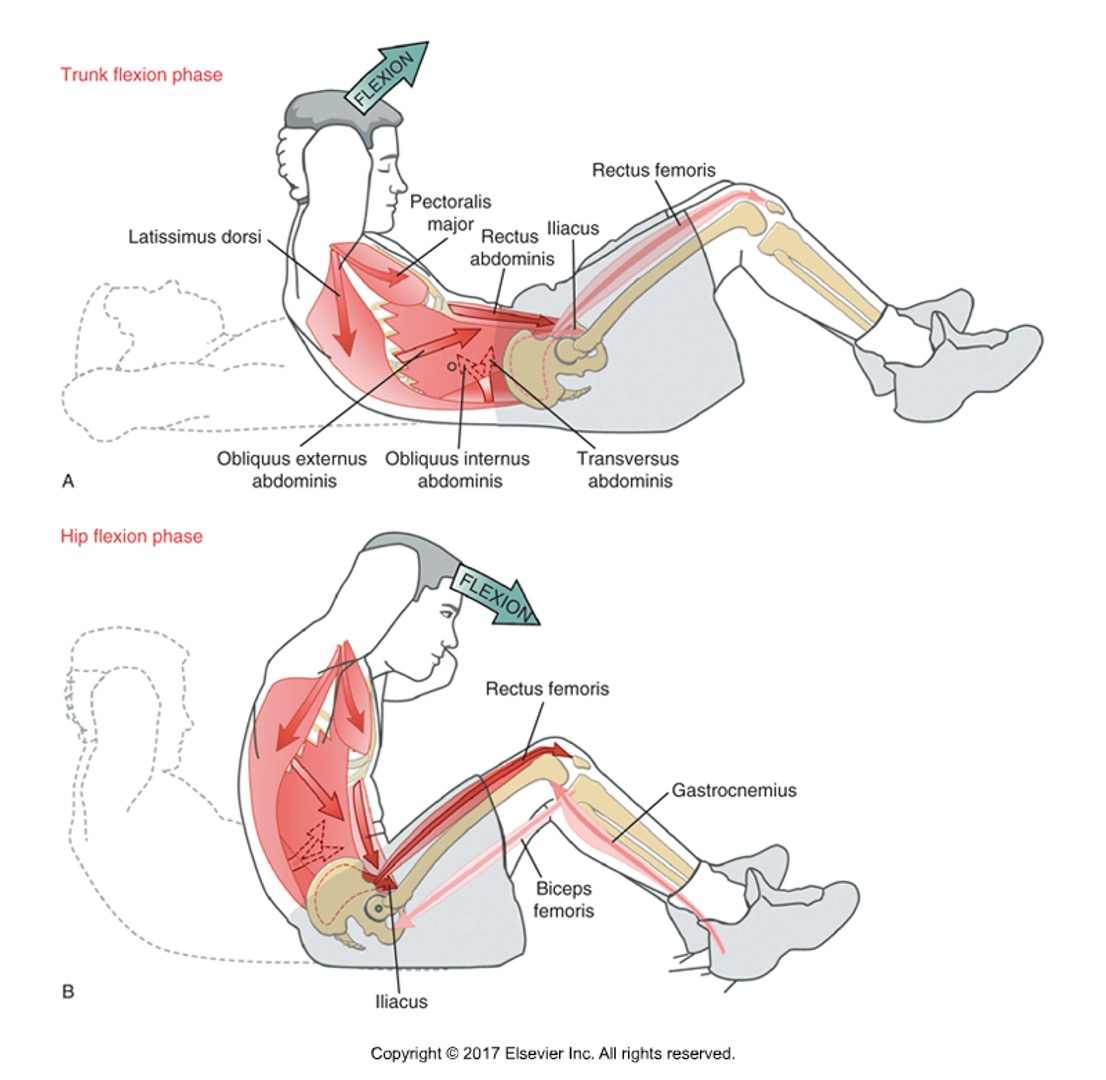
Describe the movement of the trunk and hip during a standard sit up
abdominal muscles flex trunk while also posteriorly tilting pelvis. biceps femoris eccentrically activated due to hip flexion
Explain the significance of the stabilizing function of the abdominals and lumbar multifidi
abdominal muscles often activate before other actions due to anticipatory and subconscious feedforward mechanisms (transversus abdominus and internal oblique activate before the deltoid with shoulder flexion)
Explain the relationship between chronic low back pain and core activation
some evidence shows a delay in transversus abdominus activation, or an overactivation leading to fatigue
List the muscles of the craniocervical region
SCM, scalenes, longus colli/capitis, rectus capitis, splenius cervicis/capitis, suboccipitals
What are some causes of chronic forward head posture?
