Marketing Attitudes: Components, Functions, and Persuasion Techniques
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
What are attitudes in marketing?
Relatively enduring overall evaluations of objects, products, services, issues, or people.
How are attitudes related to consumer value?
Consumers have positive attitudes toward products that deliver value.
What does the ABC approach to attitudes stand for?
Affect, Behavior, and Cognition.
The ABC approach to attitudes:
Suggest that attitudes possess one’s affect, behavior, and cognitions (or beliefs) toward an object
What does the affect component of attitudes refer to?
Feelings about an object. EX. “I love Apple products”
What does the cognition component of attitudes refer to?
Beliefs that consumers have about an object. EX. “I think Apple products are innovative”
What does the behavior component of attitudes refer to?
Overt behavior that consumers exhibit as well as their intentions to behave. EX. “I always check for the latest Apple products”
Functional Theory of Attitudes:
theory of attitudes that suggests that attitudes perform four basic functions: Utilitarian, Knowledge, Value-expressive, and Ego-defensive.
What is the utilitarian function of attitudes?
Used as a method to obtain rewards and minimize punishment.
What does the knowledge function of attitudes allow consumers to do?
Simplify their decision-making processes. Refers to our need which is consistent and relatively stable
What is the value-expressive function of attitudes?
Enables consumers to express their core values, self-concept, and beliefs to others.
What is the ego-defensive function of attitudes?
Works as a defense mechanism to avoid facts or defend against low self-concept. EX. use of makeup
What is the hierarchy of effects in attitude formation?
Attitude approach that suggests that affect, behavior, and cognitions form in a sequential order
What is the difference between high involvement and low involvement in the hierarchy of effects?