hyperextension injury of craniocervical muscles leading to guarding, pain/weakness of deep neck flexors, poor ergonomics
True or false: lifting heavy objects generates large compression, tension, and shear forces
true, especially in lumbopelvic region
True or false: the extensor muscle moment arm is relatively large and gives a mechanical advantage relative to external loads
False: the extensor moment arm is relatively small and gives a mechanical disadvantage relative to external loads
Which of these is NOT a way to reduce force demands on back muscles while lifting?
increasing the rate of lifting
What is the most effective way to reduce the force demands on back muscles while lifting?
reduce the length of external moment arm of external load (i.e. lift the load between the knees)
How can you increase the moment arm of the low back extensors?
increase lumbar lordosis
Which of these is considered a safe lifting technique?
lift with a moderately wide and slightly staggered BOS
How does the valsalva maneuver reduce demands on the lumbar extensors during lifting?
creates modest extension torque, lowering muscular based compression forces
which abdominal muscle is responsible for the “corset effect”?
transversus abdominis due to horizontal attachments into thoracolumbar fascia
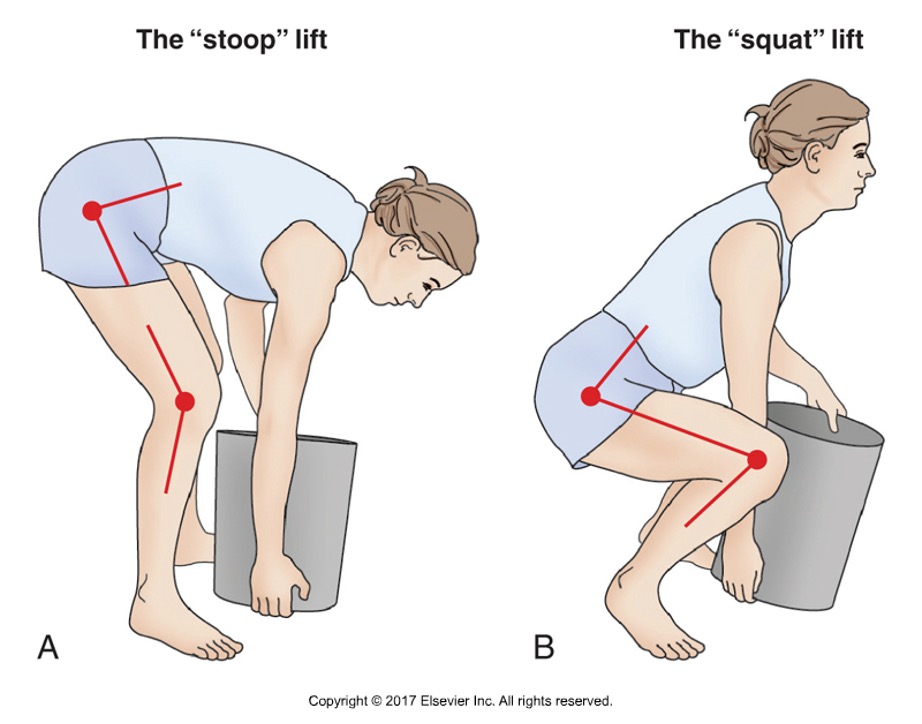
True or false: the stoop lift is safer than the squat lift
false: both are biomechanical extremes, but the squat lift has less stress on the low back
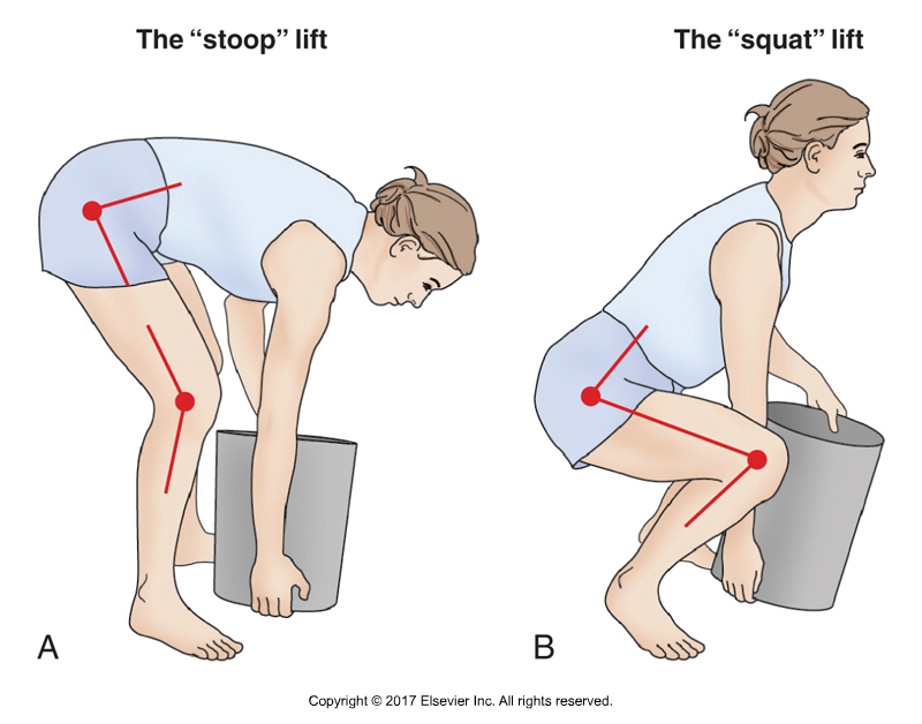
Describe the stoop lift
extending the hips and lumbar region while knees are slightly flexed
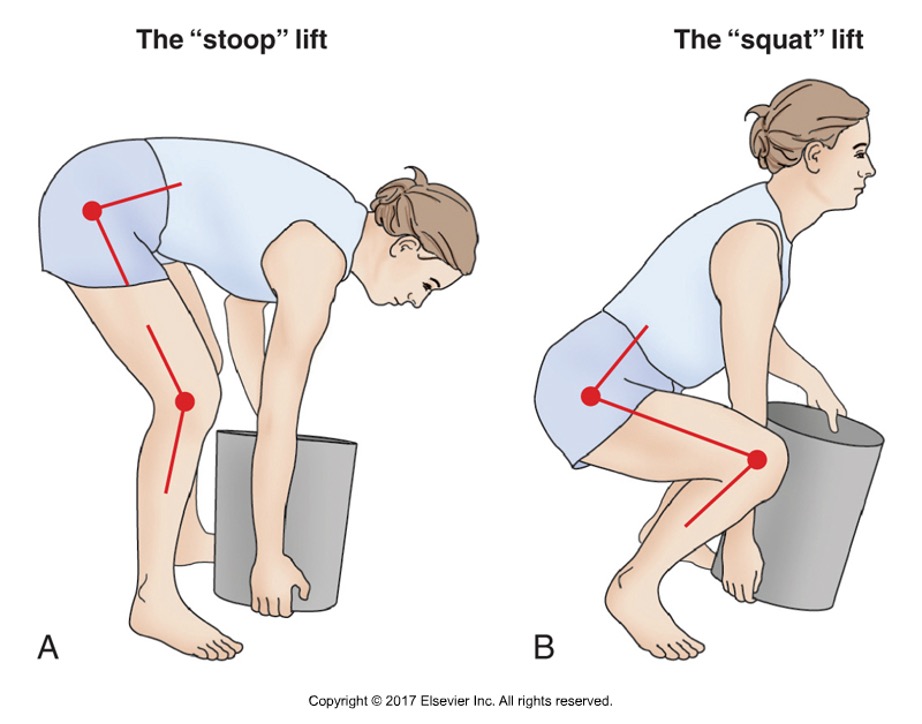
Describe the squat lift
knees are maximally flexed, hips and knees extend during the lift
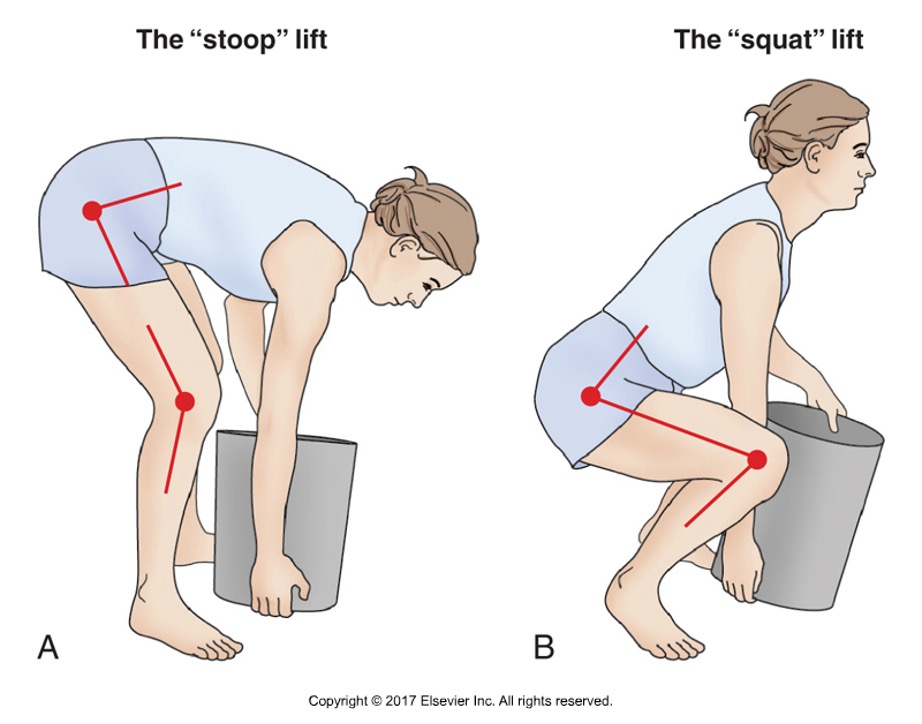
True or false: the stoop lift is more metabolically efficient
true: stoop is 20-30% more metabolically efficient due to less body mass being moved through space
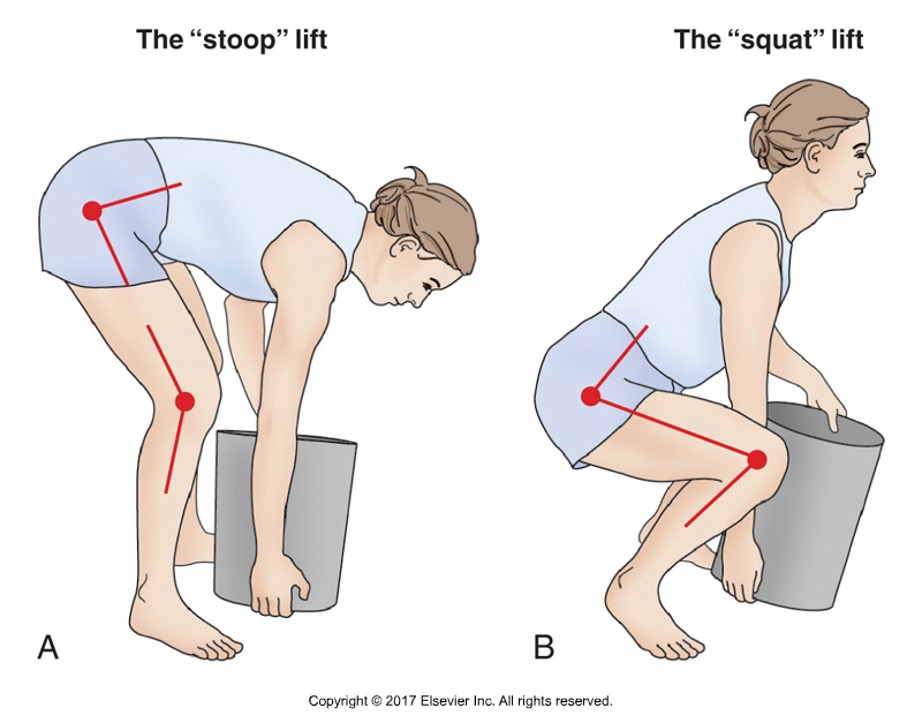
Which squat technique is most effective for the real world?
a freestyle combination between stoop and squat
Which abdominal muscles are responsible for feedforward control?
transversus abdominus, internal oblique, external oblique
how does the contact area and pressure change with trunk flexion?
decreased contact area, increased pressure
how does the contact area and pressure change with trunk extension?
increased contact area, decreased pressure
What are the three component parts of the interbody joint?
IV disc, vertebral body, end plates
Why is the annulous fibrosus susceptible to injury?
due to the orientation of the fibers
What ligament is responsible for limited flexion torque in the thoracolumbar region?
supraspinous ligament
What percentage of body weight runs through the interbody joints and posterior element while standing?
80 percent interbody, 20 percent posterior element
The ligamentum nuchae arises from which ligament?
supraspinous ligament
What is the closed pack position of the SI joint
posterior pelvic tilt/ sacral nutation
In which direction does the sacrum move during nutation?
anteriorly
In which direction does the pelvis move during nutation?
posteriorly
Which of the following ligaments is NOT tensioned during nutation?
long posterior SI ligament
In which direction does the sacrum move during counter-nutation?
posteriorly
In which direction does the pelvis move during counter-nutation?
anteriorly
Which of the following is anterior tilt associated with?
narrowing the IV foramen
Which of the following is posterior tilt associated with?
shifting the nucleus proprious posteriorly
Which muscles are involved with the valsalva maneuver?
abdominals, pelvic floor, diaphragm