High involvement involves cognition first, while low involvement may lead to behavior occurring without strong beliefs or feelings.
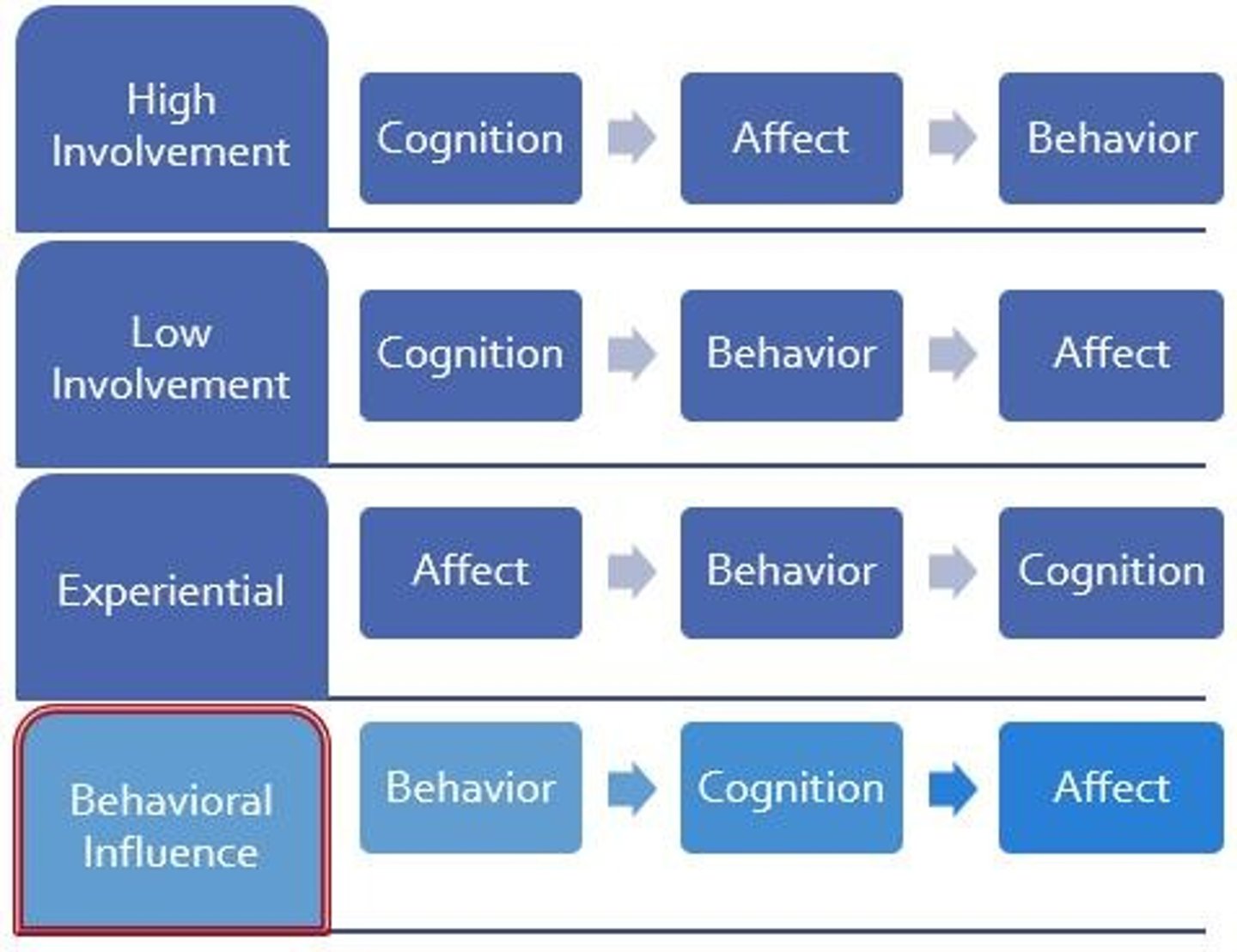
High Involvement:
Cognition → Affect → Behavior; Occurs when a consumer faces a high-involvement decision or addresses a significant problem.
Low Involvement:
Cognition → Behavior → Affect; Consumers have basic beliefs about products without
having strong feelings toward them
Experiential:
Affect → Behavior → Cognition; Explains impulse purchases
Behavioral Influence:
Behavior → Cognition → Affect; Some behaviors occur without either beliefs or affect being strongly formed beforehand.
What does the Attitude-Toward-the-Object (ATO) model involve?
Evaluating attributes, the strength of beliefs, and the attractiveness of those attributes. Also, Apply the formula for calculating ATO and Analyze the data.
What is the formula for calculating ATO?
A = Σ (bi * ei) where bi is the strength of belief and ei is the attractiveness of an attribute.
What is the Behavioral Intentions Model?
Evaluates beliefs about performing a behavior and the normative beliefs of reference groups.
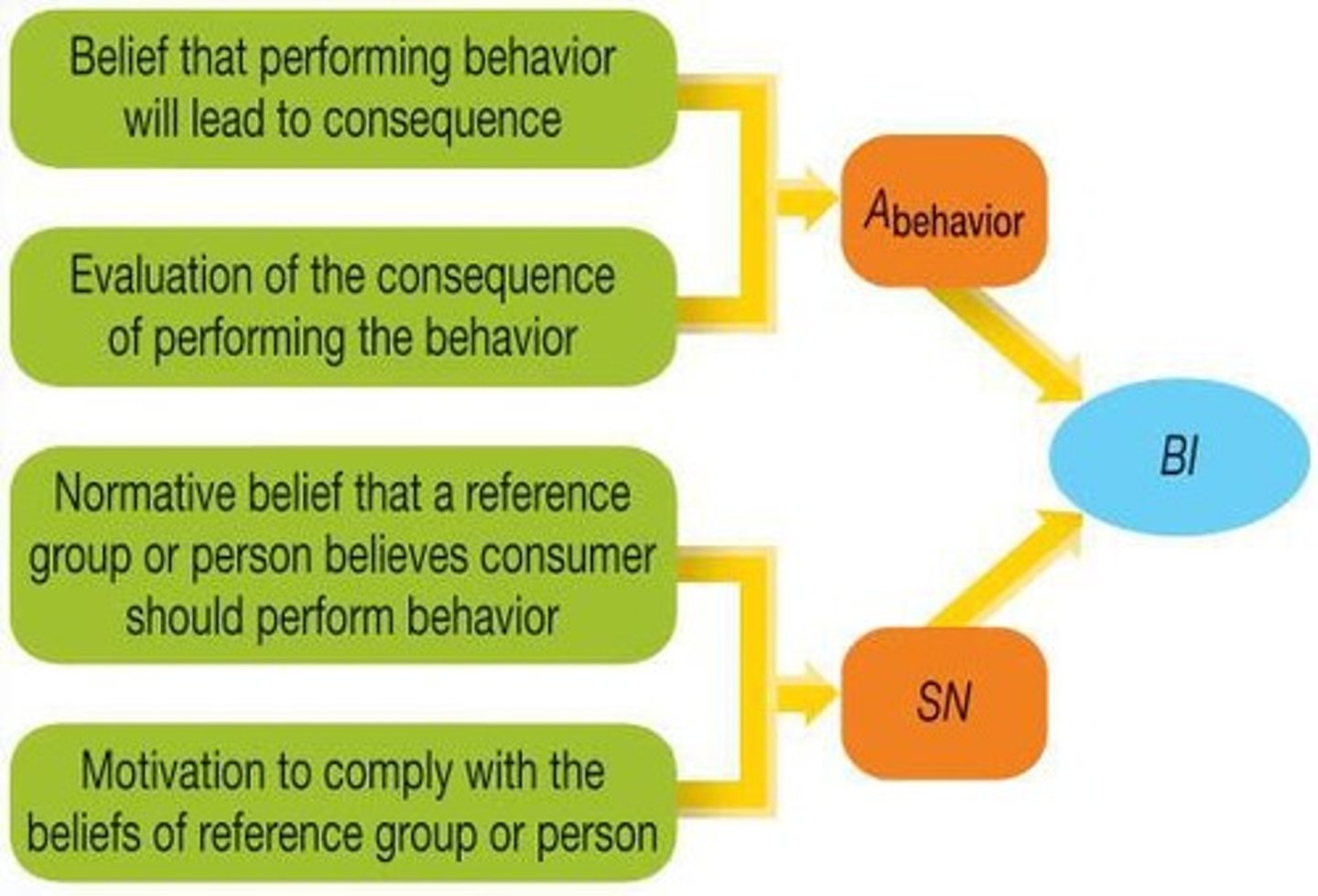
What are the components of the Behavioral Intentions Model?
Belief about behavior leading to a consequence, normative belief, and motivation to comply.
What is the equation for the BIM?
B ~ BI = w (A behavior) + w (SN)
A behavior:
Evaluate the belief that performing a behavior will lead to a consequence.
W1:
Evaluate the consequences of performing a behavior.
SN:
Normative belief that a reference group or person believes consumer should perform behavior
W2:
Motivation to comply with the beliefs of a reference group
What are persuasive techniques in marketing?
Methods used to change consumer attitudes through altering beliefs or feelings.
ATO (Attitudes-Towards-the-Object) Approach:
Marketers can attempt to change consumer attitudes by:
- Changing beliefs or creating new beliefs about product feature
- Changing evaluations of product attributes
Changing beliefs, Changing the perceived importance of attributes, Adding new attributes
Behavioral Influence Approach:
Proposes that behavior precedes cognition and affect.
- Visual Merchandising
- Scent Marketing
- Sound Marketing
Remember: Behavior → Cognition → Affect
What is the schema-based affect approach?
The idea that schemas contain affective and emotional meanings that can influence attitudes.
What’s an example of the schema-based affect approach being used irl that we learned in class?
Dominos changes Japanese consumer’s image of tomato based products; made reindeer deliver pizza to customers.
What does the elaboration likelihood model explain?
This model illustrates how attitudes are changed based on differing levels of consumer involvement. Explains different ways of processing stimuli and how that affects attitudes.
What is the balance theory in attitude change?
Consumers are motivated to maintain perceived consistency among their beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors through the consistency principle. Marketers should carefully monitor any changes that occur in how a target market perceives an endorser.
Consistency principle:
Human beings prefer consistency among their beliefs, attitudes, and behaviors.
What does social judgment theory propose?
Consumers compare new information to their existing attitudes about an object or issue.
Attitude change depends upon:
how consistent the information is with the initial attitude
Marketers should construct messages in a manner that:
they fall within the targeted customer’s latitude of acceptance
What are the types of message appeals in marketing?
Emotional vs Rational, Humor, Sex, and Fear.
What is the goal of marketers in changing consumer attitudes?
To influence consumer behavior by changing their beliefs or feelings.
What is the significance of understanding attitudes in marketing?
It helps marketers tailor their strategies to influence consumer perceptions and behaviors effectively.